Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
M.E. (Marine Engineering & Mechanical Handling) : Scheme of Instruction & Scheme of Examinations
Загружено:
David VictorОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
M.E. (Marine Engineering & Mechanical Handling) : Scheme of Instruction & Scheme of Examinations
Загружено:
David VictorАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
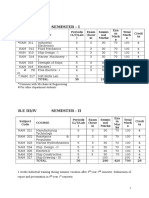
SCHEME OF INSTRUCTION & SCHEME OF EXAMINATIONS
M.E.(MARINE ENGINEERING & MECHANICAL HANDLING)
I SEMESTER
Sessional
Subject Periods Exam Exam Credits
Course Marks Total
Code L/T/Lab Hours Marks
Advanced Engineering
MEMH1.1 4 3 30 70 100 4
Mathematics
Principles of Material
MEMH1.2 4 3 30 70 100 4
handling devices
Advanced Mechanics
MEMH1.3 4 3 30 70 100 4
of solids
MEMH1.4 Marine Engineering-I 4 3 30 70 100 4
70 100
MEMH1.5 Theory of vibrations 4 3 30 4
MEMH1.6 Mechanics and Design 4 30 70** 100 4
of Cargo handling
equipment **
Total 24 180 420 600 24
** Viva-Voce Examination with a committee consisting of Head of the Department,
concerned teacher & one examiner. No written Examination.
II SEMESTER
Subject Course Periods Exam Sessional Exam Total Credits
Code L/T/Lab Hours Marks Marks
MEMH 2.1 Structural Design of 4 3 30 70 100 4
Mechanical Handling
equipment
MEMH 2.2 Marine 4 3 30 70 100 4
Instrumentation &
Stress Analysis
MEMH 2.3 Marine Engineering 4 3 30 70 100 4
II
MEMH 2.4 Elective* 4 3 30 70 100 4
MEMH 2.5 Introduction to 4 3 30 70 100 4
Computational Fluid
Dynamics
MEMH 2.6 Seminars 4 100 100 2
Total 24 250 350 600 22
M.E. (Marine Engineering and Mechanical Handling) Syllabus Page 1 of 16
\
III SEMESTER
Course Periods Exam Sessional Exam Total Credits
L/T/Lab Hours Marks Marks
Dissertation ( to be
continued in 4th
semester)
Total
IV SEMESTER
Course Grading of Thesis
Dissertation Award of grading such as, A,B,C and F for the thesis.
(continued from 3rd (A= excellent;
semester)*** B= Very good;
C= Good
F= not accepted.)
Elective* (2nd Semester):
1. Naval Architecture
2. Industrial Management
3. Control Engineering
** Viva-Voce Examination with a committee consisting of Head of the Department,
concerned teacher & one examiner. No written Examination.
*** Pre-examination appraisal through Seminar by a committee consisting of BOS
Chairman, Head of the Department and Guide.
*** Final presentation followed by Viva-Voce Examination with the following members.
1. Chairman, Board of Studies.
2. Head of the Department.
3. External Examiner (External to the college)
4. Internal Guide
5. (And) External Guide ( if any)
The award of class will be given based on CGPA obtained in theory/practical/lab
and award a separate grading, such as, A,B,C and F for the thesis.(A= excellent;
B= Very good; C= good and F= not accepted.)
----------
M.E. (Marine Engineering and Mechanical Handling) Syllabus Page 2 of 16
\
SYLLABUS
M.E.(MARINE ENGINEERING & MECHANICAL HANDLING)
I SEMESTER
MEMH 1.1 ADVANCED ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS
Periods per week: 4 Examination: 70 Marks
Credits: 4 Sessionals : 30 Marks
1. Matrices and linear systems of equations: Basic classification, solution of linear
systems by Matrix inversion method, Gaussion elimination methods, iterative
methods and the eigen value problem.
2. Numerical differentiation and integration: Numerical differentiation, Maximum and
minimum values of a tabulated function. Numerical integration by Trapezoidal rule
and Simpson rule, Rambera integration, Numerical double integration.
3. Numerical solution of ordinary differential equations: Solution by Taylor's series.
Picard method of successive approximations, Euler's method. Runge-kutta methods.
Predictor corrector methods, simultaneous and Higher-order equations, Boundary
value problems.
4. Numerical solution of partial differential equations: Finite difference approximations
to derivatives. Laplace equation by Jacobin’s method, Gauss-Seidal method,
parabolic equations. Interactive methods for the solution of equations.
Text books:
Chapters 4, 5, 6 and 7 of Introductory Methods-- Numerical Analysis by S.S.Sastry,
Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Limited. Publication year 1981.
