Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
WS2 Chloride
Загружено:
Anish KarthikeyanАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
WS2 Chloride
Загружено:
Anish KarthikeyanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Sodium Chloride Content in Ketchup
by Precipitation Titration
Background
Sodium chloride is one of the most common substances found in nature. Knowing
the salt content in food products is important not only for taste but also for health
and compliance of recognized standards. One of the methods most commonly used
to determine the NaCl content is the precipitation reaction with silver nitrate in an
acidic medium. The result is usually calculated as percent of sodium chloride.
Reaction
H+
NaCl + AgNO3 AgCl + NaNO3
analyte titrant precipitate
58.44 g/mol 169.88 g/mol
Safety
Always take the necessary safety precautions when working in the laboratory: work
carefully; wear a lab coat, protective gloves and safety goggles. Silver nitrate causes
serious skin and eye irritation. It stains skin and other materials black. Potassium
dichromate is very toxic and corrosive. Please read the material safety data sheet
(MSDS) carefully before working with it. Potassium dichromate must only be used
for manual titration. Titration solutions are dangerous to the environment as they
contain contaminants such as heavy metals. Please dispose of solutions according
to the instructions below.
Tasks
1. Titer determination:
Perform a titer determination (standardization) of the titrant AgNO3 c = 0.1 mol/L by
titrating a standard sodium chloride solution (c = 0.1 mol/L). Add exactly 5 mL of
the standard solution into a titration beaker by using a pipette.
For a manual titration with visual equivalence point determination add 40 mL of
deionized water and a few drops of saturated potassium dichromate indicator
solution. Place the beaker under the burette and start the titrating by slowly adding
titrant to the standard sodium chloride titration solution under permanent stirring.
Titrate until the equivalence point is reached as is evident by a color change from
yellow to orange-red. Note the volume consumed. Calculate the titer by using the
correct formula.
Workshop 2 1 Powered by METTLER TOLEDO
If you use an automatic titrator with a potentiometric electrode (silver ring electrode)
add 40 mL of H2SO4 solution, c = 0.02 mol/L, to the titration beaker. This dilutes
and acidifies the standard solution. Immerse the titration tube and the electrode in the
titration solution and start the titration. The titration will stop automatically when the
endpoint is reached or when the maximum volume of titrant is added. The result,
consumed titrant and titer, will be displayed.
Determine the titer at least three times. Calculate the mean value, standard deviation
(s) and relative standard deviation (srel).
2. Sodium chloride content determination:
To determine the sodium chloride content in ketchup first weight about 1.5 g of
ketchup accurately into the titration beaker. Dissolve the sample in deionised water.
Then follow the same sample preparation and titration procedure as for the titer
determination above.
Determine the sodium chloride content (in %) at least three times and calculate the
mean value, standard deviation (s) and relative standard deviation (srel).
Waste disposal
Filter the titration solutions and dispose of the precipitate as special waste in the bins
labelled heavy metal waste. The liquid phase must be neutralized (pH 7) before it
can be disposed of as waste water.
Note
Be careful not to add too much acid to titration solution. The optimal value is pH 4-
5. If the solution is too acidic it will begin to dissolve the silver in the electrode thus
releasing silver ions. These silver ions bind the chloride in solution and give a falsely
low chloride concentration measurement.
Workshop 2 2 Powered by METTLER TOLEDO
Sodium Chloride Content in Ketchup
by Precipitation Titration
Equipment
Manual titration:
- 1x Analytical balance
- 1x Accurate pipette (5 mL or 1 – 10 mL)
- 1x Manual burette (10 mL)
- 6x Titration beakers (e.g. 100 mL glass beakers)
- 1x Magnetic stirrer
- 3x Magnetic stirrer bars
Automated titration:
- 1x Analytical balance
- 1x Accurate pipette (5 mL or 1 – 10 mL)
- 1x Mettler-Toledo Easy Cl or Easy Pro titrator with 10 mL burette and tubing
- 1x EM45-BNC pH Electrode
- 6x Titration beakers
- 3x Magnetic stirrer bars
Chemicals
The quantities below were roughly estimated for 5 titer determinations and 5 acetic
acid determinations.
