Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lecture 4 - Types of Computer
Загружено:
MeAnnLarrosaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lecture 4 - Types of Computer
Загружено:
MeAnnLarrosaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
UNDERSTANDING COMPUTER
A computer is one of the most brilliant inventions of mankind. Thanks to the computer technology, we were able to achieve storage
and processing of huge amounts of data; we could rest our brains by employing computer memory capacities for storing information.
Due to computers, we have been able to speed up daily work, carry out critical transactions and achieve accuracy and precision in
work. Computers of the earlier years were of the size of a large room and were required to consume huge amounts of electric power.
However, with the advancing technology, computers have shrunk to the size of a small watch. Depending on the processing power
and size of computers, they have been classified under various types. Let us look at the classification of computers.
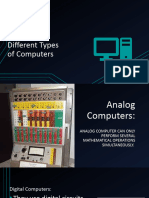
Different Types of Computers
Based on the operational principle of computers, they are categorized as analog, digital and hybrid computers.
1. Analog Computers: These are almost extinct today. These are different from a digital computer because an analog computer
can only perform several mathematical operations simultaneously. It uses continuous variables for mathematical operations
and utilizes mechanical or electrical energy.
2. Digital Computers: They use digital circuits and are designed to operate on two states, namely bits 0 and 1. They are
analogous to states ON and OFF. Data on these computers is represented as a series of 0s and 1s. Digital computers are
suitable for complex computation and have higher processing speeds. They are programmable. Digital computers are either
general purpose computers or special purpose ones. Special purpose computers, as their name suggests, are designed for
specific types of data processing while general purpose computers are meant for general use.
3. Hybrid Computers: These computers are a combination of both digital and analog computers. In this type of computers, the
digital segments perform process control by conversion of analog signals to digital ones.
Classification of Computers
The following are the classification of the different types of computers based on their sizes and functionalities:
1. Mainframe Computers: Large organizations use mainframes for highly critical applications such as bulk data processing and
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning). Most of the mainframe computers have the capacities to host multiple operating systems
and operate as a number of virtual machines and can substitute for several small servers.
2. Minicomputers: In terms of size and processing capacity, minicomputers lie in between mainframes and microcomputers.
Minicomputers are also called mid-range systems or workstations. The term began to be popularly used in the 1960s to refer
to relatively smaller third generation computers.
3. Servers: They are computers designed to provide services to client machines in a computer network. They have larger storage
capacities and powerful processors. Running on them are programs that serve client requests and allocate resources like
memory and time to client machines. Usually they are very large in size, as they have large processors and many hard drives.
They are designed to be fail-safe and resistant to crash.
4. Supercomputers: The highly calculation-intensive tasks can be effectively performed by means of supercomputers. Quantum
physics, mechanics, weather forecasting, molecular theory are best studied by means of supercomputers. Their ability of
parallel processing and their well-designed memory hierarchy give the supercomputers, large transaction processing powers.
5. Microcomputers: A computer with a microprocessor and its central processing unit it is known as a microcomputer. They do
not occupy space as much as mainframes do. When supplemented with a keyboard and a mouse, microcomputers can be
called personal computers. A monitor, a keyboard and other similar input output devices, computer memory in the form of
RAM and a power supply unit come packaged in a microcomputer. These computers can fit on desks or tables and prove to
be the best choice for single-user tasks.
Personal computers come in different forms such as desktops, laptops and personal digital assistants. Let us look at each of these types
of computers.
A. Desktops: A desktop is intended to be used on a single location. The spare parts of a desktop computer are readily available
at relatively lower costs. Power consumption is not as critical as that in laptops. Desktops are widely popular for daily use in
the workplace and households.
B. Laptops: Similar in operation to desktops, laptop computers are miniaturized and optimized for mobile use. Laptops run on
a single battery or an external adapter that charges the computer batteries.
C. Net books: They fall in the category of laptops, but are inexpensive and relatively smaller in size. They had a smaller feature
set and lesser capacities in comparison to regular laptops, at the time they came into the market.
D. Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs): It is a handheld computer and popularly known as a palmtop. It has a touch screen and a
memory card for storage of data. PDAs can also be used as portable audio players, web browsers and smart phones. Most of
them can access the Internet by means of Bluetooth or Wi-Fi communication.
E. Tablet Computers: Tablets are mobile computers that are very handy to use. They use the touch screen technology. Tablets
come with an onscreen keyboard or use a stylus or a digital pen. Apple's iPod redefined the class of tablet computers.
F. Wearable Computers: A record-setting step in the evolution of computers was the creation of wearable computers. These
computers can be worn on the body and are often used in the study of behavior modeling and human health. Military and
health professionals have incorporated wearable computers into their daily routine, as a part of such studies. When the users'
hands and sensory organs are engaged in other activities, wearable computers are of great help in tracking human actions.
Wearable computers do not have to be turned on and off and remain in operation without user intervention.
Вам также может понравиться
- Understanding ComputerДокумент18 страницUnderstanding ComputerJerson E. RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Computer Module 3 Lesson 1Документ2 страницыComputer Module 3 Lesson 1yuuna yuunaОценок пока нет
- 2 Understanding ComputerДокумент2 страницы2 Understanding ComputerAngel Marie TisadoОценок пока нет
- ComputersДокумент4 страницыComputersZujajah Gull100% (1)
- Understanding ComputerДокумент3 страницыUnderstanding ComputerHelner TaghapОценок пока нет
- A Computer Is One of The Most Brilliant Inventions of MankindДокумент1 страницаA Computer Is One of The Most Brilliant Inventions of MankindAmor Lorenzo MirabunaОценок пока нет
- Different Types of ComputersДокумент27 страницDifferent Types of ComputersJanine B. JavierОценок пока нет
- Information Sheet 1.2: Types of ComputerДокумент23 страницыInformation Sheet 1.2: Types of ComputerBerlin AlcaydeОценок пока нет
- Classification OF ComputerДокумент36 страницClassification OF ComputerJohnry Guzon ColmenaresОценок пока нет
- Different Types of Computers: Hom e Topi Cs Arti Cle SДокумент4 страницыDifferent Types of Computers: Hom e Topi Cs Arti Cle SSantosh KumarОценок пока нет
- Understanding Computers ICT Grade 9Документ21 страницаUnderstanding Computers ICT Grade 9Achilles Charles GrandezaОценок пока нет
- Lesson 5 Understanding Computer (Autosaved)Документ27 страницLesson 5 Understanding Computer (Autosaved)alma agnasОценок пока нет
- Kinds of ComputersДокумент44 страницыKinds of ComputersGerald TorrezОценок пока нет
- Understanding ComputerДокумент27 страницUnderstanding ComputermarkОценок пока нет
- Information Communication Technology: Understanding Computers Classification of ComputersДокумент2 страницыInformation Communication Technology: Understanding Computers Classification of ComputersLawrenceОценок пока нет
- Introduction Computers NotesДокумент88 страницIntroduction Computers NoteswilbertОценок пока нет
- Md. Al Mamun IT Officer CRP-MirpurДокумент37 страницMd. Al Mamun IT Officer CRP-Mirpurmamun183Оценок пока нет
- Classifying Computers by Operating Principle, Purpose, CapacityДокумент4 страницыClassifying Computers by Operating Principle, Purpose, CapacityLata SharmaОценок пока нет
- Classification of ComputersДокумент16 страницClassification of ComputersTEEОценок пока нет
- De Nition 1Документ14 страницDe Nition 1brian mburuОценок пока нет
- Classification On The Basis of SizeДокумент2 страницыClassification On The Basis of SizeKyungsoo DoОценок пока нет
- Types of ComputersДокумент41 страницаTypes of Computerssubramani muthusamyОценок пока нет
- Igcse Ict Notes 2023 PDFДокумент82 страницыIgcse Ict Notes 2023 PDFLoago Seropola100% (1)