M.E. (Marine Engineering and Mechanical Handling) Syllabus Page 3 of 16
\
MEMH 1.2 PRINCIPLES OF MATERIAL HANDLING DEVICES
Periods per week: 4 Examination: 70 Marks
Credits: 4 Sessionals : 30 Marks
(a) Principles of Material Handling: Classifications of the materials handling equipment,
their characteristics and application, principles, packaging and storage of materials,
operation analysis and study of travel diagrams and flow process charts. Preparation of a
new proposal for an integrated materials handling system. Protective devices handling of
fluids and multiphase systems. Handling of refrigerated cargo.
(b) Theory and construction of the various parts of Mechanical Handling devices, wire
ropes and chains, hooks, shackles, grabs, ladles and lifting electromagnets, sheaves,
sprockets and drums, runners and rails, buffers and limit switches.
(c) Design of simple mechanical handling devices, viz., screw jacks, pulley blocks,
winches, hoists and capstans, wind lasses.
Text Books:
1. Materials Handling - John R. Immer and Mc Graw Hill, 1953.
2.Materials Handling Equipment - N. Rudenco, MIR Publish.
3.Materials Handling - Apple.
M.E. (Marine Engineering and Mechanical Handling) Syllabus Page 4 of 16
\
MEMH 1.3 ADVANCED MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
Periods per week: 4 Examination: 70 Marks
Credits: 4 Sessionals : 30 Marks
1. Three dimensional stress and strain - Principal stresses and strains-Mohr's circle
representation of triaxial state of stresses and strains, theories of failure. Elementary
treatment of contact stresses for point and line contacts
2. Shear Centre: Shear Centre for sections having one axis of symmetry - open channel
sections, I-sections, t- sections.
3. Unsymmetrical bending: Unsymmetrical bending in sections having double axis of
symmetry - Unsymmetrical bending in sections having one axis of symmetry.
4. Torsion: Torsional resistance of bars having rectangular sections - Membrane analogy.
5. Beams on elastic foundation: Beams on continuous elastic foundation, Infinite beams
and semi-infinite beams.
6. Buckling of columns, beams and shafts.
7. Elementary treatment of flat plates: Rectangular and circular plates freely supported
and clamped edges.
8. A brief introduction to the Mathematical theory of Elasticity: Introduction,
Elementary theory of Elasticity, Essential Difference between method of ordinary
Mechanics and theory of Elasticity.
Text books:
1. Advanced Mechanics of Materials by Seely and Smith.
2. Mechanics of Materials by R.C. Hibbeler
3. Advanced Strength of Materials by Den Hartog.
4. Strength of Materials Vols I and II by S. Timoshenko.
M.E. (Marine Engineering and Mechanical Handling) Syllabus Page 5 of 16
\
MEMH 1.4 MARINE ENGINEERING –I
Periods per week: 4 Examination: 70 Marks
Credits: 4 Sessionals : 30 Marks
1. Marine Diesel Engines – Low speed and medium speed engines – Auxiliary
engines – Scavenging and supercharging systems – Starting and reversing gear –
Maintenance – Automation – Hazards in engine room.
2. Marine Nuclear power installation - Principles of operation of Atomic Reactors –
Different types of Reactors – Use of Nuclear reactors in sea going vessels -
Radiation hazards and safety – Radioactive waste disposal.
3. Marine Turbines – Steam turbine Classification based on impulse and reaction
principles – Flow thro’ blade passages and design – Losses and performance –
Compounding, velocity triangles – Starting and Maintenance procedures.
4. Marine gas turbines – Practical cycles and shaft arrangements - Power turbine –
Applications.
5. Marine Refrigeration – Cycles – Compressors, Condensers, Evaporators and
thermostatic valves – Space coolers – Maintenance and Auxiliary equipment.
6. Marine Air-conditioning – cooling, Heating, Humidication process – Types of Air
conditioning systems – Ducting controls.
7. Ventilation – Requirements and provision – Insulation protection of materials and
maintenance.
8. Marine Boilers – Composite and water tube boilers – Waste heat boilers Arrangement
of boiler room – Feed water treatment for Marine boilers – feed supply systems and
control.
Text Books:
1. Marine Power plant Engineering - Akimov.P
2. Marine I.C Engines-A.B Kane
3. Principles and practice of Marine Diesel Engines – D.K Sanyal
4. Refrigeration and air-conditioning- P.L. Ballaney
5. Marine Steam Boilers- Milton J.H.
M.E. (Marine Engineering and Mechanical Handling) Syllabus Page 6 of 16
\
MEMH 1.5 THEORY OF VIBRATIONS
Periods per week: 4 Examination: 70 Marks
Credits: 4 Sessionals : 30 Marks
1. Single degree of freedom systems: Free and forced vibrations, damping, classification
and damped systems. Energy methods. Vibration isolation and transmissibility.
Vibration measuring instruments such as displacement, velocity, acceleration and
frequency measurements, Dunkerley's equation.
