Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter 33 Notes
Загружено:
Claudia MezaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 33 Notes
Загружено:
Claudia MezaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 33: Drugs for Inflammation and fever
33.1
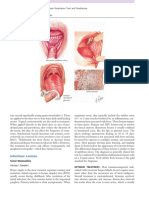
Inflammation is a nonspecific defense of the body.
Large numbers of chemicals and microorganisms can be neutralized through this
defense
The purpose of inflammation is to contain or destroy the invading microorganism
Signs of inflammation:
o Swelling
o Pain
o Warmth
o Redness to area
Can be acute or chronic, acute lasting about 8-10 days, sometimes longer which
makes it chronic.
Chronic inflammation has a slower onset and can be caused by autoimmune
disorders, persisting for many years and can oftentimes get worse
o Systemic lupus
o Rheumatoid arthritis
o Seasonal allergies
33.2
When the tissue is damaged, the mast cells release chemical mediators to notify
the body of injury:
o Histamine- causes vasodilation, smooth-muscle constriction, tissue
swelling
o Leukotrienes- like histamine, contribute to symptoms of asthma and
allergies
o Bradykinin-vasodilator causing pain
o Complement- stimulates histamine release
o Prostaglandins- brings WBC to site, causes pain and induces fever
When mediators are released on a large rapid scale = ANAPHYLAXIS (life
threatening allergy response)
33.3
Inflammation is not a disease, try to find cause so treatment can be more
effective
Use ice and R.I.C.E. (rest, ice, compress, elevate)
Topical anti-inflammatory agents that are OTC should be used when applicable
due to fewer adverse effects
Two drug classes used for nonspecific inflammation
o NSAIDs- moderate pain, inflammation and fever
o Corticosteroids- severe or disabling, used short term due to adverse
effects, pt then switched to NSAIDs.
33.4 NSAIDs
Available OTC
NSAIDs inhibit prostaglandins (promote inflammation) and block COX 1 (present
in all tissue for protective function) and 2(formed after tissue injury and
promoted inflammation)
Salicylates: Aspirin
o For mild pain and inflammation
o Small doses taken for preventing blood clot formation, MI, and stroke
o Can cause GI upset, heartburn, salicylism: tinnitus, and dizziness
Not for kids, Reyes syndrome- can be fatal
Ibuprofen: Motrin, Advil
o Pain, fever, inflammation
o Low adverse effects (vomiting, nausea)
o Less likely to cause GI upset and potential to bleed (like aspirin)
Alternative to aspirin
Not for patients with renal impairments
celecoxib: Celebrex
o COX 2 inhibitor (only) used for chronic inflammation
o No GI upset, no effect on blood coagulation
o Must build up level to achieve optimum (intended) level
o Reduces colorectal polyps in adults
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
Mutation in gene= hundreds of polyps
Almost 100% risk of colon cancer
33.5 Corticosteroids
The most effective at treating severe inflammation disorders
Sometimes referred to as glucocorticoids
Natural hormones released by adrenal cortex, dose is many times higher than
naturally present in blood
Used to treat:
o Neoplasia (cancer)
o Asthma
o Arthritis
Inhibit prostaglandins (like NSAIDs) and suppress histamine release
Adverse effects:
o Hyperglycemia
o Mood changes
o Cataracts
o Peptic ulcers
o Electrolyte imbalances
o Osteoporosis
Can mask infection
Only used short-term
o Long term effects can cause Cushing’s syndrome
Must be discontinued gradually or it can cause lack of adrenal function
o Medrol
33.6 Treating fever with antipyretics
Antipyretic: substance that reduces fever
o Acetaminophen: Tylenol
Natural defense against foreign organisms
Many types of bacteria are killed by high fever
Fevers can be more of a discomfort, but sometimes prolonged high fevers can be
life threatening
o Rhabdomyolysis (breakdown of body tissue)
o Can lead to delirium and/or coma
o Can be fatal (rare)
Come in many forms
o Gels, caplets, enteric-coated, suspensions
o Aspirin and acetaminophen available as suppositories
When fever cannot be diagnosed, drug patient is taking or has stopped taking
might be at fault
Drugs that might cause fevers:
o Anti-infectives: most common to induce fevers
o SSRI
Paxil: for depression and mood
