Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Onllorln I e As L Al O RL e - Irsi X Erlences: Sum M Arq'
Загружено:
Salcedo Rodriguez SteveОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Onllorln I e As L Al O RL e - Irsi X Erlences: Sum M Arq'
Загружено:
Salcedo Rodriguez SteveАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
@u @ u @ @ @ * z
. *
O n llo rln I e as l al O rl e*
. IrSI X e rle n ce s
SatoshiKashima.ExecutiN'
eDirector.Yukikazu Yanaka.Director.NlaintenanceDepartment.ShuichiSuzuki.Nlanager.
EngineeringDevelopmentDivision.Long-span BridgeEngineeringCentre.Kunihisa Nlori,GeneralManager.TarumiOperation
O ffice.FirstO perittionsBureatl.Honshu Shikoku Bridge Authority.Kobe.Japan
Sum m arq' effectiq'
eness was confirn-led during
strong u'inds.using GPS forthe n'
lolli-
toring.
Fronnl monitoring and I
naintenance work on the AkashiKaikyo Bridge.a super
long-span suspension blidge-new inform ation has been obtained.This paper This paperintroducessonle 01-the i1)-
describessonze ofthe new technologiesused.To protectthe m ain cables fronz fornlation acquired fron) naonitoring
corrosion.a dry-airiniection syslem wasnewly developed and found capable and m aintenance work on the A kashi
ofkeeping the relative hum idity low enough in the cable bundles.To stlppress Kaikyo Bridge over a period of two
unexpected Nvind-induced oscillation observed in hangerropes.an aerodynam ic years.
countermeasure was employed and itsperformance wasconfirmed in typhoon-
strength Nvinds.Girder displacement records were stored b)'monitoring with
G lobalPositioning System (GPS)m easuring instrum ents.The relationshipsbe- C orrosion Protection fot
tween girderdisplacem entand both wind speed and temperattlre were analysed the M ain Cables
to com pare actualbridge behaviourwith design values.Resultsindicate thepos-
sibility ofmore accurately diagnosing the soundnessofbridges.Thesetechnolo- To exanline the corrosion protectiol l
giesare expected to contribute towardsmaintaining the soundnessofthe Akashi systenl used for the A'kashi K tlikq' o
Kaikyo Bridge. Bridge cables. several stlrveq's urere
condtlcted on the condition t)fexisting
stlspension bridge cables anàong the
different H onshtl Shikoku Bridges-
thereby verifj'ing tht? reliabilitl' of
Introduction pared with conventional corrosion
conN'entionalcorrosion protection s)'s-
protection sy.stem s.The cffectiveness
The A kashi Kaikyo Bridge. w hich ofthe new system wasinvestigated by tenns.
opened to traffic on A,pr:l5- 1998.is observing the relative htlm idity in the Generally.bundled cablesare protect-
a S-span.z-hinged suspelpsion bridge cablebundles. ed from w-ater ingress by overlal'ing
with the w orld-slongestcentre span of
o Bridge uras de- them with a paste.wrapping the bun-
1.99l nn (Fiv.l).'- as con- The
fhe bridge u' A kashi K aikq'
dle in steel u' ire. and the11 coatil' lg
structed aspartoftheH onshu Shikoku signed to withstand windsof6()m/sat it with paint. H ow eq'er- frol' n N'
isual
deck level.aswellasearthquakesof8.5
Bridge Proiect.aimed to form partof m agnitude on the R ichterscale having checksoncablesoftheH 01)shuShikoku
the trunk road network in Japan.
an epicentre distance of 150 km .Thus. Bridges.as wellas a sul aqel'ofthe in-
A sthe A kashiKaikyo Bridge crosses m onitoring bridge l aehaq'iourin harsh t ernati onal li
ter atur e on stlspension
the straits betu'een the m ainland and naturalconditions was considered in- br idge cables. this n'lethod u'asshow n
A wal'ilsland in the Seto lnland Sea. dispensable for confirming lhe bridge to offer inadequat e protect i
tln.Corro-
protection from corrosion in a saltq'at- design.Recordsofgirderdisplaceluent s ion w as found on wr appi ng wiresand
m osphere rem ains an im portantissue dueto large-scaletyphoonswerestored the upper layer o1 'cabltts i
n sus pension
for bridge m aintenance. A new anti- and analysed to confirm assum ptions br idge s.
ctlrrosion sl'
stem forthem ain cables.a in the bridge design.ln addition. an ' T'he cause of the corrosion svas diag-
dry-air iniection system.u' as devel- aerodynam ic stabilisation m ethod for nosed.and tests ail'ned at iluproving
oped to achieve higherreliability com - hanger ropes was developed.and its the quality ofsheathing n' laterialsand
paints u' ere im plenAented.The restllts
'
. .. .. c......u. .êU.
()fthese efforts.ho' weN' er-den-lonstrat-
.. ?<
.h.
