Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
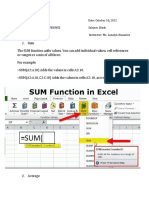
How To Use Excel's DSUM Function
Загружено:
Syed Ali HaiderОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
How To Use Excel's DSUM Function
Загружено:
Syed Ali HaiderАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
How to Use Excel's DSUM Function
By an eHow Contributor
Excel's DSUM function is short for "database sum." It adds the values in a column of a
database that match the specified criteria. DSUM then calculates its return value in the same
manner as SUM, which simply takes its values directly from the argument list. The following
steps will show how to use Excel's DSUM function.
Difficulty: Moderate
Instructions
1.
Learn the syntax of DSUM (database, field, criteria). Database is a cell range
that specifies the database, field is a column in the database from which
DSUM will add values and criteria is a cell range with the criteria to be used in
selecting the values.
2.
Define the database for DSUM. The first cell in the range will indicate the
upper left corner of the database array and the second cell will indicate the
lower right corner of the array. The first row of the array must contain the
column names.
3.
Specify the field for DSUM. It can include the column name enclosed in
double quotation marks or a number representing the column's position in the
database where 1 is the first column, 2 is the second column and so on.
4.
Supply the criteria for DSUM. This cell range must contain at least one
column name and one condition for that column. The condition will generally
be of the form ="condition." Thus, a value of ="=Apple" would select rows
where the value in the specified column is equal to "Apple."
5.
Enter the following in the first four columns of an Excel spreadsheet:
Row 1: Tree, Height, Age and Yield;
Row 2: ="=Apple" and =">10" (nothing in columns three and four);
Row 3: ="=Pear" (nothing in columns two, three and four);
Row 4: Tree, Height, Age and Yield;
Row 5: Apple, 18, 20 and 14;
Row 6: Pear, 12, 12 and 10;
Row 7: Cherry, 13, 14 and 9;
Row 8: Apple, 14, 15 and 10;
Row 9: Pear, 9, 8 and 8; and
Row 10: Apple, 8, 9 and 6.
6.
Interpret the formula =DSUM(A4:D10,"Yield",A1:B2) as follows: The database
is defined as the array A4:D10. Note the column names in the first row of this
array. "Yield" is the column name from which the values will be taken. The
criteria are given by A1:B2 which indicates that the column named Tree must
contain "Apple" and the column named Height must contain a value greater
than 10. DSUM(A4:D10,"Yield",A1:B2) will therefore be evaluated as
SUM(14,10)=24.
If Function
One of the most useful functions in Excel is the IF function. What it does is test a value in a specific cell to
see if that value meets a certain condition. If the value does meet the condition, one result will happen, if
false, a different action will occur.
Writing the IF function:
=IF(logical_test, value_if_true, value_if_false)
IF Function example:
=IF(D1 < 26, 100, 200)
Breaking the example down into its three parts we have:
logical test: D1 < 26, ("<" means less than)
value if true: 100
value if false: 200
The results of this function will be:
1) If the value in D1 is less than 26, the value shown will be 100.
2) If the value in D1 is NOT less than 26, the value shown will be 200.