- 1 L deionized water (mainly for manual titration and rinsing)
- 500 mL sulphuric acid solution, c = 0.02 mol/L (2.06 g H2SO4 95 % in 1 L
solution, for automated titration)
- 200 mL silver nitrate solution, c = 0.1 mol/L (16.99 g solid silver nitrate in
1 L solution)
- 10 mL of saturated potassium dichromate solution (about 1.2 g potassium
dichromate in 10 mL solution, only for manual titration)
- 30 mL sodium chloride standard solution, c = 0.1 mol/L (titration standard)
- 10 g ketchup as sample
Preparation
- Prepare the titrant and indicator solutions.
- Rinse the burette of the automatic titrator with titrant at least twice to dispel
any air bubbles trapped in the burette and tubing.
Comments
- This method may be slightly adapted depending on the sample used and its
chloride content.
Teacher Information 3 Powered by METTLER TOLEDO
Solution
1. Titer determination:
Calculation:
m
t =
VEQ ∙ c ∙ C
1
C =
cst ∙ z
t: Titer of the titrant (no unit)
m: Volume used (in mL, here: NaCl standard solution)
VEQ: Titrant consumption at the equivalence point (in mL)
c: Nominal concentration of the titrant (in mol/L, here: AgNO3, c = 0.1 mol/L)
C: Constant (in L/mol, see equation above)
cst: Concentration of the standard solution (in mol/L, here: NaCl, cst = 0.1
mol/L)
z: equivalence number (here: 1)
Expected result:
The titer should be around 1 for a fresh titrant solution.
2. Sodium chloride content determination:
Calculation:
VEQ · c ∙ t ∙ C
R =
m
M
C =
10 ∙ z
R: Result, content (in %, here: sodium chloride content)
VEQ: Titrant consumption at the equivalence point (in mL)
c: Nominal concentration of the titrant (in mol/L, here: AgNO3, c = 0.1 mol/L)
t: Titer of the titrant, as determined before (no unit)
C: Constant (in g·%/mmol, see equation above)
m: Sample weight (in g)
M: Molar mass of the analyte (in g/mol, here: NaCl, M = 58.44 g/mol)
10: Factor for mg to g and % conversion (in mg/(g·%))
z: equivalence number (no unit, here: 1)
Expected result:
The sodium chloride content in ketchup is usually around 3%. The expected
concentration is declared on the label of the bottle.
Teacher Information 4 Powered by METTLER TOLEDO
Example
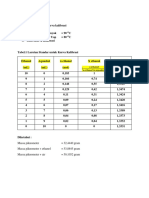
1. Titer determination:
Three titer determinations were performed by titrating 5 mL of sodium chloride
standard solution (c = 0.1 mol/L). The sample volume and results are shown in the
following table.
Nr. m VEQ t
1 5 mL 5.050 mL 0.9901
2 5 mL 5.062 mL 0.9878
3 5 mL 5.041 mL 0.9919
The titer of the first measurement was calculated as follows:
1 1 L
C = = = 10
cst ∙ z 0.1 mol ∙ 1 mol
L
m 5 mL
t = = = 0.9901
VEQ ∙ c ∙ C 5.050 mL∙ 0.1 mol ∙ 10 L
L mol
The mean, standard deviation (s) and the relative standard deviation (srel) were
calculated for the three measurements:
Mean: 0.9899
s: 0.0021
srel: 0.21 %
2. Sodium chloride content determination:
Three measurements of a ketchup sample were performed to determine the sodium
chloride content. The following table shows the sample weight and results.