'. . . -'x.-,
. ..:%
-g ..
. . .
lj - .... . .zljk$,..-...a)n . .-
. 'VyM-l..'F. ed that this conventional prtltection
cQ='
--. ' . ' ' syslel'
n cannot adeqtlately protecttlle
@ ' ..x-
=-rB - . # .' ' 9 '' .;
'''. !
zT ---- --
cabl es Nvhen svaterispresentsvithi1 .
1the
v . ..-.=zJ= .= '. .. 1
cablebu1-
1dlegl..
?.3j.
I
.I l
G iven thisproven difficulty in protect-
I
I
ing a cable bundle l'rol'
n u'ater ingress
over the long terln.itsvas decided that
.. ..
.. .*g*
<'
Y S.ïu
-
' xv
* ïN
''Q .#
f' . J .' the corrosive environlnelltvvithin the
y
'Z.
X
.
'
XI 'Cf*
S**'T- Y
:'5''L'C-''NY'' Z - *'
bundle should be inlprosred.Studiest)f
...@%'' '.
'rf. x'
& '''M''' various nzethods led to the adoption
. !. <.C...
.. .,
ofa neu' 'corrosion protection systelu
. . . :
employing a drq'-ai1-i11iection syste111.
Nvhereby the cable bundle isI'
nadctail--
tightvia a sheath and dry air is thu11
f'
ig.1:--l/
x-ff.
UziA-tI//
v-î'
t?Bridqv blown into the bundle.
StructuralEngineering International 2/201,1
Injt
zclionmoulh
A ExhCïusttlpening
'
j .1
. 'Dehunlidi1.iera:ld
bltpBer
A
'fter studying the 1-esults o1-several
testsforthedry-airinjectionsystem-a
new corrosion protection system was 1no.whmg.,. . I . js ..'.
' ....
=' +<.x.
z'' .
adopted forthe :Ak-ashiKaikyoB ridge 0.g..
.-
.
. .
. ''
'r
.. . Ire'
ck:ur.at.
-(3ntro1h.'''tl5.'u'
.r'
t
'zzë-i.
cables.To enhance air tightness and 'x.
xJ..'>. .. .-.
.H
protection against water perlneation. ' . XII-l17ICt.tI()'
IR1-)1D.C . '- '2'
s''
t'j'
.+- < '
the conventionalwire wrap is enhan-
cedbywrappingwitlzrubber.Ft0'
.J,.
?
and4show thedry-airiljectionsysten'
l '''x
j '
adopted forthe A'kashiK aikyo Bridge. ' In>17t2CtltJn Wi11dO%!,' ' .2' l
..' s . .. = * '. . f
Nforeover-itw asdecided to introduce .; . J . ,. . . i
.
.. .. .
. ..
.
. 1
.. & :
the sal-
ne corrosion protection systenA
on the existing HonshtlShikoku Brid- k+.. + .
gesand otherbridgesin Japan. .v. -: - -.. Jfl's'Pt:
.yu
..t1()n uiI.jf.jou '-'.. .
Afterinstallation ofthe corrosion pro- ..
. . >'
.M:.x
*.
T
'Pre '. ' >N=.
. .k
e
tection system ontt)thtlm ain cable of . . . . .. .'.
'B.A.'a.... A.'..;.
. ..
..
*...nv ... sw-=
+.;.t...
g/-x-
,-.
..
-GE.:
..
.. C
u'
'x'..'' . '
the A kashiK aikyo Bridge.changes in e. . .-
% . .Y. . 1.z . 4,
0.
relative hum iditywithin the cablebun- -
dleshave been recorded overaperiod -
. .. . ..ww%w . ..J.,.@ <.'$,.V..-.-=xo..%..
of two years as shown in Fie 5.This . Alr-I1.1Ik:wtIq,1:ut,.cr
.
figure illustrates thatthe relative hu-
Fig
'
;.4:zlir-lîll
'
ecti()Il('
-f?T
.,
t?/'ol
'
lf/?t
,Cablt
. ?
midity hasbeen keptbelow nearly 400,o-
the n'lanagen-lenttargetatthe sites.im -
pressing vortex-induced oscillation.
plying that this corrosion protection because their centre spacing is only
some were broken by large-amplitude
system is considered to be effective. oscillation in typhoon w indsasshown 9tim esthe diam eter.sm allerthan that
ofpo-y
ver-transm ission wires.
