Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Mineria 10
Загружено:
Michael AltamiranoОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Mineria 10
Загружено:
Michael AltamiranoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
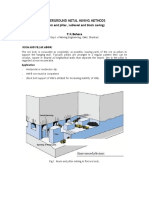
Mine access[edit]
Underground access[edit]
Accessing underground ore can be achieved via a decline (ramp), inclined vertical
shaft or adit.
Decline portal
Declines can be a spiral tunnel which circles either the flank of the deposit or circles
around the deposit. The decline begins with a box cut, which is the portal to the
surface. Depending on the amount of overburden and quality of bedrock, a galvanized
steel culvert may be required for safety purposes. They may also be started into the
wall of an open cut mine.
Shafts are vertical excavations sunk adjacent to an ore body. Shafts are sunk for ore
bodies where haulage to surface via truck is not economical. Shaft haulage is more
economical than truck haulage at depth, and a mine may have both a decline and a
ramp.
Adits are horizontal excavations into the side of a hill or mountain. Adits are used for
horizontal or near-horizontal ore bodies where there is no need for a ramp or shaft.
Declines are often started from the side of the high wall of an open cut mine when the ore
body is of a payable grade sufficient to support an underground mining operation, but the
strip ratio has become too great to support open cast extraction methods. They are also
often built and maintained as an emergency safety access from the underground workings
and a means of moving large equipment to the workings.
Ore access[edit]
Levels are excavated horizontally off the decline or shaft to access the ore
body. Stopes are then excavated perpendicular (or near perpendicular) to the level into the
ore.
Development mining vs. production mining[edit]
There are two principal phases of underground mining: development mining and production
mining.
Development mining is composed of excavation almost entirely in (non-valuable) waste
rock in order to gain access to the orebody. There are six steps in development mining:
remove previously blasted material (muck out round), scaling (removing any unstable slabs
of rock hanging from the roof and sidewalls to protect workers and equipment from
damage), installing support or/and reinforcement using shotcrete etceteras, drill face rock,
load explosives, and blast explosives. To start the mining, the first step is to make the path
to go down. The path is defined as 'Decline' as describe above. Before the start of Decline
all preplanning of Power facility, drilling arrangement, dewatering, ventilation and, muck
withdrawal facilities are required.[2]
Production mining is further broken down into two methods, long hole and short hole. Short
hole mining is similar to development mining, except that it occurs in ore. There are several
different methods of long hole mining. Typically, long hole mining requires two excavations
within the ore at different elevations below surface, (15 m – 30 m apart). Holes are drilled
between the two excavations and loaded with explosives. The holes are blasted and the
ore is removed from the bottom excavation.
Ventilation[edit]
Main article: Underground mine ventilation
Door for directing ventilation in an old lead mine. The ore hopper at the front is not part of the
ventilation.
Вам также может понравиться
- 1mining Through Adit, Incline, Decline and ShaftДокумент11 страниц1mining Through Adit, Incline, Decline and ShaftAkhil Sai KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Coiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!От EverandCoiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Pre Feasibility StudyДокумент4 страницыPre Feasibility StudyMichael AltamiranoОценок пока нет
- Pre Feasibility StudyДокумент4 страницыPre Feasibility StudyMichael AltamiranoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ14 страницChapter 1MekonenОценок пока нет
- Introduction UG Mine SafetyДокумент58 страницIntroduction UG Mine Safetygiyat_prcОценок пока нет
- 2 - ClassificationДокумент38 страниц2 - Classificationluch33savesОценок пока нет