2. Two degrees of freedom system. Free, forced, damped and undamped motions matrix
formulation, matrix method, using of Lagrange's equations to determine equations of
motion, Dynamic vibration absorbers, principle of Orthogonality. Semi-definite
systems. Combined rectilinear and angular modes. Torsional systems.
3. Multi degrees of freedom systems: Free and forced vibrations of Longitudinal,
torsional, and lateral modes. Critical speeds of rotors Matrix formulation, stiffness
and flexibility influence coefficients. Eigen value problem Matrix method, Matrix
iteraction technique for eigen values and eigen vectors. Stodola's method, Hozler's
Method.
4. Continuous Systems: Axial vibrations of bars, torisonal vibrations of shafts,
transverse vibrations of strings and bending vibrations of beams. Free and forced
vibration of strings classical and energy methods.
5. Ship vibration : Introduction to ship hull vibration-- Mathematical basis of ship
vibration - calculation of ship hull vibration.
Text books:
1. Mechanical Vibrations - G.K. Grover
2. Elements of Mechanical Vibration : Merovitch
3. Theory of Vibrations with applications: W.T. Thomson
4. Ship Hull Vibrations: Todd
5. Mechanical vibrations, Schaum's outline series- William W. Seto
M.E. (Marine Engineering and Mechanical Handling) Syllabus Page 7 of 16
\
MEMH 1.6 MECHANICS AND DESIGN OF CARGO HANDLING
EQUIPMENT
Periods per week: 4 Examination: 70 Marks
Credits: 4 Sessionals : 30 Marks
Kinematic, dynamic analysis and design procedures of various components,
Mechanisms of (a) scraper, apron and flight conveyors, (b) roller and belt conveyors,
(c) belt and chain bucket elevators (d) screw and ribbon conveyors (e) overhead chain
trolley conveyors and (f) vibrating trough and shaker conveyors, rope ways.
Kinematic and dynamic analysis of the various components, mechanisms and design
procedures of (a) floor and wall mounted jib cranes (b) hand chain and electric
operated overhead travelling cranes (c) Stationery and travelling rotary jib cranes with
fixed adjustable level luffing arrangements (d) Goliath and semi goliath cranes, (e)
Derrick Cranes (f) tower cranes (g) mobile cranes (h) Telphers.
Text books:
1. Materials handling equipment - N. Ruderno, Mir publications.
2. Materials handling equipment- M.P. Alexandrov, Mir Publications.
3. Conveyors and related equipment - A Spirakovsky and V.Dyachkov, Mir
Publications
M.E. (Marine Engineering and Mechanical Handling) Syllabus Page 8 of 16
\
M.E.(MARINE ENGINEERING & MECHANICAL HANDLING)
II SEMESTER
MEMH 2.1 STRUCTURAL DESIGN OF MECHANICAL HANDLING
EQUIPMENT
Periods per week: 4 Examination: 70 Marks
Credits: 4 Sessionals : 30 Marks
Analysis of forces of determinate, indeterminate and redundant framed structure,
detailed force analysis and design of overhead travelling crane structures. Analysis of
force and detailed design of the Jib of fixed and luffing types of rotary jib cranes.
Design of structures pertaining to derricks, gantries, columns, portals and supporting
trusses for belt conveyers.
Text books:
1. Theory of structures - Morley, Lonmans.
2. Materials Handling Equipment - N. Rudenko
MEMH 2.2 MARINE INSTRUMENTATION & STRESS ANALYSIS
Periods per week: 4 Examination: 70 Marks
Credits: 4 Sessionals : 30 Marks
Generalized measuring systems – calibration – damping - Dynamic signals –
Basic detectors Transducer elements – Intermediate modifying systems – terminating
devices.
Measurement of force and torque, Measurement of pressure – High pressure and
low pressure, Measurement of fuel flow – Positive displacement methods – Obstruction
meters – Hotwire anemometer.
Measure of temperature – Thermocouples – Pyrometry, Vibration and shock
measurement – Accelerometers – Vibrometers – Seismic devices. Acoustic
measurements – Sound measuring techniques.
Stain gauges – Photo elastic, Electrical, resistance gauges, cements and cementing
of Gauges – Bridge circuits – balanced and unbalanced, Calibration gauge rosettes –
Evaluation of Principal stresses – Static and dynamic gauges for various applications.
Stress analysis – Whole field techniques by photo elasticity, brittle coatings, Grid
methods & Moire – Applications to the solution of engineering problems.
Text Books:
1. Mechanical Measurements - T.G Beckwith & N.Lewis Buck.
2. Mechanical and industrial Measurements - R.K Jain.
3. Experimental methods for engineers. - J.P Holman
4. Applied Stress Analysis- A.J. Durelli.
M.E. (Marine Engineering and Mechanical Handling) Syllabus Page 9 of 16
\
MEMH 2.3 MARINE ENGINEERING II
Periods per week: 4 Examination: 70 Marks
Credits: 4 Sessionals : 30 Marks
1. Engine room arrangements for different power plants – Functions of Auxiliary
equipment – Bilge and ballast systems – Other Auxiliaries.
