Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Hukum Gas Persamaan Keadaan Gas Pada Tekanan Rendah Dibentuk Dengan Menggabungkan Serangkaian Hukum Empiris
Загружено:
Yuliantari YuliantariАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Hukum Gas Persamaan Keadaan Gas Pada Tekanan Rendah Dibentuk Dengan Menggabungkan Serangkaian Hukum Empiris
Загружено:
Yuliantari YuliantariАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Proceedings of the National Seminar of Chemical Engineering "Kejuangan" ISSN 1693-4393
Development of Chemical Technology for Processing of Natural Resources Indonesia
Yogyakarta, 17Maret 2016
Cyanide Adsorption Studies of Gold Tailings Processing
method Resin-In-Pulp
Latitude ninik EW *, Cut Shafira, Palguno Helyoso
D-IV Studies Program Cleaner Production of Chemical Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, Polytechnic of Bandung,
D-III Study Program of Chemical Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, Polytechnic of Bandung,
Gegerkalong Jalan Hilir, Ds Ciwaruga, Bandung
* E-mail : niniklintang@yahoo.com
Abstract
Cyanidation is an efficient and inexpensive process extracting gold from ore, allowing recovery of gold from low-grade ore Carried out
economically. The disadvantage of cyanidation process is the generation of highly toxic cyanide-containing tailings. Such tailings need to
be treated prior to disposal, in order to comply with environmental requirements. There are two methods to Overcome cyanide-containing
tailings , By recycling and recovery. cyanide recovery will Eliminate the cost and a cyanide destruction will reduce purchasing cost of fresh
cyanide. Cyanide adsorption (as part of Hannah Process) has been studied using batch adsorption
techniques, to examine the contact time, adsorbent dose, and maximum adsorption capacity of Lewatit U-SO 4
resin for cyanide removal. Results revealed that the adsorption rate Initially Increased rapidly, and the optimum removal efficiency was
Reached within two hours. Further increase is in contact time did not show a significant change in the equilibrium concentration; that means,
the adsorption has Reached equilibrium. The adsorption isotherms could be fitted well by the Langmuir models. The R L value in the
investigation was less than one, indicating that the adsorption of cyanide onto the resin is favorable. The resin optimum dose was 44 g / L
and the maximum capacity was20 mg CN / g resin, equivalent to 0.846eq / L resin.
Keywords: Adsorption, cyanide, resins, cyanide recovery, Hannah Process
preliminary
The gold-silver extraction from ore using cyanide has been applied since 1887, as very economical and provides acquisition of gold-silver
maximum, either for the extraction of low gold grade ores or ore refractory ( Logsdon et al, 1999). In the process of cyanidation, gold ore is
contacted with cyanide solution with a concentration of 100 to 500 ppm, so that the gold-silver complex compound formed with cyanide.
Waste generated from cyanidation process is tailings, that is slurry of particles of rock / ore size of 200 mesh with a solids content of about 40%,
and containing cyanide with a concentration of about 300 ppm. Cyanide is a highly toxic compound, brief exposure to cyanide in humans can cause
health problems, such as tremors and other neurological effects, while exposure to the long term can lead to weight loss, thyroid and nervous
system damage.
In accordance with environmental regulations and sustainability of the operation, in general tailings bersianida treated before discharge into the
environment, with destruction of reagent (INCO process SO 2 / Degussa air or copper-catalyzed process H 2 O 2), and continued with the natural
destruction by ultraviolet light from the sun (Michael M. Botz 2001) .In cyanide, waste tailings also contains other metals that are not extracted as
copper, iron, zinc, lead (Prasetyo, Radyan 2008) yangperlu considered in the waste management ..
Cyanide contained in tailings still allows for in- recovery and can be reused, thereby reducing the cyanide consumption for leaching. There are
three methods to Me- recovery cyanide from gold ore processing, one of which is by adsorption methods Resin In Pulp, because it is not necessary pre-treatment
for separation particle padatandari larutan.Sianida is carbonnitrogen polyatomic anion (CN-), which typically forms a complex with the transition
metal compound or alkali metal ionic bonds. Cyanide compounds can be classified into four types of bonds, namely free cyanide, simple bonding
cyanide ( simple cyanide compounds), weak acid dissociable ( WAD) cyanide, and strong cyanide complex compounds ( moderately strong cyanide
complexes) ( Logsdon et al.1999).
The third method of recovery of cyanide, the SART ( Sulphidization, Acidification, Recycling and Thickening) AVR ( Acidification, Volatilization and
Reneutralization) and prosesHannah.