- 360° Introduction To The Mining Industry (Text Level) Category Xcourse&course Xstreet&session Doc0301.xml&level Text&lang ENДокумент26 страниц360° Introduction To The Mining Industry (Text Level) Category Xcourse&course Xstreet&session Doc0301.xml&level Text&lang ENMihaelaCeciliaОценок пока нет
- 2.mining MethodsДокумент4 страницы2.mining MethodsAzaz Alam KhanОценок пока нет
- Safari - Jan 10, 2024 at 12:01 AM 5 PDFДокумент1 страницаSafari - Jan 10, 2024 at 12:01 AM 5 PDFsyansyncОценок пока нет
- Sub Level CavingДокумент3 страницыSub Level CavingFirman CahyadiОценок пока нет
- Seminar Report PDFДокумент27 страницSeminar Report PDFrudresh ojhaОценок пока нет
- Metodos AtlasCopcopage35Документ5 страницMetodos AtlasCopcopage35lautaroi77Оценок пока нет
- Drivage of RoadsДокумент12 страницDrivage of RoadsLavudiya RajkumarОценок пока нет
- Mining TerminologyДокумент44 страницыMining Terminologysenawayne191Оценок пока нет
- TerminologiДокумент19 страницTerminologiiqbal ramadhanОценок пока нет
- Underground Mining - Unsupported MethodsДокумент15 страницUnderground Mining - Unsupported MethodsPuvanendran GajananОценок пока нет
- 04-2 - Supported - NT DevelopmentДокумент39 страниц04-2 - Supported - NT Developmentbonganimduduzi466Оценок пока нет
- 25-04-2015 Underground Mine MethodsДокумент50 страниц25-04-2015 Underground Mine MethodsCo-leigh CornerОценок пока нет
- 08 TESME Underground Mining 1Документ7 страниц08 TESME Underground Mining 1softminestudioОценок пока нет
- Mine DevelopmentДокумент40 страницMine DevelopmentAbhijeetPandey50% (6)
- Lecture 3-Types of Underground Mining Methods - Lecture 3.Документ9 страницLecture 3-Types of Underground Mining Methods - Lecture 3.HILLARY FRANCIS SHENJEREОценок пока нет
- Técnicas en Minería SubterráneaДокумент17 страницTécnicas en Minería SubterráneaHenrry Rosas TorresОценок пока нет
- Underground Metal Mining Methods II - Pdf-DesbloqueadoДокумент7 страницUnderground Metal Mining Methods II - Pdf-DesbloqueadodavidОценок пока нет
- 3 4 Tahapan PenambanganДокумент24 страницы3 4 Tahapan PenambanganSalsabila Rizqie AmaliaОценок пока нет
- Elements of Mining TechnologyДокумент18 страницElements of Mining Technologyrishav baishyaОценок пока нет
- Block Caving Method: Virendra SuryawanshiДокумент11 страницBlock Caving Method: Virendra SuryawanshiFlakis GuerreroОценок пока нет
- Shrinkage StopingДокумент5 страницShrinkage StopingklouserОценок пока нет
- Shrinkage StopingДокумент5 страницShrinkage StopingUgo Velazco FloresОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Mine SurveyingДокумент7 страницIntroduction To Mine SurveyingJoshua Miguel MejiasОценок пока нет
- Metal Mining (19121066)Документ7 страницMetal Mining (19121066)Shivani ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ8 страницChapter 1John Yaw AmankrahОценок пока нет
- Underground Mining-Caving MethodsДокумент11 страницUnderground Mining-Caving MethodsPuvanendran GajananОценок пока нет
- Transportasi (Tambang) Bawah Tanah # 1Документ73 страницыTransportasi (Tambang) Bawah Tanah # 1januar789Оценок пока нет
- Shrinkage Stoping (19121066)Документ7 страницShrinkage Stoping (19121066)Shivani ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- As A Christ-Centered Paulinian, I Am A Dedicated, Transformative SUPPORTER and Steward of All CREATION, Impelled by Compassion and Charity For All."Документ32 страницыAs A Christ-Centered Paulinian, I Am A Dedicated, Transformative SUPPORTER and Steward of All CREATION, Impelled by Compassion and Charity For All."Erika EludoОценок пока нет
- 3 4 Tahapan PenambanganДокумент20 страниц3 4 Tahapan PenambanganFikri RahmanОценок пока нет
- GM 231 Introduction To Geology and MiningДокумент24 страницыGM 231 Introduction To Geology and Mininghaggai ngosaОценок пока нет
- Underground Mining MethodsДокумент3 страницыUnderground Mining Methodskichys50% (2)
- Stoping MethodДокумент51 страницаStoping MethodRathnakar Reddy100% (1)
- Students: Guerra Esquivel Cristian Hidalgo Pizarro Jimmy Paredes Saldivar JulberДокумент14 страницStudents: Guerra Esquivel Cristian Hidalgo Pizarro Jimmy Paredes Saldivar JulberLalo CotaОценок пока нет
- Mine DevelopmentДокумент4 страницыMine DevelopmentsunilsinghmОценок пока нет
