Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
2 Types of Seizures
Загружено:
Ratu Palar0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
6 просмотров1 страницаqwqw
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документqwqw
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
6 просмотров1 страница2 Types of Seizures
Загружено:
Ratu Palarqwqw
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
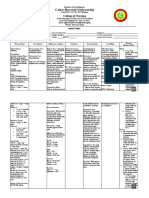
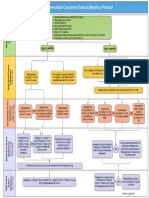
Pediatric Seizure
History Signs and Symptoms Differential
Fever Observed seizure activity Fever
Prior history of seizures Altered mental status Infection
Seizure medications Hot, dry skin or elevated body Head trauma
Reported seizure activity temperature Medication or Toxin
History of recent head trauma Hypoxia or Respiratory failure
Congenital abnormality Hypoglycemia
Metabolic abnormality / acidosis
Tumor
Universal Patient Care Protocol Legend
MR
Pediatric Airway Protocol B EMT B
I EMT- I I
Actively Seizing Post-ictal P EMT- P P
Pediatric and OB Protocols
M Medical Control M
Airway Protocol Assess Patient
I IV Protocol I Blood Glucose Glucose <60
Midazolam (Nasal/IM/IV/PR) Glucose >60 10% Dextrose
or I I
Glucagon if no IV
Lorazepam (IM/IV/PR)
P P Evidence of Trauma?
or
Pediatric Head Injury Protocol
Diazepam (IV/PR)
Obtain Temperature Febrile
May Repeat X 1 after 5 min
Seizure Recurs
Midazolam (Nasal/IM/IV/PR) Cooling Measures
or If Available
Blood Glucose P Lorazepam (IM/IV/PR) P B Tylenol B
If < 60 or (if > 3 months of age)
I I
10% Dextrose Diazepam (IV/PR) or Ibuprofen
Glucagon if no IV B B
May Repeat X 1 after 5 min (if > 6 months of age)
Still Seizing? No
Notify Destination or
Yes M M
Contact Medical Control
Pearls
Recommended Exam: Mental Status, HEENT, Heart, Lungs, Extremities, Neuro
Items in Red Text are key performance measures used to evaluate protocol compliance and care
Addressing the ABCs and verifying blood glucose is more important than stopping the seizure
Avoiding hypoxemia is extremely important
Status Epilepticus is defined as two or more successive seizures without a period of consciousness or recovery.
This is a true emergency requiring rapid airway control, treatment, and transport.
Grand mal seizures (generalized) are associated with loss of consciousness, incontinence, and tongue trauma.
Focal seizures (petit mal) effect only a part of the body and do not usually result in a loss of consciousness.
Jacksonian seizures are seizures which start as a focal seizure and become generalized.
Be prepared to assist ventilations especially if a benzodiazipine is used.
If evidence or suspicion of trauma, spine should be immobilized.
In an infant, a seizure may be the only evidence of a closed head injury.
Rectal Diazepam/Fentanyl/Lorazepam: Draw drug dose up in a 3 ml syringe. Remove needle from syringe and
attached syringe to an IV extension tube. Cut of the distal end of the extension tube leaving about 3 or 4 inches of
length. Insert tube in rectum and inject drug. Flush extension tube with 3 ml of air and remove.
