Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
UPSC Economics Optional Syllabus
Загружено:
sakfdlkОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
UPSC Economics Optional Syllabus
Загружено:
sakfdlkАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
154 THE GAZETTE OF INDIA : EXTRAORDINARY [PART I—SEC.
1]
ECONOMICS (iv) Floating Rates and their Implications for
PAPER—I Developing Countries : Currency Boards.
1. Advanced Micro Economics : (v) Trade Policy and Developing Countries.
(a) Marshallian and Varrasiam Approaches to Price (vi) BOP, adjustments and Policy Coordination in
determination. open economy macromodel.
(b) Alternative Distribution Theories; Ricardo, Kaldor, (vii) Speculative attacks.
Kaleeki. (viii) Trade Blocks and Monetary Unions.
(c) Markets Structure : Monopolistic Competition, (ix) WTO : TRIMS, TRIPS, Domestic Measures,
Duopoly, Oligopoly. Different Rounds of WTO talks.
(d) Modern Welfare Criteria : Pareto Hicks and Scitovsky, 5. Growth and Development :
Arrow’s Impossibility Theorem, A. K. Sen’s Social
(a) (i) Theories of growth : Harrod’s model;
Welfare Function.
(ii) Lewis model of development with surplus labour.
2. Advance Macro Economics :
(iii) Balanced Unbalanced Growth.
Approaches to Employment Income and Interest Rate
determination : Classical, Keynes (IS)-LM) curve, (iv) Human Capitals and Economic Growth.
Neo-classical synthesis and New classical, Theories (v) Research and Development and Economic Growth.
of Interest Rate determination and Interest Rate
(b) Process of Economic Development of less developed
Structure.
courtries : Myrdal and Kuzments on economic
3. Money-Banking and Finance : development and structural change : Role of Agriculture
(a) Demand for and Supply of Money : Money Multiplier in Economic Development of less developed countries.
Quantity Theory of Money (Fisher, Pique and (c) Economic Development and International Trade and
Friedman) and Keyne’s Theory on Demand for Investment, Role of Multinationals.
Money, Goals and Instruments of Monetary
(d) Planning and Economic Development : changing role of
Management in Closed and Open Economies.
Markets and Planning, Private-Public Partnership.
Relation between the Central Bank and the Treasury.
Proposal for ceiling on growth rate of money. (e) Welfare indicators and measures of growth—Human
Development Indices. The basic needs approach.
(b) Public Finance and its Role in market Economy : In
stabilisation of supply, allocative, of resources and (f) Development and Environmental Sustainability—
in distribution and development. Sources of Renewable and Non-renewable Resources,
Government revenue, forms of Taxes and Subsidies, Environmental Degradation, Intergenerational equity
their incidence and effects. Limits to taxation, loans, development.
crowding-out effects and limits to borrowings. Public PAPER-II
expenditure and its effects.
Indian Economics in Post-Independence Era :
4. International Economics :
Land System and its changes, Commercialization of
(a) Old and New theories of International Trade. agriculture Drain theory, Laissez faire theory and critique.
(i) Comparative advantage, Manufacture and Transport : Jute, Cotton, Railways, Money
(ii) Terms of Trade and Offer Curve. and Credit.
(iii) Product Cycle and Strategic Trade Theories. Indian Economy after Independence :
(iv) Trade as an engine of growth and theories of A. The Pre-Liberalization Era :
underdevelopment in an open economy.
(i) Contribution of Vakil, Gadgil and V.K.R.V. Rao.
(b) Forms of Protection : Tariff and quota.
(ii) Agricultrure : Land Reforms and land tenure system,
(c) Balance of Payments Adjustment : Alternative Green Revolution and capital formation in agriculture.
Approaches.
(iii) Industry Trends in composition and growth, Role of
(i) Price versus income, income adjustments public and private sector, small scale and cottage
under fixed exchange rates. industries.
(ii) Theories of Policy Mix.
(iv) National and Per capita income : Patterns, trends,
(iii) Exchange rate adjustments under capital aggregate and sectoral composition and changes
mobility. therein.
¹Hkkx Iµ[k.M 1º Hkkjr dk jkti=k % vlk/kj.k 155
(v) Broad factors determining National Income and waves. Transmission lines : travelling and standing waves,
distribution, Measures of poverty, Trends in poverty impedance matching, Smith chart.
and inequality.