Because it is stillil-
nportant to clarifl' in Fig.6.
long-ternlperform ance and rationalise Afterses'eralu'ind tunnelteststo ex-
z
7Xisoscillation wasconsidered to be a
operation ofthe system .obserq'ing the am ine the cause of the oscillation.it
kind ofwake-induced flutter.which is
relative hunRidity and inspecting the often observed in pou'er-transm ission w as found that the wake frol' n wind-
surface ofthe Iuain cable through in- w ard ropeexcitedoscillation ofleeward
wires whose spacing is l() or more
spection willdowscontinues. tim esthediam eter.In theconstruction rope as shtlw'n in Fig.7 even though
their centre spacing is less than 1()
stage ofthe bridge.ithad been antici-
pated thatwake-induct zd flutterwould til-
nestheirdianleterg41.From the re-
A erodynam ic Stabilisation hardly everoccur in the hangel -ropes
sults of wind tunnel tests for suitable
forH angerR opes
PrefabricatedparalIe1u'irestrandsNvith
polyethylene coNvering w ere el-
nployed
for the hanger ropes of the A kashi
K aikyo Bridge. which situated tAvo
strands for each panel.
O riginally. a connecting type dam per
using high dam ping rubber was in-
stalled am id apairo1'ropesto suppress
vortex-induced oscillation.w hich had
lim ited am plitude and Nvas generated
al relativelj'1ou'wind spetld.Though
the dam pers wert '
l effectiq'e for sup-
StructuralEngineering International 2/2001
l #
: ,G- ... ''
J
I è.
: 3%
I ir Fig.9. 'zls./'
/'t
'
?/?.gt
?/?itp/sf(?/'Q'
. -
JP.
St'
?//t
'
/Ii
nllpclzltti/'e.îJtgt?.
'
;d?/'/
'
?!t)
Fig.t i-'Bl'
okell.î/t,(
..'
/?é?/?/(
.
't I)ill,g/pcp'illsîal- //?yr?'If???t2??f5'
?/ .
/t?J il?11al?vf
-
zF-R()p(a5'
' behind its design.as wellas releN'
ant K aik)'o Bridge.an'leanN' alueofj.4lnl
ï$'111dqard Rkypk.r constants. during strong winds and and a N' ibration am pIitude of 2.56 n'
l
(1)= S':7r!1I11) earthquak
-es.Another subiectamong were obtained r51.Though there was
ïs'
ind
basic structural characteristics is the generally good agreenAentu'ith regard
4 .
$'$ktkq
' !
'.
I-.cu.uart j behaviourof the bridge under chang- to the l'
nean N' alue o1'horizon(:11dis-
z. r. Rtljn,us ing tem peraturesand otherconditions placem ent. the nleasured vibrati01)
in its nornlal state. - A m onitoring anlplitude wason1)'aboutone-thiI-d ol'
sl'slennNvasinstalled to inN'estigatethese lhe calculated N'alue.
nlatters.D uringtheobservations.G lob-
'T'
he reason forthisdifference betu' een
('
c1
)1crSpttcing=t
?D >!
'
alPositioning Systelu (G PS)nleasuring calculated and n- !tlasurttd valtIe svas
r instruluents w'ere em ployed to n' lea-
sttldied b3'tlsinggtlstresptlnse analjr sis
sure deform ation o1-both the girder
and fieId 0l7serN':1t1on data of 1 -1aturaI
and tower.z A.s shown in Fig.t .
).GPS
yvinds.From these studies-itu'asl' ound
m eastlring instrulnents are located in
the tbllowing threelocations: thatthe actualN' alue lklrspatiitlcorre-
lation in thenaturalu' ind w'asloyver-in
-
uppersurfaceofthe !-A anchorage thelow'frequencyregion.thanthespa-
- uppersurface ofthe saddle coN'eron tialcorrelation assul ned in the q'ind-
the w estsidt?of the top of the 2P resistantdesign standard.
tow er
-
east side 01-a stiffening girder near Fig.12 shoB'stherelationship betïveen
the cable tenlperature at the tt'p of
the m iddle ofthe centre span.
the 2P tou'er and the centralN'ertical
Fig.l()showsthe G PS sensorinstalled displacel -nentof the girder.I '
neasured
on the girder near the centre span. using G PS ()N'ersix n' lonthso1-l'nonit01--
Fig.ll shows the tim e histoo 'data for ing.H ere.Nvith regard to ll' le atl-
ntls-
ten nAinutes before and ten nRinutes pheric teluperature and tI' le calAle
afterthe tim e thalthe n-laxin-
lun-
lhori- teluperatureatt11etop ()1'the2P toNver.
zontaldisplaceluentofthegirderin the the graph shou' s the ctlnlbinlltion ol'
centre span w asrecorded. (a)daily records at4:0()êt.I-n..and (b#
Thel'neasured horizontaldisplaceluenl records at 1
(l-nnint
lte int
er vals.
ael-odyl-
lam ic COUNtCFRICê1StlI'CS to SLIP-
press wake-induced flutter- l() l' nnl- showed a m ean value of. 5.l7 n'
land a '
-fhen- 1ain characteristicsal-e asftlllous
diam eter spiral ropes Nvound up the N'ibration anlplittlde ()f().78 m at the 1
)612
hanger ropes w' ere elnployed. This I'naxinnun-lrecorded w ind speed.From -l-he relationship (
- .)1*the centralNrk2rti-
the calculations.using the u'ind-resis- caldisplacen- lenlofthe girdert(. )thkz
counternleasurew asdeveloped to with-
stand bot1-1 wake-induced flutte1-and tant design standard of the A kashi cable ten- lperature al tht)top o1-the
vortex-induced oscillation.N eu' ly de-
veloped robots sinlultaneouslq'wotlnd
tw o spiral ropes up a pltir ofhanger
ropesasshow n in Fie.8.