Protocol 47 2009
Any local EMS System changes to this document must follow the NC OEMS Protocol Change Policy and be approved by OEMS
Вам также может понравиться
- 7698alorithm SeizureДокумент3 страницы7698alorithm Seizureboromeus abyasa daniswara100% (1)
- Metocloprramide HydrochlorideДокумент2 страницыMetocloprramide HydrochlorideBeatrizz P GellaОценок пока нет
- Neonatalseizureclinicalguideline PDFДокумент15 страницNeonatalseizureclinicalguideline PDFNURUL NADIA BINTI MOHD NAZIR / UPMОценок пока нет
- Terbutalin E Sulfate: Adults and Children Age 12 and OlderДокумент4 страницыTerbutalin E Sulfate: Adults and Children Age 12 and OlderHikari 光 ShidouОценок пока нет
- Evaluation and Management of Status Epilepticus in ChildrenДокумент13 страницEvaluation and Management of Status Epilepticus in ChildrenAyan BiswasОценок пока нет
- Febrile Seizures: Status EpilepticusДокумент34 страницыFebrile Seizures: Status EpilepticusSAIMA BATOOLОценок пока нет
- Child With Fits in ED - Srl.Документ2 страницыChild With Fits in ED - Srl.azeemОценок пока нет
- EpinephrineДокумент4 страницыEpinephrinegovind_soni_15Оценок пока нет
- 9 PropofolДокумент2 страницы9 PropofolAbdelhafiz Susmiran100% (3)
- Propofol Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыPropofol Drug StudyAngelica shane Navarro100% (2)
- Adiel Joy P. Calsa Drug Study March 9, 2022Документ5 страницAdiel Joy P. Calsa Drug Study March 9, 2022Adiel CalsaОценок пока нет
- Propofol Dosage, Side Effect MIMS - Com PhilippinesДокумент2 страницыPropofol Dosage, Side Effect MIMS - Com PhilippinesWay LyanОценок пока нет
- Status Epilepticus Pediatric DR - RPДокумент4 страницыStatus Epilepticus Pediatric DR - RPAdnin NugrohoОценок пока нет
- Agitated PatientДокумент2 страницыAgitated PatientCassandra GeldenhuysОценок пока нет
- PEDIATRIC NotesДокумент79 страницPEDIATRIC NotesM A83% (6)
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingДокумент1 страницаAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12Оценок пока нет
- Clinical Pathway Peds Sepsis 2012Документ3 страницыClinical Pathway Peds Sepsis 2012Kim MedairosОценок пока нет
- PediatricseizureДокумент2 страницыPediatricseizureRifrita Fransisca HalimОценок пока нет
- Epilepsy Recovery Period - Second YrДокумент3 страницыEpilepsy Recovery Period - Second YrBrian MaloneyОценок пока нет
- Ventricular Fibrillation/ Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia AlgorithmДокумент2 страницыVentricular Fibrillation/ Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia AlgorithmsafasayedОценок пока нет
- Midwifery Pharmacology-9Документ1 страницаMidwifery Pharmacology-9georgeloto12Оценок пока нет
- Pediatric Status Epilepticus CPGДокумент7 страницPediatric Status Epilepticus CPGAndriОценок пока нет
- Status Epilepticus and ICPДокумент9 страницStatus Epilepticus and ICPjoomds51Оценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыDrug StudyanonymousОценок пока нет
- 4 SeizuresДокумент11 страниц4 SeizuresApple MaeОценок пока нет
- Flip Chart-Converted 2Документ10 страницFlip Chart-Converted 2anisah mahmudah0% (1)
- AcetaminophenДокумент3 страницыAcetaminophenShaira Tan100% (1)
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityДокумент5 страницCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityChelsea WuОценок пока нет
- Status Epilepticus GuidelineДокумент1 страницаStatus Epilepticus GuidelineYuzhi PhuahОценок пока нет
- Drug Study: Adult: Induction: 40 MGДокумент2 страницыDrug Study: Adult: Induction: 40 MGpretty_mary100% (4)
- DS Male SurgicalДокумент6 страницDS Male SurgicalErryl Justine AdvinculaОценок пока нет
- Concept Map of DMДокумент1 страницаConcept Map of DMRobert Timothy YapОценок пока нет
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension Joseph JanДокумент11 страницPregnancy Induced Hypertension Joseph JanJan Joseph BanzuelaОценок пока нет
- Afebrile SeizuresДокумент6 страницAfebrile SeizuresKristoffer EscletoОценок пока нет