4. Analog Electronics :
B. The Post-Liberalization Era :
Characteristics and equivalent circuits (large and small-
(i) New Economic Reform and Agriculture : Agriculture signal) of Diode, BJT, JFET and MOSFET. Diode circuits :
and WTO, Food processing, subsidies, Agricultural Clipping, clamping, rectifier. Biasing and bias stability. FET
prices and public distribution system, Impact of public amplifiers. Current mirror; Amplifiers : single and multi-stage,
expenditure on agricultural growth. differential, operational feedback and power. Analysis of
(ii) New Economic Policy and Industry : Strategy of amplifiers; frequency-response of amplifiers. OPAMP circuits.
industrialization, Privatization, Disinvestments, Role Filters; sinusoidal oscillators : criterion for oscillation; single-
of foreign direct investment and multinationals. transistor and OPAMP configurations. Function generators
and wave-shaping circuits. Linear and switching power
(iii) New Economic Policy and Trade : Intellectual supplies.
property rights : Implications of TRIPS, TRIMS, GATS
and new EXIM policy. 5. Digital Electronics :
(iv) New Exchange Rate Regime : Partial and full Boolean algebra; minimisation of Boolean functions;
convertibility, Capital account convertibility. logic gates; digital IC families (DTL, TTL, ECL, MOS, CMOS).
Combinational circuits : arithmetic circuits, code converters,
(v) New Economic Policy and Public Finance : Fiscal multiplexers and decoders. Sequential circuits: latches and
Responsibility Act, Twelfth Finance Commission and flip-flops, counters and shift-registers. Comparators, timers,
Fiscal Federalism and Fiscal Consolidation. multivibrators. Sample and hold circuits, ADCs and DACs.
(vi) New Economic Policy and Monetary System. Role Semiconductor memories. Logic implementation using
of RBI under the new regime. programmable devices (ROM, PLA, FPGA).
(vii) Planning : From central Planning to indivative 6. Energy Conversion :
planning, Relation between planning and markets
Principles of electromechanical energy conversion :
for growth and decentralized planning : 73rd and 74th
Torque and emf in rotating machines. DC machines :
Constitutional amendments.
characteristics and performance analysis; starting and speed
(viii) New Economic Policy and Employment : Employment control of motors. Transformers : principles of operation and
and poverty, Rural wages, Employment Generation, analysis; regulation, efficiency; 3-phase transformers.
Poverty alleviation schemes, New Rural, Employment 3-phase induction machines and synchronous machines :
Guarantee Scheme. characteristics and performance analysis; speed control.
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 7. Power Electronics and Electric Drives :
PAPER-I Semi-conductor power devices : diode, transistor,
1. Circuits—Theory : thyristor, triac, GTO and MOSFET-static characteristics and
principles of operation; triggering circuits; phase control
Circuit components; network graphs; KCL, KVL; Circuit rectifiers; bridge converters : fully-controlled and half-
analysis methods : nodal analysis, mesh analysis; basic controlled; principles of thyristor choppers and inverters; DC-
network theorems and applications; transient analysis : RL, DC converters; Switch mode inverter; basic concepts of speed
RC and RLC circuits; sinusoidal steady state analysis; resonant control of dc and ac motor drives applications of variable-
circuits; coupled circuits; balanced 3-phase circuits. Two-port speed drives.
networks.
8. Analog Communication :
2. Signals and Systems :
Random variables : continuous, discrete; probability,
Representation of continuous-time and discrete-time probability functions. Statistical averages; probability models;
signals and systems; LTI systems; convolution; impulse Random signals and noise : white noise, noise equivalent
response; time-domain analysis of LTI systems based on bandwidth; signal transmission with noise; signal to noise
convolution and differential/difference equations. Fourier ratio. Linear CW modulation : Amplitude modulation : DSB,
transform, Laplace transform, Z-transform, Transfer function. DSB-SC and SSB. Modulators and Demodulators; Phase and
Sampling and recovery of signals DFT, FFT Processing of Frequency modulation : PM & FM signals; narrows band
analog signals through discrete-time systems. FM; generation & detection of FM and PM, Deemphasis,
3. E.M. Theory : Preemphasis. CW modulation system : Superhetrodyne
receivers, AM receivers, communication receivers, FM
Maxwell’s equations, wave propagation in bounded receivers, phase locked loop, SSB receiver Signal to noise
media. Boundary conditions, reflection and refraction of plane ratio calculation or AM and FM receivers.
