Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Viruses Notebook
Загружено:
osamaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Viruses Notebook
Загружено:
osamaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Name Date
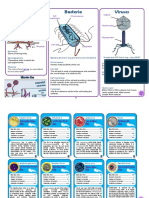
Bacteria and Viruses
Section 2 Viruses and Prions
Main Idea Details
Scan the table and time line in Section 2 of the chapter. Write three
facts you discovered about viruses from these elements.
1.
2.
3.
Review
Vocabulary Use your book or dictionary to define protein.
protein
New
Vocabulary Use the new vocabulary terms in the left column to complete the
following paragraph.
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
capsid A is genetic material within a protein coat, but
it has no organelles or other characteristics of life. The genetic
lysogenic cycle material lies inside its , or outer layer of protein. In
the , viral genes instruct the host cell to make
lytic cycle
many copies of the viral RNA or DNA. Some viruses replicate in a
, in which the viral DNA integrates into a host
prion
chromosome and lies dormant for some time. A ,
retrovirus such as the HIV virus, contains RNA instead of DNA. Mutation in
the genes of a normal protein called a is responsible
virus for diseases such as “mad cow.”
Academic
Vocabulary Define widespread to show its scientific meaning.
widespread
Bacteria and Viruses 183
Name Date
Section 2 Viruses and Prions (continued)
Main Idea Details
Viruses Model of one type of virus. Label its parts.
I found this information
on page .
Viral Infection Synthesize why many viruses cannot pass from one species to
I found this information another.
on page .
Label steps A, B, C, D, and E of a lytic cycle in the figure below.
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Use the following terms.
• Assembly • Attachment • Entry
• Lysis and Release • Replication
Bacteriophage
Bacterial DNA
Nucleic
acid
Bacterial
host cell
A B
The bacteriophage
injects its nucleic acid
into the bacterial cell.
E
The host cell breaks open and
releases new virus particles.
C
D The host’s
metabolic
New virus machinery makes
particles are viral nucleic acid
assembled. and proteins.
184 Bacteria and Viruses
Name Date
Section 2 Viruses and Prions (continued)
Main Idea Details
Sequence the steps of a lysogenic cycle.
Viral DNA integrates into a chromosome of a host cell.
Retroviruses Evaluate and discuss the role of reverse transcriptase in the
I found this information replication cycle of HIV.
on page .
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Prions Summarize information about prions by completing the table.
I found this information What is a prion? What causes a prion to become
on page . harmful?
How might humans contract a What is the result of prion
prion-caused disease? infection?
S UMM ARIZE Conclude whether viruses that replicate by the lytic cycle or
the lysogenic cycle are more dangerous. Explain your reasoning.
Bacteria and Viruses 185
Name Date
Tie It Together
Create a quiz to help you review key topics in this
S YNTHESIZE
chapter. Write one question with its answer for each major topic listed below.
Topic: Diversity of Prokaryotes Topic: Metabolism of Prokaryotes
Question: Question:
Answer: Answer:
Topic: Prokaryote Structure Topic: Ecology of Bacteria
Question: Question:
Answer: Answer:
Topic: Identifying Prokaryotes Topic: Viruses
Question: Question:
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Answer: Answer:
Topic: Reproduction of Prokaryotes Topic: Retroviruses
Question: Question:
Answer: Answer:
Topic: Survival of Bacteria Topic: Prions
Question: Question:
Answer: Answer:
186 Bacteria and Viruses
Вам также может понравиться