A fterintroducing the counterl-neastlre.
neither u'ake-induced fltttter nor y'01--
tzx-induced oscillation have been ob-
served.even though two typhoons at-
tacked thebridge.
A M onitoring System
using G PS
Since the A kashiKaikyo Bridge was
constructed using a new ly developed
wind-resistantand seismicdesign.itis
necessarl'to confirm the assum ptions
StructuralEngineering Internatiflnal 2/21401
E 1Fl4) -, -
2P tower is-6.87 cm/degree.This is :., . '$'=-6.39()-.J
'x - l:fI.l)1 .- 1y(J.
.-
. + N= -j)->'('?.1Qx - 'r-'a
-'%kk
.-. . R cuu() (
?rof w R =1
.i' )
close to the calculated value of-6.7 =
:.p 1
3().. a** A.â. '' - -
c
uu 1'21)' . .
= I x
cm /degree based on the m ostrecent =2 >()
3 *'
= zf
dat:1. =:7- 3t) w -- R() â ' '
- Plotting ll'e ten-
lperature againsttbc
7 otp --
-
centralverticaldisplacenRent.thecor- ..--.:'-- .
-
a() .
l() 41 '(ï a(l .F'1 .zdi '-- - 19
.! (, It! atl RfI 4()
relation coefficientis().996-showing > >
D
ArnltlsphericTenlperattkrcin lhcc,cnlcr4 t'--)
Atnltlhkpllerictcnlptrrattlrt..111thtlcenlert(''1
good correlation.
The diagnosis of suspension bridges
% I(
- h;1) c.p 1
: 5
'y(j.
for (he presence of abnornAalities is ..
w'''
-
5'= -0..s4'Vl7'
<- lt)n().
1 @ N.. uuu .(
ak)()4k)x .y.jk)(j7-'
--.
:
. .-
- . ' u = .).f)k).cJ.
considered possible by measuring ca- Du1.n
-lj R = t1.u)q,
;:-h63
= .
ble tem peratures and G PS N'alues of Lz
= x4)
I :.p
u
= (
q(j
.
the centralN'erticaldisplacem ents.and A
then N'erifq'
ing the deN'iation from the =. Ofj * 7(1
regression Jine. lt is also considered Uuy-O
-(
.1 = --3.pj
u
*
thatN'erification o1'these valuesw ould > -1() i) 1(1
' A( R4) 4th ..> - !4) (1 1d1 n(1 2(p 4(I
btz one n-leans to evaluate suspension
bridgesforthepresenceofabnormali-
tiesafterstrongw indsorearthquakes.
'
eferences
(l1E-
'L'RL''
b'
..
t.l
' k..etaI.Colu
l'l.
t.
b'
it??8Pr()l'
t,
t'
J@
'
t??i?
-
r)?
'
'
I'
he folloNving information has been J/ztz.!.'tli
't.
k(''//.
b/(.0 (?t'.h'1/b,;)ell5l(.
'F2.B1'iLlz.
''(.'.à.1.-'ï.I
BSE
' draw n from experiencesofm onitoring Sq'm r.'k''kiun2. Ktllnu'. Nbl. 79. sklpteulbtlr 1(?t)1hl.
45 and lnaintenance o11the AkashiKaikyo pp..34l-34fa.
.- . 4(!
-A
.- Ejcj B ridge: (-'1FL'JIIQZ
AAN'
..
Y.H.c!al.(-fb''
' l'
(;.
%i('
$llJàrrlrtpt'
rfrlp?
w= Rt)
. '
7-7 oG - From observation ofrelatiq' e hum idi- /'
f)!'.iflf.
$;iyf.a/lA/
'f)llS/'drt/zt.'C-hbles.Proc.01*2 Inter-
# >11 . natik)a:1lSusllcnsikln Bridgc ('lperatt)I''sConI't2r-
:Z
--u
Iq
i'
.. t),
'in the m ain cablesoN'era period of ttnckl.NNkstPt'int.April-( 'D)()t).
- l() -... m ore thanoneyear.itw asconfirm ed
> .
5I i
f thatadry-airinjectionsj'stem wasef-
l1I11t)(sq.tcbJl)(..
1) fective in keeping relative hul uidily
below the m anagem enttarget.
- D tlring typhoonsand strong u'indsit
was found that spiralropes B' ound
tlp the hangerropes functioned well
as a counternAeasure 1-()1
-170th w ake-
induced flutter and vortex-induced
oscillation.