Chemical Engineering Program, FTI, UPN "Veteran" Yogyakarta I8 - 1
Proceedings of the National Seminar of Chemical Engineering "Kejuangan" ISSN 1693-4393
Development of Chemical Technology for Processing of Natural Resources Indonesia
Yogyakarta, 17Maret 2016
a. SART ( Sulphidization, Acidification, Recycling and Thickening)
Developed SART process developed by SGS Lakefield and Teckcominco Corporation to handle a solution containing WAD compounds
(especially copper cyanide, zinc, and nickel cyanide). During sulfidation and acidification, a cyanide solution is added to the sulfide ions and sulfuric
acid to produce a pH of 4 to 5, and the metals precipitate in solution as sulphide concentrate (eg, Cu 2 S or ZnS), economic value, while the cyanide
in solution into the gas HCN. SART process corresponding to the processing solution with a content base metal high as WAD cyanide complex. But
the SART process produces free cyanide, then the excess solution still contains cyanide and should didestruksi before being discharged into the
environment.
b. AVR (Acidification, Volatilization and Reneutralization, Ritcey and McNamara, 1978)
At the AVR process, tailings added sulfuric acid to a pH of 6-7 to change all the free cyanide into cyanide, and then brought into contact with the
air counter-current in the column, and the gas absorbed HCN formed with a strong caustic solution in the absorber column to be converted into
cyanide ions. AVR process is a new cyanide recovery technology applied on an industrial scale by Michael Botz Elbow Creek Engineering (Botz,
2001).
c. Hannah process
Hannah process uses strong base resin to absorb cyanide compounds from tailings. The process consists of several stages of adsorption, elution,
and absorption. free cyanide and WAD will diadsorp compounds using a resin, then cyanide is released ( elution) from the resin with a solution of
concentrated acid, to produce HCN gas which is then absorbed by a solution of caustic soda (NaOH). Hannah appropriate process for dealing with a
solution containing copper cyanide, cyanide-free, other metal cyanide complexes, even anions thiocyanate. According to Nesbit (1996), with a
cyanide adsorption resins environmentally friendly because it does not produce the toxic substance between.
The research objective was to determine the optimum adsorption time, the optimum dose and the maximum capacity of the resin Lewatit resins
U SO 4 in mengadsorp cyanide.
adsorption
Adsorption is a process in which the absorption of one component (solute) from a solution (fluid) to move to the surface of solids (adsorbent).
Adsorption is divided into two types, namely physical adsorption and chemical adsorption. Physical adsorption occurs because of the Van der Waals
forces, where the force of attraction between the solute component with an adsorbent component is greater than the component of the solute with
the solvent. While the chemical adsorption occurs due to a chemical reaction between the solute with an adsorbent. According to Atkins (1999)
chemical adsorption process begins with physical adsorption, solute dimanakomponen closer to the surface of the adsorbent for their style of Van
Der Waals or hydrogen bonds. Solute component bound to the surface of the adsorbent and forming chemical bonds (covalent bonds in general) to
maximize the capacity of the room / porous adsorbent. 4 a chemical adsorption, with the reaction:
R-SO 4 + MCN •• R (CN) 2+ M 2 SO 4 (1)
Adsorption performance is influenced by the particle size of the adsorbent, pengadukanuntuk speed increase contact between the adsorbent with a
solute, temperature and operating pressure.
In the physical adsorption of adsorbate molecules can be released from the surface of the adsorbent unchanged at low pressure or temperature
higher than the adsorption conditions. While the release of the chemical adsorption adsorbate much more difficult. In the physical adsorption of
molecules formed adsorbat double layer (multi-molecular layers), and took place very quickly (intantaneous), while the chemical adsorption always
formed a single layer, and typically require activation energy.
Research methods
Materials used are tailings the form slurry with a solids content of about 35%, the cyanide content of 100, 200 and 300 ppm, resin Lewatit U-SO 4, ( the
average grain size of 0.85 (+/- 0.05) in mm; kapasitastotal 1.0 eq / L; densitas1.1 g / mL), a solution of AgNO 3 ( 100 ppm) as titrant for the analysis of
cyanide levels, indicators rhodamine 0.002% and the standard solution base metal ( Ag, Cu and Zn).
Equipment for adsorption experiments was beaker 1 L, flokulator, measuring cups 1 L, 100 mL beakers, analytical balance, petri dishes, funnels,
Erlenmeyer flask, burette, Spectrophotometer ( AAS).