- Glencoe Life Science2Документ93 страницыGlencoe Life Science2Cosmina MariaОценок пока нет
- Virus Ly Tic Cycles eДокумент5 страницVirus Ly Tic Cycles eElleОценок пока нет
- Classification Notes WorksheetДокумент5 страницClassification Notes WorksheetsenjicsОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 CK-12 Biology Chapter 2 Worksheets PDFДокумент23 страницыChapter 2 CK-12 Biology Chapter 2 Worksheets PDFIlincaVasilescuОценок пока нет
- Human Reproduction Question BankДокумент23 страницыHuman Reproduction Question Bankkaustubhchoudhary2005Оценок пока нет
- IB Biology Topic 1 Notes SummaryДокумент9 страницIB Biology Topic 1 Notes SummaryKJannat Mahmood owaitanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11 - ExcretionДокумент46 страницChapter 11 - Excretionapi-372850875% (4)
- Human Reproduction - "Darts" Answer Sheet: Female Reproductive SystemДокумент3 страницыHuman Reproduction - "Darts" Answer Sheet: Female Reproductive SystemmawitterОценок пока нет
- Test 1 Chapter 5: Cell Division Sub Topic: Mitosis: BPK/Biology Item /Method1-Analogy & Role Play1/MitosisДокумент3 страницыTest 1 Chapter 5: Cell Division Sub Topic: Mitosis: BPK/Biology Item /Method1-Analogy & Role Play1/MitosisYan MLОценок пока нет
- 3.5.4 VirusesДокумент9 страниц3.5.4 VirusesFrankie KavanaghОценок пока нет
- Prokaryotic Cells: Cell Membrane Cell Wall Capsule Pili Plasmid Flagella Nucleoid Region Ribosomes CytoplasmДокумент3 страницыProkaryotic Cells: Cell Membrane Cell Wall Capsule Pili Plasmid Flagella Nucleoid Region Ribosomes CytoplasmErvin WilliamsОценок пока нет
- Biology Ch. 23Документ80 страницBiology Ch. 23Juliet HipolitoОценок пока нет
- Cell Anatomy WorksheetДокумент1 страницаCell Anatomy WorksheetJayson LumagasОценок пока нет
- WORKSHEET 5.10 Cell & Mitosis Crossword PuzzleДокумент4 страницыWORKSHEET 5.10 Cell & Mitosis Crossword PuzzleNurul Huda IsaОценок пока нет
- Biology Revision - Cell StructureДокумент21 страницаBiology Revision - Cell StructureTosis MajidОценок пока нет
- 06 - IB Biology 2023 New Syllabus A2.2 Cell Structure PowerPoint (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Документ76 страниц06 - IB Biology 2023 New Syllabus A2.2 Cell Structure PowerPoint (Autosaved) (Autosaved)mike bevnОценок пока нет
- 2 Compressed Notes EcologyДокумент15 страниц2 Compressed Notes EcologyLIM ZHI SHUENОценок пока нет
- Coordination and Response in OrganismsДокумент11 страницCoordination and Response in OrganismsDrRemyaranjith Menon100% (1)
- Biology WorkbookДокумент20 страницBiology WorkbookSaleem MominОценок пока нет
- Biology - Digestion and Absorption Revision Notes PDFДокумент24 страницыBiology - Digestion and Absorption Revision Notes PDFanna robertsonОценок пока нет
- AP Biology - Worksheet - Pedigrees 2 PDFДокумент3 страницыAP Biology - Worksheet - Pedigrees 2 PDFVictoria LowmanОценок пока нет
- Thecirculatorysystem 130618021608 Phpapp01Документ70 страницThecirculatorysystem 130618021608 Phpapp01Mikel VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- Physics 2 - Speed, Velocity and AccelerationДокумент75 страницPhysics 2 - Speed, Velocity and AccelerationMicheal Xavier100% (1)
- CH 12 Study GuideДокумент4 страницыCH 12 Study Guideapi-342334216100% (1)
- Unit 2 Chemistry of Life Review PacketДокумент7 страницUnit 2 Chemistry of Life Review PacketShannon ErdmanОценок пока нет
- Fungi 2Документ11 страницFungi 2Nur QistinaОценок пока нет
- CH 11.4 MeiosisДокумент9 страницCH 11.4 MeiosisKelsey Koehler0% (1)
- New World International School Biology Igcse Notes Chapter - 1Документ15 страницNew World International School Biology Igcse Notes Chapter - 1Noor Samir100% (1)
- Al Rowad International School, Riyadh: Biology IGCSE CambridgeДокумент154 страницыAl Rowad International School, Riyadh: Biology IGCSE CambridgeNicayne RamnarineОценок пока нет