Вам также может понравиться
- Evans Analytics2e PPT 02Документ29 страницEvans Analytics2e PPT 02qunОценок пока нет
- Excel Vba ExamplesДокумент133 страницыExcel Vba Examplesggkmurty100% (1)
- Knowledge of The Unseen (Khalis Itiqad)Документ3 страницыKnowledge of The Unseen (Khalis Itiqad)haqq92Оценок пока нет
- MS Excel (Advanced Functions)Документ16 страницMS Excel (Advanced Functions)Meneer DossiОценок пока нет
- Basic - All - Excel - Function PDFДокумент395 страницBasic - All - Excel - Function PDFsam_gandaОценок пока нет
- Basic - All Excel FunctionДокумент395 страницBasic - All Excel FunctionRama VexОценок пока нет
- Basic-All Excel FunctionДокумент395 страницBasic-All Excel FunctionJannatun Amira Al AqilahОценок пока нет
- Advance Excel FormulasДокумент34 страницыAdvance Excel FormulasfamsonОценок пока нет
- Excel Array FormulasДокумент12 страницExcel Array Formulasrohan12septОценок пока нет
- Logical Functions Logical: Logical Is A Computer Solution Based Upon True or False Answers, Instead of NumericДокумент9 страницLogical Functions Logical: Logical Is A Computer Solution Based Upon True or False Answers, Instead of NumericChristine joyce MagoteОценок пока нет
- Bahan Kursus Ms Excel 2007 Dipkg AmpangДокумент8 страницBahan Kursus Ms Excel 2007 Dipkg AmpangDequeNo Mohd NoorОценок пока нет
- Dynamic Named Range With INDEXДокумент12 страницDynamic Named Range With INDEXsehrishb01Оценок пока нет
- Database FunctionsДокумент11 страницDatabase FunctionsRanjan RoyОценок пока нет
- Array FormulasДокумент12 страницArray FormulasAyyagari SatyanarayanaОценок пока нет
- Putting Advanced Array Formulas To Work - ExcelДокумент3 страницыPutting Advanced Array Formulas To Work - Excelnksuthar5399Оценок пока нет
- Orca Share Media1601367041808 6716620188926428611Документ38 страницOrca Share Media1601367041808 6716620188926428611John Edward PangilinanОценок пока нет
- 10Документ6 страниц10bertinОценок пока нет
- Dbase & LookupДокумент7 страницDbase & LookupCheryl EcalnirОценок пока нет
- Dsum Function: Database FunctionsДокумент10 страницDsum Function: Database FunctionsMitesh WaghelaОценок пока нет
- SS1 3RD Term DP NoteДокумент17 страницSS1 3RD Term DP NoteMhiz Oluchukwu CynthiaОценок пока нет
- Excel AssignmentДокумент3 страницыExcel AssignmentNihal KocheОценок пока нет
- Prepared By: Ralph John B. BubanДокумент55 страницPrepared By: Ralph John B. BubanNathalia Ysabelle ReigoОценок пока нет
- Excel 1Документ6 страницExcel 1dhstheaОценок пока нет
- Excel 50 FormulasДокумент37 страницExcel 50 FormulaschiragraizadaОценок пока нет
- Dbms Manual PДокумент26 страницDbms Manual PDeepak kumarОценок пока нет
- SQL CommandsДокумент22 страницыSQL Commandsutsav kakkadОценок пока нет
- SUM (Number1, (Number2), ) 2.: SumifДокумент2 страницыSUM (Number1, (Number2), ) 2.: SumifAdeeba FatimaОценок пока нет
- Excel With NumericsДокумент20 страницExcel With NumericsSp AmОценок пока нет
- ExcelДокумент28 страницExcelHaydee LuyangОценок пока нет
- Microsoft Excel-FunctionsДокумент17 страницMicrosoft Excel-FunctionsWiner EmolotrabОценок пока нет
- SQL Alias:: To Make Selected Columns More Readable.Документ17 страницSQL Alias:: To Make Selected Columns More Readable.Ankit NischalОценок пока нет
- Class VI Ch-4-29-8-2020Документ9 страницClass VI Ch-4-29-8-20207A04Aditya MayankОценок пока нет
- Apii 4 DBДокумент10 страницApii 4 DBGideon MogeniОценок пока нет