Feed (750 ml) with particular cyanide levels (100, 200.300 ppm) were introduced into a beaker, then each
each added resin with a certain dose (22 gpl; 27.5 gpl; 38.5 gpl and 44 gpl). After the mixture was stirred
Chemical Engineering Program, FTI, UPN "Veteran" Yogyakarta I8 - 2
Proceedings of the National Seminar of Chemical Engineering "Kejuangan" ISSN 1693-4393
Development of Chemical Technology for Processing of Natural Resources Indonesia
Yogyakarta, 17Maret 2016
by flokulator with a rotation speed of 200 rpm for a specific adsorption (1, 2, 4, 8 hours). After adsorption was completed, filtration, and the filtrate
was analyzed and the content of the cyanide content base metal ( Ag, Cu and Zn). To get the maximum capacity of the resin is done by using a high
concentration of cyanide solution (900 ppm) without solid. Briefly stage trial presented at the G amber 1 '
Determining the optimum time
Determining the optimum dosage resin Determination of the maximum capacity of the resin
NaCN Resin (22 slurryN NaCN Resin 22-44 gpl NaCN 900 Resin: 0; 5; 10; 20; 40 gpl
slurry gpl) ppm
Adsorption batch N = Adsorption batch N = Adsorption batch N =
200 rpm 200 rpm The optimum 200 rpm t = 8
t = 1,2,4,8 hours time hours
filtration filtration filtration
residue
residue residue
filtrate filtrate
filtrate
Analysis Analysis Analysis of the levels of
kadarCN & base kadarCN & base CN and base mtl
metal memetal
metal
time of adsorption The optimum The maximum
optimum dosage resin capacity of the
resin
Figure 1. Trial stages
Results and Discussion
time of adsorption
Bait ( tailings) with a solids content of 34%, the concentration of the initial CN 340 ppm, Cu content of 7.94 ppm, 4.44 ppm Ag, and Zn 26 ppm, is
contacted with the resin with stirring speed 200 rpm, giving the results of adsorption as shown in Figure 2.
100
80
60
Cu
percent Adsorption
Zn
40
Ag
20
CN
0
0 5 10 15 20 25
Time, hours
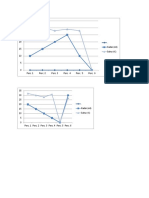
Figure 2. Effect of Percent Adsorption Against Time
At the time of the adsorption of up to two hours per cent increase in cyanide adsorption is significant, but after more than two hours of increase
slowed down, and on the hour to 24 is almost constant, which means it's a balance. for adsorption base metal, at the time of adsorption of one hour
per cent direct adsorption reached equilibrium in the first two hours, because of the concentration base metal in the feed is very low.
dose Resin
To study the effect of dose on the level of adsorption resins performed at different contact time, ie one and two hours, and is presented in
Figure 3.
Chemical Engineering Program, FTI, UPN "Veteran" Yogyakarta I8 - 3
Proceedings of the National Seminar of Chemical Engineering "Kejuangan" ISSN 1693-4393
Development of Chemical Technology for Processing of Natural Resources Indonesia
Yogyakarta, 17Maret 2016
100
80
Adsorption percent CN
60
40
20
0 10 20 30 40 50
Resin Dose (g / L)
1 hour 2 hours
Figure 3 Dose Effect of Resin Against PersenAdsorpsi
Effect of dose on the percent resin adsorption of cyanide showed that when different adsorption resins increased doses increase the percent
adsorption of cyanide with a tendency ( trend) the same, and at a dose of 44 g / L of adsorption almost reached equilibrium (percent adsorption of
83.3%).
To study the performance of a cyanide adsorption resin solution with varying doses (0, 10, 20 and 40 g / L) was done with cyanide solution with
initial concentration of 900 ppm (without solids / tailings) and is presented in Figure 4.
100
80
without resin
percent Adsorption
60 resin 10 gpl
resin 20 gpl
40
resin 40 gpl
20
0 5 10
Time, (h)
Figure 4. At the dose level Cyanide Adsorption Resin Varies
In experiments with blank solution (a cyanide solution without resin), was a decrease in the levels of cyanide from time to time, this is caused by
the evaporation of cyanide. At a dose of resin 10, 20 and 40 g / L per cent significant adsorption on contact time of two hours (35%, 61.7% and
81.7%), further improvement adsorption time up to 8 hours provide increased percent adsorption linearly but not significant. In the resin dose of 40 g
/ L effect on the percent adsorption time significantly by hours to two, with high effectiveness, and on the hour to the eight already close to balance
Theoretically increasing doses of resin will increase the surface area of contact between the adsorbent with a solution, so that the percent of
adsorption increased by an increase in the surface area of contact. But the increase in percent of adsorption is not linear with increasing doses of
resin, this is evidenced in the other adsorption studies (Das et al,
2015).
, Because at the time of adsorption two-hour difference between the dose level of adsorption resins which berbedacukup significant, then the adsorption
isotherm analysis and capacity of the resin is based on the contact time of 2 hours.