- Disease and Immunity - IGCSE NotesДокумент20 страницDisease and Immunity - IGCSE Notesjanani sellapandianОценок пока нет
- Energy changes in reactionsДокумент2 страницыEnergy changes in reactionsSamandarbek Numonov100% (1)
- Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis Biology LectureДокумент39 страницCell Division Mitosis Meiosis Biology LectureYonathan ChristyantoОценок пока нет
- Virus, Viroids and PrionsДокумент29 страницVirus, Viroids and PrionscatherinejoaquinОценок пока нет
- Cell CycleДокумент3 страницыCell Cycleapi-502781581Оценок пока нет
- Atlas Biology Genetics Evolution s1Документ11 страницAtlas Biology Genetics Evolution s1Tan Jha100% (1)
- Cell Division WorksheetДокумент2 страницыCell Division WorksheetFabian Gutierrez CarbonellОценок пока нет
- Biotechnology & Genetic Engineering 2 QPДокумент8 страницBiotechnology & Genetic Engineering 2 QPAzween SabtuОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 - EnzymesДокумент5 страницUnit 3 - EnzymesWaseem AhmedОценок пока нет
- Viruses and Bacteria WorksheetДокумент2 страницыViruses and Bacteria Worksheetlavievan99100% (1)
- Igcse BiologyДокумент39 страницIgcse BiologylordeОценок пока нет
- Biology NIOSДокумент927 страницBiology NIOSApshar RizwanОценок пока нет
- Class: Name: ( ) Date: Reproduction in flowering plantsДокумент11 страницClass: Name: ( ) Date: Reproduction in flowering plantsada lumОценок пока нет
- Osmosis Worksheet SolutionsДокумент2 страницыOsmosis Worksheet SolutionsRhynnieОценок пока нет
- Activity Sheet 1 Bacteria Take OverДокумент6 страницActivity Sheet 1 Bacteria Take OverAmor Reyes EngОценок пока нет
- Worksheet Ib HL - Chapter A2.1& 2.2Документ12 страницWorksheet Ib HL - Chapter A2.1& 2.2elizabethОценок пока нет
- (My Revision Notes) King, Rob - AQA AS - A-Level Chemistry-Hodder Education Group (2015)Документ107 страниц(My Revision Notes) King, Rob - AQA AS - A-Level Chemistry-Hodder Education Group (2015)successhustlerclubОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Biology Section 5 Lesson 1Документ92 страницыIGCSE Biology Section 5 Lesson 1salmaОценок пока нет
- b1 Cell Structure and Transport Exam QuestionsДокумент38 страницb1 Cell Structure and Transport Exam QuestionsVotu Kulu100% (1)
- Enzymes QuestionsДокумент21 страницаEnzymes QuestionsJordan WanОценок пока нет
- Topic 16 Inherited Change 2021-22 A Level Biology 9700 Notes by Mr. ADEEL AHMADДокумент23 страницыTopic 16 Inherited Change 2021-22 A Level Biology 9700 Notes by Mr. ADEEL AHMADADEEL AHMAD100% (1)
- 35 - 2 Worksheet - StudentДокумент2 страницы35 - 2 Worksheet - StudentAlmeida100% (1)
- Teaching Background Year 3Документ6 страницTeaching Background Year 3api-316789542Оценок пока нет
- CH 5 Study GuideДокумент8 страницCH 5 Study Guidetrung tranОценок пока нет
- Cell Biology Worksheet Blank4Документ10 страницCell Biology Worksheet Blank4Loveena SteadmanОценок пока нет
- 3 Enzymes Paper 2 - N-MQДокумент67 страниц3 Enzymes Paper 2 - N-MQMostafa AmerОценок пока нет
- Cell Structure QuizДокумент2 страницыCell Structure QuizshavindriОценок пока нет
- Phy Solved Paper 1 PDFДокумент16 страницPhy Solved Paper 1 PDFSaira ZiaОценок пока нет
- CIE IGCSE Biology Key NotesДокумент20 страницCIE IGCSE Biology Key NotesMuhammad Hader AzizОценок пока нет
- Bacteria WorksheetДокумент4 страницыBacteria WorksheetosamaОценок пока нет
- Bacteria Fungi Viruses: Chromosome Cell Membrane CapsidДокумент4 страницыBacteria Fungi Viruses: Chromosome Cell Membrane CapsidDemiana MagdyОценок пока нет
- Forms of Energy - Print - QuizizzДокумент6 страницForms of Energy - Print - Quizizzosama100% (1)
- Read To LearnДокумент5 страницRead To LearnosamaОценок пока нет