- Here Are Some Common and Useful Excel Formulas That Can Help Make Your Work Easier and More EfficientДокумент2 страницыHere Are Some Common and Useful Excel Formulas That Can Help Make Your Work Easier and More EfficientAli MurtazaОценок пока нет
- EXCEL Advanced Lessons - Collection 1Документ43 страницыEXCEL Advanced Lessons - Collection 1banglecowboyОценок пока нет
- Informatics Practices Class 12 Cbse Notes Data HandlingДокумент17 страницInformatics Practices Class 12 Cbse Notes Data Handlingellastark0% (1)
- Unit Nine Data StructuresДокумент19 страницUnit Nine Data StructuresKimani JohnОценок пока нет
- SQL101 Classotes - 2Документ7 страницSQL101 Classotes - 2rohtihr2611Оценок пока нет
- Using Array Formulas in Excel OFC-10 Bob UmlasДокумент5 страницUsing Array Formulas in Excel OFC-10 Bob Umlastuku67Оценок пока нет
- Excel 2010 Fórmulas - Parte83Документ5 страницExcel 2010 Fórmulas - Parte83xdpablo328Оценок пока нет
- What Is SQL?Документ33 страницыWhat Is SQL?Kartik Juneja100% (2)
- Excel If Cell Contains Formula ExamplesДокумент9 страницExcel If Cell Contains Formula ExamplesP Singh KarkiОценок пока нет
- How To Look Up A Value in A List and Return Multiple Corresponding ValuesДокумент14 страницHow To Look Up A Value in A List and Return Multiple Corresponding Valuesdban21Оценок пока нет
- SQLДокумент29 страницSQLsamalparthaОценок пока нет
- Displaying Data From Multiple TablesДокумент32 страницыDisplaying Data From Multiple TablesanilkumarpvОценок пока нет
- Lab 4 UpdatedДокумент8 страницLab 4 UpdatedbolОценок пока нет
- My-Sql: Learning ObjectivesДокумент22 страницыMy-Sql: Learning ObjectivesHarshit PandeyОценок пока нет
- Basic ExcelДокумент13 страницBasic ExcelRakesh SharmaОценок пока нет
- Excel GuideДокумент21 страницаExcel Guidesans42699Оценок пока нет
- Test 2: Compsci 100: Owen Astrachan November 11, 2009Документ9 страницTest 2: Compsci 100: Owen Astrachan November 11, 2009Gobara DhanОценок пока нет
- Hackr Excel Cheat Sheet PDFДокумент8 страницHackr Excel Cheat Sheet PDFNaveed AhmedОценок пока нет
- Formulas On MS ExcelДокумент9 страницFormulas On MS ExcelTooba shafiqОценок пока нет
- SIN (X), COS (X), TAN (X), (X ACOS (X), EXP (X), LN (X), LOG (X), LOG (X, Y), COSH (X), ABS (X), FACT (X)Документ14 страницSIN (X), COS (X), TAN (X), (X ACOS (X), EXP (X), LN (X), LOG (X), LOG (X, Y), COSH (X), ABS (X), FACT (X)JonahJuniorОценок пока нет
- Arrays: Instructor: S/L NaveedДокумент22 страницыArrays: Instructor: S/L Naveedhmxa91Оценок пока нет
- Etech 2Документ19 страницEtech 2Charmaine WarnerОценок пока нет
- My Lecture of SQLДокумент11 страницMy Lecture of SQLshahinmandaviya100% (1)
- Pomagalo ComДокумент18 страницPomagalo ComИнж. Хранимир БешковОценок пока нет
- Class 9 Electronic Spreadsheet NotesДокумент6 страницClass 9 Electronic Spreadsheet Notesbraviauser865192Оценок пока нет
- 3 Understanding The Meaning of DataДокумент5 страниц3 Understanding The Meaning of DataRafael CasilangОценок пока нет
- UNIT7 Literature From Around The WorldДокумент21 страницаUNIT7 Literature From Around The WorldSyed Ali HaiderОценок пока нет
- Arif CVДокумент4 страницыArif CVSyed Ali HaiderОценок пока нет
- IdiomsДокумент5 страницIdiomsSyed Ali HaiderОценок пока нет
- Words Meanings SentencesДокумент6 страницWords Meanings SentencesSyed Ali HaiderОценок пока нет
- ICT Ethics and SecurityДокумент4 страницыICT Ethics and SecuritySyed Ali HaiderОценок пока нет
