Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Roof and Roofing Materials: Engr. Lito I. Mauro
Загружено:
Gerald Primavera0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
25 просмотров32 страницыRoof
Оригинальное название
Lecture 8 Space Truss Full Page
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документRoof
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
25 просмотров32 страницыRoof and Roofing Materials: Engr. Lito I. Mauro
Загружено:
Gerald PrimaveraRoof
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 32
Roof and Roofing Materials
Engr. Lito I. Mauro
Roof – the top covering of a building that
serves as a protective covering from
the weather.
Roofing materials refer to the kind of
materials used in the construction of
the roof.
Roofing material is the outermost layer on the
roof of a building, sometimes self-supporting,
but generally supported by an underlying
structure.
The roofing material of building provides shelter
from the natural elements.
The outer layer of a roof shows great variation
dependent upon availability of material, and
the nature of the supporting structure.
Roofing materials may be placed on top of a
secondary water-resistant material called
underlayment.
Roofing is an industry where one works
on roofs.
This industry is a high risk industry due to
the injuries that one can sustain in this
job environment.
Roofing is focused on the upper layer of a
house or building.
Roofing on a house is considered
residential and building as commercial.
What to Look for in a Roof
• How long will it last?
• Does it hold up during natural disasters such as
wildfires or hurricanes?
• Is it too heavy for the existing roof framing?
• Does the roof have enough slope?
• Will the look complement the style of the
house?
• Are the materials eco-friendly and recyclable?
• Is the type of roofing allowed by local building
codes?
• And finally, how much does it cost?
Pros and Cons
Slope of the roof and strength of the framing
could limit the choices for roofing
materials.
In areas prone to wildfires or typhoons, look
for a product with a high fire rating or
good wind resistance.
Steps can be taken during the installation of
many types of roofing to improve their
resistance to fire or wind.
Forms of roofing classified according to
the materials used
1. Fiber 2. Reinforced concrete
3. Wood 4. Tiles
5. Metal 6. Fiberglass
7. Slate 8. Plastics
The roof is not just a structure over our
heads but it is also known as the
“spine,” or the backbone of the
structure – the one that protects or
shields the home‟s “vital organs.”
Galvanized iron sheets
Galvanized iron roofing is either plain or
corrugated.
The thickness is measured in terms of “Gauge”
from numbers 14 to 30.
The sheet becomes thinner as the gauge number
increases, gauge 20 is thinner than gauge 18.
The price of G.I. sheets varies per unit length
depending upon the thickness.
Gauge 26 is the most commonly used for roofing
although gauge 24 is sometimes preferred by
those who can afford it.
Corrugated G.I. sheet is the most
common and extensively used
roofing materials.
Galvanized roofing is popular because of
its cost, availability, durability and
ease of installation.
The standard commercial size width is
32” (.80m) with length that ranges
from 5’ to 12’ (1.50m to 3.60m)
Prepainted products can last up to 15 years
against corrosion.
They also perform better against leaks, being
cut according to the length required, thus
avoiding horizontal overlapping, which
is one of the causes of leaks.
They are also installed using a special type of
screw called the „tekscrew‟ with rubber
washer, which is water tight.
Pre-painted long span metal roofing is
practical and economical.
Less joints mean less chances of leaks.
Long-span metal roofing is better to use than
commercial-length roofing sheets to
eliminate overlapping joints and
minimize the potential for leaks.
Long-span sheets cover more area, requiring
less joints.
Both ordinary and long span sheets are readily
available in the market.
In the Philippines, prepainted long-span
metal roofing made of GI sheets are
the most preferred.
Being prepainted, the GI sheets are already
factory-painted (and usually coated
with zinc-aluminum to make it more
durable and rust resistant).
GI roofing sheets is what is referred to when
the term „bubong na yero‟ is used.
Corrugated G.I. roofing fasteners
1. Riveting – Required are G.I. rivets, lead
washers and G.I. washers. Two
tinsmiths do the job.
2. Nailing – Simplest and most economical
method where G.I. roofings are
anchored to the purlins by the use of
roof nails and lead washers.