Adsorption isotherms
The results of adsorption experiments cyanide in the resin at room temperature are correlated with Langmuir models
C e / Q e = { 1 / (Q 0 b)} + C e / Q 0 (2)
Chemical Engineering Program, FTI, UPN "Veteran" Yogyakarta I8 - 4
Proceedings of the National Seminar of Chemical Engineering "Kejuangan" ISSN 1693-4393
Development of Chemical Technology for Processing of Natural Resources Indonesia
Yogyakarta, 17Maret 2016
where C e is the concentration of cyanide in solution at equilibrium (mg / L), Q e is cyanide adsorbed per gram of adsorbent at equilibrium (mg / g), Q 0 and
b is the Langmuir constants for capacity and energy of adsorption. The relationship between C e / Q e to C e shown in Figure 5.
20
Ce / Qe (g R / L)
15
y = 0.0505x + 4.3343
10 R ² = 0.987
0 50 100 150 200 250 300
Ce (CN mg / L)
Figure 5 Adsorption Langmuir isotherm
Langmuir adsorption isotherm curve is a straight line (linear) with R 2 = 0.987, indicating the enforceability
Langmuir isotherm model of the system, and also indicates the formation of a single layer on the surface of the adsorbent. Q value 0 and b (Langmuir
constants) obtained from the slope and curve intercep. The slope of the curve (1 / Q 0) is 0.05; then the capacity of the resin is 20 mg CN / g resin, or
the equivalent of 0.846 eq / L. Rated capacity of the resin is ideal compared to the characteristics of the resin Lewatit U-SO 4 , ie 1.0 eq / L. Further
analysis of the Langmuir equation can be done on the basis of the balance of dimensionless parameter R L, otherwise known as the separation factor,
according to the equation 3.
R L = 1 / (1 + bC i) (3)
If the value of R L between 0 and 1 then the ideal adsorption ( favorable), if R L greater than 1 then the less favorable adsorption ( unfavorable). Rated
R L the research is mengindikasikanbahwa 0154 cyanide adsorption on the resin follows the model of Langmuir isotherm.
Conclusion
From the study of adsorption of cyanide from tailings with resin Lewatit U-SO 4 it can be concluded that the percent of adsorption increases
initially and reaches the optimum at 2 hours. Adsorption isotherm according denganmodel
Langmuir, with value R L 0.154 ( less than one), which mengindikasikanbahwa cyanide adsorption on the resin is quite good. Dosage The optimum resin 44 g /
L and the maximum capacity of the resin 20 mg CN / g resin or equivalent to 0,846eq / L.
Bibliography
Botz, MM, " Overview of Cyanide Treatment Methods', Mining Environmental Management, Mining Journal Ltd.,
London, UK, pp. 28-30, May 2001. Das, Radharani et al, 2015 Utilization of Fly Ash as Low Cost Adsorbent for the Treatment of Textile Dying
Industry
Effluents: Kinetics and isotherms, International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering Website: www.ijetae.com (ISSN
2250-2459, ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Journal, Volume 5, Issue 2, February
2015)
Fleming, Chris, 2010, Cyanide Management in the gold industry Increasingly onerous restrictions are forcing the
sector to better manage the use and disposal of cyanide, Mining Environmental Management Logsdon, MJ et al. 1999 The Management Of
Cyanide In Gold Extraction ,. International Council On Metals And
The Environment, Ontario Prasetyo, Radyan 2008, Gold Mining Waste Utilization Study (Case Study: Pemanaatan Tailings in
PT Antam UBPE Pongkor)
PW Atkins. 1999. Chemical Physics. Jakarta. Erland SGS Group Management SA. 2013. Hannah Process. USA. SGS Lakefield. SGS Société
Générale de Surveillance SA. 2013. Cyanide Recovery. USA. SGS Lakefield. Strangfeld, Vinzenz Klaus. 2000. The Recovery of Metal cyanides by
Ion Exchange Resins. Cape Peninsula
University of Technology.
Chemical Engineering Program, FTI, UPN "Veteran" Yogyakarta I8 - 5
Proceedings of the National Seminar of Chemical Engineering "Kejuangan" ISSN 1693-4393
Development of Chemical Technology for Processing of Natural Resources Indonesia
Yogyakarta, 17Maret 2016
Sheet FAQ
Moderator: Yuliusman (University of Indonesia, Depok) Minutes
: Susanti Rina (UPN " Veteran " Yogyakarta)
1. questioner : Satriyo (UPN)
Question Why at time 0 - 2 hours adsorption occurs very quickly?
answer : Activity groups are still good (active) whereas at the time above the surface
group many have reacted so adsorption down.