2. Piping – Piping fittings and valves – Control valves, materials and corrosion in
pipes – Colorcodes – Steam traps, Drains and glands.
3. Pumping systems. General principles - Simple and duplex pumps – Rotary
positive displacement pumps –– Centrifugal pumps – Axial flow pumps - Bilge ,
ballast & sanitary pumps – Boiler feed pumps – air pumps and Ejectors.
4. Centrifugal compressors – Working principles – Impeller and diffuser design.-
Performance characteristics – Blade profiles.
5. Airflow compressors –Working principles – Types – Performance characters –
Aerofoil theory – Blade design.
6. Condensers, Evaporators, Deaerators and purifiers - Auxiliary condensers –
Evaporating plant – Distillation plant – Feed heaters deaerators oil purifiers –
Self-changing purifiers.
7. Steering gear- Types Steam steering gear, Telemotor gear, Hand steering gear,
Hydraulic systems, Electro hydraulic steering gear – Electrical steering gear.
Text Books:
1. The running and maintenance of marine Machinery - J Cowley.
2. Marine Auxiliary machinery - W.J Fox.
3. Marine Auxiliary machinery and systems - M Khetaguroo
4. Theory and design of steam and gas turbines - Lee.
M.E. (Marine Engineering and Mechanical Handling) Syllabus Page 10 of 16
\
ELECTIVE
MEMH 2.4(1). NAVAL ARCHITECTURE
Periods per week: 4 Examination: 70 Marks
Credits: 4 Sessionals : 30 Marks
1. Introduction: Types of ships, Geometry 0f ship, Displacement, TPC, Coefficient
of form, Wetted surface area.
2. Area Volume, First and second moments using Simpson’s rule, Center of gravity,
Effect of addition of mass, Effect of movement of mass, Effect of suspended
mass.
3. Transverse Stability of ships: Statistical stability at small angles of heel,
Calculation of B.M, metacentric diagram, Inclining experiment, free surface
effect.
4. Trim: Change on draughts due to added masses, Change of mean draught and end
draughts due to density, Change in mean draught and end draughts due to bilging.
6. Resistance: Frictional, residuary and total resistance, admiralty Coefficient, fuel
Coefficient and Consumption.
7. Propellers: Apparent and real slip, Wake, Thrust, relation between mean pressure and
speed, measurement of pitch, Cavitation, Solid propellers and other systems of
propellers.
8. Rudder theory: Force on rudder, Torque on stock, angle of heel due to force on
rudder, angle of heel on turning.
9. Launching: Launching curves, Ground ways and sliding ways, Dynamics of launching
Docking stability – Launching lubricants and their properties.
Text Books:
1. Reed’s Naval Architecture for Marine Engineering.
2. Naval Architecture for Marine Engineers by W.Muckle.
3. Basic ship theory by K.J Rawson & E.C Tupper.
M.E. (Marine Engineering and Mechanical Handling) Syllabus Page 11 of 16
\
ELECTIVE
MEMH 2.4 (2) INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING AND MANAGEMENT
Periods per week: 4 Examination: 70 Marks
Credits: 4 Sessionals : 30 Marks
1.Management and Organization: Functions of Management, Principles of Management,
Principles of Organization: Line, Staff and functional organizations, Forms of business
ownership, Entrepreneurship.
2.Facilities location and Layout: Factors for selection of a location, Urban, Suburban and
rural locations, Types of layouts, process and product layouts, Line balancing, Shipyards
and port layouts.
3.Material Handling: Principles of material handling, Types of material handling
equipment, Selection of material handling equipment.
4.Inventory control: Costs of inventory, ABC Analysis, Economic order quantity,
Economic lot-size quantity, Basic inventory models.
5.Quality Control: Quality and product design, Control charts.
6. Network analysis: Network techniques of program management, CPM and its
advantages, Difference in PERT & CPM, steps in CPM technique, Steps in the technique
of PERT planning, Estimation of activity duration. Float or slack, Latest finish time,
resource leveling program, crash of the project.
7.Management information Systems (MIS): Impact of MIS on management, accounting
information system, Objective of information systems, Computer based information
management system, Management by direction, by result, management in objectives,
Influence of computer based on management by direction.
8. Industrial Psychology and personnel management: Functions of functional
management, Industrial legislation of India, Factories act and the industrial disputes act,
Elements of industrial psychology, Hawthrone studies, Theories of motivation- Maslow,
Mc Gregor.
