Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Hyperandrogenism
Загружено:
evangelineОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Hyperandrogenism
Загружено:
evangelineАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1.
PCOS produce an atrophic endometrium -> thin
Def: polycystic ovary syndrome is a hormonal condition endometrial stripe -> amenorrhea)
yang dapat mempengaruhi kemampuan perempuan o biasa yg ada PCOS dari masa menarche (baru
hamil, bikin irregular menstruasi, acne and unwanted mulai mens) juga sudah experience irregular
hair, meningkatkan risk DM n hipertensi menstruation
nama polycyst ga berarti pasti pny cyst, bisa ga bisa o BUT 50% postmenarchal girls normally have
iya irregular periods 2-4 years due to HPA axis
immaturity —> makanya some diagnosis bilang
cause: unknown, tapi genetic katanya berpengaruh to confirm PCOS harus >18 y.o
terutama ibu, sistes, or twins. Trs ada bbrp penelitian yg
blg autosomal dominant inheritence with expression. Hyperandrogenism
pathophysiology: terjadi gangguan hormone: symptoms: hirsutism, acne, androgenic alopecia
Gonadotropins: GnRH yang disekresi secara
pulsatile -> produksi LH increase dibandingkan dg a. Hirsutism
FSH.
Insulin resistance: tubuh ga bisa manage blood coarse, dark, terminal hairs like those in males
sugar yg ada. Dikarenakan tjd abnormality di within a hair follicle, testosterone is converted by
insulin receptor-mediated signal transduction. the enzyme 5alpha-reductase to DHT
insulin juga berperan thd irregular mens and (dihydrotestosterone)
hirsutism. Selain itu, Insulin resistence jg bikin
testosterone and DHT convert short, solf vellus hair
high risk in DM2, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and
to coarse terminal hair (DHT lebih effective than
cardiovascular dz.
testosterone) conversion is IRREVERSIBLE
Androgen: insulin dan LH yg tinggi simulate
most affected area: upper lip, chin, sideburn, chest,
production Androgen (by theca cell) -> ovary
linea alba of lower abd. (escutcheon)
secrete testosterone n androstenedione.
Tingginya androstenedione -> aromatase -> tinggi
estrogen Ferriman-Gallwey Scoring system - degree of
Tinginya free testosterone -> hirsutismg - hirsutism if score >8
dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS – male
sex hormone yg play role in secondary sexual at b. Acne
puberty)
Symptoms: hair loss, unwanted hair, susah hamil o blockage of follicular opening by hyperkaratosis
Sex hormone-binding Globulin: di perempuan o sebum production
PCOS, SHBG rendah. Karena sintesis SHBG o proliferation of commensal propionibacterium
disuppressed sama insulin, androgen, corticoid, acnes
progestins, and growth hormone. SHBG ini o inflammation
gunanya buat bind sex steroid. in hair follicle, testosterone is converted within
SHBG rendah -> androgen n testosterone gak bisa sebaceous gland to DHT by 5-alpha reductase
bind sm receptor endorgan androgen excess —> overstimulation of androgen
Makanya walaupun total testosterone masih receptor in pilosebaceous unit —> increased sebum
normal, tp secara klinis udh hyperandrogenic krn production —> inflammation and comedone
free testosterone yg tinggi. formation
Low SHBG jg linked to risk of DM2 inflammation —> long term side effect e.g.
