Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Control Infection FDC
Загружено:
Deny RakhmanОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Control Infection FDC
Загружено:
Deny RakhmanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Control Infection
Make a clean and safe dental practice
Logo dan alamat atau informasi atau
pendaftaran
Sick people are seeking medical help and the waiting room of an office practice
may be a concentrated environment of communicable diseases. Infection is not
only spread person-to-person, but can also be spread indirectly through inanimate
objects known as fomites. Examples of fomites: magazines,toys, waiting
room surfaces.
.
We have divided this document into three major sections consisting of issues that relate
primarily to the care of patients, health care workers, and the environment
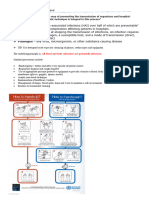
Bagaimana terjadinya transmisi/perpindahan
Airborne Transmission Precautions
Droplet Transmission Precautions
Contact Transmission Precautions
Four main routes spread organisms: contact (direct, indirect or droplet); airborne;
vehicle; and vectorborne transmission.
Infections are spread if the following criteria are satisfied:
(i) the presence of a susceptible host;
(ii) the presence of pathogenic micro-organisms;
(iii) there must be a portal of entry via which the organisms invade and colonize the
susceptible host.
Absence of any one of these requisites will prevent the transmission of an infectious
disease. Therefore, the goal of infection control is to eliminate one, two, or all of these
criteria. It should be understood that exposure to micro-organisms and infection are not
synonymous. It is impossible to avoid being exposed to micro-organisms; however,
exposure will not cause disease unless the three previously mentioned criteria are
present.
Routine Practices
“Routine practices” refers to the standards of practice that should be followed for the care of ALL
patients at ALL times.
There are three principles that are inherent in routine practices:
• Hand hygiene
• Personal protective equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) are worn to protect the health care
worker and to prevent the health care worker from becoming a vector.
Masks, Protective Eyewear, Face Shields
Protective glasses, masks or face shields should be worn by operators and
close-support dental surgery assistants to protect the eyes against the spatter and
aerosols which may occur during cavity preparation, scaling and the cleaning of
instruments.
Protective Clothing
Uniforms should be changed regularly and whenever soiled. Gowns or aprons
should be worn during procedures that are likely to cause spattering or splashing of
blood.
Glove
Gloves must be worn for procedures involving contact with blood, saliva or
mucous membrane. A new pair of gloves should be used for each patient. If a glove
is damaged, it must be replaced immediately. Hands should be washed thoroughly
with a proprietary disinfectant liquid soap prior to and immediately after the use of
gloves. Disposable paper towels are recommended for drying of hands. Any cuts or
abrasions on the hands or wrists should be covered with adhesive waterproof
dressings at all times.
Sterilization and Disinfectionof Patient-Care Items
HEALTH CARE WORKERS
As the employer, implement reasonable measures to minimize the risk of your employees
acquiring or spreading infection.
Immunization of Personnel
Medical office workers will be exposed to communicable diseases, and should be
immune to vaccine preventable illness.
THE ENVIRONMENT
General Housekeeping of the Office
Waste Disposal
Disposal of waste
Sharp items including needles and scalpels and local anaesthetic cartridges,
should
be placed into puncture proof containers which should be securely sealed. These,
together with all medical waste must be disposed of in red bags, securely fastened. Red
plastic bags are to be picked up by a special collection service for hospitals and clinics.
Non infective waste should be disposed of in thick black plastic bags securely
fastened.
Liquid waste should be carefully poured into a drain and then flushed with water.
Spatter and splash should be avoided.
Cleaning, Disinfection and Sterilization
of Medical Instruments
All instruments should be cleaned thoroughly before sterilization by rinsing and
scrubbing with detergent and water. Splashing of water should be avoided. Heavy duty
gloves and, where appropriate, face protection shield, should be worn.