Text Books:
1. Industrial engineering and management -O.P Khanna
2. Industrial Management - K.K.Ahuja, Khanna Publishers.
References:
1. Principles of Management - Koontz & O Donnel.
2. Production and Operations Management - Everette Adam &Ronald Ebert.
3. Operations Management - John Mc Clain & Joseph Thames.
M.E. (Marine Engineering and Mechanical Handling) Syllabus Page 12 of 16
\
ELECTIVE
MEMH 2.4 (3) CONTROL ENGINEERING
Periods per week: 4 Examination: 70 Marks
Credits: 4 Sessionals : 30 Marks
Introduction, automatic control systems, on/off controllers, step controllers, continuous
controllers, basic equation of a servo mechanism, transient analysis, transfer - function
analysis, the laplace transformation.
Equations of physical systems: Introduction, mechanical system - translational, rotational,
mechanical systems, thermal, hydraulic, pneumatic and electrical systems .
Transient analysis of servo mechanisms, block diagram concept of a control system,
analysis of proportional error, servo mechanism time and frequency responses.
Transfer functions: Definition, deviation of transfer functions - algebra of block diagrams
and transfer functions.
Graphical representation of transfer functions: The frequency response concept and
transfer function, basic relationship between amplitudes and phase, logarithm of the
transfer functions, bode diagrams, diagrams of the basic terms.
Analysis of servo mechanism performance, absolute stability, general discussion,
instability from inspection of the differential equation, routh's criterion. Ny quists,
criterion steady state and transient performance from transfer function plots.
Control system components: Error detectors, controllers, servo motors for DC, AC,
Mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic and thermal systems (one example each).
Text Books:
1. Thalore and Bronz, Analysis and design of feed back control systems - International
students edition ( chapters 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7) and appendix B.C.D)
M.E. (Marine Engineering and Mechanical Handling) Syllabus Page 13 of 16
\
MEMH 2.5 Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics
Periods per week: 4 Examination: 70 Marks
Credits: 4 Sessionals : 30 Marks
I Introduction and Basic Numerical Methods:
Introduction to CFD, Approximation and interpolation, Numerical integration, Finite
difference approximations of derivatives
II The Finite Volume Method for Model Problems:
1-D diffusion, Thomas algorithm for tri-diagonal systems, 1-D convection-diffusion, 2-D
model problems
III Modelling Navier Stokes Equations:
Governing equations for fluid mechanics, Staggered grids, Pressure-velocity coupling –
the SIMPLE algorithm, Steady flows, Unsteady flows, Implementation of boundary
conditions
Commercial CFD codes, Reynolds averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) equations and
turbulence modeling
Text Books:
1. Introduction to CFD the finite volume method by Malalasekera & Versfeeg
2. Computational FM and heat transfer by Anderson, Tennehill and Pletchen.
M.E. (Marine Engineering and Mechanical Handling) Syllabus Page 14 of 16
\
.
MEMH 2.6 SEMINARS
Periods per week: 4
Credits: 2 Sessionals : 100 Marks
The student has to give at least three seminars on relevant topics of
his choice but related to Marine Engineering and Mechanical handling.
M.E. (Marine Engineering and Mechanical Handling) Syllabus Page 15 of 16
\
M.E.(MARINE ENGINEERING & MECHANICAL HANDLING) III SEMESTER
Dissertation ( to be continued in 4th semester)**
M.E.(MARINE ENGINEERING & MECHANICAL HANDLING) IV SEMESTER
Dissertation (continued from III semester)**
** Pre-examination appraisal thro’ Seminar by a committee consisting of BOS
Chairman, Head of the
Department and Guide.
** Final presentation followed by Viva-Voce Examination with the following members.
1. Chairman, Board of Studies.
2. Head of the Department.
3. External Examiner (External to the college)
4. Internal Guide
5. (And) External Guide ( if any)
The award of class will be given based on CGPA obtained in theory/practical/lab
and award a separate grading, such as, A,B,C and F for the thesis.(A= excellent;
B= Very good; C= good and F= not accepted.)