Progesterone: hormone progesterone terganggu yg scarring
bikin irregular mens
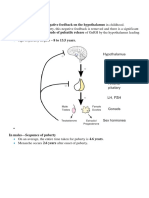
Anovulation: krn produksi GnRH secara pulsatility c. Alopecia
and impaired gonadotropin secretion berpengaruh
thd irregular mens. Anovulation jg mempengaruhi
hari loss progress slowly
thd insulin resistence
caused by: excess 5alpha reductase activity in hair
follicle lead to increase in DHT and increased
Sign n symp:
Short term: obese, infertility, depression, sleep apnea, androgen receptor
irregular menses, abnormal lipid level, hirsutism, acne,
alopecia, insulin resistence Insulin Resistance
Long term: DM, endometrial ca, cardiovascular dz
Menstrual dysfunction: a. Acanthosis Nigricans
o Every woman beda2 bisa amenorrhea (absence 3
month) to oligomenorrhea (fever than 8 mens in 1 - thickened, gray brown plaques seen on back of
month). nexk, axilla, waist, groin
o Without ovulation and progesterone prod from
corpus luteum -> menstrual period is not - insulin resistance —> hyperinsulinemia —>
triggered. stimulate keratinocyte and dermal fibroblast
o Amenorrhea can be caused by increased androgen growth —> produce skin changes
level (androgen can counteract estrogen to
b. increased risk of impaired glucose tolerance hydroxyprogesterone, 17-hydroxypregneolone
(IMG) and DM Type 2 accumulate in the adrenal cortex and circulate in blood
Endometrial neoplasia 6. Cortisol
- PCOS —> increase risk endometrial cancer
(3x) -Cushing syndrome: exposure to endo/ exogenous
Infertility glucocorticoid
- due to anovulatory cycle -Cushing disease: increase ACTH secretion by pituitary
Pregnancy loss tumor
- PCOS —> increase rate early miscarriage (30- -Sx: menstrual dysfunction, androgen excess, truncal obesity,
dyslipidemia, glucose intolerance
50%)
- can be due to LH hypersecretion, women with 8. Sonography
PCOS taking metformin (lower insulin level)
-histology: PCOS —> increase no. of ripening and atretic
DIAGNOSIS follicle, cortical stromal thickness, no. of hilar cell nests
-PCOS: >12 small cysts (2-9mm in diameter) or
1. Thyroid-stimulating Hormone and Prolactin -increase in volume (>10 mL) or both
-thyroid disease can lead to menstrual dysfunction TREATMENT
-hyperprolactinemia —> inhibit GnRH secretion —>
irregular menstruation, amenorrhea, galactorrhea 1. Oligo/Anovulation (<8 menses per year)
2.Testosterone
o Hormonal agent- oral contraceptive pills (COCs)
-ovary or adrenal tumor —> produce testosterone —> which induces:
virilization regular mesntrual cycle
-sx: clitoromegaly — clitoral index (>35mm2 abnormal) lower androgen level
-total testosterone more sensitive than free testosterone level thin the endometrium
-total testosterone >200 ng/dL —> ovarian lesion suppress gonadotropin release —> decrease
ovarian androgen production
3. Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate (DHEAS) estrogen level in COCs increase SHBG —> bind to
-hormone produced by the adrenal gland free androgen
-DHEAS >700 μg/dL —> adrenal neoplasm o Insulin sensitizing agent- Metformin —> decrease
androgen level —>
4. Gonadotropins increase rate of ovulation
-measure FSH, LH and estradiol level —> to exclude 2. Hirsutism
premature ovarian failure and hypogonadotropic
hypogonadism a. Lowered effective androgen level
-LH to FSH ratio >2:1
- COCs
5. 17-alpha Hydroxyprogesterone - GnRH agonist
- 5alpha-reductase inhibitor —> block conversion of
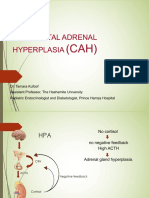
-congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) —> autosomal testosterone to DHT
recessive disorder —> result from complete/partial def.
of enzyme 21-hydroxylase or 11-hydroxylase —> b. Androgen-receptor antagonist — competitive inhibitor of
androgen production androgen binding to the androgen receptor; side effect:
-sx: ambiguous genitalia, life-threatening hypotension metrorrhagia (bleeding from uterus)