Advantages of G.I. rivets
1. Rigidity – The entire roofing acts as one
solid covering on top of the roof
frame with all parts connected by
rivets and washers.
2. Flexibility – The anchorage on the
purlins by G.I. straps allow free
movement of the materials brought
about by the thermal expansion and
contraction.
Disadvantages of G.I rivets
1. Expensive – due to the various accessories
involved aside from the high cost of
labor.
2. Difficulty of repair or replacement of
defective parts which include
dismantling of the ceiling underneath to
give access to tinsmithing activities.
3. Statistically, roof damage caused by
typhoon are mostly of the riveted types.
Advantages of G.I. nails
1. Economical because only nails and
washers are involved.
2. Easy to repair or replace defective parts.
3. Failure of roof in case of typhoon will
not result to total damage of the
entire roof and framing structure.
Disadvantages of G.I. nails
1. Water might leak into the nails if not
provided with roof cement during
the fastening operation.
2. Loose nails allow roof-play and
movement which usually invite
water to penetrate into the hole.
Lapping
1. Side lapping is either 1 ½ or 2 ½
corrugations.
2. End lapping ranges from 20cm to
30cm depending upon the slope of
the roof and the number of sheet in
a longitudinal row.
Roof gutter
Roof gutter uses Plain G.I. sheet with
gage #24.
Gutter is either concealed or exposed
type in various forms and designs.
It runs level in appearance but should be
sloped at 5mm/m run for effective
drainage.
Flashing
Flashing makes intersections and other
exposed parts of the house watertight.
It provides a smooth border line giving
beauty to the structure considering the
unlimited variety of designs.
Ridge and Hip roll
Ridge and hip rolls are unlikely to leak
because of the slope that water
tends to slide down. Because of its
prominency in the structure, it is
important to have it well done.
Valley roll
It is always concealed underneath between
the intersecting angles of the roof.
The design is limited to a semicircular, U-
shape or square type.
The gutter needs careful attention to avoid
overflow or leak of water.
Downspout
Downspout conveys the water from the
gutter down to the storm drain.
The most common size of G.I downspout is
the 2” x 4” (5cm x 10cm) ready made
commercial standard.
For residential works, allow 6sq.cm.
downspout to every 10sq.m. roof area
with a minimum spacing of 6m apart
and a maximum distance of 15m.
Roof shingles
Вам также может понравиться
- Roof and Roofing MaterialsДокумент29 страницRoof and Roofing MaterialsChristian BeninОценок пока нет
- Roofs Building ConstructionДокумент38 страницRoofs Building Constructionisaacwabbi100% (3)
- Your Home Inspected: An Addendum for Residential Home Inspection ReportsОт EverandYour Home Inspected: An Addendum for Residential Home Inspection ReportsОценок пока нет
- Types of RoofingДокумент24 страницыTypes of RoofingShayne GaloОценок пока нет
- The Functions and Classification of RoofsДокумент6 страницThe Functions and Classification of RoofsKevin De Silva86% (7)
- Roofing MaterialsДокумент14 страницRoofing MaterialsYashiq YousufОценок пока нет
- Cladding Systems: Manufactured Aluminum and Steel CladdingДокумент32 страницыCladding Systems: Manufactured Aluminum and Steel CladdingsalmaMB50% (2)