Items which will penetrate tissues must be sterilized in an autoclave or hot air
steriliser. Items which will touch mucous membrane but not penetrate tissues should
similarly be sterilized by heat, or, if not possible, disinfected, e.g., by immersion in 2%
glutaraldehyde solution in a closed container according to the manufacturer’s
instructions. All chemical residues must then be removed by thorough rinsing before use
or storage.
Handpieces, ultrasonic scaler inserts/tips and air-water syringe tips where
detachable should be flushed for 30 seconds, dismantled, cleaned, oiled where required,
and autoclaved between patients. (Handpieces, etc. left overnight should be allowed to
discharge water for two minutes at the beginning of the day). Handpieces which cannot
be autoclaved are disinfected with an appropriate virucidal agent.
Following sterilization, all instruments should be stored in clean containers to
prevent recontamination. Surgical and endodontic instruments should be kept in closed
containers. It may be necessary to re-sterilize them immediately before they are used and
care should be taken to ensure the instruments are cool prior to use.
Surface disinfection
Surfaces that are likely to become contaminated may be de-contaminated after
treatment or protected with disposable coverings before they become contaminated.
Effective cross-infection control is aided by a strict system of zoning and the use of
sterilizable trays. Procedures should be adopted which limit the areas touched and
contaminated each time a patient is treated.
5
Between clinical sessions, work surfaces should be thoroughly cleaned and
decontaminated with ethyl alcohol (70%). If there is visible blood or pus, the surface
should be cleaned and disinfected with sodium hypochorite (0.5%), followed by water
rinse. Protective gloves should be worn and care taken to minimise direct skin, mucosal
or eye contact with these disinfectants.
Dental Unit Waterlines, Biofilm,and Water Quality
Вам также может понравиться
- The Infection Control Manual: Standard PrecautionsДокумент5 страницThe Infection Control Manual: Standard Precautionszenagit123456Оценок пока нет
- Infection Contro Lin The DentalclinicДокумент117 страницInfection Contro Lin The DentalclinicFaye Nervanna Alecha AlferezОценок пока нет
- Infection Control inДокумент45 страницInfection Control inmohdmaghyreh100% (2)
- WHO EVD Guidance IPC 14.1 EngДокумент6 страницWHO EVD Guidance IPC 14.1 Engdhoo_babyОценок пока нет
- Infection ControlДокумент44 страницыInfection Controlkalpanagokul44Оценок пока нет
- IMPLEMENT INFECTION CONTROL POLICIESДокумент8 страницIMPLEMENT INFECTION CONTROL POLICIESRubz BulquerinОценок пока нет
- Guidelines On Infection Control in Dental ClinicsДокумент10 страницGuidelines On Infection Control in Dental ClinicsHare RamОценок пока нет
- Lecture 8 Infection ControllingДокумент9 страницLecture 8 Infection ControllingDt omarОценок пока нет
- Lec 11 PDFДокумент8 страницLec 11 PDFFlorida ManОценок пока нет
- Infection ControlДокумент24 страницыInfection Controlمحمد العراقيОценок пока нет
- Lec 4 Precautions - A Lec 6Документ19 страницLec 4 Precautions - A Lec 6mqbljbr529Оценок пока нет
- By: Mary Angelie M. Atienza: Infection Control Nurse Bicol Regional Training and Teaching HospitalДокумент70 страницBy: Mary Angelie M. Atienza: Infection Control Nurse Bicol Regional Training and Teaching HospitalCiao AtienzaОценок пока нет