2. questioner : Yuliusman (UI)
Question How resin treatment after the process?
answer : Resin recycled
Chemical Engineering Program, FTI, UPN "Veteran" Yogyakarta I8 - 6
Вам также может понравиться
- Journal of Molecular LiquidsДокумент11 страницJournal of Molecular LiquidsDo Khanh TungОценок пока нет
- A Comparative Isothermal and Kinetic Study of The Removal of Lead (II) From Aqueous Solution Using Different SorbentsДокумент21 страницаA Comparative Isothermal and Kinetic Study of The Removal of Lead (II) From Aqueous Solution Using Different Sorbentssagar dasguptaОценок пока нет
- Research ArticleДокумент13 страницResearch ArticlesrinuОценок пока нет
- Hydrogen Sulfide Removal Using Various Metal OxideДокумент44 страницыHydrogen Sulfide Removal Using Various Metal OxideOmar HishamОценок пока нет
- Journal of The Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers: Tawfik A. Saleh, Gaddafi I. DanmalikiДокумент9 страницJournal of The Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers: Tawfik A. Saleh, Gaddafi I. DanmalikiPrativa BeheraОценок пока нет
- Sriprang2014 Article AmorphousTitaniumDioxideAsAnAdДокумент10 страницSriprang2014 Article AmorphousTitaniumDioxideAsAnAdIsti IstiqomahОценок пока нет
- Cyanide Detoxification Process by Hydrogen PeroxideДокумент6 страницCyanide Detoxification Process by Hydrogen PeroxideHéctor GarcíaОценок пока нет
- Huang Et Al. (2018) - Heavy Metal Ion Removal of Wastewater by Zeolite-Imidazolate FrameworksДокумент8 страницHuang Et Al. (2018) - Heavy Metal Ion Removal of Wastewater by Zeolite-Imidazolate FrameworksAndrea ReveloОценок пока нет
- Malaysian Journal of Biochemistry & Molecular BiologyДокумент10 страницMalaysian Journal of Biochemistry & Molecular BiologyLailan Ni'mahОценок пока нет
- Potential of Nano Crystalline Calcium Hydroxyapatite For T - 2017 - Arabian JourДокумент11 страницPotential of Nano Crystalline Calcium Hydroxyapatite For T - 2017 - Arabian Jourlucian_lovОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S2213343718307978 MainДокумент8 страниц1 s2.0 S2213343718307978 Mainharyani S.Оценок пока нет
- Ijetr021101 PDFДокумент5 страницIjetr021101 PDFerpublicationОценок пока нет
- PRB2Документ14 страницPRB2Desy RsОценок пока нет
- Removal of Silver From Photographic SolutionsДокумент10 страницRemoval of Silver From Photographic SolutionsMinh Tiến TrầnОценок пока нет
- A15.... HGFDGGSZДокумент8 страницA15.... HGFDGGSZanand sagarОценок пока нет
- Separation and Purification Technology: Jin-Wei Zhang, Sarah Mariska, Sabolc Pap, Hai Nguyen Tran, Huan-Ping ChaoДокумент11 страницSeparation and Purification Technology: Jin-Wei Zhang, Sarah Mariska, Sabolc Pap, Hai Nguyen Tran, Huan-Ping ChaoLoc TonОценок пока нет
- Removal of Cadmium From Water Using Natural Phosphate As AdsorbentДокумент8 страницRemoval of Cadmium From Water Using Natural Phosphate As AdsorbentJavier Alejandro RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Application of Ultrasonic-Enhanced Active Seed Crystals in The Removal of Sodium Oxalate From Alumina Refinery Waste LiquorДокумент10 страницApplication of Ultrasonic-Enhanced Active Seed Crystals in The Removal of Sodium Oxalate From Alumina Refinery Waste LiquornirupamadastaneОценок пока нет
- Warer PurificationДокумент4 страницыWarer PurificationShweta SinghОценок пока нет
- Synthesis and Application of Tio2/Sio2/Fe3O4 Nanoparticles As Novel Adsorbent For Removal of CD (Ii), HG (Ii) and Ni (Ii) Ions From Water SamplesДокумент14 страницSynthesis and Application of Tio2/Sio2/Fe3O4 Nanoparticles As Novel Adsorbent For Removal of CD (Ii), HG (Ii) and Ni (Ii) Ions From Water SamplesIsti IstiqomahОценок пока нет
- Sun 2019 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 218 012142 PDFДокумент6 страницSun 2019 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 218 012142 PDFMujassim KhanОценок пока нет
- Zinc BagasseДокумент6 страницZinc BagassePRATYUSH TRIPATHYОценок пока нет
- 功能化含钨介孔硅材料的直接合成表征及其在多相氧化脱硫中的应用Документ8 страниц功能化含钨介孔硅材料的直接合成表征及其在多相氧化脱硫中的应用Pedro lopezОценок пока нет
- Production and Characterization of Granular Activated Carbon From Activated SludgeДокумент10 страницProduction and Characterization of Granular Activated Carbon From Activated SludgejshrikantОценок пока нет