- Roof Design Principles: GenerallyДокумент55 страницRoof Design Principles: Generallyrcxy98Оценок пока нет
- Suspended CeilingДокумент26 страницSuspended CeilingVarun Malhotra100% (2)
- Field Duct Sizing ChartДокумент1 страницаField Duct Sizing ChartmemorydearОценок пока нет
- Design of Circular ShaftДокумент7 страницDesign of Circular Shaftจอม อรรฐาเมศร์Оценок пока нет
- Manual For The Design of Reinforced Concrete Building Structures To EC2Документ15 страницManual For The Design of Reinforced Concrete Building Structures To EC2heinsteinzОценок пока нет
- CladdingДокумент23 страницыCladdingSampada Kumbhe100% (1)
- Guidance RoofingДокумент42 страницыGuidance RoofingMujjo SahbОценок пока нет
- Member List 2017Документ13 страницMember List 2017Sithick MohamedОценок пока нет
- Householders Guide To Flat RoofingДокумент24 страницыHouseholders Guide To Flat RoofingBudi SudrajatОценок пока нет
- Two Way Flat Plate Reinforced Concrete Slab Floor System Design & Detailing (ACI 318 14)Документ65 страницTwo Way Flat Plate Reinforced Concrete Slab Floor System Design & Detailing (ACI 318 14)Lee Tai100% (1)
- FILE - 20220516 - 160427 - Lean Implementation Within Vinci ConstructionДокумент15 страницFILE - 20220516 - 160427 - Lean Implementation Within Vinci ConstructionTrung PhanОценок пока нет
- Prepare Construction Materials and Tools FinalДокумент89 страницPrepare Construction Materials and Tools FinalCarwill TesdaОценок пока нет
- Tata Durashine ManualДокумент16 страницTata Durashine ManualBudha SinghОценок пока нет
- Steel Roof Trusses 2Документ35 страницSteel Roof Trusses 2ASRОценок пока нет
- Construction Technology. 4th Sem CivilДокумент12 страницConstruction Technology. 4th Sem CivilZerro erAОценок пока нет
- Presented By: T.Masilamani (17MC67) M.E Structural Engg (Part Time) Industrial StructuresДокумент30 страницPresented By: T.Masilamani (17MC67) M.E Structural Engg (Part Time) Industrial StructuresMASILAMANI TОценок пока нет
- Roof CoveringsДокумент24 страницыRoof Coveringsdavid adawo100% (1)
- Roof - Functional Purpose: BE - 1105 Building Design and Construction Lecture Note - 06Документ11 страницRoof - Functional Purpose: BE - 1105 Building Design and Construction Lecture Note - 06Ken Ingram100% (1)
- Building Weather Cathedral Stadium Dwellings Rain Heat Sunlight Wind Conservatory VerandahДокумент24 страницыBuilding Weather Cathedral Stadium Dwellings Rain Heat Sunlight Wind Conservatory Verandahdudynayn100% (1)
- BMC V - Unit-4-Advanced Construction Techniques and MaterialsДокумент13 страницBMC V - Unit-4-Advanced Construction Techniques and Materialsaurora krishreddyОценок пока нет
- Kle Institute of Technology, Hubli: Team MembersДокумент12 страницKle Institute of Technology, Hubli: Team MembersVijayanand PrajwalОценок пока нет
- BMT - Module 4 - RoofsДокумент51 страницаBMT - Module 4 - RoofsRemya R Kumar100% (1)
- Arch - Tech.III - ROOFS.Pitched Roofs - Flat Sheets & Corrugated R. Const.Документ39 страницArch - Tech.III - ROOFS.Pitched Roofs - Flat Sheets & Corrugated R. Const.yasin100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Roofs: Page 1 of Ch-4 A Lecture Note Compiled By: Er. Kishor ThapaДокумент6 страницChapter 4 Roofs: Page 1 of Ch-4 A Lecture Note Compiled By: Er. Kishor ThapaPratik Ghimire100% (1)
- Qs Chapter 6 - 060103Документ20 страницQs Chapter 6 - 060103Erica Mae CastilloОценок пока нет
- Flat RoofДокумент9 страницFlat RoofAdrian Mosquisa100% (1)