- Infection Control in Operation TheatreДокумент8 страницInfection Control in Operation Theatresyedsalimahmed100% (7)
- Standard Precautions in HealthcareДокумент4 страницыStandard Precautions in HealthcareCityhealthoffice SantiagoОценок пока нет
- First AidДокумент53 страницыFirst AidJett LabillesОценок пока нет
- Aseptic Technique in DentistryДокумент52 страницыAseptic Technique in Dentistrynew biee100% (1)
- Infection Control in DentistryДокумент37 страницInfection Control in DentistryIsha AroraОценок пока нет
- PathogensДокумент6 страницPathogensdeoОценок пока нет
- K3 Dalam Keperawatan Mencegah Penularan PenyakitДокумент44 страницыK3 Dalam Keperawatan Mencegah Penularan PenyakitDinda tri agustinОценок пока нет
- Infection Control and Standard Safety MeasuresДокумент25 страницInfection Control and Standard Safety MeasuresManisha Thakur100% (1)
- Infection Control in Dental OfficeДокумент12 страницInfection Control in Dental OfficeMayank AggarwalОценок пока нет
- Standard PrecautionДокумент51 страницаStandard PrecautionLovelights ZamoraОценок пока нет
- Infection Control in DentistryДокумент69 страницInfection Control in DentistryShahrukh ali khanОценок пока нет
- Appendix A:: Standard PrecautionsДокумент1 страницаAppendix A:: Standard PrecautionsKim RamosОценок пока нет
- Infection Control 1Документ33 страницыInfection Control 1samar yousif mohamedОценок пока нет
- Sterilization of Ortho Instruments / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyДокумент57 страницSterilization of Ortho Instruments / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyОценок пока нет
- Carilion Infection Control PacketДокумент16 страницCarilion Infection Control PacketKomite PpiОценок пока нет
- Arjumand Zargar Anp@AARUSIMIДокумент69 страницArjumand Zargar Anp@AARUSIMIArjumand ZargarОценок пока нет
- Bio Safety - Clinical PartДокумент43 страницыBio Safety - Clinical PartDinesh SreedharanОценок пока нет
- A SepsisДокумент5 страницA SepsisAi KogaОценок пока нет
- Infection ControlДокумент27 страницInfection ControlKarim ElmakasОценок пока нет
- لقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٤-٠١-٣١ في ١٠.٤٣.٠٦ صДокумент40 страницلقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٤-٠١-٣١ في ١٠.٤٣.٠٦ صzaydalmthylОценок пока нет
- Document Ambulance - Guidelines Reducing Infection in Prehospital FINAL 271Документ10 страницDocument Ambulance - Guidelines Reducing Infection in Prehospital FINAL 271Agustinus BethaОценок пока нет
- Urinalysis and Other Body FluidsДокумент64 страницыUrinalysis and Other Body FluidsJahre Mark ToledoОценок пока нет
- Infectious Control Measures (Dental Clinic)Документ7 страницInfectious Control Measures (Dental Clinic)Susan JilhanoОценок пока нет
- Infection ControlДокумент14 страницInfection ControlShiba AbdullahОценок пока нет
- Standard PrecautionsДокумент19 страницStandard PrecautionsOscar SmithОценок пока нет
- Infection Control in Dentistry FinalДокумент12 страницInfection Control in Dentistry FinalDevAshish BОценок пока нет
- Universal Precautions Quiz 14 15Документ8 страницUniversal Precautions Quiz 14 15O.r. CadzОценок пока нет
- Routine PracticesДокумент5 страницRoutine PracticesGreg van BeekОценок пока нет
- Asepsis in EndodonticsДокумент55 страницAsepsis in EndodonticsVidya AnandОценок пока нет
- Glove SOP For Glove by DR Mohamed RifasДокумент3 страницыGlove SOP For Glove by DR Mohamed RifasDrMohamed RifasОценок пока нет