- Itwasdemonstrated thata m onitor-
ing system using GPS could be a '
tkasible m ethod for diagnosing the '#r (
)
6(N1L-R: AT- A.NI.u't; .
ll.31(ï1lil(lrilly Ctif?t'izl'l?'
f1-
??lt't'f/,c ..lké/b'il/ IY-Lfikk'l)B1'1(1jyrt'JI$'lb?(!C.;7P.%
Fie I1:7- //??t, I- lis:()1.j.' //.
) 1.4'il?J l)il' ecljlllt, configuration ofsuspension bridges Fîr. kt l1'
1tern:ttionalC'onferelpce of .AJNances i1-1
1,1
.:111(1.
$'
pt.
-t?//.(llïd C',-/?'t'
/cr.1)i.b
'illat'
(?ll?(???lf/lf!'- through comparison of obserNration StructtlraI l. il'lttl
'nee1'ing and Nlechêtï'lics Seoul.
?'/?.g (tf)y?/?(.'(,
41?(l4. '13-I4. '-
?.?-Sei. )t(?lzlI)el.22. recordsand analyticaldata. -Augt lfktiQ)t)t?.pp..l317-1. F22.
1Qf/(
i
j
'7/J'/
StructuralEngineering Internatitmal 2/2001 Rep()r1s 1-
>.
7
Вам также может понравиться
- BRG Iabse KashimaДокумент4 страницыBRG Iabse KashimaErrolHTОценок пока нет
- AmitДокумент46 страницAmitsairam saiОценок пока нет
- Cap. 1Документ34 страницыCap. 1Paola Medina GarnicaОценок пока нет
- LWR From SWRДокумент18 страницLWR From SWRdeepakОценок пока нет
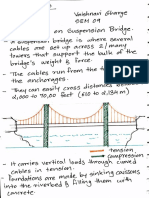
- TOS Suspension Bridge Sem 9Документ3 страницыTOS Suspension Bridge Sem 9VAISHNAVI GHARGEОценок пока нет
- 4 Aerodynamic Stability of Cable Stayed Bridges SimplifiedДокумент4 страницы4 Aerodynamic Stability of Cable Stayed Bridges SimplifiedHuda AlrikabiОценок пока нет
- A Critical Analysis of Arthur Ravenel Jr. Bridge New Cooper River BridgeДокумент7 страницA Critical Analysis of Arthur Ravenel Jr. Bridge New Cooper River BridgeHoàng LongОценок пока нет
- Review of Electromagnetic Methods in Wait1979Документ13 страницReview of Electromagnetic Methods in Wait1979shah naumanОценок пока нет
- Ultimate Load Capacity of Cable-Stayed Bridges With Different Deck and Pylon ConnectionsДокумент19 страницUltimate Load Capacity of Cable-Stayed Bridges With Different Deck and Pylon ConnectionsLogan PatrickОценок пока нет
- Pamphlet On Maintenance of Track in Traction AreasДокумент4 страницыPamphlet On Maintenance of Track in Traction Areaskamlesh kumarОценок пока нет
- Life-Cycle: Cost Concrete Road Bridge AcrossДокумент5 страницLife-Cycle: Cost Concrete Road Bridge AcrossAbhishek KumarОценок пока нет
- Cable StayedДокумент24 страницыCable StayedGellian ForniasОценок пока нет
- Al-P-Si Schottky Diode PaperДокумент3 страницыAl-P-Si Schottky Diode PaperHassaОценок пока нет
- Inter Penertrating Polymer Network CBRI Paper PDFДокумент8 страницInter Penertrating Polymer Network CBRI Paper PDFRadha KrishnanОценок пока нет
- Frequency-Domain Analysis of Otec CW Pipe and Platform DynamicsДокумент12 страницFrequency-Domain Analysis of Otec CW Pipe and Platform DynamicsYoyok SetyoОценок пока нет
- Fused Arcing Horns: and Grading RingsДокумент3 страницыFused Arcing Horns: and Grading RingsPriska Dwi AnggitaОценок пока нет
- Pipe Sticks SupportДокумент8 страницPipe Sticks SupportAmitОценок пока нет
- Design of A Curved Incrementally Launched BridgeДокумент6 страницDesign of A Curved Incrementally Launched BridgeAlexandros GiОценок пока нет
- Inclined Cable Aerodynamics of Cable-Stayed BridgesДокумент7 страницInclined Cable Aerodynamics of Cable-Stayed Bridgesafzal taiОценок пока нет
- Effect of The Different Shapes of PylonsДокумент4 страницыEffect of The Different Shapes of PylonsTanjil MominОценок пока нет
- Non-Linear Earthquake-Response Analysis of Long Span Cablestayed Bridge ApplicationДокумент14 страницNon-Linear Earthquake-Response Analysis of Long Span Cablestayed Bridge ApplicationTanjil MominОценок пока нет
- B Ridges W Ith M Ultiple C Able-Stayed SpansДокумент22 страницыB Ridges W Ith M Ultiple C Able-Stayed SpansprakharОценок пока нет
- Carrier Injection and Transport in Organic Field-Effect Transistor Investigated byДокумент4 страницыCarrier Injection and Transport in Organic Field-Effect Transistor Investigated byajayiitm05Оценок пока нет
- Analysis of Cable-Stayed Bridges During Construction by Cantilever MethodsДокумент18 страницAnalysis of Cable-Stayed Bridges During Construction by Cantilever MethodsprakharОценок пока нет
- Calvi-Conceptual Seiismic Design of Cable Stayed BridgesДокумент34 страницыCalvi-Conceptual Seiismic Design of Cable Stayed BridgesAyman ShamaОценок пока нет
- Seismic Time History Analysis For Cable-Stayed Bridge Considering Different Geometrical Configuration For Near Field EarthquakesДокумент8 страницSeismic Time History Analysis For Cable-Stayed Bridge Considering Different Geometrical Configuration For Near Field EarthquakesAamir KhanОценок пока нет