- Computers Are Classified According To Their Data Processing SpeedДокумент3 страницыComputers Are Classified According To Their Data Processing SpeedArchay Tehlan70% (10)
- Classifying computers by size, function and data handlingДокумент2 страницыClassifying computers by size, function and data handlingMamta Mohit DhandaОценок пока нет
- Fundamental of Computer Input/ Output, Processing and Memory DeviceДокумент12 страницFundamental of Computer Input/ Output, Processing and Memory Devicenandkishor joshiОценок пока нет
- Understanding Computers in Under 40Документ23 страницыUnderstanding Computers in Under 40Maricor HernandezОценок пока нет
- Basic Parts of ComputerДокумент96 страницBasic Parts of ComputerDawin DessertОценок пока нет
- Zimsec O Level NotesДокумент73 страницыZimsec O Level NotesClinton Chikengezha100% (1)
- Computer Studies NotesДокумент73 страницыComputer Studies NotesSalome MupambireiОценок пока нет
- Media Unit 3 NotesДокумент4 страницыMedia Unit 3 NotesMohd ShifanОценок пока нет
- Understanding ComputerДокумент15 страницUnderstanding ComputerMilagross FabregasОценок пока нет
- Personal ComputerДокумент23 страницыPersonal ComputerJERWIN HONRADOОценок пока нет
- Types of computers classified by principles and configurationsДокумент4 страницыTypes of computers classified by principles and configurationsKundaiОценок пока нет
- Week4 5understanding ComputerДокумент20 страницWeek4 5understanding ComputerNefarious MitsiukieОценок пока нет
- 1.4 Types of Computer in Our Society: 1. Analog ComputersДокумент2 страницы1.4 Types of Computer in Our Society: 1. Analog ComputersJhonna Sanchez CelestinoОценок пока нет
- Evolution of Computers Through GenerationsДокумент29 страницEvolution of Computers Through GenerationsAjay DerashriОценок пока нет
- Classification of ComputersДокумент7 страницClassification of ComputersscsdfvdgОценок пока нет
- Classification of Computers According To SizeДокумент8 страницClassification of Computers According To SizeAnonymous RMO9Hzixvc50% (2)
- Different Types of Operating SystemДокумент91 страницаDifferent Types of Operating SystemDawin DessertОценок пока нет
- Git Unit 3Документ2 страницыGit Unit 3Vivien LancinОценок пока нет
- Types of ComputersДокумент15 страницTypes of ComputersverskieОценок пока нет
- Computer AwarenessДокумент64 страницыComputer Awarenessgauravgupta_pusa365Оценок пока нет
- Types of Computer SystemsДокумент23 страницыTypes of Computer SystemsVinoth Raj100% (3)
- Various Types of ComputersДокумент35 страницVarious Types of ComputersRayad AliОценок пока нет
- Occupational Health and Safety Understanding ComputerДокумент2 страницыOccupational Health and Safety Understanding ComputerRegina Fe EmpasОценок пока нет
- ICT in Science Education: An Overview of Information and Communication Technology Tools and ResourcesДокумент18 страницICT in Science Education: An Overview of Information and Communication Technology Tools and ResourcesYusha'u SaniОценок пока нет
- COMPUTERДокумент16 страницCOMPUTERLiam Zhaeden TavuОценок пока нет
- Computer: Different Types of ComputersДокумент29 страницComputer: Different Types of ComputersShiv SharmaОценок пока нет
- Topic 1 NotesДокумент7 страницTopic 1 NotesAshley MainaОценок пока нет
- INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING Part1Документ9 страницINTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING Part1Kasanda StephenОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Computing GeekforgeeksДокумент4 страницыIntroduction To Computing GeekforgeeksNoshadTechОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Computing PrelimДокумент29 страницIntroduction To Computing PrelimApril Jane AndresОценок пока нет
- 2 ClassificationofComputerДокумент4 страницы2 ClassificationofComputerGina BrownОценок пока нет
- Classification of Computers According To Technology and SizeДокумент12 страницClassification of Computers According To Technology and SizeNadun Mihiranga Herath90% (20)