- Asepsis and Infection ControlДокумент120 страницAsepsis and Infection Controlnagarjungali100% (1)
- IDA Recommendations For Dental Professionals On The Coronavirus ThreatДокумент5 страницIDA Recommendations For Dental Professionals On The Coronavirus ThreatAli Faraz SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- HandwashingДокумент36 страницHandwashingidelleequibalОценок пока нет
- Hospital-Acquired Infections: Strategic Management, Control and PreventionДокумент13 страницHospital-Acquired Infections: Strategic Management, Control and PreventionGyanesh_DBОценок пока нет
- MODULE 7 Infection ControlДокумент43 страницыMODULE 7 Infection ControlBitoy AlarconОценок пока нет
- Report Ko TomДокумент15 страницReport Ko Tomskjet44Оценок пока нет
- Principles Underlying Medical and Surgical AsepsisДокумент12 страницPrinciples Underlying Medical and Surgical AsepsisKiyoteru Hiyama0% (1)
- Asepsis and Health Illness NotesДокумент10 страницAsepsis and Health Illness NotesAgnes Jeane EnriquezОценок пока нет
- Hand Hygiene and Aseptic TechniqueДокумент3 страницыHand Hygiene and Aseptic TechniqueimadhassanОценок пока нет
- SOPs for Hospitals in ChhattisgarhДокумент62 страницыSOPs for Hospitals in ChhattisgarhFifty One71% (7)
- 2StandardOperatingProceduresforHospitals PDFДокумент62 страницы2StandardOperatingProceduresforHospitals PDFJoseph JordanОценок пока нет
- Nursing Foundation: Unit Xi Infection Control in Clinicl SettingДокумент45 страницNursing Foundation: Unit Xi Infection Control in Clinicl Settingbemina jaОценок пока нет
- Medical Asepsis TechniquesДокумент6 страницMedical Asepsis TechniquesChetan KumarОценок пока нет
- Standard and Isolation PrecautionДокумент31 страницаStandard and Isolation PrecautionMarriam LegazpiОценок пока нет
- Survival Skills: How to Survive Anything and Anywhere in the World (A Comprehensive Guide to Preparing for and Overcoming Challenges of Earthquakes)От EverandSurvival Skills: How to Survive Anything and Anywhere in the World (A Comprehensive Guide to Preparing for and Overcoming Challenges of Earthquakes)Оценок пока нет
- Basic Guide to Infection Prevention and Control in DentistryОт EverandBasic Guide to Infection Prevention and Control in DentistryОценок пока нет
- Abstrak - Modern Dressing - EnglishДокумент3 страницыAbstrak - Modern Dressing - EnglishDeny RakhmanОценок пока нет
- Abstrak - Modern DressingДокумент1 страницаAbstrak - Modern DressingDeny RakhmanОценок пока нет
- Andreasen ClassificationДокумент1 страницаAndreasen ClassificationDeny RakhmanОценок пока нет
- Seeing Much, Suffering Much and Studying Much Are The Three Pillars of Learning.Документ43 страницыSeeing Much, Suffering Much and Studying Much Are The Three Pillars of Learning.Deny RakhmanОценок пока нет
- Technique Tongue FlapДокумент2 страницыTechnique Tongue FlapDeny RakhmanОценок пока нет
- 19 142 1 PBДокумент5 страниц19 142 1 PBajikwaОценок пока нет
- Historical Development of Modern SurgeryДокумент16 страницHistorical Development of Modern SurgeryDeny RakhmanОценок пока нет
- Microbiology Testing and Sterilization Methods for Pharmaceutical ProductsДокумент1 страницаMicrobiology Testing and Sterilization Methods for Pharmaceutical ProductsThomas Niccolo Filamor ReyesОценок пока нет
- Syphilis: DR Gregg Eloundou UhcwДокумент22 страницыSyphilis: DR Gregg Eloundou UhcwSamuel Sebastian SirapanjiОценок пока нет
- Guidelines for infected OHCPs manage risksДокумент37 страницGuidelines for infected OHCPs manage risksYeoh Wei KeongОценок пока нет
