Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Enzyme Deficiencies Chart
Загружено:
Meera Patel0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
14 просмотров2 страницыEnzyme Deficiency Chart
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документEnzyme Deficiency Chart
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
14 просмотров2 страницыEnzyme Deficiencies Chart
Загружено:
Meera PatelEnzyme Deficiency Chart
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
Enzyme Deficiencies Chart
Red=distinguishing (though not inclusive of all key) features
Enzyme Pathway it is Presentation of pt/description of scenario Any important associations/tx/notes
part of
Glucose 6- Glycogenolysis Von Gierkes Type 1 GSD. Hepatomegaly, hepatic Expressed only in liver and kidney, so does not affect
phosphatase steatosis, fasting hypoglycemia, lactic acidosis, muscles—no hypotonia, etc.
hyperuricemia, hyperlipidemia
Acid α- Glycogenolysis Pompe Type 2 GSD. Normal glucose. Severe Is a lysosomal E that breaks down small amts of
glucosidase//Aci cardiomegaly. Profound hypotonia. Macroglossia. glycogen that end up in lysosomes (most is degraded in
d Maltase Glycogen accum in lysosomes on mm biopsy cytosol) in cells with high glycogen like mm and liver.
(visualized with EM). Often presents in early infancy— Has 1,4 and 1,6 glucosidase activity (i.e. like
weak suckling, weak holding up of head in feeding, debranching E). normal glucose bc does not affect the
FTT. liver primarily, though does along with mm.
See cardiomegaly bc cardiac myocytes and skel mm are
esp susceptible to ballooning glycogen-filled lysosomes
compressing and inhibiting contractile units
Acyl-CoA Fatty acid B- Sx apparent after intense fasting only (induces state of Presentation is same for deficiency of any type of acyl-
dehydrogenase oxidation catabolism requiring FAO); pt with hypoketotic CoA dehydrogenase involved in FAO. Carnitine
hypoglycemia (=low ketones in blood bc cant be deficiency looks similar bc prevents FA entry in mito for
produced through FAO, and low gluc) —lethargy, V, B-O.
hepatomegaly, low gluc, 0 acetoacetate, inc AST ALT
Protein Glycogenesis Activates glycogen synthase by dephosphorylation and Conversely, glycogen synthase inhibited by protein
phosphatase inhibits glycogen phosphorylase, so promotes kinase A (PKA—activated by glucagon; activates
glucoseglycogen. Protein phosphatase is activated glycogen phosphorylase via GP kinase)
by PI3K pathway stimulated upon insulin binding to
TKR.
Debranching Glycogenolysis Cori Type 3 GSD. Multibranched polysaccharides Short branches indicates that glycogen phosphorylase is
enzyme (glycogen molecs) with abnormally short outer fning and thus able to remove G-1-P residues from
chains(=limit dextrins) found in hepatocyte cytosol. branches until 4 units remain, but then debranching
hepatomegaly, hypotonia, low ht and wt despite food enzymes are deficient and cannot remove remaining
intake, labs with ketotic hypoglycemia (i.e. not the FAO units. Hypotonia also helps distinguish from other GSD
deficiency kind), hepatic fibrosis on biopsy. i.e. Von Gierke
Glycogen Glycogenolysis McArdles Type 5 GSD if lose muscle GP. Weakness, Normal glycogen structures with normal length
phosphorylase fatigue, pain, cramps w/ exercise/mm use (dec branches seen in cells bc are missing first step enzyme,
exercise tolerance). Myoglobinuria. No inc in lactate rather than later debranching enzymes or other Es, so
after exercise. Excess of normally structured glycogen no cant get any change in glycogen branch length or
on mm biopsy (not short limit dextrins like Cori). structure. GP activated when PKA activates GP kinase
Hers Type X GSD if lose hepatic GP. Mild hypoglycemia, activation upon glucagon stim of Gs-AC pathway.
ketosis, hepatomegaly. Excess of normally structured GlucagonGs-ACPKAGPKGP activation.
glycogen in hepatocytes on biopsy. No mm sx.
Pyruvate TCA Lactic acidosis. Neuro deficits. Developmental delays, PDH links glycolysis to TCA by taking pyruvate from
Dehydrogenase failure to thrive, episodic seizures. glycolysis and making A-CoA that can be used in TCA.
Inherited inborn error of metabolism. Diet—high fat low carb moderate protein IOT force
ketone body prod from fat and AA metab and dec
glucose content so no pyruvate is prod so no lactate is
prod. Can supplement diet with lysine or leucine=the
only exclusively ketogenic AAs that are metab to the
ketone body precursor A-Coa and cannot be metab to
pyruvate, so cannot be shunted into LA pathway, thus
doesn’t further inc serum lactate which is good, unlike
glucogenic AAs which are metab to prod pyruvate or
other TCA intermediates that can be converted to
glucose by gluconeogenesis, which would then result in
inc serum lactate bc the pyruvate generated from the
glucose via glycolysis cannot go into TCA bc of PDH
deficiency, so gets shunted to LA pathway.