- Investigación de Carbón Activo REV. 28 Sep - Es.enДокумент4 страницыInvestigación de Carbón Activo REV. 28 Sep - Es.enGeomar VelezОценок пока нет
- Alas Heh 2003Документ6 страницAlas Heh 2003Nila AzizahОценок пока нет
- 10 11648 J Ajac 20180601 14Документ10 страниц10 11648 J Ajac 20180601 14viktorija bezhovskaОценок пока нет
- IJEAS0302014Документ11 страницIJEAS0302014erpublicationОценок пока нет
- Removal of Arsenic From Aqueous Solutions by An Adsorption Process With Titania-Silica Binary Oxide Nanoparticle Loaded Polyacrylonitrile PolymerДокумент10 страницRemoval of Arsenic From Aqueous Solutions by An Adsorption Process With Titania-Silica Binary Oxide Nanoparticle Loaded Polyacrylonitrile PolymerBenjamín Vitón TapiaОценок пока нет
- De La Luz Et Al - 2020Документ10 страницDe La Luz Et Al - 2020Angel LopezОценок пока нет
- Adsorption Characteristics of Spent Co As An Alternative Adsorbent For Cadmium in SolutionДокумент12 страницAdsorption Characteristics of Spent Co As An Alternative Adsorbent For Cadmium in Solutionhaneen radОценок пока нет
- A Novel Approach To Extract SiO2 From Fly Ash and Its ConsiderableДокумент10 страницA Novel Approach To Extract SiO2 From Fly Ash and Its ConsiderableAssem TahaОценок пока нет
- Atmospheric Oxidation of Refractory Gold-Containing Concentrates and OresДокумент6 страницAtmospheric Oxidation of Refractory Gold-Containing Concentrates and OresLevent ErgunОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S1387700322006748 MainДокумент10 страниц1 s2.0 S1387700322006748 MainIkram ADNANEОценок пока нет
- Bead FRMTNДокумент9 страницBead FRMTNMeetika GuptaОценок пока нет
- Activated Charcoal Preparation, Characterization andДокумент6 страницActivated Charcoal Preparation, Characterization andMadhanОценок пока нет
- Report GeoHydrologyДокумент8 страницReport GeoHydrologyRobert Oliver Brito MatamorosОценок пока нет
- El Feky2022 Article FacileFabricationOfNano SizedSДокумент13 страницEl Feky2022 Article FacileFabricationOfNano SizedSmohamed samirОценок пока нет
- Reductive Leaching of Manganese From Low-Grade Manganese Dioxide Ores Using Corncob As Reductant in Sulfuric Acid SolutionДокумент4 страницыReductive Leaching of Manganese From Low-Grade Manganese Dioxide Ores Using Corncob As Reductant in Sulfuric Acid SolutionFilipe CruzОценок пока нет
- Kansal 2007Документ10 страницKansal 2007Hailer Yesid Romero PalaciosОценок пока нет
- Minerals Engineering: J.J. Eksteen, E.A. OrabyДокумент7 страницMinerals Engineering: J.J. Eksteen, E.A. Orabyjuan9gonzalez_9100% (1)
- LogamДокумент9 страницLogamSabina AzharОценок пока нет
- Removal of Cyanide From Water and Wastewater Using Granular Activated CarbonДокумент6 страницRemoval of Cyanide From Water and Wastewater Using Granular Activated CarbonarodriguezhОценок пока нет
- Report: Introduction To Nano Technology (CH3580) Water Filtration: Nano TechnologyДокумент3 страницыReport: Introduction To Nano Technology (CH3580) Water Filtration: Nano TechnologyMohammed Wasay MudassirОценок пока нет
- Journal of Alloys and CompoundsДокумент10 страницJournal of Alloys and Compoundsuroojkamran584Оценок пока нет
- IJEAS0301037Документ5 страницIJEAS0301037erpublicationОценок пока нет
- Febriana 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 858 012047Документ9 страницFebriana 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 858 012047mattОценок пока нет
- SILIKAДокумент7 страницSILIKAauria.121330093Оценок пока нет
- Kinetic Investigation and Dissolution Behavior of Cyanide Alternative Gold Leaching ReagentsДокумент10 страницKinetic Investigation and Dissolution Behavior of Cyanide Alternative Gold Leaching ReagentsCiprian AndreicaОценок пока нет
- Photocatalytic Activity of Cu Ag BNCs Synthesized by The Green Method Photodegradation Methyl Orange and Indigo CarmineДокумент12 страницPhotocatalytic Activity of Cu Ag BNCs Synthesized by The Green Method Photodegradation Methyl Orange and Indigo Carminelucas italoОценок пока нет
- Journal of Industrial and Engineering ChemistryДокумент9 страницJournal of Industrial and Engineering ChemistryHoracio Piña SpeziaОценок пока нет
- The Leaching and Adsorption of Gold Using Low Concentration Ami 2015 MineralДокумент7 страницThe Leaching and Adsorption of Gold Using Low Concentration Ami 2015 MineralHeyner MillánОценок пока нет
