Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
OSI Model Layer Functions
Загружено:
SaadОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
OSI Model Layer Functions
Загружено:
SaadАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
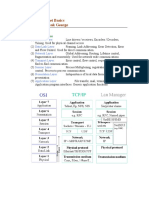
Part I – Internetworking ISO’s(International Organization for Standardization) OSI (Open Systems
Interconnection) Model: Layer PDUs Remarks, Examples 7 Application WWW, E-mail gateways,
user interface. Also responsible for understanding the resources needed to communicate between two
devices and establish their availability. SMTP, FTP. 6 Presentation Translates and converts data
into a known format such as ASCII, JPEG, MIDI, MPEG, encryption, compression. The only layer that can
actually change data. 5 Session Data Keeps different applications’ data separate, NFS, SQL, RPC,
NetBIOS names, X Window. Offers three modes – full-duplex, half-duplex and simplex. Maintains
communication channels and provides dialogue control. Managing, setting up and tearing down
sessions. 4 Transport Segments Reliable or unreliable delivery, error correction before retransmit,
TCP/UDP. Performs flow control, end-toend connection. Port numbers are used at this layer.
Multiplexing, teardown of virtual circuits. Reassemble the data stream. 3 Network Data and Route
Update Packets or Datagrams Logical addressing, routing, IP and IPX. Route update packets are sent at
this layer, in addition to the data packets. Layer 3 devices such as routers break up broadcast domains
and collision domains. 2 Data-Link Frames Layer 2 devices such as switches or bridges break up
collision domains whereas hubs do not. Uniquely identifies each device on a local network. This layer
uses service access points, identify network layer protocol used, flow control and sequencing of control
bits (LLC – Logical Link Control - sublayer) and deals with the protocol access to the physical medium,
network topology and error detection/notification (MAC – Media Access Control - sublayer). A MAC
address on a NIC (Network Interface Card) is a 48 bits address formatted in 12 hexa digits grouped in
twos as such: AF-98-C0-72-A3-2B 1 Physical Bits Moves bits between devices, specify voltages, wire
speed and pin-out cables. Hubs are also known as multiport repeaters and operate at this layer
Default Subnet Masks for the IP Address Classes Class Decimal Mask Binary Mask
A 255.0.0.0 11111111 00000000 00000000 00000000
B 255.255.0.0 11111111 11111111 00000000 00000000
C 255.255.255.0 11111111 11111111 11111111 00000000
http://uap.unnes.ac.id/ebook/Dummies%20Ebooks,%2055%20Ebooks/Wiley%20Publishing%20-
%20CCNA%20For%20Dummies%20%5B2000%5D.pdf
Вам также может понравиться
- Serial Port Complete: COM Ports, USB Virtual COM Ports, and Ports for Embedded SystemsОт EverandSerial Port Complete: COM Ports, USB Virtual COM Ports, and Ports for Embedded SystemsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (9)
- CCNA Crash Course Day 01Документ198 страницCCNA Crash Course Day 01JJohnny100% (1)
- OSI ModelДокумент6 страницOSI ModelmushahidОценок пока нет
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1От EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыCheat SheetDevan TillyОценок пока нет
- OSI ModelДокумент32 страницыOSI ModelBhanu Singh0% (1)
- Computer Network Layers CIS748 Class NotesДокумент10 страницComputer Network Layers CIS748 Class Notesanon-54811Оценок пока нет
- Networking Chapter 2: OSI LAYER Chapter 2 OSI LAYERДокумент4 страницыNetworking Chapter 2: OSI LAYER Chapter 2 OSI LAYERRaymart BuendiaОценок пока нет
- T OSI: He Seven Layers of The ModelДокумент4 страницыT OSI: He Seven Layers of The Modellolimazn1Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Device Configuration PDFДокумент24 страницыChapter 1 Device Configuration PDFShambel WorkuОценок пока нет