- DR StudyДокумент7 страницDR StudyWestley RubinoОценок пока нет
- Drug Tab RLE Sept. 7 2021Документ6 страницDrug Tab RLE Sept. 7 2021Marco VelaОценок пока нет
- Drug Study-ncp-Abruptio Placentae (Oxytocin) - PeregrinoДокумент3 страницыDrug Study-ncp-Abruptio Placentae (Oxytocin) - PeregrinoJOYCE ANN PEREGRINOОценок пока нет
- Drug Study SalbutamolДокумент2 страницыDrug Study Salbutamolliza sian100% (2)
- OxytocinДокумент2 страницыOxytocinNurkholis AminОценок пока нет
- Status Elipticus April 2018Документ2 страницыStatus Elipticus April 2018walidОценок пока нет
- Phenobarbital SodiumДокумент1 страницаPhenobarbital SodiumKevin Gonzales100% (1)
- NRP Basics OPNF 7th EdДокумент8 страницNRP Basics OPNF 7th EdRazil AgilОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент12 страницDrug Studyjoaqiun100% (1)
- Nursing Pharmacology HandoutsДокумент10 страницNursing Pharmacology HandoutsMICHAELA TIMBOLОценок пока нет
- Flowchart 1 Immediate Management of An Asphyxiated NewbornДокумент3 страницыFlowchart 1 Immediate Management of An Asphyxiated Newborndessy pratiwiОценок пока нет
- ConnectorДокумент4 страницыConnectoryetaung8Оценок пока нет
- Age 2 Months Age 2monthsДокумент1 страницаAge 2 Months Age 2monthsd'Agung NugrohoОценок пока нет
- Status EpilepticusДокумент3 страницыStatus EpilepticusVandeosОценок пока нет
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyДокумент10 страницChlorpromazine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezОценок пока нет
- Flowchart 1 Immediate Management of An AsphyxiatednewbornДокумент3 страницыFlowchart 1 Immediate Management of An Asphyxiatednewborndessy pratiwiОценок пока нет
- ERDrug Study DimayugaДокумент25 страницERDrug Study DimayugaSophia DimayugaОценок пока нет
- Empirical Antimicrobial Therapy Prescribing Guidance For AdultsДокумент1 страницаEmpirical Antimicrobial Therapy Prescribing Guidance For AdultsPsychology TodayОценок пока нет
- Table RevalidaДокумент7 страницTable RevalidaReinhaMaeDaduyaОценок пока нет
- Medical EmergencyДокумент3 страницыMedical EmergencyIbrar HumayunОценок пока нет
- Toaz - Info Nursing Oral Revalida Reviewer PRДокумент43 страницыToaz - Info Nursing Oral Revalida Reviewer PRcarlaОценок пока нет
- Seizures: DR Jonny Taitz, FRACP Geschn Paediatrician Sept 2003Документ18 страницSeizures: DR Jonny Taitz, FRACP Geschn Paediatrician Sept 2003alishba100% (2)
- Estatus EpilépticoДокумент16 страницEstatus EpilépticoLizbeth PalomecОценок пока нет
- Drug Therapeutic Record No. 1 (ANIMA BSN 2C)Документ2 страницыDrug Therapeutic Record No. 1 (ANIMA BSN 2C)Rhea Mae S. AnimaОценок пока нет
- Drug Study: Propofol: CNS Depressants: AdditiveДокумент5 страницDrug Study: Propofol: CNS Depressants: AdditiveShara Lailanie A. AzisОценок пока нет
- Task 11 (VII Grade Online Class)Документ2 страницыTask 11 (VII Grade Online Class)Ratu PalarОценок пока нет
- Task 13Документ1 страницаTask 13Ratu PalarОценок пока нет
- Mengamati Teks Berikut Dan Tentukan Jenis Teks, Fungsi Sosial, Struktur Teks, Serta Unsur KebahasaannyaДокумент4 страницыMengamati Teks Berikut Dan Tentukan Jenis Teks, Fungsi Sosial, Struktur Teks, Serta Unsur KebahasaannyaRatu PalarОценок пока нет
- Pengurus Masjid At-Taqwa Dan Majelis Ta'Lim An-Nur Blok C Bumi Tamalanrea Permai MakassarДокумент2 страницыPengurus Masjid At-Taqwa Dan Majelis Ta'Lim An-Nur Blok C Bumi Tamalanrea Permai MakassarRatu PalarОценок пока нет
- Absence SeizureДокумент2 страницыAbsence SeizureRatu PalarОценок пока нет
- Daftar Kata Kerja Tak Beraturan (Irreguler Vers)Документ7 страницDaftar Kata Kerja Tak Beraturan (Irreguler Vers)Ratu PalarОценок пока нет
- UndanganДокумент1 страницаUndanganRatu PalarОценок пока нет
- Management of Alopecia Areata: An Update: Imran Majid and Abid KeenДокумент3 страницыManagement of Alopecia Areata: An Update: Imran Majid and Abid KeenRatu PalarОценок пока нет