o Antipsychotic drugs
o Cytotoxic drugs: used in chemo to prevent transplant rejection
People with G6PD deficiency: at risk for developing hemolysis
o Do not give acetaminophen: Tylenol
Complementary and Alternative therapies
Fish oils (marine oils) and Omega-3 have anti-inflammatory abilities
Diets in high fish oil show to be beneficial for conditions such as:
o RA
o Asthma
o IBS
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Marketing Authorisation: The Evaluation ProcessДокумент21 страницаMarketing Authorisation: The Evaluation Processlalooprasad15Оценок пока нет
- Bench MarkingДокумент16 страницBench MarkingNorj BaraniОценок пока нет
- CPHQ Review Course Nov 28-29 2012Документ195 страницCPHQ Review Course Nov 28-29 2012Khaskheli Nusrat100% (2)
- Gold Foil: Safety Data SheetДокумент4 страницыGold Foil: Safety Data SheetSyawatulshuhada SyawalОценок пока нет
- Therapeutic Communication TechniquesДокумент4 страницыTherapeutic Communication TechniquesJustine Plaza100% (1)
- Netter 39 S Internal Medicine 2nd Edition Pages 65, 68Документ2 страницыNetter 39 S Internal Medicine 2nd Edition Pages 65, 68Burca EduardОценок пока нет
- Nadi Literally MeansДокумент9 страницNadi Literally MeansThomas DürstОценок пока нет
- 2021-2022 Sem 2 Lecture 2 Basic Tests in Vision Screenings - Student VersionДокумент123 страницы2021-2022 Sem 2 Lecture 2 Basic Tests in Vision Screenings - Student Versionpi55aОценок пока нет
- Drugs & Cosmetics ActДокумент70 страницDrugs & Cosmetics ActAnonymous ibmeej9Оценок пока нет
- OB Meds WorksheetДокумент18 страницOB Meds WorksheetrickyandsheenaОценок пока нет
- Maharashtra Government PGM Admissions 2015-2016 Round 2 Selection ListДокумент30 страницMaharashtra Government PGM Admissions 2015-2016 Round 2 Selection ListAbhinav BhardwajОценок пока нет
- Rekapitulasi Laporan Psikotropika Bandung BaratДокумент8 страницRekapitulasi Laporan Psikotropika Bandung BaratFajarRachmadiОценок пока нет
- Sat-Asatkaryavada in DiseaseДокумент7 страницSat-Asatkaryavada in DiseaseSamhitha Ayurvedic ChennaiОценок пока нет
- The SCARE Statement Consensus-Based Surgical Case ReportДокумент7 страницThe SCARE Statement Consensus-Based Surgical Case ReportIhsan KОценок пока нет
- Scalp Acupuncture BasicsДокумент27 страницScalp Acupuncture BasicsGanga SinghОценок пока нет
- 2322 Part B DCHB IndoreДокумент278 страниц2322 Part B DCHB Indoreksanjay209Оценок пока нет
- Eosinophin in Infectious DiseaseДокумент29 страницEosinophin in Infectious DiseasentnquynhproОценок пока нет
- Refacere Dinti Frontali Cu Cape de CeluloidДокумент5 страницRefacere Dinti Frontali Cu Cape de CeluloidSorina NeamțuОценок пока нет
- John Paul PeraltaДокумент5 страницJohn Paul PeraltaAndrea Joyce AngelesОценок пока нет
- Empowerment Through Nature's Wishing Tree (The Banyan TreeДокумент9 страницEmpowerment Through Nature's Wishing Tree (The Banyan TreeAndrea KoumarianОценок пока нет
- The Herbal Market of Thessaloniki N GreeДокумент19 страницThe Herbal Market of Thessaloniki N GreeDanaОценок пока нет
- Observational Tools For Measuring Parent-Infant InteractionДокумент34 страницыObservational Tools For Measuring Parent-Infant Interactionqs-30Оценок пока нет
- Male Stress Urinary Incontinence: Giulio Del Popolo Donatella Pistolesi Vincenzo Li MarziДокумент189 страницMale Stress Urinary Incontinence: Giulio Del Popolo Donatella Pistolesi Vincenzo Li MarziVeronika AtaОценок пока нет
- Correlation of Sound and Colour - Paul Foster CaseДокумент30 страницCorrelation of Sound and Colour - Paul Foster Casesrk777100% (7)
- Minha Biblioteca Catalogo Julho 2022 Novos TitulosДокумент110 страницMinha Biblioteca Catalogo Julho 2022 Novos TitulosMarcelo SpritzerОценок пока нет
- Acute Lymphoblastic LeukaemiaДокумент3 страницыAcute Lymphoblastic LeukaemiamelpaniОценок пока нет
- ECTДокумент22 страницыECTRubz Bulquerin0% (1)
- Child Health Course: Amref Directorate of Learning SystemsДокумент25 страницChild Health Course: Amref Directorate of Learning SystemsEirehc Eam Aiboro SamorОценок пока нет
- Prismaflex CRRT Competency Based Tool PDFДокумент5 страницPrismaflex CRRT Competency Based Tool PDFalex100% (1)
- Cardiovascular SystemДокумент10 страницCardiovascular SystemitsmesuvekshaОценок пока нет