- Roof Coverings: Building MaterialsДокумент38 страницRoof Coverings: Building Materialssoniya bhandariОценок пока нет
- Report GuideДокумент5 страницReport GuideclaireОценок пока нет
- A Research Into The Use of Plasterboards in Building ConstructioДокумент63 страницыA Research Into The Use of Plasterboards in Building ConstructioGamor Wonie SharonОценок пока нет
- Local Materialsnotes M, Eng. 4 Students of Enstp Yaoundé: Roofs For Natural BuildingДокумент11 страницLocal Materialsnotes M, Eng. 4 Students of Enstp Yaoundé: Roofs For Natural BuildingHervé Jabea100% (1)
- Cladding For BuildingsДокумент8 страницCladding For BuildingsCaryl Louise ObcianaОценок пока нет
- Cen 204 Roofing MaterialsДокумент54 страницыCen 204 Roofing MaterialsIntsik LvnОценок пока нет
- Building Enclosures Exterior Building Materials: Madhav Institute of Technology and Science GwaliorДокумент18 страницBuilding Enclosures Exterior Building Materials: Madhav Institute of Technology and Science Gwalioratharvasaxena93Оценок пока нет
- L8 - 17080 - Via - 13501 - Mix DetailsДокумент38 страницL8 - 17080 - Via - 13501 - Mix Detailsakhileshsharma94Оценок пока нет
- 2.2.3.1 Buildex® Screw Fasteners: 2.2.3.1.1 Fastener Assembly and DesignationДокумент11 страниц2.2.3.1 Buildex® Screw Fasteners: 2.2.3.1.1 Fastener Assembly and DesignationJoseph BookerОценок пока нет
- External Cladding MaterialДокумент11 страницExternal Cladding Materialsampada100% (1)
- Rooftop Pipe Support EBookДокумент22 страницыRooftop Pipe Support EBookdhanu_lagwankarОценок пока нет
- HWno.8.4 BSA-1A CORDIALДокумент9 страницHWno.8.4 BSA-1A CORDIALCharles Godwin CordialОценок пока нет
- Building Construction: Report OnДокумент15 страницBuilding Construction: Report Ony2kareinОценок пока нет
- BT AssignmentДокумент12 страницBT AssignmentRosemarie EscaroОценок пока нет
- Roofing TilesДокумент33 страницыRoofing TilesJeewanshu UttamОценок пока нет
- Roof CoveringДокумент34 страницыRoof Coveringasd dsaОценок пока нет
- BC CladdingДокумент21 страницаBC CladdingEla SharmaОценок пока нет
- Buildingmaterials 161105084923Документ17 страницBuildingmaterials 161105084923Glistering Dhar100% (1)
- Chapter 5.4 Roof & Roof Coverings (Part-2)Документ10 страницChapter 5.4 Roof & Roof Coverings (Part-2)ashenafi zerihunОценок пока нет
- Walls: ' T Io TDT .1F!. .'1oiiiu ' (LL - Scmon PJ Bi2S1 ".Документ27 страницWalls: ' T Io TDT .1F!. .'1oiiiu ' (LL - Scmon PJ Bi2S1 ".esubalew yayenaОценок пока нет
- Walls: ' T Io TDT .1F!. .'1oiiiu ' (LL - Scmon PJ Bi2S1 ".Документ21 страницаWalls: ' T Io TDT .1F!. .'1oiiiu ' (LL - Scmon PJ Bi2S1 ".esubalew yayenaОценок пока нет
- Research 1 PDFДокумент5 страницResearch 1 PDFKukishin KrimОценок пока нет
- Roofing System: Hafiz Uzair Naeem Ud Din M. ARCH #13. Building Design System Submitted To: Sir IshfaqДокумент23 страницыRoofing System: Hafiz Uzair Naeem Ud Din M. ARCH #13. Building Design System Submitted To: Sir IshfaqUzair SiddiqueОценок пока нет
- AK RoofingДокумент25 страницAK RoofingSampat Kumar100% (1)
- Ceiling Board With ApplicationДокумент12 страницCeiling Board With ApplicationRoland CepedaОценок пока нет
- 5.CE 315 - Chapter 2C - Roof Plan 3CE-2Документ8 страниц5.CE 315 - Chapter 2C - Roof Plan 3CE-2Mt KulisОценок пока нет
- Details of Residential ScopeДокумент5 страницDetails of Residential ScopeSyed ZamanОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes 9Документ16 страницLecture Notes 9AMESHAОценок пока нет