- 1 Soal Ulangan Mid Semester Kelas Ix SMP Maha Putratello Baru Makassar Semester Genap Tahun Ajaran 2018Документ2 страницы1 Soal Ulangan Mid Semester Kelas Ix SMP Maha Putratello Baru Makassar Semester Genap Tahun Ajaran 2018Ratu PalarОценок пока нет
- Correlations (Dataset0)Документ12 страницCorrelations (Dataset0)Ratu PalarОценок пока нет
- Physico-Chemical Properties of Nutmeg (Myristica Fragrans Houtt) of North Sulawesi NutmegДокумент9 страницPhysico-Chemical Properties of Nutmeg (Myristica Fragrans Houtt) of North Sulawesi NutmegZyuha AiniiОценок пока нет
- Risk Analysis and Assessment Methodologies in Work SitesДокумент49 страницRisk Analysis and Assessment Methodologies in Work SitesNhut NguyenОценок пока нет
- Shift in Business Strategy of 10 Minute School - B2B To B2CДокумент40 страницShift in Business Strategy of 10 Minute School - B2B To B2CSadiaОценок пока нет
- Inspection Report For Apartment Building at 1080 93rd St. in Bay Harbor IslandsДокумент13 страницInspection Report For Apartment Building at 1080 93rd St. in Bay Harbor IslandsAmanda RojasОценок пока нет
- Maharashtra State Board 9th STD History and Political Science Textbook EngДокумент106 страницMaharashtra State Board 9th STD History and Political Science Textbook EngSomesh Kamad100% (2)
- Autodesk Nastran In-CAD PDFДокумент43 страницыAutodesk Nastran In-CAD PDFFernando0% (1)
- P1 Chp12 DifferentiationДокумент56 страницP1 Chp12 DifferentiationbobОценок пока нет
- Forces L2 Measuring Forces WSДокумент4 страницыForces L2 Measuring Forces WSAarav KapoorОценок пока нет
- GA Power Capsule For SBI Clerk Mains 2024 (Part-2)Документ82 страницыGA Power Capsule For SBI Clerk Mains 2024 (Part-2)aa1904bbОценок пока нет
- PR Earth Users Guide EMILY1Документ2 страницыPR Earth Users Guide EMILY1Azim AbdoolОценок пока нет
- MPT EnglishДокумент5 страницMPT Englishkhadijaamir435Оценок пока нет
- Icici PrudentialДокумент52 страницыIcici PrudentialDeepak DevaniОценок пока нет
- Guidelines For Plenipotentiary - 1Документ6 страницGuidelines For Plenipotentiary - 1Oladimeji Ibukun IjaodolaОценок пока нет
- Instruction Manual 115cx ENGLISHДокумент72 страницыInstruction Manual 115cx ENGLISHRomanPiscraftMosqueteerОценок пока нет
- MSC ACFN2 RD4 ClassДокумент25 страницMSC ACFN2 RD4 Classmengistu jiloОценок пока нет
- Introduction To FluidizationДокумент9 страницIntroduction To FluidizationEriCisacОценок пока нет
- Scrum Handbook: Scrum Training Institute PressДокумент66 страницScrum Handbook: Scrum Training Institute PressFranky RiveroОценок пока нет
- AppcДокумент71 страницаAppcTomy lee youngОценок пока нет
- English 2nd Quarter Week 7 Connotation DenotationДокумент28 страницEnglish 2nd Quarter Week 7 Connotation DenotationEdward Estrella GuceОценок пока нет
- SAP HR - Legacy System Migration Workbench (LSMW)Документ5 страницSAP HR - Legacy System Migration Workbench (LSMW)Bharathk KldОценок пока нет
- Arithmetic-Progressions - MDДокумент8 страницArithmetic-Progressions - MDJay Jay GwizaОценок пока нет
- XU-CSG Cabinet Minutes of Meeting - April 4Документ5 страницXU-CSG Cabinet Minutes of Meeting - April 4Harold John LaborteОценок пока нет
- FHHR 013 Red Tag Procedure PDFДокумент5 страницFHHR 013 Red Tag Procedure PDFN3N5YОценок пока нет
- Micro - Systemic Bacteriology Questions PDFДокумент79 страницMicro - Systemic Bacteriology Questions PDFShashipriya AgressОценок пока нет
- Annex To ED Decision 2013-015-RДокумент18 страницAnnex To ED Decision 2013-015-RBurse LeeОценок пока нет
- Nse 2Документ5 страницNse 2dhaval gohelОценок пока нет
- Book Speos 2023 R2 Users GuideДокумент843 страницыBook Speos 2023 R2 Users GuideCarlos RodriguesОценок пока нет
- Energy-Roles-In-Ecosystems-Notes-7 12bДокумент10 страницEnergy-Roles-In-Ecosystems-Notes-7 12bapi-218158367Оценок пока нет
- Jurnal 1 Ieevee LPF PDFДокумент4 страницыJurnal 1 Ieevee LPF PDFNanda SalsabilaОценок пока нет
- Strategic Audit of VodafoneДокумент35 страницStrategic Audit of VodafoneArun Guleria89% (9)