Nr. m VEQ R
1 1.367 g 7.553 mL 3.196 %
2 1.268 g 7.058 mL 3.180 %
3 1.166 g 6.422 mL 3.186 %
Teacher Information 5 Powered by METTLER TOLEDO
The detailed calculation for the first measurement is:
g
M 58.44 g∙%
C = = mol = 5.844
10 ∙ z 10 mg ∙ 1 mmol
g·%
mol g∙%
VEQ · c ∙ t ∙ C 7.553 mL ∙ 0.1 L ∙ 0.9899 ∙ 5.844 mmol
R = = = 3.196 %
m 1.367 g
For these three measurements the mean, s and srel are as follows:
Mean: 3.187%
s: 0.008 %
srel: 0.26 %
Teacher Information 6 Powered by METTLER TOLEDO
Вам также может понравиться
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisОт EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Hydrogen Peroxide Determination: by Redox TitrationДокумент6 страницHydrogen Peroxide Determination: by Redox Titrationdaniel_12Оценок пока нет
- Titrimetric Methods and Precipitation TitrimetryДокумент24 страницыTitrimetric Methods and Precipitation TitrimetryS. MartinezОценок пока нет
- LAB REPORT ChloridesДокумент2 страницыLAB REPORT ChloridesahxssdswfwОценок пока нет
- Complexometric Determination of Water Hardness Lab ReportДокумент5 страницComplexometric Determination of Water Hardness Lab ReportMichelle50% (2)
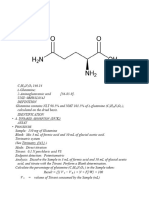
- Glutamine USPДокумент3 страницыGlutamine USPJai MurugeshОценок пока нет
- 20180305082145lab TherДокумент5 страниц20180305082145lab TherrazuriОценок пока нет
- Lab Report: Edvair Paula Moreira Filho 000837578Документ7 страницLab Report: Edvair Paula Moreira Filho 000837578Edvair FilhoОценок пока нет
- Titration, Acetic Acid, Household Vinegar, Sodium Hydroxide (Naoh) TitrantДокумент6 страницTitration, Acetic Acid, Household Vinegar, Sodium Hydroxide (Naoh) TitrantPatrickTulayОценок пока нет
- CHM 421 Analytical Chemistry Experiment 4: Solubility of Ionic Salts in SeawaterДокумент14 страницCHM 421 Analytical Chemistry Experiment 4: Solubility of Ionic Salts in SeawaterIntan SapuraОценок пока нет
- Preparation of A Standard Acid SolutionДокумент4 страницыPreparation of A Standard Acid SolutionfaithОценок пока нет
- Total Acid Number (TAN) (ASTM D664) : Potentiometric Titration Application: Petrochemical OilsДокумент5 страницTotal Acid Number (TAN) (ASTM D664) : Potentiometric Titration Application: Petrochemical OilsI H AnsariОценок пока нет
- Chloride MeasurementДокумент2 страницыChloride MeasurementEshwar NukalaОценок пока нет
- Exp 4 Solubility of Ionic Salts in Sea Water Chm421Документ7 страницExp 4 Solubility of Ionic Salts in Sea Water Chm421AimanОценок пока нет
- Titrations: Taking Advantage of Stoichiometric ReactionsДокумент18 страницTitrations: Taking Advantage of Stoichiometric ReactionsAngelica Camille B. AbaoОценок пока нет
- Analytical Chem Chap11Документ18 страницAnalytical Chem Chap11Nicole Ann PedriñaОценок пока нет
- Journal of Colligative PropertiesДокумент9 страницJournal of Colligative PropertiesMuhammad Baihaqi100% (1)
- Determination of Chloride in Water 4500DДокумент3 страницыDetermination of Chloride in Water 4500Dpious_chemОценок пока нет
- EPA Method 3101 PDFДокумент3 страницыEPA Method 3101 PDFJalpit MardenОценок пока нет
- Experiment 4 (28.1)Документ7 страницExperiment 4 (28.1)Patrick Parcon67% (3)
- Ammonia Determination in Hair Dye: Application Note No. 117 / 2013Документ6 страницAmmonia Determination in Hair Dye: Application Note No. 117 / 2013Amit PaulОценок пока нет
- Kel F3 - Ca Laktat KompleksometriДокумент10 страницKel F3 - Ca Laktat Kompleksometridavidkenny fanyОценок пока нет
- Titration ApplicationДокумент2 страницыTitration Applicationasla_sharee5374Оценок пока нет
- Sodium Chloride in 48% Sodium Hydroxide: Application NoteДокумент4 страницыSodium Chloride in 48% Sodium Hydroxide: Application NoteAnonymous T32l1RОценок пока нет