- Network Models: Ambo University Woliso Campus Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceДокумент73 страницыNetwork Models: Ambo University Woliso Campus Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceNoel GirmaОценок пока нет
- 7 Layer of OSI ModelДокумент2 страницы7 Layer of OSI ModelTerence FocasanОценок пока нет
- 7-Layer OSI MODELДокумент11 страниц7-Layer OSI MODELBabu CamОценок пока нет
- Seven Layers of OSI Reference ModelДокумент4 страницыSeven Layers of OSI Reference ModelpervezkanjuОценок пока нет
- OSI Model ReportДокумент9 страницOSI Model Reportmahamd saiedОценок пока нет
- TCP Ip ProtocolДокумент11 страницTCP Ip ProtocolHackers NationОценок пока нет
- Open Systems Interconnection Model (OSI) PDFДокумент20 страницOpen Systems Interconnection Model (OSI) PDFLink NguyenОценок пока нет
- OSI ModelДокумент10 страницOSI ModelRajkumar TiwariОценок пока нет
- OSItables PDFДокумент3 страницыOSItables PDF900913n008Оценок пока нет
- The OSI ModelДокумент5 страницThe OSI ModelNidhi ChoudhariОценок пока нет
- Osi and Tci-Ip ModelДокумент17 страницOsi and Tci-Ip ModelSohaibDanishОценок пока нет
- Osi 1Документ36 страницOsi 1api-216820839Оценок пока нет
- Week 3Документ5 страницWeek 3hiren_keepsmilingОценок пока нет
- Computer Network Layers CIS748 Class NotesДокумент9 страницComputer Network Layers CIS748 Class NotesSuresh KumarОценок пока нет
- CCNANOTESДокумент86 страницCCNANOTESSunkadahalli Govindaiah Bhanu PrakashОценок пока нет
- Capture All HTTP Packets by Using Wireshark and Try To Fetch All HTTP Usernames & PasswordsДокумент38 страницCapture All HTTP Packets by Using Wireshark and Try To Fetch All HTTP Usernames & PasswordsCandy AngelОценок пока нет
- Computer Networks Set 2Документ19 страницComputer Networks Set 2madhavibandari609Оценок пока нет
- Assignment 1: Computer Networks LabДокумент11 страницAssignment 1: Computer Networks LabNickОценок пока нет
- Computer Networks-Module1Документ34 страницыComputer Networks-Module1Sreedevi YashpalОценок пока нет
- "Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away": Layer 7: Application LayerДокумент3 страницы"Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away": Layer 7: Application LayerAndres GonzalezОценок пока нет
- What Is OSI Model 17.01.2024Документ7 страницWhat Is OSI Model 17.01.2024aloishp36Оценок пока нет
- LAN and Ethernet Basics - Deepak George: OSI Network LayersДокумент12 страницLAN and Ethernet Basics - Deepak George: OSI Network LayersUseful Videos DevotionalОценок пока нет
- Assignment 4Документ10 страницAssignment 4anil rajputОценок пока нет
- The 7-layer OSI model networking frameworkДокумент2 страницыThe 7-layer OSI model networking frameworknlly4uОценок пока нет
- Net 102 Prelim ModulesДокумент36 страницNet 102 Prelim ModulesNovy Airhris MianaОценок пока нет
- What Is OSI ModelДокумент18 страницWhat Is OSI Modelsoulxd1910Оценок пока нет
- CCNET Handbook - Good Summary For Networking IdeasДокумент42 страницыCCNET Handbook - Good Summary For Networking IdeasAnas ElgaudОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ8 страницLecture 2jasmhmyd205Оценок пока нет
- DC and CN Chapt-5-1Документ88 страницDC and CN Chapt-5-1habtamud655Оценок пока нет
- SemSim CCNA Cram SheetsДокумент9 страницSemSim CCNA Cram SheetsMohan KumarОценок пока нет
- VSATДокумент11 страницVSATShashwat TiwariОценок пока нет
- CN 16 Marks With AnswersДокумент35 страницCN 16 Marks With AnswersSankar GaneshОценок пока нет
- 1 - OSI Model: Network Revision - Reference ModelДокумент5 страниц1 - OSI Model: Network Revision - Reference Modelyaasir_7868868Оценок пока нет
- A. OSI Model 1. The 7 Layers of OSI Model AreДокумент2 страницыA. OSI Model 1. The 7 Layers of OSI Model ArekyansongeОценок пока нет
- User Interface: Protocols: FTPДокумент4 страницыUser Interface: Protocols: FTPAngates1Оценок пока нет