- CultureДокумент3 страницыCultureSyed Ali HaiderОценок пока нет
- ch1 Computer6thДокумент3 страницыch1 Computer6thSyed Ali HaiderОценок пока нет
- GeographyДокумент7 страницGeographySyed Ali HaiderОценок пока нет
- IdiomsДокумент5 страницIdiomsSyed Ali HaiderОценок пока нет
- In English Grammar There Are 8 Parts of SpeechДокумент4 страницыIn English Grammar There Are 8 Parts of SpeechNurasyikin RusleОценок пока нет
- Data Science and Big Data Analysis McqsДокумент53 страницыData Science and Big Data Analysis McqsansonjoelОценок пока нет
- Compendium of Trick Plays - Nihon KiinДокумент220 страницCompendium of Trick Plays - Nihon KiinFrédéric Vieira100% (2)
- Image Processing (RCS082) Unit V Huffman CodingДокумент12 страницImage Processing (RCS082) Unit V Huffman CodingFlask TutorialОценок пока нет
- INGLES There Are Two Ways of Telling Somebody What Another Person SaidДокумент5 страницINGLES There Are Two Ways of Telling Somebody What Another Person Saidcatherin gonzalezОценок пока нет
- Arc @Документ1 страницаArc @Steven LongОценок пока нет
- 2012 - Fail-Over ClusteringДокумент34 страницы2012 - Fail-Over ClusteringAbdul KasimОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan With Accommodations 2Документ3 страницыLesson Plan With Accommodations 2api-340854624Оценок пока нет
- How To Paraphrase in The IELTS TestДокумент6 страницHow To Paraphrase in The IELTS TestNgọc Quân TrươngОценок пока нет
- Pre School Report Card 2006 07Документ4 страницыPre School Report Card 2006 07anon-385406100% (6)
- STM 32 WL 55 JCДокумент147 страницSTM 32 WL 55 JCDaniel Gustavo Martinez MartinezОценок пока нет
- Chapt 2Документ213 страницChapt 2pawОценок пока нет
- Day of Prayer 2021 Orthodox BooksДокумент4 страницыDay of Prayer 2021 Orthodox BooksJhuvikОценок пока нет
- Tonelli - Philosophy of D'alembertДокумент19 страницTonelli - Philosophy of D'alembertCharlybrownОценок пока нет
- Monsters Are Due On Maple Street. Lesson - StoryДокумент24 страницыMonsters Are Due On Maple Street. Lesson - StoryRENATA AMETОценок пока нет
- Bab 2Документ31 страницаBab 2Grace Padios MadriagaОценок пока нет
- SpriteKit PGДокумент99 страницSpriteKit PGjose cegriОценок пока нет
- Iqti Ādī Karīm by Rafīq Yūnus Al-Ma Rī)Документ15 страницIqti Ādī Karīm by Rafīq Yūnus Al-Ma Rī)Ahmad Ghozin Abdil Aziz AHMADОценок пока нет
- R&W Lesson PlanДокумент4 страницыR&W Lesson Planمحمد فاريزОценок пока нет
- Fluid Statics PrintДокумент16 страницFluid Statics PrintJoanne SoloriaОценок пока нет
- AntakiДокумент614 страницAntakiLina CorreaОценок пока нет
- ConsessionДокумент17 страницConsessionHasna Amada RamaniaОценок пока нет
- Viewport 2.0 APIДокумент3 страницыViewport 2.0 APIRüud WolvawabОценок пока нет
- DOC0245293001 410 19edДокумент102 страницыDOC0245293001 410 19edA SofyanОценок пока нет
- Linq - Beyond Queries: LINQ For Better Business LogicДокумент15 страницLinq - Beyond Queries: LINQ For Better Business LogicDanish QureshiОценок пока нет
- Al MumtahinaДокумент9 страницAl MumtahinaAyesha KhanОценок пока нет
- Xpolakm5 Computer Vision Eye Blink DetectionДокумент4 страницыXpolakm5 Computer Vision Eye Blink Detectionapi-288461888Оценок пока нет
- Fiver e PDFДокумент279 страницFiver e PDFShobujurRahmanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 - Verilog Tasks and FunctionsДокумент25 страницChapter 7 - Verilog Tasks and FunctionsPhạm Gia LongОценок пока нет