- Experiment 4 CHM421Документ9 страницExperiment 4 CHM421Abg Khairul Hannan Bin Abg AbdillahОценок пока нет
- Chm421-Experiment 3 - Neutralization Capacity of CommercialДокумент9 страницChm421-Experiment 3 - Neutralization Capacity of Commercialnipale hiОценок пока нет
- T-72 Ti Application Note No.: Title: Reducing Sugars in Wine and SweetsДокумент2 страницыT-72 Ti Application Note No.: Title: Reducing Sugars in Wine and SweetsBogdan NechitaОценок пока нет
- Expt 5 Analysis of Soda AshДокумент8 страницExpt 5 Analysis of Soda AshJustine Camille CastilloОценок пока нет
- Acid Value - Metrohm Application Balletin No. 80-3 eДокумент7 страницAcid Value - Metrohm Application Balletin No. 80-3 e陳丹庭Оценок пока нет
- Preparation of A T-Butyl Chloride From T-Butyl Alcohol LabДокумент5 страницPreparation of A T-Butyl Chloride From T-Butyl Alcohol Labapi-548204552100% (1)
- BIO 2A - Group 5 - Lab Exp 5-CompressedДокумент17 страницBIO 2A - Group 5 - Lab Exp 5-CompressedJoyce Mariele RomeroОценок пока нет
- Exp 3Документ4 страницыExp 3Kirthinee JegatheesanОценок пока нет
- Preparing Standard Acid and BaseДокумент7 страницPreparing Standard Acid and Basebrittany obrienОценок пока нет
- Lab Report CHM421 (Exp4)Документ10 страницLab Report CHM421 (Exp4)sarah nabilaОценок пока нет
- T-14 Ti Application Note No.: Title: Chlorhexidine in Wash LotionДокумент1 страницаT-14 Ti Application Note No.: Title: Chlorhexidine in Wash LotionJaime Jabiel RoddriguezОценок пока нет
- Niosh 2554 PDFДокумент4 страницыNiosh 2554 PDFMICROLABORATORIO S.A de C.VОценок пока нет
- PREPARATION AND STANDARDIZATION OF HCL SOLUTION WITH PRIMARY STANDARD Na CO SOLUTION (CHM256)Документ10 страницPREPARATION AND STANDARDIZATION OF HCL SOLUTION WITH PRIMARY STANDARD Na CO SOLUTION (CHM256)maisarah20salwaОценок пока нет
- Experiment 13: Volumetric Analysis II: Determination of Active Ingredients in Commercial Bleach and Vinegar OutcomesДокумент5 страницExperiment 13: Volumetric Analysis II: Determination of Active Ingredients in Commercial Bleach and Vinegar OutcomesSafwan m.tОценок пока нет
- Adamson University College of EngineeringДокумент14 страницAdamson University College of EngineeringJosef RentaОценок пока нет
- Chemy 310 Experiment 2Документ5 страницChemy 310 Experiment 2Faisal MumtazОценок пока нет
- EPA Method 3101Документ3 страницыEPA Method 3101skrim240Оценок пока нет
- Analytical Chemistry - Experiment 2 CHM 256Документ12 страницAnalytical Chemistry - Experiment 2 CHM 256mhd sssyamilОценок пока нет
- Get AttachmentДокумент7 страницGet AttachmentGaurav PatelОценок пока нет
- Indicate (Signal) The Endpoint.: StandardizationДокумент7 страницIndicate (Signal) The Endpoint.: StandardizationasaОценок пока нет
- Indicate (Signal) The Endpoint.: StandardizationДокумент7 страницIndicate (Signal) The Endpoint.: StandardizationasaОценок пока нет
- Practical No.1 Preparation and Standardization of Standard Solutions Preparation and Standardization of Sodium Hydroxide AimДокумент7 страницPractical No.1 Preparation and Standardization of Standard Solutions Preparation and Standardization of Sodium Hydroxide AimMahamoud Mohammed AhmedОценок пока нет
- Experiment No. 1 Vinegar AnalysisДокумент8 страницExperiment No. 1 Vinegar AnalysisRobin TorresОценок пока нет
- Determination of Concentration of Acetic Acid in Vinegar Sample Using Titrimetric AnalysisДокумент3 страницыDetermination of Concentration of Acetic Acid in Vinegar Sample Using Titrimetric AnalysisRole Victor Toring SudariaОценок пока нет
- IntroductionДокумент13 страницIntroductionapi-242192662Оценок пока нет
- Experiment 1Документ6 страницExperiment 1safaОценок пока нет