- Mine Development Mining MethodsДокумент31 страницаMine Development Mining MethodsTamani MoyoОценок пока нет
- Metal Mining Stoping MethodsДокумент51 страницаMetal Mining Stoping MethodsAjeet KumarОценок пока нет
- Metal Mining Stoping MethodsДокумент51 страницаMetal Mining Stoping MethodsSheshu BabuОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Surface & Underground MiningДокумент22 страницыIntroduction To Surface & Underground MiningJasper CastorОценок пока нет
- Drilling RigsДокумент18 страницDrilling RigsegyinspectoryahooОценок пока нет
- Caving Methods - Longwall MiningДокумент19 страницCaving Methods - Longwall Miningabhimanyu choudharyОценок пока нет
- Modes of AccessДокумент24 страницыModes of AccessANSHUL YADAVОценок пока нет
- Shrinkage Stoping Mining MethodДокумент3 страницыShrinkage Stoping Mining MethodRyvan GibranОценок пока нет
- 12 Teknologi Batubara (Edit)Документ24 страницы12 Teknologi Batubara (Edit)Zul BafaroОценок пока нет
- 03 - Classification of Mining SystemsДокумент14 страниц03 - Classification of Mining Systemseaglesniper008Оценок пока нет
- Mining Magazine - Sinking SkilfullyДокумент14 страницMining Magazine - Sinking SkilfullyLehlohonolo MoqekelaОценок пока нет
- A Presentation On Underground Stoping Methods - IIДокумент68 страницA Presentation On Underground Stoping Methods - IIANSHUL YADAV100% (1)
- MPBT - Pertemuan 12Документ31 страницаMPBT - Pertemuan 12Ardiansyah Ay11Оценок пока нет
- Drilling Engineering Chapter 1Документ41 страницаDrilling Engineering Chapter 1Wong Jin Yang100% (2)
- Coal Mining: Coal Mining Is The Process of Extracting CoalДокумент20 страницCoal Mining: Coal Mining Is The Process of Extracting CoalsunilsinghmОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ9 страницChapter 1Senju HashiramaОценок пока нет
- Key Technologies of Drilling Process With Raise BoДокумент11 страницKey Technologies of Drilling Process With Raise BoSohaib SFAIRIОценок пока нет
- AnswerДокумент1 страницаAnswersaeedaumar1954Оценок пока нет
- Building Landmarks - Bridges, Tunnels and Buildings - Architecture and Design | Children's Engineering BooksОт EverandBuilding Landmarks - Bridges, Tunnels and Buildings - Architecture and Design | Children's Engineering BooksОценок пока нет
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXVIII, Sept. 1910 The New York Tunnel Extension of the Pennsylvania Railroad. The East River Tunnels. Paper No. 1159От EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXVIII, Sept. 1910 The New York Tunnel Extension of the Pennsylvania Railroad. The East River Tunnels. Paper No. 1159Оценок пока нет
- Ore and Country Rock Strength: Rockmass ClassificationДокумент12 страницOre and Country Rock Strength: Rockmass ClassificationMichael AltamiranoОценок пока нет
- The Geological ModelДокумент12 страницThe Geological ModelMichael AltamiranoОценок пока нет
- Pre-Evaluation Study: Author: John WrightДокумент4 страницыPre-Evaluation Study: Author: John WrightMichael AltamiranoОценок пока нет
- Design Topics: The General Environment in Which The Mine ExistsДокумент7 страницDesign Topics: The General Environment in Which The Mine ExistsMichael AltamiranoОценок пока нет
- Geotechnical Factors Influencing Selection of Mining MethodДокумент4 страницыGeotechnical Factors Influencing Selection of Mining MethodMichael AltamiranoОценок пока нет
- Feasibility Study: Author: John WrightДокумент4 страницыFeasibility Study: Author: John WrightMichael AltamiranoОценок пока нет
- Ventilation: Area Ground SupportДокумент2 страницыVentilation: Area Ground SupportMichael AltamiranoОценок пока нет
- X AdaptationДокумент58 страницX AdaptationJames JonesОценок пока нет
- Caveability: Fundamentals of Block Caving Geomechanics June 21-25 2010Документ57 страницCaveability: Fundamentals of Block Caving Geomechanics June 21-25 2010Michael AltamiranoОценок пока нет
- Alwyn Cosgrove Strength and Conditioning InterrogationsДокумент140 страницAlwyn Cosgrove Strength and Conditioning Interrogationsomarou18100% (1)
- Will Brink - Creatine ReportДокумент43 страницыWill Brink - Creatine ReportDusmanescu Nicolae100% (1)