Pyruvate Kinase Glycolysis Chronic hemolytic anemia Converts PEP to pyruvate for subsequent TCA.
Hemolysis bc RBCs use glycolysis aerobic respiration as
main energy source.
Glycogen Glycogenolysis Activates glycogen phosphorylase, so Stim by PKA, Ca-CAM, Ca.
phosphorylase glycogenglucose.
kinase
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Gupta-Program PDF Retrain-Your-BrainДокумент46 страницGupta-Program PDF Retrain-Your-BrainAle iОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular Blood VesselsДокумент12 страницCardiovascular Blood VesselswatuwaitingforОценок пока нет
- Automated Counters3Документ14 страницAutomated Counters3Jacky SharmaОценок пока нет
- 19 HPND Blood Gas ValuesДокумент1 страница19 HPND Blood Gas ValuesSara OchoaОценок пока нет
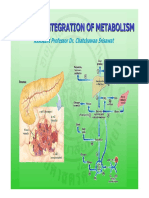
- Integration of Metabolism WebДокумент72 страницыIntegration of Metabolism WebLini Anisfatus SholihahОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Psychology: States of ConsciousnessДокумент27 страницIntroduction To Psychology: States of ConsciousnessCharlie Ken Cruz-GrazaОценок пока нет
- Case Report Uterine InversionДокумент64 страницыCase Report Uterine InversionFelicia Yumita Winata100% (1)
- Laboratory Result Proteolytic EnzymeДокумент2 страницыLaboratory Result Proteolytic EnzymeWinter SnowОценок пока нет
- Bio ACE Form 4Документ3 страницыBio ACE Form 4Myramel KlarisОценок пока нет
- UsmleДокумент3 страницыUsmleuwandfaОценок пока нет
- Thinking Like A Plant - HoldregeДокумент4 страницыThinking Like A Plant - HoldregeMartin BungeОценок пока нет
- 1.bioacoustics 2021 01 18Документ81 страница1.bioacoustics 2021 01 18krueg3rОценок пока нет
- Conditions That Cause Interference On Most Hematology AnalyzersДокумент2 страницыConditions That Cause Interference On Most Hematology AnalyzersSamantha IsabelОценок пока нет
- NCM 116 - Nursing Care of Patients With Neurologic DysfunctionДокумент11 страницNCM 116 - Nursing Care of Patients With Neurologic DysfunctionRigel Kent C. TobiasОценок пока нет
- PathophysiologyДокумент9 страницPathophysiologypaul andrew laranjo asuncionОценок пока нет
- Physical Education Skeletal SystemДокумент35 страницPhysical Education Skeletal SystemScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosОценок пока нет
- Red Flags For The MRCGPДокумент3 страницыRed Flags For The MRCGPUsm LeeОценок пока нет
- Plant and Animal Cell WorksheetДокумент3 страницыPlant and Animal Cell WorksheetCorey ColeОценок пока нет
- Liver Cleanse Thesis PDFДокумент123 страницыLiver Cleanse Thesis PDFjuliusghica100% (1)
- Bu LesДокумент91 страницаBu LesAnonymous zQ72D9cPrCОценок пока нет
- Introduction To The Body As A WholeДокумент29 страницIntroduction To The Body As A Wholekhizer hayatОценок пока нет
- Handout Orthopedic Nursing Assisstive DevicesДокумент14 страницHandout Orthopedic Nursing Assisstive DevicesPaul Christian P. Santos, RN100% (2)
- Non-Specific Epithelial Tumors (Organo-Nonspecific) - Benign and Malignant Tumors of Soft Tissues. - 0Документ104 страницыNon-Specific Epithelial Tumors (Organo-Nonspecific) - Benign and Malignant Tumors of Soft Tissues. - 0Mișulică CerlatОценок пока нет
- Different Kinds of Fish According To Their Dwelling PlacesДокумент6 страницDifferent Kinds of Fish According To Their Dwelling Placesroselle jane pasquinОценок пока нет
- Amino AcidsДокумент18 страницAmino AcidsShreesh MohanОценок пока нет
- Features of The Muscular SystemДокумент34 страницыFeatures of The Muscular SystemQuỳnh NhưОценок пока нет
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/13Документ16 страницCambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/13Eain ThuОценок пока нет
- Puberphonia 11Документ19 страницPuberphonia 11jaguar1979100% (2)
- Silva Meditation 5 Fall Asleep - Alarm - Stay AwakeДокумент4 страницыSilva Meditation 5 Fall Asleep - Alarm - Stay AwakeMichiel PaulusОценок пока нет
- RL Vs NaclДокумент12 страницRL Vs NaclTri MaryantiОценок пока нет