- Javanmardi Et Al - Seismic Response Characteristics of A Base Isolated Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Moderate and Strong Ground MotionsДокумент14 страницJavanmardi Et Al - Seismic Response Characteristics of A Base Isolated Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Moderate and Strong Ground MotionsPhan TumОценок пока нет
- ICFAI IUP 2014 - Effects of Side Span Length On The Behavior of Long Span Hybrid Cable-Stayed SuspДокумент10 страницICFAI IUP 2014 - Effects of Side Span Length On The Behavior of Long Span Hybrid Cable-Stayed SuspjaswantОценок пока нет
- Ascecf 1943-5509 0000381Документ16 страницAscecf 1943-5509 0000381Agus Setyo MuntoharОценок пока нет
- An Experimental Study On The Resistance and MovemeДокумент11 страницAn Experimental Study On The Resistance and MovemeHaytham AlmaghariОценок пока нет
- Applied SciencesДокумент27 страницApplied SciencesbluedancerОценок пока нет
- Precast-Prestressed Concrete I-Beam BridgesДокумент10 страницPrecast-Prestressed Concrete I-Beam BridgesSigmaE107Оценок пока нет
- V I Fistul' 1962 Sov. Phys. Usp. 5 430Документ31 страницаV I Fistul' 1962 Sov. Phys. Usp. 5 430Amal AntonyОценок пока нет
- Ambient Vibration Survey of The Bosporus Suspension Bridge: J. M. W. BrownjohnДокумент21 страницаAmbient Vibration Survey of The Bosporus Suspension Bridge: J. M. W. BrownjohnAhmedОценок пока нет
- West Rail Advance Pile Test Study: Stephen Hill Glen PlumbridgeДокумент2 страницыWest Rail Advance Pile Test Study: Stephen Hill Glen PlumbridgeSomesh SiddharthОценок пока нет
- (Asce) 1084 0702 (1999) 4 3 (151) - 2Документ6 страниц(Asce) 1084 0702 (1999) 4 3 (151) - 2Hamdi Yoga PratamaОценок пока нет
- Preliminary Design of Very Long-Span Suspension Bridges PDFДокумент8 страницPreliminary Design of Very Long-Span Suspension Bridges PDFp rОценок пока нет
- Fabrication and Characterization of SNS Josephson Juntions With An Aluminum BarrierДокумент4 страницыFabrication and Characterization of SNS Josephson Juntions With An Aluminum BarrierjamesОценок пока нет
- Beagp 32156 0008Документ211 страницBeagp 32156 0008dewei chenОценок пока нет
- L-S16 (Specification For Telephone Installation)Документ20 страницL-S16 (Specification For Telephone Installation)MUHAMMAD KHUDRI BIN HALIM BASHAH, IR. (JKR)100% (1)
- Tension Member: Done By: Ragul Ganesh.rДокумент12 страницTension Member: Done By: Ragul Ganesh.rRagul ganeshОценок пока нет
- Extra High Voltage XLPE Cables: LntrodllctiollДокумент3 страницыExtra High Voltage XLPE Cables: LntrodllctiollNika ThaiОценок пока нет
- Rocker Pipe PDFДокумент8 страницRocker Pipe PDFJide ZubairОценок пока нет
- Quantum Spin Hall Insulator State in HgTe Quantum WelsДокумент6 страницQuantum Spin Hall Insulator State in HgTe Quantum WelsJohnОценок пока нет
- Curran 2023Документ3 страницыCurran 2023Lahcen BenchouafОценок пока нет
- Instrumen ProcedureДокумент17 страницInstrumen ProcedureSuswantoro ToroОценок пока нет
- Railway Sleepers and Fastenings On The South African RailwaysДокумент11 страницRailway Sleepers and Fastenings On The South African RailwaysFang NinaОценок пока нет
- Bridge Bearing Replacement Using Flat JacksДокумент9 страницBridge Bearing Replacement Using Flat JacksKamal AlkurdiОценок пока нет
- Failure Analysis With RDSOДокумент2 страницыFailure Analysis With RDSOP.S.RoyОценок пока нет
- The Seismic Behaviour of Plywood Sheathed Shearwall-S J. A. Dean, W. G. Stewart and A. J. CarrДокумент16 страницThe Seismic Behaviour of Plywood Sheathed Shearwall-S J. A. Dean, W. G. Stewart and A. J. CarrJibbs OyawoyeОценок пока нет
- The Impedance Properties of Narrow Radiating Slots in The Broad Face of Rectangular Waveguide Part IДокумент8 страницThe Impedance Properties of Narrow Radiating Slots in The Broad Face of Rectangular Waveguide Part IDanielОценок пока нет
- The Flexibility of Box-Loop', Cross Loop' and Vertical Loop' Systems in The Vertical Plane PDFДокумент6 страницThe Flexibility of Box-Loop', Cross Loop' and Vertical Loop' Systems in The Vertical Plane PDFAthira JithendranathОценок пока нет
- Design and Fabrication of Rotary Tiller BladeДокумент3 страницыDesign and Fabrication of Rotary Tiller BladeAnonymous CUPykm6DZОценок пока нет
- Advanced Dam Engineering 08 (219-255)Документ37 страницAdvanced Dam Engineering 08 (219-255)chandra adriawanОценок пока нет