- Analyzing The PedigreeДокумент1 страницаAnalyzing The PedigreeosamaОценок пока нет
- Lesson 3 - Moving Cellular Material: Student Labs and Activities Appropriate ForДокумент20 страницLesson 3 - Moving Cellular Material: Student Labs and Activities Appropriate ForosamaОценок пока нет
- Writing A Lab ReportДокумент26 страницWriting A Lab ReportosamaОценок пока нет
- Respiratory QuizДокумент5 страницRespiratory QuizosamaОценок пока нет
- Standardized Test Practice Answers and Correlation Tables: Chapter 33: Nervous SystemДокумент1 страницаStandardized Test Practice Answers and Correlation Tables: Chapter 33: Nervous SystemosamaОценок пока нет
- Practice ProblemsДокумент1 страницаPractice ProblemsosamaОценок пока нет
- Cell Theory and Types of Microscopes - Print - QuizizzДокумент4 страницыCell Theory and Types of Microscopes - Print - QuizizzosamaОценок пока нет
- Kinetic Energy Worksheet: The Energy Due To MotionДокумент1 страницаKinetic Energy Worksheet: The Energy Due To MotionosamaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Energy Review - Print - QuizizzДокумент5 страницChapter 5 Energy Review - Print - QuizizzosamaОценок пока нет
- Cell Transport & Homeostasis - Print - QuizizzДокумент3 страницыCell Transport & Homeostasis - Print - Quizizzosama100% (1)
- Chapter 5 - Energy Notes - CompleteДокумент22 страницыChapter 5 - Energy Notes - CompleteosamaОценок пока нет
- Calculating Acceleration - Print - QuizizzДокумент6 страницCalculating Acceleration - Print - QuizizzosamaОценок пока нет
- The Heart - Print - QuizizzДокумент5 страницThe Heart - Print - Quizizzosama100% (1)
- Respiratory System - Print - QuizizzДокумент5 страницRespiratory System - Print - QuizizzosamaОценок пока нет
- Concept Mapping Circulatory Respiratory and Excretory Systems EditableДокумент2 страницыConcept Mapping Circulatory Respiratory and Excretory Systems EditableosamaОценок пока нет
- Study Guide: Section 2: The Respiratory SystemДокумент3 страницыStudy Guide: Section 2: The Respiratory SystemosamaОценок пока нет
- Section Quick Check Organization of The Nervous System EditableДокумент2 страницыSection Quick Check Organization of The Nervous System EditableosamaОценок пока нет
- Study Guide: Section 3: The SensesДокумент3 страницыStudy Guide: Section 3: The SensesosamaОценок пока нет
- Balancing Equations 10Документ4 страницыBalancing Equations 10Ignacio Jr. PaguyoОценок пока нет
- Microscope Labeling Worksheet: Focus, Objectives, Parts & MagnificationДокумент1 страницаMicroscope Labeling Worksheet: Focus, Objectives, Parts & MagnificationosamaОценок пока нет
- Cell Structure and Function The Cel PDFДокумент6 страницCell Structure and Function The Cel PDFEric VerunacОценок пока нет
- Excretory System - Print - QuizizzДокумент4 страницыExcretory System - Print - Quizizzosama0% (1)
- Classifying Organisms Lesson Explains Kingdoms, Domains, and Scientific NamesДокумент33 страницыClassifying Organisms Lesson Explains Kingdoms, Domains, and Scientific NamesosamaОценок пока нет
- Circulatory System Study GuideДокумент4 страницыCirculatory System Study GuideosamaОценок пока нет
- Research SampleДокумент11 страницResearch SampleosamaОценок пока нет
- Week 5 Research Skills and CitationДокумент7 страницWeek 5 Research Skills and CitationosamaОценок пока нет
- Ch34-L1 Reading EssentialДокумент6 страницCh34-L1 Reading EssentialosamaОценок пока нет
- Study Guide: Section 2: The Respiratory SystemДокумент3 страницыStudy Guide: Section 2: The Respiratory SystemosamaОценок пока нет
- Outline - Script Lesson Plan For Bacteria - Field IДокумент3 страницыOutline - Script Lesson Plan For Bacteria - Field Iapi-328213101Оценок пока нет
- Biological Classification 1Документ3 страницыBiological Classification 1Dr. D. kumar Harshit -apexОценок пока нет