- Analytical ChemДокумент18 страницAnalytical Chemziya75100% (1)
- Determinacion Cloruro Carnicos - TituladorДокумент1 страницаDeterminacion Cloruro Carnicos - TituladoranyeОценок пока нет
- Title: Titration:: To Determine The Purity of The Unknown Potassium Acid Phthalate (KHP)Документ5 страницTitle: Titration:: To Determine The Purity of The Unknown Potassium Acid Phthalate (KHP)Mellyame AkauОценок пока нет
- Acidimetric Analysis Model 1: Acidimetry: Prepared By: ENGR. RENA P. MORA 1Документ4 страницыAcidimetric Analysis Model 1: Acidimetry: Prepared By: ENGR. RENA P. MORA 1Aliza EsplanadaОценок пока нет
- DataДокумент6 страницDataRizqi AmaliyahОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5.1. Fundamentals of Volumetric AnalysisДокумент7 страницChapter 5.1. Fundamentals of Volumetric AnalysisAmir KasimОценок пока нет
- Potentiometric Determination of Cyanide 692960 - AB-046 - 2 - ENДокумент7 страницPotentiometric Determination of Cyanide 692960 - AB-046 - 2 - ENMaximino AlvarezОценок пока нет
- Fidas200 Data SheetДокумент3 страницыFidas200 Data SheetAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- Ambient Air Quality Modelling Studies (AAQMS) For Industrial Area of Mysore Using ISCST3Документ6 страницAmbient Air Quality Modelling Studies (AAQMS) For Industrial Area of Mysore Using ISCST3Anish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- EESIFLO International Pte LTDДокумент30 страницEESIFLO International Pte LTDAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- 5) Hd651enCP VarithermДокумент3 страницы5) Hd651enCP VarithermAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- 1.B.2.c Venting and Flaring 2019Документ15 страниц1.B.2.c Venting and Flaring 2019Anish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- Project End User Country Year Applica-Tion No of Analyzer: Analytical InstrumentsДокумент6 страницProject End User Country Year Applica-Tion No of Analyzer: Analytical InstrumentsAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- TE-Wilbur-Product-Manual-REV-2.23-2 Flow Set PointДокумент2 страницыTE-Wilbur-Product-Manual-REV-2.23-2 Flow Set PointAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- Ammonia and Nitrogen Oxides Analyzer Model AC32M-CNH3: Ambient Air Quality M OnitoringДокумент2 страницыAmmonia and Nitrogen Oxides Analyzer Model AC32M-CNH3: Ambient Air Quality M OnitoringAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- Project Title: Study On Customer Perception Towards Biometrics in Mantra Softech (India) Pvt. Ltd-Bangalore What Is Customer Perception?Документ6 страницProject Title: Study On Customer Perception Towards Biometrics in Mantra Softech (India) Pvt. Ltd-Bangalore What Is Customer Perception?Anish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- 1.a) DenA23462000 - Monitor - AMI - CACEДокумент2 страницы1.a) DenA23462000 - Monitor - AMI - CACEAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- Safety Data Sheet Sodium Nitrate, 1.0 Molar Solution: Section 1 Product DescriptionДокумент4 страницыSafety Data Sheet Sodium Nitrate, 1.0 Molar Solution: Section 1 Product DescriptionAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- 50 PRPCДокумент39 страниц50 PRPCAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- P+F Purge Panel PDFДокумент148 страницP+F Purge Panel PDFAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- Ammonia and Nitrogen Oxides Analyzer Model AC32M-CNH3: Ambient Air Quality M OnitoringДокумент2 страницыAmmonia and Nitrogen Oxides Analyzer Model AC32M-CNH3: Ambient Air Quality M OnitoringAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- PDS E JES301 Accessories v4.1Документ2 страницыPDS E JES301 Accessories