- SYNTHESIS OF ZnO NANOPARTICLES FOR ORGANIC POLLUTANT DEGRADATION PDFДокумент9 страницSYNTHESIS OF ZnO NANOPARTICLES FOR ORGANIC POLLUTANT DEGRADATION PDFumar raza khanОценок пока нет
- A Short Review On Arsenic Removal From Water: Sunil Jayant KulkarniДокумент4 страницыA Short Review On Arsenic Removal From Water: Sunil Jayant KulkarniInternational Journal of Scientific Research in Science, Engineering and Technology ( IJSRSET )Оценок пока нет
- Ijems 12 (3) 248-258Документ10 страницIjems 12 (3) 248-258buattugasmetlitОценок пока нет
- Activated Carbon With Optimum Pore Size Distribution For Hydrogen StorageДокумент6 страницActivated Carbon With Optimum Pore Size Distribution For Hydrogen StorageArif HidayatОценок пока нет
- D. Adsorptive Capacity of Calcinated Hen EggshellДокумент16 страницD. Adsorptive Capacity of Calcinated Hen EggshellAbreham BekeleОценок пока нет
- Removal of ZN (II) From Aqueous Solution Onto Kaolin by Batch DesignДокумент12 страницRemoval of ZN (II) From Aqueous Solution Onto Kaolin by Batch DesignHalida SophiaОценок пока нет
- Ion Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionОт EverandIon Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Structural Analysis, Material Optimization Using FEA and Experimentation of Centrifugal Pump ImpellerДокумент9 страницStructural Analysis, Material Optimization Using FEA and Experimentation of Centrifugal Pump ImpellerYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- Macro Micro - En.idДокумент6 страницMacro Micro - En.idYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- Hydrometallurgy: Yuna Zhao, Guocai Zhu, Zhuo ChengДокумент7 страницHydrometallurgy: Yuna Zhao, Guocai Zhu, Zhuo ChengYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- MetallographyДокумент6 страницMetallographynicksoldenОценок пока нет
- Bakan2006 PDFДокумент8 страницBakan2006 PDFYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- Large Eddy Simulation of Hydrocyclone - Prediction of Air-Core Diameter and ShapeДокумент14 страницLarge Eddy Simulation of Hydrocyclone - Prediction of Air-Core Diameter and ShapeYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- Hydrometallurgy: Yuna Zhao, Guocai Zhu, Zhuo ChengДокумент7 страницHydrometallurgy: Yuna Zhao, Guocai Zhu, Zhuo ChengYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- Design and Static Structural Analysis of Crank Shaft: ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.04, Issue.07, March-2015, Pages:1393-1398Документ6 страницDesign and Static Structural Analysis of Crank Shaft: ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.04, Issue.07, March-2015, Pages:1393-1398Yuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamic Properties and Characterizations of Chitosan Nano-Particles Corrosion..Документ10 страницThermodynamic Properties and Characterizations of Chitosan Nano-Particles Corrosion..Yuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- Hydrometallurgy: Yuna Zhao, Guocai Zhu, Zhuo ChengДокумент7 страницHydrometallurgy: Yuna Zhao, Guocai Zhu, Zhuo ChengYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S0301751606001384 MainДокумент1 страница1 s2.0 S0301751606001384 MainYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- Diesel EngineДокумент37 страницDiesel EngineYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S0301751606001384 MainДокумент1 страница1 s2.0 S0301751606001384 MainYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- Hydrometallurgy: Arao J. Manhique, Walter W. Focke, Carvalho MadivateДокумент7 страницHydrometallurgy: Arao J. Manhique, Walter W. Focke, Carvalho MadivateYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- The Propertie1Документ1 страницаThe Propertie1Yuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- Hydrometallurgy: Arao J. Manhique, Walter W. Focke, Carvalho MadivateДокумент7 страницHydrometallurgy: Arao J. Manhique, Walter W. Focke, Carvalho MadivateYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- ElectroplatingДокумент1 страницаElectroplatingYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- TitaniumДокумент7 страницTitaniumYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- 19 65 1 PBДокумент8 страниц19 65 1 PBDarmawanSetyadiОценок пока нет