- Q1 - Lesson 6Документ5 страницQ1 - Lesson 6JEROME DIAZОценок пока нет
- Understanding Computers: LessonДокумент32 страницыUnderstanding Computers: LessonRonnil QuietaОценок пока нет
- Allied EssentialsOfComputers^0BioinformaticsДокумент156 страницAllied EssentialsOfComputers^0Bioinformaticssamikshajohn03Оценок пока нет
- Tools Bar.: To Be "Grouped"Документ1 страницаTools Bar.: To Be "Grouped"MeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- Tools Bar.: To Be "Grouped"Документ1 страницаTools Bar.: To Be "Grouped"MeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- Tools Bar.: To Be "Grouped"Документ1 страницаTools Bar.: To Be "Grouped"MeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- Product Dev't - BrandingДокумент7 страницProduct Dev't - BrandingMeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- Descriptive LinguisticsДокумент2 страницыDescriptive LinguisticsMeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- Tools Bar.: To Be "Grouped"Документ1 страницаTools Bar.: To Be "Grouped"MeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- Exercises No. 1: ST ND RD THДокумент1 страницаExercises No. 1: ST ND RD THMeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- C-CHS LM Module 1 PECs and Module2 EMДокумент35 страницC-CHS LM Module 1 PECs and Module2 EMHari Ng Sablay95% (21)
- Lecture 1Документ2 страницыLecture 1MeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- Diagnose and Troubleshoot Computer SystemsДокумент27 страницDiagnose and Troubleshoot Computer SystemsMeAnnLarrosa100% (1)
- AnthropologyДокумент2 страницыAnthropologyMeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- Massage Therapists: Refers To The Standards and Conduct of Behavior of An Individual or Professional GroupДокумент2 страницыMassage Therapists: Refers To The Standards and Conduct of Behavior of An Individual or Professional GroupMeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- TG Dressmaking G10Документ96 страницTG Dressmaking G10MeAnnLarrosa73% (22)
- Printers and Other Hardware: Applets To Configure Devices Connected To Your ComputerДокумент1 страницаPrinters and Other Hardware: Applets To Configure Devices Connected To Your ComputerMeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- Corporate CultureДокумент3 страницыCorporate CultureMeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- After 5 Years of 4ps, What's NextДокумент45 страницAfter 5 Years of 4ps, What's NextMeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- Anthropology of EducationДокумент7 страницAnthropology of EducationshangОценок пока нет
- PracticeДокумент1 страницаPracticeMeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- Basic computer parts explainedДокумент17 страницBasic computer parts explainedMeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- K To 12 Dressmaking and Tailoring Learning ModulesДокумент132 страницыK To 12 Dressmaking and Tailoring Learning ModulesHari Ng Sablay94% (142)
- IntroductionДокумент39 страницIntroductionMeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- Computer Systems Servicing Learning Module K To 12Документ136 страницComputer Systems Servicing Learning Module K To 12MeAnnLarrosa86% (50)
- Computer PortsДокумент2 страницыComputer PortsMeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- Kto12 BASIC EDUCATION CURRICULUM TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION HOME ECONOMICS-BEAUTY CARE (NAIL CARE) SERVICESДокумент12 страницKto12 BASIC EDUCATION CURRICULUM TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION HOME ECONOMICS-BEAUTY CARE (NAIL CARE) SERVICESMary Rhea Revestir Ileto67% (3)
- EssentialДокумент50 страницEssentialMeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- Web Page DesigningДокумент2 страницыWeb Page DesigningMeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- ComputerPorts, Cables and WiresДокумент2 страницыComputerPorts, Cables and WiresMeAnnLarrosa100% (2)