v4.1Anish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- 26.M.E. InstrumenДокумент44 страницы26.M.E. InstrumenAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- Sample Gas Compressor CoolerДокумент4 страницыSample Gas Compressor CoolerAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- Thermo Scientific 49iq: Ozone Analyzer-UV PhotometricДокумент2 страницыThermo Scientific 49iq: Ozone Analyzer-UV PhotometricAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- JCM-310 and JCMF-310: Peltier Sample Gas CoolersДокумент4 страницыJCM-310 and JCMF-310: Peltier Sample Gas CoolersAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- Thermo Scientific 48iq: Carbon Monoxide Analyzer-Gas Filter CorrelationДокумент2 страницыThermo Scientific 48iq: Carbon Monoxide Analyzer-Gas Filter CorrelationAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- Thermo Scientific Model 5028i: Continuous Particulate MonitorДокумент2 страницыThermo Scientific Model 5028i: Continuous Particulate MonitorAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- Sara - Spectroscopic Gamma Detector: FeaturesДокумент2 страницыSara - Spectroscopic Gamma Detector: FeaturesAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- Mira - Gamma Dose Rate Monitoring System: General Technical Data Mira With Solar Panel and TripodДокумент2 страницыMira - Gamma Dose Rate Monitoring System: General Technical Data Mira With Solar Panel and TripodAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- Density Meter Error OutputsДокумент1 страницаDensity Meter Error OutputsAnish KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Fracturing Theory and Practice: R. D. Barree Barree & Associates LLCДокумент18 страницHydraulic Fracturing Theory and Practice: R. D. Barree Barree & Associates LLCmoorpvrОценок пока нет
- Fast Blue BДокумент1 страницаFast Blue BAchuthanand MukundanОценок пока нет
- Heat Capacity of Sodium Silicate Liquids: Pascal RichetДокумент3 страницыHeat Capacity of Sodium Silicate Liquids: Pascal RichetDaniel SetyadiОценок пока нет
- MMU 0102, MMA 0204, MMB 0207 - Professional: Vishay BeyschlagДокумент13 страницMMU 0102, MMA 0204, MMB 0207 - Professional: Vishay BeyschlagJan KowalskiОценок пока нет
- 006-MS For Purging of Stainless Steel PDFДокумент18 страниц006-MS For Purging of Stainless Steel PDFKöksal PatanОценок пока нет
- UV Coating Flooring - Radtech 2003 - D. Bontinck M. IdacageДокумент6 страницUV Coating Flooring - Radtech 2003 - D. Bontinck M. IdacageJuan Antonio Tito Esp CalОценок пока нет
- Msds FormaldehydeДокумент6 страницMsds Formaldehydemkhurram79Оценок пока нет
- Medidor Caudal Kobold Flotador UrkДокумент4 страницыMedidor Caudal Kobold Flotador UrkBase SistemasОценок пока нет
- Nesrine-2021-2016 P4 QPДокумент686 страницNesrine-2021-2016 P4 QPMostafa HaithamОценок пока нет
- E Grout Mc050Документ2 страницыE Grout Mc050Tori SmallОценок пока нет
- tmp12B1 TMPДокумент29 страницtmp12B1 TMPFrontiersОценок пока нет
- Biodegradable Wastes: Hospital WasteДокумент4 страницыBiodegradable Wastes: Hospital WasteFAIZA A PASCUALОценок пока нет
- Current Anaesthesia & Critical Care: Mark Hayman, Peter C.A. KamДокумент6 страницCurrent Anaesthesia & Critical Care: Mark Hayman, Peter C.A. Kamnuraji090689Оценок пока нет
- Factors Affecting Drug Absorption PDFДокумент2 страницыFactors Affecting Drug Absorption PDFRobОценок пока нет
- Chiroptical Spectroscopy: Theory and Applications in Organic ChemistryДокумент32 страницыChiroptical Spectroscopy: Theory and Applications in Organic ChemistryDavid SantiagoОценок пока нет
- One Step Extraction of Essential Oils and Pectin From Pomelo (Citrus Grandis) PeelsДокумент5 страницOne Step Extraction of Essential Oils and Pectin From Pomelo (Citrus Grandis) PeelsHuy Hoàng Lê ĐứcОценок пока нет