- H12326974 PDFДокумент6 страницH12326974 PDFYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- The Propertie1Документ1 страницаThe Propertie1Yuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- Multistage Random SamplingДокумент17 страницMultistage Random SamplingYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- SulfurДокумент3 страницыSulfurYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- All 8Документ9 страницAll 8Yuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- Grafik KimiaДокумент2 страницыGrafik KimiaYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- The Propertie1Документ1 страницаThe Propertie1Yuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- Grafik KimiaДокумент2 страницыGrafik KimiaYuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- Gelombang 8Документ3 страницыGelombang 8Yuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- 9 14Документ11 страниц9 14Yuliantari YuliantariОценок пока нет
- Liquid Epoxy Type E: Force-Cure Epoxy For Superior 3-Layer Corrosion ProtectionДокумент2 страницыLiquid Epoxy Type E: Force-Cure Epoxy For Superior 3-Layer Corrosion ProtectionamirhosseinОценок пока нет
- Manual GISДокумент36 страницManual GISDanil Pangestu ChandraОценок пока нет
- SiUS121602E Service ManualДокумент222 страницыSiUS121602E Service ManualpqcrackerОценок пока нет
- Labour Laws in India FINALДокумент55 страницLabour Laws in India FINALSneha Periwal0% (1)
- Review Related LiteratureДокумент3 страницыReview Related LiteratureHanz EspirituОценок пока нет
- Medical Gases: NO. Item Brand Name OriginДокумент4 страницыMedical Gases: NO. Item Brand Name OriginMahmoud AnwerОценок пока нет
- Gec 014 Prelim ExaminationДокумент2 страницыGec 014 Prelim ExaminationcykablyatОценок пока нет
- Raymond Lo - The Feng Shui of Swine FluДокумент1 страницаRaymond Lo - The Feng Shui of Swine Fluay2004jan100% (1)
- Matriculation Chemistry Amino Acids-Part-1Документ24 страницыMatriculation Chemistry Amino Acids-Part-1iki292Оценок пока нет
- Conceptual Design and Development of Shredding Machine For Agricultural WasteДокумент7 страницConceptual Design and Development of Shredding Machine For Agricultural WasteVJ CarbonellОценок пока нет
- Microbiiology Lab LayoutДокумент9 страницMicrobiiology Lab LayoutNageswara raoОценок пока нет
- Music Therapy: Treatment For Grade 11 Stem Students Who Suffer Stress From Basic CalculusДокумент12 страницMusic Therapy: Treatment For Grade 11 Stem Students Who Suffer Stress From Basic CalculusArvinel L. VileganoОценок пока нет
- From Crème Fraîche To Sour Cream: What's The Difference?Документ14 страницFrom Crème Fraîche To Sour Cream: What's The Difference?Maricel BautistaОценок пока нет
- Heating Ventilation Air Conditioning Hvac ManualДокумент4 страницыHeating Ventilation Air Conditioning Hvac ManualShabaz KhanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ5 страницChapter 2ERICKA MAE NATOОценок пока нет
- Battle Healing PrayerДокумент9 страницBattle Healing PrayerSolavei LoanerОценок пока нет
- 3 Composites PDFДокумент14 страниц3 Composites PDFKavya ulliОценок пока нет
- O o o O: (Approval and Adoption of BCPC AWFP) (Approval and Adoption of BCPC AWFP)Документ2 страницыO o o O: (Approval and Adoption of BCPC AWFP) (Approval and Adoption of BCPC AWFP)Villanueva YuriОценок пока нет
- YuzurtДокумент2 страницыYuzurtFranco Ascari100% (1)
- Marine Turtle Survey Along The Sindh CoastДокумент106 страницMarine Turtle Survey Along The Sindh CoastSyed Najam Khurshid100% (1)
- Child DevelopmentДокумент12 страницChild DevelopmentPija Mohamad100% (1)
- Colonel SandersДокумент17 страницColonel SandersAmandaОценок пока нет
- TinyEYE Online Speech Therapy Media GuideДокумент4 страницыTinyEYE Online Speech Therapy Media GuideTinyEYE Therapy ServicesОценок пока нет
- Exercise 3 ASC0304 - 2019-1Документ2 страницыExercise 3 ASC0304 - 2019-1Nuraina NabihahОценок пока нет
- Pia AlgebraДокумент12 страницPia AlgebraCarvajal EdithОценок пока нет
- Remote Control RC902V1 ManualДокумент3 страницыRemote Control RC902V1 ManualdezdoОценок пока нет
- Corporate Security Policy TemplateДокумент4 страницыCorporate Security Policy TemplateCoronaОценок пока нет
- Polymer LedДокумент14 страницPolymer LedNaveenОценок пока нет
- 1635 The Papal Stakes - Eric FlintДокумент1 813 страниц1635 The Papal Stakes - Eric Flintwon100% (2)
- MCQДокумент5 страницMCQJagdishVankar100% (1)