--------------------------------
M.E. (Marine Engineering and Mechanical Handling) Syllabus Page 16 of 16
\
Вам также может понравиться
- M.tech Civil (Structural) Engg 2ND Sem SyllabusДокумент17 страницM.tech Civil (Structural) Engg 2ND Sem Syllabushod civilОценок пока нет
- M.Tech. (Computer Aided Chemical Engineering) (Effective From The Admitted Batch of 2019-20)Документ35 страницM.Tech. (Computer Aided Chemical Engineering) (Effective From The Admitted Batch of 2019-20)Gowri ShankarОценок пока нет
- 591 - Syllabus (4th Sem) Mechanical Engg. Dept.Документ22 страницы591 - Syllabus (4th Sem) Mechanical Engg. Dept.Rushikesh WakodeОценок пока нет
- Syllabus - BE Mech III Wef 2013-14Документ39 страницSyllabus - BE Mech III Wef 2013-14lucasОценок пока нет
- M.Tech - CAD - CAM - Syllabus UpdatedДокумент47 страницM.Tech - CAD - CAM - Syllabus Updatedgaurav tripathiОценок пока нет
- 3rd SEMДокумент19 страниц3rd SEMAnjali BaghОценок пока нет
- Pec IiiДокумент6 страницPec Iii3111hruthvikОценок пока нет
- RTM Nagpur University Mechanical Engineering Machining Processes Syllabus (Theory) Course code-BEME401TДокумент27 страницRTM Nagpur University Mechanical Engineering Machining Processes Syllabus (Theory) Course code-BEME401TxaloliОценок пока нет
- M.tech Syllabus PDFДокумент51 страницаM.tech Syllabus PDFAnonymous MR8PLYОценок пока нет
- Savitribai Phule University Pune Structure and Syllabus of Be (Petroleum Engineering) (COURSE - 2012) W.E.F. 2015-2016Документ28 страницSavitribai Phule University Pune Structure and Syllabus of Be (Petroleum Engineering) (COURSE - 2012) W.E.F. 2015-2016Avishek PrasadОценок пока нет
- Petroleum EngineeringДокумент7 страницPetroleum EngineeringMohammed BahramОценок пока нет
- M - Tech - Mechanical Engineering (Design) - Course - STR - and - SyllabusДокумент23 страницыM - Tech - Mechanical Engineering (Design) - Course - STR - and - Syllabusrushimali777555Оценок пока нет
- B.E. NAME 2nd YearДокумент19 страницB.E. NAME 2nd YearShyamshesha GiriОценок пока нет
- Visvesvaraya Technological University, Belgaum: M.TECH. Machine Design I SemesterДокумент71 страницаVisvesvaraya Technological University, Belgaum: M.TECH. Machine Design I SemesterVasudeva BhattarОценок пока нет
- Revised Syllabus BE-civil First Sem-1....Документ26 страницRevised Syllabus BE-civil First Sem-1....baralganesh211Оценок пока нет
- B.E. NAME 2nd YearДокумент22 страницыB.E. NAME 2nd YearShyamshesha GiriОценок пока нет
- MMFM V Sem 2018-19 Course FileДокумент17 страницMMFM V Sem 2018-19 Course FileSrikanth RangdalОценок пока нет
- National University of Engineering College of Geological, Mining and Metallurgical Engineering Metallurgical Engineering ProgramДокумент3 страницыNational University of Engineering College of Geological, Mining and Metallurgical Engineering Metallurgical Engineering ProgramJhair JhamidhОценок пока нет
- ME 4th Sem Lesson Plans Even 2018 19Документ67 страницME 4th Sem Lesson Plans Even 2018 19kinganbruОценок пока нет
- 4th SemДокумент14 страниц4th SemManoj kumarОценок пока нет
- Sem VIДокумент46 страницSem VIRushi TutorОценок пока нет
- Mechatronics SyllabusДокумент41 страницаMechatronics SyllabusElstonD'cruzОценок пока нет
- Course Outline - DJJ2093 - Latest PDFДокумент1 страницаCourse Outline - DJJ2093 - Latest PDFThaneswaran BaluОценок пока нет
- AutomotiveДокумент39 страницAutomotiveyathin KLОценок пока нет
- ABAQUS For Petroleum Geomechanics BrochureДокумент3 страницыABAQUS For Petroleum Geomechanics BrochureUdhamОценок пока нет
- Code Semester/Year Pre-Requisite (S) Course Name Instructional Duration CreditДокумент2 страницыCode Semester/Year Pre-Requisite (S) Course Name Instructional Duration CreditThaneswaran BaluОценок пока нет
- 2.Pdf3rd DiplomaДокумент23 страницы2.Pdf3rd DiplomapinkyОценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент13 страницPDFSurajit SenapatiОценок пока нет
- Kerala University Mtech - Me - Ind Refrigeration 2013 SchemeДокумент59 страницKerala University Mtech - Me - Ind Refrigeration 2013 SchemerebyroyОценок пока нет
- (With Effect From 2016-2017 Admitted Batch Onwards) : Under Choice Based Credit SystemДокумент220 страниц(With Effect From 2016-2017 Admitted Batch Onwards) : Under Choice Based Credit SystemKïråñ MñskОценок пока нет