late onset CAH: enzyme def. leads to cortisol def. —> in
response ACTH level is increased to normalize cortisol 3. Surgical therapy
production (can cause adrenal gland hyperplasia)
normally affect 21-hydroxylase, kalo def. —> Laparoscopic ovarian drilling — restore ovulation in
accumulation of 17-hydroxyprogesterone women thats resistant to Clomiphene citrate
17-hydroxyprogesterone >200 ng/dL —> ACTH Oophorectomy — for women not seeking fertility
stimulation test
ACTH Stimulation test
-synthetic ACTH 250 μg injected —> 1 hour later —> level
17-hydroxyprogesterone is measured
-ACTH given stimulate uptake of cholesterol and synthesis
of pregnenolon
-kalo 21-hydroxylase rusak —> progesterone, 17-
Вам также может понравиться
- A Research On The Relationship Between Ejaculation and Serum Testosterone Level in MenДокумент5 страницA Research On The Relationship Between Ejaculation and Serum Testosterone Level in MenAnonymous XsYOMYarrvОценок пока нет
- AMS Guide To Equivalent HRT DosesДокумент3 страницыAMS Guide To Equivalent HRT DosesuioОценок пока нет
- PДокумент5 страницPmedstudОценок пока нет
- DR Nyoman. Sistem EndokrinДокумент93 страницыDR Nyoman. Sistem EndokrinAnnisaОценок пока нет
- Lourence M. Patagoc Block 1 SGD Group 1 Module 2 GYNE Case Hirsutism and VirilizationДокумент48 страницLourence M. Patagoc Block 1 SGD Group 1 Module 2 GYNE Case Hirsutism and VirilizationFernando AnibanОценок пока нет
- Skin Abnormality and Hairloss: The Reproductive Endocrinological ViewpointДокумент6 страницSkin Abnormality and Hairloss: The Reproductive Endocrinological ViewpointZenithОценок пока нет
- PBL Week 1 Jumat EndocrineДокумент29 страницPBL Week 1 Jumat EndocrineHelena PadilahОценок пока нет
- Rep 101 Slide Hiperandrogenemia Mia HirsutismeДокумент9 страницRep 101 Slide Hiperandrogenemia Mia HirsutismeKaren MogiОценок пока нет
- Jurnal PCOSДокумент39 страницJurnal PCOSGian Alodia RisamasuОценок пока нет
- Infertility 001Документ257 страницInfertility 001Habtamu Nigussie100% (1)
- Physiology of Female ReproductionДокумент3 страницыPhysiology of Female ReproductionAntoine JeriОценок пока нет
- Week 2 Endocrine Anatomy and Physiology Review & Pituitary DisturbancesДокумент27 страницWeek 2 Endocrine Anatomy and Physiology Review & Pituitary DisturbancesZiqri Dimas SandyОценок пока нет
- Hirsutism and HomoeopathyДокумент9 страницHirsutism and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD HomОценок пока нет
- Amenorrhea, Hirsutism & Polycystic Ovary SyndromeДокумент15 страницAmenorrhea, Hirsutism & Polycystic Ovary SyndromeSecret ManОценок пока нет
- Gyne PcosДокумент50 страницGyne PcosPrecious Medina100% (1)
- Micropenis or Cryptorchidism Kallman's Syndrome:: Thyroid-Stimulating (TSH) DeficiencyДокумент4 страницыMicropenis or Cryptorchidism Kallman's Syndrome:: Thyroid-Stimulating (TSH) DeficiencyYessamin Paith RoderosОценок пока нет
- Endo Part IVДокумент40 страницEndo Part IVChippy RabeОценок пока нет
- Secondary AmenorrheaДокумент21 страницаSecondary AmenorrheaCecilia CabanagОценок пока нет
- Investigations For Pcos: Rajhmuniran KandasamyДокумент21 страницаInvestigations For Pcos: Rajhmuniran KandasamyRajhmuniran KandasamyОценок пока нет
- Pituitary PathologyДокумент5 страницPituitary PathologyNada MuchОценок пока нет
- Anovulatory InfertilityДокумент57 страницAnovulatory InfertilityUsha AnengaОценок пока нет
- Pcos NotesДокумент24 страницыPcos NotesPreet RayatОценок пока нет
- Hormonal Disturbances in FemalesДокумент37 страницHormonal Disturbances in FemalesSonali SoumyashreeОценок пока нет
- Endocrine System - LectureДокумент213 страницEndocrine System - LectureRosita Antiquina Elopre100% (1)
- Menopause Semester 6 (IMTU)Документ37 страницMenopause Semester 6 (IMTU)nyangaraОценок пока нет
- Androgen Excess and PCOSДокумент50 страницAndrogen Excess and PCOSRica MarquezОценок пока нет