- Chap5 Osi 2015Документ20 страницChap5 Osi 2015semakulaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3Документ30 страницLecture 3Muhammad NadeemОценок пока нет
- Networking OverviewДокумент87 страницNetworking Overviewhaiprodt3Оценок пока нет
- OSI Model ExplainedДокумент8 страницOSI Model ExplainedRenegade DiverОценок пока нет
- Understanding the OSI ModelДокумент4 страницыUnderstanding the OSI ModelMey VaioОценок пока нет
- MCSE - A guide to networking fundamentals and Microsoft certificationДокумент163 страницыMCSE - A guide to networking fundamentals and Microsoft certificationArun TiwariОценок пока нет
- UNIT 1 Computer Networks NotesДокумент18 страницUNIT 1 Computer Networks NotesdoctoraseenОценок пока нет
- OSI LAYERS - A GUIDE TO THE 7-LAYER OSI REFERENCE MODELДокумент19 страницOSI LAYERS - A GUIDE TO THE 7-LAYER OSI REFERENCE MODELJayanthikrishnan SОценок пока нет
- Layer 7 ApplicationДокумент12 страницLayer 7 ApplicationprasadОценок пока нет
- NetworksДокумент8 страницNetworksGaby MbuguaОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentДокумент5 страницNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentSukanya SinghОценок пока нет
- The OSI ModelДокумент7 страницThe OSI Modelprashanty_14Оценок пока нет
- CSC Unit-3Документ21 страницаCSC Unit-3Smita AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Subject Title: Code: NAT121 Credit Units: 3 Instructor: Jerico D. MacatangayДокумент11 страницSubject Title: Code: NAT121 Credit Units: 3 Instructor: Jerico D. MacatangayJM McSnatchОценок пока нет
- 101 To 115 To Best Word McqsДокумент5 страниц101 To 115 To Best Word McqsSaadОценок пока нет
- Ms Word Mcqs Top FiveДокумент1 страницаMs Word Mcqs Top FiveSaadОценок пока нет
- Security Other Mcqs BetДокумент3 страницыSecurity Other Mcqs BetSaadОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Central Processing Unit and Execution of Programs MCQ 1: Register Which Is Used To Store Values of Arithmetic and LДокумент3 страницыChapter 2 Central Processing Unit and Execution of Programs MCQ 1: Register Which Is Used To Store Values of Arithmetic and LSaadОценок пока нет
- Security McqsДокумент4 страницыSecurity McqsSaadОценок пока нет
- 151 To 160 Ms Word Mcqs Best McqsДокумент2 страницы151 To 160 Ms Word Mcqs Best McqsSaadОценок пока нет
- 171 To 180 Word Mcqs Best McqsДокумент2 страницы171 To 180 Word Mcqs Best McqsSaadОценок пока нет
- Security Other Mcqs BetДокумент3 страницыSecurity Other Mcqs BetSaadОценок пока нет
- 101 To 120 Ms Word Mcqs Best McqsДокумент4 страницы101 To 120 Ms Word Mcqs Best McqsSaadОценок пока нет
- 161 To 170 Word Mcqs BestДокумент2 страницы161 To 170 Word Mcqs BestSaadОценок пока нет
- 121 To 135 Top Word Mcqs BestДокумент3 страницы121 To 135 Top Word Mcqs BestSaadОценок пока нет
- Find Format Painter Tool on Formatting ToolbarДокумент3 страницыFind Format Painter Tool on Formatting ToolbarSaadОценок пока нет
- Top 100 Word McqsДокумент19 страницTop 100 Word McqsSaadОценок пока нет
- Top 20 Data Structure McqsДокумент8 страницTop 20 Data Structure McqsSaadОценок пока нет
- Subject: Resignation From FFTTC Service: TH THДокумент1 страницаSubject: Resignation From FFTTC Service: TH THSaadОценок пока нет
- Different Units of ComputerДокумент2 страницыDifferent Units of ComputerSaadОценок пока нет
- IBPS SO OS Study NotesДокумент23 страницыIBPS SO OS Study NotesSaadОценок пока нет
- Text and Memo Data TypesДокумент3 страницыText and Memo Data TypesSaadОценок пока нет
- The Law & Justice Minister of Pakistan Is Mr. Zahid Hmaid As at May 10, 2016Документ2 страницыThe Law & Justice Minister of Pakistan Is Mr. Zahid Hmaid As at May 10, 2016SaadОценок пока нет
- Q.No.1 Block Diagram of Computer and Different ComponentsДокумент1 страницаQ.No.1 Block Diagram of Computer and Different ComponentsSaadОценок пока нет