- Mechanical EngineeringДокумент23 страницыMechanical EngineeringAditya ShindeОценок пока нет
- ME3491 Course PlanДокумент9 страницME3491 Course Planmanoj1316kumar_63152Оценок пока нет
- 5 TH Semester of 3 Years Diploma in Mechanical Engineering: 36 HRS: 800Документ32 страницы5 TH Semester of 3 Years Diploma in Mechanical Engineering: 36 HRS: 800VK DОценок пока нет
- University of Mumbai: Scheme of Evaluation (R 2007)Документ30 страницUniversity of Mumbai: Scheme of Evaluation (R 2007)friends_isОценок пока нет
- DKOM Lab ManualДокумент24 страницыDKOM Lab Manualaakash chakrabortyОценок пока нет
- Syllabus - Mining Engineering - BE - III - Revised - 2013Документ12 страницSyllabus - Mining Engineering - BE - III - Revised - 2013virendra behraОценок пока нет
- MTech Machine Design PDFДокумент41 страницаMTech Machine Design PDFswapnilОценок пока нет
- Qualifying Exam Topic ListДокумент15 страницQualifying Exam Topic ListAnastasiya DobrovaОценок пока нет
- 18 MN216 Fluid Mechanics IДокумент2 страницы18 MN216 Fluid Mechanics Ijorge luisОценок пока нет
- 1Документ4 страницы1Niren PatelОценок пока нет
- Syllabus CurriculumДокумент27 страницSyllabus CurriculumChitraSKОценок пока нет
- INDUSTRIAL-ELECTX R PDFДокумент155 страницINDUSTRIAL-ELECTX R PDFAkash JaiswalОценок пока нет
- Second Year Chemical Engineering SyllabusДокумент26 страницSecond Year Chemical Engineering SyllabusSuchitra BandiОценок пока нет
- MA505-N-C Modern Manufacturing ProcessesДокумент3 страницыMA505-N-C Modern Manufacturing Processeshrana287Оценок пока нет
- 00 B.Tech IIДокумент22 страницы00 B.Tech IIkushalОценок пока нет
- M.tech - Manufacturing - and - Automation 2nd Year SllybusДокумент7 страницM.tech - Manufacturing - and - Automation 2nd Year SllybusShubham JangraОценок пока нет
- MACHINEDESIGNДокумент35 страницMACHINEDESIGNBrandon AllenОценок пока нет
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Machine Design & AnalysisДокумент23 страницыDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Machine Design & AnalysisKrishnarjun ParidaОценок пока нет
- Syllabus OuДокумент26 страницSyllabus OuTharun KumarОценок пока нет
- Aeronautical Engineering PDFДокумент147 страницAeronautical Engineering PDFcrazy gamingОценок пока нет
- JNTU Kakinada M.tech CAD-CAM SyllabusДокумент18 страницJNTU Kakinada M.tech CAD-CAM SyllabusTony AryanОценок пока нет
- Digital Electx 1Документ147 страницDigital Electx 1TwishaОценок пока нет
- ME4213Документ2 страницыME4213هاني زيادةОценок пока нет
- DOM Course FileДокумент14 страницDOM Course FileNdvs PrasadОценок пока нет
- Machine Design Revised NewДокумент52 страницыMachine Design Revised NewJenny John MattamОценок пока нет
- Scheme of Instruction & Examination B.E. V - Semester (Mechanical Engineering)Документ20 страницScheme of Instruction & Examination B.E. V - Semester (Mechanical Engineering)Mohammed ShoaebОценок пока нет
- Schaums Outline of Thermodynamics for Engineers, Fourth EditionОт EverandSchaums Outline of Thermodynamics for Engineers, Fourth EditionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Differential Quadrature and Differential Quadrature Based Element Methods: Theory and ApplicationsОт EverandDifferential Quadrature and Differential Quadrature Based Element Methods: Theory and ApplicationsОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Optical Waveguide Analysis: Solving Maxwell's Equation and the Schrödinger EquationОт EverandIntroduction to Optical Waveguide Analysis: Solving Maxwell's Equation and the Schrödinger EquationОценок пока нет
- Lec 11Документ24 страницыLec 11David VictorОценок пока нет
- JNTUACEA UG 1 Hostel Admission Info AY 2019 20Документ4 страницыJNTUACEA UG 1 Hostel Admission Info AY 2019 20David VictorОценок пока нет
- CompositesДокумент39 страницCompositesArif Othman100% (1)
- I B Tech Instructions Feedetails 2019 20Документ2 страницыI B Tech Instructions Feedetails 2019 20David VictorОценок пока нет
- New Doc 2019-01-03Документ3 страницыNew Doc 2019-01-03David VictorОценок пока нет
- CompositesДокумент29 страницCompositesDavid VictorОценок пока нет
- CamДокумент6 страницCamDavid VictorОценок пока нет