- 2023 Med SurgДокумент87 страниц2023 Med Surgkhaidkhan0609Оценок пока нет
- Homeopathy and Facial HairДокумент13 страницHomeopathy and Facial Hairpawajee100% (1)
- Endocrine System: Practical PartДокумент58 страницEndocrine System: Practical PartAmy AmyОценок пока нет
- Lecture - 5 - 6 - Goal - Symposium - STI - PCOS - Pregnancy Disorder - Breast CancerДокумент11 страницLecture - 5 - 6 - Goal - Symposium - STI - PCOS - Pregnancy Disorder - Breast CancerAPOORVA SHANDILYAОценок пока нет
- The Pituitary GlandДокумент2 страницыThe Pituitary GlandGerelОценок пока нет
- Hirsutism: Androgen Metabolism in The FemaleДокумент4 страницыHirsutism: Androgen Metabolism in The FemaleDaniel ZarateОценок пока нет
- Physio Bull BORRABLEДокумент11 страницPhysio Bull BORRABLEfrhasseyОценок пока нет
- Oncology - ProlactinomaДокумент2 страницыOncology - Prolactinoma20094113Оценок пока нет
- Polycystic Ovarian SyndromeДокумент17 страницPolycystic Ovarian SyndromeAhmed ElmohandesОценок пока нет
- 11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)Документ3 страницы11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)fariha khanОценок пока нет
- Endorine SystemДокумент27 страницEndorine SystemBenjamin YickОценок пока нет
- Secamenhyper 120208102817 Phpapp02Документ31 страницаSecamenhyper 120208102817 Phpapp02Mohan DassОценок пока нет
- Pituitary Gland DisordersДокумент80 страницPituitary Gland DisordersNang KhamОценок пока нет
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaДокумент46 страницCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaSarahОценок пока нет
- My PCOSДокумент54 страницыMy PCOSanees_aneessОценок пока нет
- Menstrual Physiology, Amenorrhea: Page 1 of 5Документ5 страницMenstrual Physiology, Amenorrhea: Page 1 of 5seth10Оценок пока нет
- ENDO #6 - Reproductive Endocrinology of The Female - 13.10.23Документ22 страницыENDO #6 - Reproductive Endocrinology of The Female - 13.10.23sbobine.imsОценок пока нет
- Endo-2 Hyperprolactinemia DIДокумент40 страницEndo-2 Hyperprolactinemia DIalhusien.abd2000Оценок пока нет
- Seminar: Guide: Co-Guide: Pramoted byДокумент35 страницSeminar: Guide: Co-Guide: Pramoted byDhara MeenaОценок пока нет
- Steroidogenesis:: Adrenal GlandДокумент6 страницSteroidogenesis:: Adrenal GlandRani SinghОценок пока нет
- Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Definition and EtiologyДокумент33 страницыCongenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Definition and Etiologylotp12Оценок пока нет
- Endocrinologie Si Nursing Curs 3Документ4 страницыEndocrinologie Si Nursing Curs 3gabiflori100% (1)
- Adrenal Gland 3: Dr. Hani Rjoob Dr. Rami AlayasaДокумент34 страницыAdrenal Gland 3: Dr. Hani Rjoob Dr. Rami AlayasaMahmoud Abu MayalehОценок пока нет
- Zoology Notes: 018 Chapter 14Документ3 страницыZoology Notes: 018 Chapter 14humanupgrade100% (1)
- Kuliah PituitariДокумент48 страницKuliah PituitariLona Veronika HutajuluОценок пока нет
- Transes EndoДокумент20 страницTranses EndoISABEL REGASPIОценок пока нет
- DR SaboriДокумент56 страницDR Saboridery2707Оценок пока нет
- ENDOCRINE SYSTEM and Disorders LectureДокумент153 страницыENDOCRINE SYSTEM and Disorders LectureAnthony Riggs100% (1)
- Sexuality and IntersexualityДокумент23 страницыSexuality and IntersexualityManu BharadwazОценок пока нет
- Precocious Puberty: ObjectiveДокумент16 страницPrecocious Puberty: ObjectiveZafar JavedОценок пока нет
- OB - GYN (5) - Alaa SalmanppДокумент6 страницOB - GYN (5) - Alaa Salmanppmotasem.med120Оценок пока нет
- Dr. Shehla Jamal Assistant Professor: OBG S M S & RДокумент69 страницDr. Shehla Jamal Assistant Professor: OBG S M S & RAppy LoveОценок пока нет
- Crie2014 987272 PDFДокумент4 страницыCrie2014 987272 PDFwatiОценок пока нет
- Lecture 7Документ8 страницLecture 7hossam369Оценок пока нет
- Laboratory Investigation of Amenorrhea:: DefinitionsДокумент8 страницLaboratory Investigation of Amenorrhea:: DefinitionsAmelia SetiawatiОценок пока нет