- DM s2015 158Документ23 страницыDM s2015 158MeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- INTRODUCTIONДокумент28 страницINTRODUCTIONMeAnnLarrosaОценок пока нет
- Basic Circuits, Laws, and Measurements: Chapter ObjectivesДокумент20 страницBasic Circuits, Laws, and Measurements: Chapter ObjectivesSneha PavithranОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Centrifugal Pump ExperimentДокумент3 страницыIntroduction To Centrifugal Pump ExperimentQHalimОценок пока нет
- Bearings Seals Greases Chapter 53 Page 762Документ13 страницBearings Seals Greases Chapter 53 Page 762AbdurhamanОценок пока нет
- PRS NCO3 Data Sheet EnUS 11145053835Документ4 страницыPRS NCO3 Data Sheet EnUS 11145053835Rio DwirahayuОценок пока нет
- Doshi Price List MODIFIED 1st Jan 2011 3 PDFДокумент24 страницыDoshi Price List MODIFIED 1st Jan 2011 3 PDFDaniel Edward OmondiОценок пока нет
- Rohm Bu2090Документ12 страницRohm Bu2090Alberto Carrillo GuerreroОценок пока нет
- KSG Flash-2 - User Manual PDFДокумент107 страницKSG Flash-2 - User Manual PDFMarcelo DominguezОценок пока нет
- Esiweld 1G Automated Pipe Welding System CatalogueДокумент1 страницаEsiweld 1G Automated Pipe Welding System CatalogueAlexОценок пока нет
- Geared VS Gearless Drive Solutions For Grinding MillsДокумент15 страницGeared VS Gearless Drive Solutions For Grinding MillsLuis B100% (1)
- Instruction Manual: Operates With ISO9001 Certified Quality SystemДокумент13 страницInstruction Manual: Operates With ISO9001 Certified Quality SystemdomagojОценок пока нет
- 7700-7720 Manual Servicio RaymondДокумент497 страниц7700-7720 Manual Servicio Raymondmontacargasgamma montacargas100% (2)
- Schindler 5300IN elevator specificationsДокумент6 страницSchindler 5300IN elevator specificationskumarОценок пока нет
- Wärtsilä lubrication system manualДокумент10 страницWärtsilä lubrication system manualLIVIAОценок пока нет
- R-Car Starterkit Hardware Manual: R-Car Starter Kit Premier R-Car Starter Kit ProДокумент37 страницR-Car Starterkit Hardware Manual: R-Car Starter Kit Premier R-Car Starter Kit ProbengaltigerОценок пока нет
- Ip Control Valve Calibration FormДокумент1 страницаIp Control Valve Calibration FormKester Ndabai0% (1)
- Timberrite Controller Parts Manual: Series HarvesterДокумент38 страницTimberrite Controller Parts Manual: Series Harvestermauricio1barrientos1100% (1)
- Manual Servico Sony HCD Gpx5Документ68 страницManual Servico Sony HCD Gpx5Realmember FoxОценок пока нет
- Dallara f308 Owners Manual 2013 AprobДокумент54 страницыDallara f308 Owners Manual 2013 AprobblancohccОценок пока нет
- Grade 9 MetalworkДокумент13 страницGrade 9 MetalworkAidan O'HaraОценок пока нет
- 2SA1568Документ13 страниц2SA1568raquelОценок пока нет
- LH2.2 & EZ-F User Manual Issue 2bДокумент73 страницыLH2.2 & EZ-F User Manual Issue 2bphilro52Оценок пока нет
- 3TN82Документ123 страницы3TN82Виталий РогожинскийОценок пока нет
- DW90A (Yuchai-Fast Transmission-Hande Axle) OM 202208001-ENДокумент214 страницDW90A (Yuchai-Fast Transmission-Hande Axle) OM 202208001-ENjaki162096Оценок пока нет
- Copie de Standards Check ListДокумент7 страницCopie de Standards Check ListAbakar MahamatОценок пока нет
- MSI BL PIEZO AXLE SENSORДокумент2 страницыMSI BL PIEZO AXLE SENSORErikoОценок пока нет
- Divertor DamperДокумент53 страницыDivertor DamperfaisalnadimОценок пока нет
- Ficha Tecnica - Bomba Hidraulica Sauer Danfoss PDFДокумент220 страницFicha Tecnica - Bomba Hidraulica Sauer Danfoss PDFpokebalomanОценок пока нет
- Ultramatch Pro Src2496: User ManualДокумент16 страницUltramatch Pro Src2496: User ManualLuka TrengovskiОценок пока нет
- Japan Auctions GradesДокумент5 страницJapan Auctions GradesAlzieОценок пока нет
- GMK Manitowoc Training Catalog 2020Документ32 страницыGMK Manitowoc Training Catalog 2020aleksandr100% (1)