- Bacteriology S23 WorksheetДокумент6 страницBacteriology S23 WorksheetblahОценок пока нет
- 1582-Article Text-10280-1-10-20220121Документ6 страниц1582-Article Text-10280-1-10-20220121Nayla Al FarisaОценок пока нет
- Corynebacterium Diphtheriae Pathogenic BacteriaДокумент3 страницыCorynebacterium Diphtheriae Pathogenic BacteriaknedhОценок пока нет
- Simple and Gram StainingДокумент4 страницыSimple and Gram Stainingqueenbullex100% (3)
- Staph aureus diseases mnemonic SOF2T PAINSДокумент10 страницStaph aureus diseases mnemonic SOF2T PAINSIan Leo SantosОценок пока нет
- WBI14 01 Que 20211016Документ36 страницWBI14 01 Que 20211016Farah AwadОценок пока нет
- Microbio ReviewerДокумент4 страницыMicrobio ReviewerfilchibuffОценок пока нет
- Medical Technology Assessment Program I: (Trans) : Bacterial Morphology and CytologyДокумент3 страницыMedical Technology Assessment Program I: (Trans) : Bacterial Morphology and CytologyLaiza JanelleОценок пока нет
- Bacteriophage Lambda-also known as The Genetic Switch of Bacteriophage Lambda (λ)Документ4 страницыBacteriophage Lambda-also known as The Genetic Switch of Bacteriophage Lambda (λ)Jeyser T. GamutiaОценок пока нет
- Vitek 2 Cards - 9315765 002 GB GДокумент6 страницVitek 2 Cards - 9315765 002 GB GAli M. RiyathОценок пока нет
- Treponema Pallidum: MicrobiologyДокумент5 страницTreponema Pallidum: MicrobiologyZeth MoturiОценок пока нет
- Mycology NotesДокумент3 страницыMycology NotesVincent MarfinОценок пока нет
- Daftar Pustaka JurnalДокумент2 страницыDaftar Pustaka JurnalsuciaprianaОценок пока нет
- Fermentos para Yogurt Marca VIVOLACДокумент3 страницыFermentos para Yogurt Marca VIVOLACManuel HernandezОценок пока нет
- Thermal Death Points and Microbial Control MethodsДокумент18 страницThermal Death Points and Microbial Control MethodsClaudia Keith McBroom43% (7)
- Lab Report 5 MicrobiologyДокумент8 страницLab Report 5 Microbiologyapi-384857069100% (1)
- General MicrobiologyДокумент68 страницGeneral MicrobiologySupriya SharmaОценок пока нет
- Viral ChartsДокумент2 страницыViral ChartsPlay ListОценок пока нет
- Tabel RBK Bakteri Escherichia ColiДокумент5 страницTabel RBK Bakteri Escherichia ColiItis MayantiОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1 Introduction To Bacteriology History Taxonomy and Bacterial Structure ModuleДокумент16 страницLesson 1 Introduction To Bacteriology History Taxonomy and Bacterial Structure ModuleTinОценок пока нет
- BBL Coagulase Plasmas: Marcescens, Enterococcus Faecalis and Strains of Streptococcus Will Clot Citrated PlasmaДокумент16 страницBBL Coagulase Plasmas: Marcescens, Enterococcus Faecalis and Strains of Streptococcus Will Clot Citrated Plasmaseb2008Оценок пока нет
- Analisis Cemaran Coliform Dan Identifikasi Escherichia Coli Dari Depo Air Minum Isi Ulang Di Kota SemarangДокумент10 страницAnalisis Cemaran Coliform Dan Identifikasi Escherichia Coli Dari Depo Air Minum Isi Ulang Di Kota SemarangBarikahidayah barikahidayahОценок пока нет
- Introduction of MicrobiologyДокумент9 страницIntroduction of MicrobiologyRahul PalsОценок пока нет
- Ninth Class Biology MCQs (Virus, Bacteria and Cyanobacteria)Документ6 страницNinth Class Biology MCQs (Virus, Bacteria and Cyanobacteria)Dr. Sajid Ali Talpur100% (3)
- Medical Mycology: DR C. O. Morton Prof. T. R. Rogers Dept of Clinical MicrobiologyДокумент40 страницMedical Mycology: DR C. O. Morton Prof. T. R. Rogers Dept of Clinical MicrobiologyKhusnul AssidikОценок пока нет
- Kingdom Monera ReadingДокумент3 страницыKingdom Monera ReadingAbirami santhanamОценок пока нет
- MicrobiologyДокумент20 страницMicrobiologySarah JaneОценок пока нет
- Plant Virus Replication and StructureДокумент24 страницыPlant Virus Replication and StructureAdarsh AdiОценок пока нет