- Endocrinology: Elizabeth H., MD. PathologistДокумент72 страницыEndocrinology: Elizabeth H., MD. PathologistABUBEKER BESHIRОценок пока нет
- Hormonal ContraceptionДокумент13 страницHormonal ContraceptionAnuradha RoopchandОценок пока нет
- Advanced Level Biology 2015 Marking SchemeДокумент29 страницAdvanced Level Biology 2015 Marking SchemeAngiee FОценок пока нет
- Sex Hormone Synthesis, Regulation, and Function - McMaster Pathophysiology ReviewДокумент7 страницSex Hormone Synthesis, Regulation, and Function - McMaster Pathophysiology ReviewWahyu W'cas PamungkasОценок пока нет
- Hormonii Axei Reproductive Andra CaragheorgheopolДокумент70 страницHormonii Axei Reproductive Andra CaragheorgheopolMadalina PavelОценок пока нет
- Sciences2lp ModakiratДокумент29 страницSciences2lp Modakiratapi-24974205850% (4)
- Endocrine Physiology) 21. Female Reproductive Cycle - Ovulation - KeyДокумент1 страницаEndocrine Physiology) 21. Female Reproductive Cycle - Ovulation - Keyhasanatiya41Оценок пока нет
- Gonadotropins in ARTДокумент37 страницGonadotropins in ARTVarun DhallОценок пока нет
- C40 The Gonadal Hormones & Inhibitors: Anita Q. Sangalang, MD, Mhped, Fpogs Faculty of Pharmacy University of Santo TomasДокумент7 страницC40 The Gonadal Hormones & Inhibitors: Anita Q. Sangalang, MD, Mhped, Fpogs Faculty of Pharmacy University of Santo TomasHydieОценок пока нет
- Lyphochek Immunoassay Plus Control Levels 1, 2 and 3: Revision Date 2020-02-05 Indicates Revised InformationДокумент2 страницыLyphochek Immunoassay Plus Control Levels 1, 2 and 3: Revision Date 2020-02-05 Indicates Revised InformationLab Lko Regency HealthcareОценок пока нет
- Gynecomastia and Premature ThelarcheДокумент14 страницGynecomastia and Premature ThelarchexanderaleОценок пока нет
- Sinh Lý Sinh SảnДокумент91 страницаSinh Lý Sinh SảnNguyễn ĐạtОценок пока нет
- Askari Lab, Gojra RD.: Reference BillДокумент1 страницаAskari Lab, Gojra RD.: Reference Billmeer haadiОценок пока нет
- Beligas InterДокумент2 страницыBeligas InterShi LoОценок пока нет
- Different Controlled Ovarian Stimulation Protocols and Their Effects On Icsi OutcomeДокумент11 страницDifferent Controlled Ovarian Stimulation Protocols and Their Effects On Icsi OutcomeMaged BedeawyОценок пока нет
- Sakala Step 2 CK GYN 2018 Color Handout 2 - PageДокумент12 страницSakala Step 2 CK GYN 2018 Color Handout 2 - PageJurian F. Kaunang100% (1)
- Gannguan PubertasДокумент56 страницGannguan PubertasAde Yosdi PutraОценок пока нет
- Gonadal Hormones 1-13Документ66 страницGonadal Hormones 1-13abstabsОценок пока нет
- AZA Wildlife Contraception Center: Current List of Available Birth Control PillsДокумент6 страницAZA Wildlife Contraception Center: Current List of Available Birth Control PillsSaad ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Puberty and The HPG AxisДокумент36 страницPuberty and The HPG AxiskjhkaОценок пока нет
- The Progestins All SimilarДокумент23 страницыThe Progestins All SimilarVladimir KljajevicОценок пока нет
- Clinical Application of Bio-Identical Hormone Replacement TherapyДокумент37 страницClinical Application of Bio-Identical Hormone Replacement Therapyshivareddych100% (4)
- Assignment of Values-Endocrine Control II-Level 2-2021052602Документ2 страницыAssignment of Values-Endocrine Control II-Level 2-2021052602Ân Đình100% (1)
- Brain Mapping KMB 1 + PenilaianДокумент5 страницBrain Mapping KMB 1 + PenilaianAnisОценок пока нет
- The Use of Hormones in Gynaecological PracticeДокумент24 страницыThe Use of Hormones in Gynaecological PracticeMuhammad AmeenОценок пока нет
- Menstrual Cycle Test 1 1Документ8 страницMenstrual Cycle Test 1 1KvmLly100% (1)
- Janeiro - 24 US Coach - XLSBДокумент8 страницJaneiro - 24 US Coach - XLSBfiscalОценок пока нет
- AndrogensДокумент19 страницAndrogensMirza Shaharyar BaigОценок пока нет