- Form Blood RequisitionДокумент2 страницыForm Blood Requisitionshubham kumar ram100% (1)
- Bloodborne Pathogen Safety TestДокумент3 страницыBloodborne Pathogen Safety TestBlanca AgueroОценок пока нет
- Determination of microbiological quality of packed vs unpacked bread and flourДокумент7 страницDetermination of microbiological quality of packed vs unpacked bread and flourHemant OjhaОценок пока нет
- Traditional Starter Cultures in CheesethДокумент88 страницTraditional Starter Cultures in CheesethCAPRINOS BAJA CALIFORNIA SUR, MEXICO100% (1)
- 1stinternational Congress On Food TechnologyДокумент571 страница1stinternational Congress On Food TechnologyPat ChuthamasОценок пока нет
- Meningococcemia GuideДокумент5 страницMeningococcemia GuidezzoOeeОценок пока нет
- Biology SLT Project TopicsДокумент3 страницыBiology SLT Project Topicskelvin carterОценок пока нет
- Evolution of Microorganisms: From Prescott's Microbiology Biology 2710 Professor W.D.WestДокумент38 страницEvolution of Microorganisms: From Prescott's Microbiology Biology 2710 Professor W.D.WestAmal IdreesОценок пока нет
- (醫學筆記) 抗生素使用 Antibiotics part.1 概論+β-lactam: by kphsien Published 97 CommentsДокумент8 страниц(醫學筆記) 抗生素使用 Antibiotics part.1 概論+β-lactam: by kphsien Published 97 Comments蔡宏達Оценок пока нет
- Sop For Environmental Monitoring For PersonnelДокумент4 страницыSop For Environmental Monitoring For PersonnelMusyoka UrbanusОценок пока нет
- Bioterrorism Agents and Their Deadly EffectsДокумент35 страницBioterrorism Agents and Their Deadly EffectsKevin FachriОценок пока нет
- Microbiology 1st Edition Wessner Solutions ManualДокумент8 страницMicrobiology 1st Edition Wessner Solutions ManualLarryPiercexteaz100% (9)
- 9.2-Epidemiology of Infectious DiseasesДокумент67 страниц9.2-Epidemiology of Infectious DiseasesMarin Jr., Reynaldo J.Оценок пока нет
- Herpes Fact SheetДокумент2 страницыHerpes Fact SheetRebecca RichardsonОценок пока нет
- Infection and Host ResistanceДокумент62 страницыInfection and Host ResistanceAndrea Marie T. Artajo-BoheromОценок пока нет
- Mdparas NotesДокумент46 страницMdparas NotesnamkimseoОценок пока нет
- Full Data AnalysisДокумент627 страницFull Data AnalysisMyMinecrafter97Оценок пока нет
- SHC ABX Dosing GuideДокумент6 страницSHC ABX Dosing GuideAndreea SasuОценок пока нет
- BorreliaДокумент17 страницBorreliaLin Sison Vitug100% (1)
- COVID-19 and Disinfectants and Sanitizers in Food PremisesДокумент5 страницCOVID-19 and Disinfectants and Sanitizers in Food Premisesnur atiqah sobriОценок пока нет
- Pediatric Vaccine Àd Vaccination PDFДокумент257 страницPediatric Vaccine Àd Vaccination PDFntnquynhpro100% (1)
- M.Sc. Foods and Nutrition PDFДокумент43 страницыM.Sc. Foods and Nutrition PDFRajaDeepak VermaОценок пока нет
- Mojbm 03 00082Документ5 страницMojbm 03 00082Sohrab RohaneОценок пока нет
- Sporeclear Device Sell Sheet GB PDFДокумент2 страницыSporeclear Device Sell Sheet GB PDFaringkinkingОценок пока нет
- Full Download Test Bank For Prescotts Microbiology 8th Edition Willey PDF Full ChapterДокумент36 страницFull Download Test Bank For Prescotts Microbiology 8th Edition Willey PDF Full Chaptergenevieveprattgllhe100% (16)
- MALDI-ToF in Clinical MicrobiologyДокумент39 страницMALDI-ToF in Clinical Microbiologytummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (1)
- Introduction of MicrobiologyДокумент52 страницыIntroduction of MicrobiologyTri Wahyudi Iman DantaraОценок пока нет