- Integrity of Subsea Control UmbilicalДокумент11 страницIntegrity of Subsea Control Umbilicalxinlin.cppОценок пока нет
- Dimensions and Design 01 Rope Reeving Components: Ly N NT U H T I Jun I NДокумент4 страницыDimensions and Design 01 Rope Reeving Components: Ly N NT U H T I Jun I NEmiddio PelosiОценок пока нет
- Yuan 2021 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1865 032083Документ12 страницYuan 2021 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1865 032083xsystemОценок пока нет
- M. Virlogex New Trends in Prestressed Concrete BridgesДокумент10 страницM. Virlogex New Trends in Prestressed Concrete BridgescdestudosОценок пока нет
- Hefner 1999Документ4 страницыHefner 1999Fer AceОценок пока нет
- 4.0 Reinforcing DeailingДокумент16 страниц4.0 Reinforcing DeailingRupesh Chaudhary EsRan TharuwaОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Cracked Prestressed Concrete Sections - A Practical ApproachДокумент12 страницAnalysis of Cracked Prestressed Concrete Sections - A Practical ApproachRushabh JainОценок пока нет
- Coupling BeamДокумент3 страницыCoupling BeamMustafa ZahidОценок пока нет
- Strengthening of Masonry Structures With Fibre Reinforced Plastics: From Modern Conception To Historical Building PreservationДокумент13 страницStrengthening of Masonry Structures With Fibre Reinforced Plastics: From Modern Conception To Historical Building PreservationNicola ChieffoОценок пока нет
- Structures 3 - Structures That Span Over A SpaceДокумент9 страницStructures 3 - Structures That Span Over A SpaceSarah HantonОценок пока нет
- 1.0 Earthquake Load Combination: Strength DesignДокумент4 страницы1.0 Earthquake Load Combination: Strength DesignAtienza ArjayОценок пока нет
- 60 Accredited Valid As On 15042018Документ7 страниц60 Accredited Valid As On 15042018Amit KumarОценок пока нет
- Lateral Bracing of Beams Provided by Standing Seam Roof System Concepts and Case StudyДокумент11 страницLateral Bracing of Beams Provided by Standing Seam Roof System Concepts and Case Studyjackcan501Оценок пока нет
- Warehouse With Solar DryersДокумент13 страницWarehouse With Solar DryersAYSON N. DELA CRUZОценок пока нет
- Structural Response and Damage Evaluation of A Typical Highrise RC Building in Dubai Under An Earthquake With Single and Multiple PeaksДокумент14 страницStructural Response and Damage Evaluation of A Typical Highrise RC Building in Dubai Under An Earthquake With Single and Multiple PeaksKaren EstradaОценок пока нет
- Questions Old 2066 & 2068 NTC Level - 7 (Elx & Comm)Документ5 страницQuestions Old 2066 & 2068 NTC Level - 7 (Elx & Comm)Prashant McFc AdhikaryОценок пока нет
- Analysis and Design of High Rise Building FramesДокумент3 страницыAnalysis and Design of High Rise Building FramesRanvier Singh100% (1)
- Lecture-1 Ver2015.9.7 3pmДокумент309 страницLecture-1 Ver2015.9.7 3pmAl KhwarizmОценок пока нет
- Pelat (TT)Документ444 страницыPelat (TT)Dummy EmailОценок пока нет
- Column Beam StairДокумент44 страницыColumn Beam StairSananda BanikОценок пока нет
- CIP 01 - Dusting Concrete SurfacesДокумент2 страницыCIP 01 - Dusting Concrete Surfacesedward the iiiОценок пока нет
- Booking Confirmation Sheet: Radiance GARDENIA HennurДокумент1 страницаBooking Confirmation Sheet: Radiance GARDENIA HennurMaddydon123Оценок пока нет
- Design of Bending MembersДокумент21 страницаDesign of Bending MembersChico AlvesОценок пока нет
- Supercrete Block Systems BrochureДокумент6 страницSupercrete Block Systems BrochureRachel IngramОценок пока нет
- Structural Analysis Report OF Office Building IN Butwal, RupandehiДокумент41 страницаStructural Analysis Report OF Office Building IN Butwal, RupandehiAsan GajurelОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Civil EngineeringДокумент17 страницIntroduction To Civil EngineeringHanumantha Raju100% (1)
- Cathodic Protection of Reinforced Concrete PDFДокумент75 страницCathodic Protection of Reinforced Concrete PDFGraham RobertsОценок пока нет
- Bondek IIДокумент24 страницыBondek IIumtancw100% (3)
- Civil 3 Sem Strength of Materials and Theory of Structures c16 Nov 2018Документ4 страницыCivil 3 Sem Strength of Materials and Theory of Structures c16 Nov 2018Jghhhsh JsjsjjsОценок пока нет
- Engineering Structures: SciencedirectДокумент14 страницEngineering Structures: SciencedirectAsr FlowerОценок пока нет
- CHLORINATION BUILDING-ARCH-001.Rev BДокумент1 страницаCHLORINATION BUILDING-ARCH-001.Rev BtumuuОценок пока нет