- Production Q A 2013 S K Mondal Mobile VersionДокумент557 страницProduction Q A 2013 S K Mondal Mobile VersionKBSMANIT67% (3)
- Ansi Isa-71.04-2013Документ30 страницAnsi Isa-71.04-2013Rubén Villamil100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Well Planning & Design PDFДокумент47 страницChapter 1 - Introduction To Well Planning & Design PDFAkrem Hkimi100% (5)
- Paper 1Документ295 страницPaper 1Shreyas TiwariОценок пока нет
- AMINE UNIT EVALUATION FORM Metric UnitДокумент4 страницыAMINE UNIT EVALUATION FORM Metric Unitandrey.glinskyОценок пока нет
- CFM SPM 70-48-00Документ8 страницCFM SPM 70-48-00ZakiHaunaОценок пока нет
- Galvaspan G450Документ2 страницыGalvaspan G450khurshedlakhoОценок пока нет
- Guía para Seleccionar Columnas HPLCДокумент52 страницыGuía para Seleccionar Columnas HPLCDiana Lilibet Sánchez MontesОценок пока нет
- Evaporation Rate of Solvents PDFДокумент2 страницыEvaporation Rate of Solvents PDFsyamlokОценок пока нет
- Ethylenediamine Complexes of ChromiumДокумент5 страницEthylenediamine Complexes of ChromiumMatt PraterОценок пока нет
- Dyestone Blue MX SDS SA-0186-01Документ5 страницDyestone Blue MX SDS SA-0186-01gede aris prayoga mahardikaОценок пока нет
- Coke Gujranawala DD 27 12Документ25 страницCoke Gujranawala DD 27 12Muhammad AmmarОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Kerja Kursus PPSIMP Sem1. (BHG 2)Документ18 страницChemistry Kerja Kursus PPSIMP Sem1. (BHG 2)Ayisy HarizОценок пока нет
- Stoichiometry: Calculations With Chemical Formulas and EquationsДокумент47 страницStoichiometry: Calculations With Chemical Formulas and EquationsAngelo Miguel GarciaОценок пока нет
- ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideОт EverandICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideAndrew TeasdaleОценок пока нет
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeОт EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (14)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincОт EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (137)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingОт EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (10)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsОт EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodОт EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (20)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactОт EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeОт EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactОт EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeОт EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- The Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesОт EverandThe Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesОценок пока нет
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsОт EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeОт EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeОценок пока нет
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideОт EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideОценок пока нет
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeОт EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (90)
- Essential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesОт EverandEssential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeОт EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (4)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsОт EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsОценок пока нет
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionОт EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)