- Basic Civil - Module 3 - RoofДокумент19 страницBasic Civil - Module 3 - RoofSEKHAR JОценок пока нет
- Tension Test Discussion Mechanics of Materials Laboratory AEM-251Документ3 страницыTension Test Discussion Mechanics of Materials Laboratory AEM-251Usman ishaqОценок пока нет
- Quantity Estimate of 600 SS RCC GumbaДокумент10 страницQuantity Estimate of 600 SS RCC GumbaKale DaiОценок пока нет
- CE Performance DeclarationДокумент2 страницыCE Performance DeclarationPEng. Tech. Alvince KoreroОценок пока нет
- New Atlanta Permaline 2021Документ2 страницыNew Atlanta Permaline 2021Glenda SibongaОценок пока нет
- Designing CLT or Glulam Beams With Notches Accounting For Moisture EffectsДокумент6 страницDesigning CLT or Glulam Beams With Notches Accounting For Moisture EffectsSujit BhandariОценок пока нет
- Consistent DeformationДокумент98 страницConsistent DeformationHarianto RamadhanОценок пока нет
- LaurieДокумент14 страницLauriebhoirpratik451523Оценок пока нет
- Bending Moment and Shear Force Diagram - Cantilever Both Ends Sse-Excel SectionДокумент1 страницаBending Moment and Shear Force Diagram - Cantilever Both Ends Sse-Excel SectionSES DESIGNОценок пока нет
- TRC Engineers, Inc.-Structural Engineering - RedactedДокумент21 страницаTRC Engineers, Inc.-Structural Engineering - RedactedL. A. PatersonОценок пока нет
- CSSBI Tablas de Carga Perfiles PDFДокумент60 страницCSSBI Tablas de Carga Perfiles PDFRamón RocaОценок пока нет
- Kalpataru - Residency - Tower A Plan BookletДокумент7 страницKalpataru - Residency - Tower A Plan BookletAditi VishwakarmaОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Comparison Research PaperДокумент5 страницAggregate Comparison Research PaperMuzammal HussainОценок пока нет
- Anvil Specifications v3Документ40 страницAnvil Specifications v3EnriqueОценок пока нет
- RIL - ETP - Pipes & Valves 14.07.2022Документ3 страницыRIL - ETP - Pipes & Valves 14.07.2022bipradasdharОценок пока нет
- Im-015-16 Siemens 4500335983 (Col)Документ1 страницаIm-015-16 Siemens 4500335983 (Col)Gustaavo Caarvaajal HeerreraОценок пока нет
- Equivalent Beam LoadsДокумент8 страницEquivalent Beam LoadsArun KumarОценок пока нет
- SSA Analysis2Документ21 страницаSSA Analysis2Jomo-Rhys GilmanОценок пока нет
- A. N. Wallis Product Catalogue Compressed-File119615Документ276 страницA. N. Wallis Product Catalogue Compressed-File119615bishuddha ranjan paridaОценок пока нет
- BSC (Hons) Quantity Surveying and Construction Management Sheffield Hallam UniversityДокумент22 страницыBSC (Hons) Quantity Surveying and Construction Management Sheffield Hallam UniversityUlfathbary ABОценок пока нет
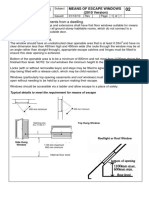
- Leaflet 2 Means of Escape WindowsДокумент1 страницаLeaflet 2 Means of Escape WindowsRuslan ZhivkovОценок пока нет
- W110 and W130 Wheel Loader Service Manual: General Tab 1Документ27 страницW110 and W130 Wheel Loader Service Manual: General Tab 1TadeleОценок пока нет
- Module 1 - Costeffective Construction TechniquesДокумент42 страницыModule 1 - Costeffective Construction TechniquesmUSIОценок пока нет
- Comfortbatt: Thermal Batt Insulation For Residential & Commercial ConstructionДокумент8 страницComfortbatt: Thermal Batt Insulation For Residential & Commercial Constructionallen andicoyОценок пока нет