- 2008-02-12 Attachment2 HCB TestДокумент5 страниц2008-02-12 Attachment2 HCB TestTefera TemesgenОценок пока нет
- Concrete Centre - Scheme Manual To EC2Документ140 страницConcrete Centre - Scheme Manual To EC2Nabil Atta100% (6)
- COMPLETE Structural Design Notes Standard Drawings AmpДокумент91 страницаCOMPLETE Structural Design Notes Standard Drawings AmpReden H. ArgawanonОценок пока нет
- Deck SlabДокумент12 страницDeck SlabAhsan SattarОценок пока нет
- Real Life: Construction Management Guide from A-ZОт EverandReal Life: Construction Management Guide from A-ZРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- The Aqua Group Guide to Procurement, Tendering and Contract AdministrationОт EverandThe Aqua Group Guide to Procurement, Tendering and Contract AdministrationMark HackettРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- A Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsОт EverandA Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (242)
- Principles of Welding: Processes, Physics, Chemistry, and MetallurgyОт EverandPrinciples of Welding: Processes, Physics, Chemistry, and MetallurgyРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Civil Engineer's Handbook of Professional PracticeОт EverandCivil Engineer's Handbook of Professional PracticeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- How to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionОт EverandHow to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialОт EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialОценок пока нет
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedОт EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Building Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 1От EverandBuilding Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 1Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (3)
- Building Physics -- Heat, Air and Moisture: Fundamentals and Engineering Methods with Examples and ExercisesОт EverandBuilding Physics -- Heat, Air and Moisture: Fundamentals and Engineering Methods with Examples and ExercisesОценок пока нет
- History of Smart Textiles: A Comprehensive Guide To E-TextilesОт EverandHistory of Smart Textiles: A Comprehensive Guide To E-TextilesОценок пока нет
- Estimating Construction Profitably: Developing a System for Residential EstimatingОт EverandEstimating Construction Profitably: Developing a System for Residential EstimatingОценок пока нет
- Post Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&AОт EverandPost Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&AОценок пока нет
- 1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideОт Everand1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (7)
- The Complete Guide to Building With Rocks & Stone: Stonework Projects and Techniques Explained SimplyОт EverandThe Complete Guide to Building With Rocks & Stone: Stonework Projects and Techniques Explained SimplyРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsОт EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- Starting Your Career as a Contractor: How to Build and Run a Construction BusinessОт EverandStarting Your Career as a Contractor: How to Build and Run a Construction BusinessРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Piping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsОт EverandPiping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- The Complete Guide to Building Your Own Home and Saving Thousands on Your New HouseОт EverandThe Complete Guide to Building Your Own Home and Saving Thousands on Your New HouseРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- EMOTIONAL EATING: How To Stop Emotional Eating Naturally And Live A Better LifeОт EverandEMOTIONAL EATING: How To Stop Emotional Eating Naturally And Live A Better LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (14)
- Essential Building Science: Understanding Energy and Moisture in High Performance House DesignОт EverandEssential Building Science: Understanding Energy and Moisture in High Performance House DesignРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Woodworking: 25 Unique Woodworking Projects For Making Your Own Wood Furniture and Modern Kitchen CabinetsОт EverandWoodworking: 25 Unique Woodworking Projects For Making Your Own Wood Furniture and Modern Kitchen CabinetsРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (4)