- SKARN GOLD NAMBIJA Fontbote PDFДокумент17 страницSKARN GOLD NAMBIJA Fontbote PDFEadwine EdОценок пока нет
- Markowski Et Al PDFДокумент21 страницаMarkowski Et Al PDFMichael AltamiranoОценок пока нет
- Chiaradia Et Al 2009 NambijaДокумент17 страницChiaradia Et Al 2009 NambijaMichael AltamiranoОценок пока нет
- SKARN GOLD NAMBIJA Fontbote PDFДокумент17 страницSKARN GOLD NAMBIJA Fontbote PDFEadwine EdОценок пока нет
- Markowski Et Al PDFДокумент21 страницаMarkowski Et Al PDFMichael AltamiranoОценок пока нет
- Vallance Et Al 2009 NambijaДокумент25 страницVallance Et Al 2009 NambijaMichael AltamiranoОценок пока нет
- The Elder Scrolls V Skyrim - New Lands Mod TutorialДокумент1 175 страницThe Elder Scrolls V Skyrim - New Lands Mod TutorialJonx0rОценок пока нет
- Review Test 1: Circle The Correct Answers. / 5Документ4 страницыReview Test 1: Circle The Correct Answers. / 5XeniaОценок пока нет
- 525 2383 2 PBДокумент5 страниц525 2383 2 PBiwang saudjiОценок пока нет
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation - DPP 01 (Of Lecture 03) - Lakshya NEET 2024Документ3 страницыPrinciples of Inheritance and Variation - DPP 01 (Of Lecture 03) - Lakshya NEET 2024sibasundardutta01Оценок пока нет
- Heart Attack Detection ReportДокумент67 страницHeart Attack Detection ReportAkhil TejaОценок пока нет
- COE301 Lab 2 Introduction MIPS AssemblyДокумент7 страницCOE301 Lab 2 Introduction MIPS AssemblyItz Sami UddinОценок пока нет
- Hamza Akbar: 0308-8616996 House No#531A-5 O/S Dehli Gate MultanДокумент3 страницыHamza Akbar: 0308-8616996 House No#531A-5 O/S Dehli Gate MultanTalalОценок пока нет
- Laminar Premixed Flames 6Документ78 страницLaminar Premixed Flames 6rcarpiooОценок пока нет
- Curriculum Vitae: Educational Background Certification Major Name of Institute PeriodДокумент2 страницыCurriculum Vitae: Educational Background Certification Major Name of Institute PeriodTHEVINESHОценок пока нет
- Warranty FormДокумент13 страницWarranty FormEmpyrean Builders Corp.Оценок пока нет
- Vialyn Group ResearchДокумент17 страницVialyn Group ResearchVial LynОценок пока нет
- MARKETING STUDY EditedДокумент48 страницMARKETING STUDY EditedRichard Rhamil Carganillo Garcia Jr.Оценок пока нет
- Couvade SyndromeДокумент5 страницCouvade SyndromejudssalangsangОценок пока нет
- Good Manufacturing Practices in Postharvest and Minimal Processing of Fruits and VegetablesДокумент40 страницGood Manufacturing Practices in Postharvest and Minimal Processing of Fruits and Vegetablesmaya janiОценок пока нет
- Principles of Volumetric AnalysisДокумент5 страницPrinciples of Volumetric AnalysisMax TennerОценок пока нет
- Army Public School No.1 Jabalpur Practical List - Computer Science Class - XIIДокумент4 страницыArmy Public School No.1 Jabalpur Practical List - Computer Science Class - XIIAdityaОценок пока нет
- HP 6940 Manual CompleteДокумент150 страницHP 6940 Manual CompletepaglafouОценок пока нет
- Dental Clinic - Floor Plan R3-2Документ1 страницаDental Clinic - Floor Plan R3-2kanagarajodisha100% (1)
- Luxi User's GuideДокумент14 страницLuxi User's GuidephilsouthОценок пока нет
- EDL E-Catalogue 2021-22 With ApticoДокумент78 страницEDL E-Catalogue 2021-22 With Apticotkteetopoi1Оценок пока нет
- Case StarbucksДокумент3 страницыCase StarbucksAbilu Bin AkbarОценок пока нет
- Microcal P20Документ2 страницыMicrocal P20ctmtectrolОценок пока нет
- Test 4 MathДокумент15 страницTest 4 MathYu ChenОценок пока нет
- A Review On PRT in IndiaДокумент21 страницаA Review On PRT in IndiaChalavadi VasavadattaОценок пока нет
- Embraer ERJ-170: Power PlantДокумент5 страницEmbraer ERJ-170: Power Plantபென்ஸிஹர்Оценок пока нет
- Project - Dreambox Remote Video StreamingДокумент5 страницProject - Dreambox Remote Video StreamingIonut CristianОценок пока нет
- JurnalДокумент12 страницJurnalSandy Ronny PurbaОценок пока нет
- Substitution Reactions - PMДокумент64 страницыSubstitution Reactions - PMprasoon jhaОценок пока нет
- The Origin, Nature, and Challenges of Area Studies in The United StatesДокумент22 страницыThe Origin, Nature, and Challenges of Area Studies in The United StatesannsaralondeОценок пока нет
- ARMY - Chapter Eight Explosive BreachingДокумент25 страницARMY - Chapter Eight Explosive Breachingrsreeth100% (1)