- Nanocrystalline Materials - Current Research and Future DirectionsДокумент40 страницNanocrystalline Materials - Current Research and Future DirectionsAttila Daniel VargaОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1Документ3 страницыAssignment 1David VictorОценок пока нет
- Post ProcessorДокумент2 страницыPost ProcessorDavid VictorОценок пока нет
- MEM201 L6-Tolerance RCДокумент31 страницаMEM201 L6-Tolerance RCKaliya PerumalОценок пока нет
- Capp in CamДокумент5 страницCapp in CamDavid VictorОценок пока нет
- Unit 5 57 PDFДокумент9 страницUnit 5 57 PDFSurendra SainiОценок пока нет
- Intermetallics ApplicationsДокумент9 страницIntermetallics ApplicationsDavid VictorОценок пока нет
- 1st Sessional Paper SolutionДокумент13 страниц1st Sessional Paper SolutionDavid VictorОценок пока нет
- Concresive 1438 PDFДокумент2 страницыConcresive 1438 PDFanon_770460118Оценок пока нет
- Fema 440Документ14 страницFema 440hauracoОценок пока нет
- Adhesion Testing CoatingsДокумент7 страницAdhesion Testing CoatingsBalaji GuruОценок пока нет
- 07 Chapter 2Документ103 страницы07 Chapter 2Mukesh Manwani100% (1)
- Assignment 2 - 2023 - SolutionsДокумент23 страницыAssignment 2 - 2023 - SolutionsLinhan ChuОценок пока нет
- Oil Tempered (OTMB) Spring SpecsДокумент1 страницаOil Tempered (OTMB) Spring SpecsCarlos Ediver Arias RestrepoОценок пока нет
- Design of Concrete Masonry Walls For Blast LoadingДокумент9 страницDesign of Concrete Masonry Walls For Blast Loadingfostbarr100% (1)
- ..Final Mec03 Deformable of Rigid Bodies Learning Guide - FinalsДокумент76 страниц..Final Mec03 Deformable of Rigid Bodies Learning Guide - FinalsMendoza Jayzel VizarraОценок пока нет
- 101 Mechanical Engineering Interview QuestionsДокумент16 страниц101 Mechanical Engineering Interview Questionsamr yosry100% (2)
- Asme Section II A Sa-302 Sa-302mДокумент4 страницыAsme Section II A Sa-302 Sa-302mAnonymous GhPzn1xОценок пока нет
- HW 5 Pro 4Документ9 страницHW 5 Pro 4ybobbyxОценок пока нет
- Istruct 2019 Bamboo PDFДокумент17 страницIstruct 2019 Bamboo PDFNiamul IslamОценок пока нет
- Fea ReportДокумент18 страницFea ReportmanticoreIIОценок пока нет
- Api 570 Piping Code Part 2Документ34 страницыApi 570 Piping Code Part 2Ike100% (1)
- Packaged Plant Prefab Tank SPAN 1401 A1 Publication 2013 (Part1)Документ48 страницPackaged Plant Prefab Tank SPAN 1401 A1 Publication 2013 (Part1)gkjimОценок пока нет
- Paper Shredder MachineДокумент16 страницPaper Shredder MachineEphraim MekonnenОценок пока нет
- ASTM A36 MildLow Carbon SteelДокумент3 страницыASTM A36 MildLow Carbon SteelAndrés MaiguaОценок пока нет
- Bolts (Al Rashed Fastners) PDFДокумент71 страницаBolts (Al Rashed Fastners) PDFAbuОценок пока нет
- HDG High Performance Steels Weldments Doug RourkeДокумент28 страницHDG High Performance Steels Weldments Doug Rourkemàrio ferreiraОценок пока нет
- Design Guide For Structural Hollow Section ConnectionsДокумент213 страницDesign Guide For Structural Hollow Section ConnectionsAnonymous 8f2veZf83% (6)
- Composites Testing MechineДокумент32 страницыComposites Testing MechineRahmawati FitrianingtyasОценок пока нет
- ASTM A193 Bolting Materials For High Temperature ServiceДокумент14 страницASTM A193 Bolting Materials For High Temperature ServiceSilmina AdzhaniОценок пока нет
- Makrolon® ET3137: Grades / ExtrusionДокумент4 страницыMakrolon® ET3137: Grades / ExtrusionDiegoTierradentroОценок пока нет
- AssignДокумент4 страницыAssignnicoleОценок пока нет
- ASTM Volume 15.06, August 2019 Adhesives: Standard Number TitleДокумент4 страницыASTM Volume 15.06, August 2019 Adhesives: Standard Number Titleارفع راسك فوق انت يمنيОценок пока нет
- Dba Manual Eur19030en PDFДокумент564 страницыDba Manual Eur19030en PDFBib GmzОценок пока нет
- Structural ShapesДокумент48 страницStructural ShapesTimbo6808Оценок пока нет
- Calculation Methods Cracked Concrete: 8. 8.1 Girder StiffnessДокумент13 страницCalculation Methods Cracked Concrete: 8. 8.1 Girder Stiffnessw1000000Оценок пока нет
- Helicoil Tangfree en 0150Документ28 страницHelicoil Tangfree en 0150NicolasSuchОценок пока нет
- Rapid Microwave Sintering of Carbon Nanotube-Filled AZ61Документ8 страницRapid Microwave Sintering of Carbon Nanotube-Filled AZ61vitorassuenaОценок пока нет