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Group 2 Main Control Valve: 1. StructureДокумент23 страницыGroup 2 Main Control Valve: 1. StructureАлексейОценок пока нет
- VES-5097 Inspection and Testing of ValvesДокумент14 страницVES-5097 Inspection and Testing of ValvesBayumi Tirta JayaОценок пока нет
- 0 - Actions On Structures Wind Loads - CIB ReportДокумент100 страниц0 - Actions On Structures Wind Loads - CIB ReportWilliam PolОценок пока нет
- v12 CompletДокумент226 страницv12 CompletLidetu AbebeОценок пока нет
- ASTM F152 Gaskets Tension TestingДокумент3 страницыASTM F152 Gaskets Tension TestingDieguitoOmarMoralesОценок пока нет
- Training Manual A 319/320/321: ATA 30 Ice and Rain ProtectionДокумент46 страницTraining Manual A 319/320/321: ATA 30 Ice and Rain ProtectionHansraj Kayda100% (1)
- Conversion & Reactor Sizing: Dr. Kelly Yong Tau LenДокумент16 страницConversion & Reactor Sizing: Dr. Kelly Yong Tau LenAmandaEdwinОценок пока нет
- SIGGRAPH2022 Advances Lumen Wright Et AlДокумент199 страницSIGGRAPH2022 Advances Lumen Wright Et AlmhazaniОценок пока нет
- Module One 4 BAKERY INGREDIENTSДокумент46 страницModule One 4 BAKERY INGREDIENTSIhsan BadshaОценок пока нет
- SAE AMS QQ A 200-9-1997 Aluminum Alloy 6063 Bar Rod Shapes Tube and Wire ExtrudedДокумент7 страницSAE AMS QQ A 200-9-1997 Aluminum Alloy 6063 Bar Rod Shapes Tube and Wire ExtrudedsabrunoОценок пока нет
- Multilevel Converters - Dual Two-Level Inverter SchemeДокумент226 страницMultilevel Converters - Dual Two-Level Inverter Schemejuancho2222Оценок пока нет
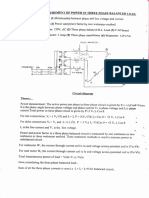
- Experiment: Measurement of Power in Three Phase Balanced LoadДокумент2 страницыExperiment: Measurement of Power in Three Phase Balanced LoadTripti GuptaОценок пока нет
- BookSellerFlyer 9781484241660Документ1 страницаBookSellerFlyer 9781484241660超揚林Оценок пока нет
- Lehmann Et Al 2013 PDFДокумент13 страницLehmann Et Al 2013 PDFJack HamiltonОценок пока нет
- Babikian Et Al Historical Fuel Efficiencies 2002Документ12 страницBabikian Et Al Historical Fuel Efficiencies 2002irockdudeОценок пока нет
- 0w 30 Yağ ÖzellikleriДокумент2 страницы0w 30 Yağ ÖzellikleriahmetОценок пока нет
- Sequential Logic: Unit-IДокумент86 страницSequential Logic: Unit-IMonika RawatОценок пока нет
- ISCSI OptimizationДокумент28 страницISCSI OptimizationrahulhclОценок пока нет
- Siemens Profiset 3030 enДокумент11 страницSiemens Profiset 3030 enBoasu FlorinОценок пока нет
- Digital Control System Analysis and Design 4th Edition by Phillips ISBN Solution ManualДокумент46 страницDigital Control System Analysis and Design 4th Edition by Phillips ISBN Solution Manualraymond100% (23)
- Exploring Linux Build Systems - Buildroot Lab ManualДокумент38 страницExploring Linux Build Systems - Buildroot Lab Manualhamzamehboob103Оценок пока нет
- Technical Analysis 1: Lg/Med Track ExcavatorsДокумент6 страницTechnical Analysis 1: Lg/Med Track ExcavatorsKang AdingОценок пока нет
- Sapmm - Spro .Path SettingsДокумент2 страницыSapmm - Spro .Path SettingsVijay AnandОценок пока нет
- Annexure 1 - Technical Bid Analysis For Emergency Relief ValveДокумент1 страницаAnnexure 1 - Technical Bid Analysis For Emergency Relief ValveNikhil KarkeraОценок пока нет
- Remote Terminal Viewer Software Release Note 1101192-A: © Foxboro Australia 2000 ACN 000 522 26Документ16 страницRemote Terminal Viewer Software Release Note 1101192-A: © Foxboro Australia 2000 ACN 000 522 26Mochamad EffendiОценок пока нет
- Synchronous Generators - 2 Marks Questions and AnswersДокумент3 страницыSynchronous Generators - 2 Marks Questions and AnswersJoseph Harindranath67% (3)
- Busiess Analytics Data Mining Lecture 7Документ37 страницBusiess Analytics Data Mining Lecture 7utkarsh bhargavaОценок пока нет
- Programming Exercise 2Документ2 страницыProgramming Exercise 2hamidahrazakОценок пока нет
- Surgical Sutures: Suture SizeДокумент7 страницSurgical Sutures: Suture SizeMei PayumoОценок пока нет
- Engineering Materials CE-105: ConcreteДокумент27 страницEngineering Materials CE-105: Concretenasir khanОценок пока нет