Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Doing Steam Table Problems
Загружено:
jimhale777Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Doing Steam Table Problems
Загружено:
jimhale777Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Guide to Using the Two Phase Property Tables
D. Abata, W. Krause
1. Look up the properties you have available (two properties identify the state) on the saturated table. In most cases the saturated table is
arranged with p as an independent variable and as T as an independent variable, i.e., there are often times two saturated tables for a pure
substance.
2. Determine if the state lies in the compressed liquid region, the mixture region, or the superheated region.
3. Go to the appropriate table to determine the dependent properties. Hint: If quality, x, is one of the independent variables, then it is
obviously a mixture.
4. Remember x = (a - av)/(ag - av), a = av + x(ag - av) where a is a thermodynamic property other than T or p.
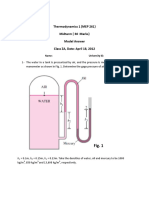
Complete the following table for water as the pure substance.
T p x v U H s phase
1 100 C 50 kPa
2 100 C 101 kPa 0.5
3 120 C 100 kPa
4 250 kPa 0.7
5 200 kPa 0.75 m3/kg
6 200 C 2000 kJ/kg
7 50 C 100 kPa
8 200 C 2.17 m3/kg
9 50 kPa 0.001 m3/kg
10 450 C 6.14 kJ/kgK
See http://www.steamtablesonline.com/steam97web.aspx or use your calculator for computed values.
Вам также может понравиться
- Me 211 Examples SolutionsДокумент30 страницMe 211 Examples SolutionsBryan Dominic Gabriel PaduaОценок пока нет
- 3Документ10 страниц3Ariel Carlos De LeonОценок пока нет
- Complete The Following Table For H O:: Chapter 3, Solution 26Документ5 страницComplete The Following Table For H O:: Chapter 3, Solution 26Uriel GuerraОценок пока нет
- Ensc 388 - P4 - 51 PDFДокумент1 страницаEnsc 388 - P4 - 51 PDFOkky JayadiОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1 (Properties of Pure Substance)Документ2 страницыAssignment 1 (Properties of Pure Substance)Huss MarsidiОценок пока нет
- Tutorial - 1 Property TablesДокумент2 страницыTutorial - 1 Property TablesNur Farah NadiahОценок пока нет
- Kevin Khein P. Biyong Bsme-2A 03-08-2021Документ3 страницыKevin Khein P. Biyong Bsme-2A 03-08-2021Kevin Khein P. BiyongОценок пока нет
- Sheet #2Документ2 страницыSheet #2Mohamed EmadОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics - 1 Midterm SolutionДокумент10 страницThermodynamics - 1 Midterm SolutionEarl Maxie Lagdamin ErederaОценок пока нет
- Problem 4.5: Chapter Iv - Properties of Pure SubstancesДокумент1 страницаProblem 4.5: Chapter Iv - Properties of Pure SubstancesLiz ArfinОценок пока нет
- CH 3Документ48 страницCH 3hadeelОценок пока нет
- Sheet 3 - Steam PropertiesДокумент2 страницыSheet 3 - Steam PropertiesYoussef Essam abdelwahabОценок пока нет
- Problems For Chapter 8: Power Cycles: A. The Rankine CycleДокумент48 страницProblems For Chapter 8: Power Cycles: A. The Rankine CycleEUGENE AICHAОценок пока нет
- XSteam V2aДокумент9 страницXSteam V2aPRABU PERUMALОценок пока нет
- ME 113 S09 HW2 SolutionДокумент3 страницыME 113 S09 HW2 SolutionallyhawОценок пока нет
- Uygulama 1-2 & Ornek SorularДокумент16 страницUygulama 1-2 & Ornek SorularMuhittin SimsekОценок пока нет
- Uygulama 1-2 & Ornek SorularДокумент16 страницUygulama 1-2 & Ornek SorularRSS RSSОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 (Numerical) GarimaДокумент43 страницыChapter 2 (Numerical) GarimaSudeep magarОценок пока нет
- HW3 SolutionДокумент14 страницHW3 SolutionBryceОценок пока нет
- Question 1. Liquid Water at 200 Kpa and 15: S S M S M T Q DT DsДокумент6 страницQuestion 1. Liquid Water at 200 Kpa and 15: S S M S M T Q DT Dsfivos_rgОценок пока нет
- Question 1 (15 Marks)Документ5 страницQuestion 1 (15 Marks)Farouk BassaОценок пока нет
- Guide To Using The Two Phase Property Tables: T P X V U H S PhaseДокумент1 страницаGuide To Using The Two Phase Property Tables: T P X V U H S PhaseMubashir GulzarОценок пока нет
- Solution of Assignment 2Документ9 страницSolution of Assignment 2Mahmoud AbdelghfarОценок пока нет
- ch03 JmsДокумент39 страницch03 Jmsdr. waleed ElbehairyОценок пока нет
- ME 63 Prob Set 2Документ2 страницыME 63 Prob Set 2RamonVannCleffRaroОценок пока нет
- I. Objective III. Problem Solving. Show Your SolutionsДокумент1 страницаI. Objective III. Problem Solving. Show Your SolutionsYsmael Alongan B. MangorsiОценок пока нет
- c08 - Pending 8.36Документ262 страницыc08 - Pending 8.36SeungMin LeeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 (Numerical+solution)Документ60 страницChapter 2 (Numerical+solution)Sudeep magarОценок пока нет
- Problem SetДокумент2 страницыProblem SetLORD BOY SILONGОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Energy Analysis For A Control VolumeДокумент103 страницыChapter 4 Energy Analysis For A Control Volumeshriramdhumal24744Оценок пока нет
- Tutorial 1.2Документ2 страницыTutorial 1.2ANIS FAIZAHОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1Документ3 страницыAssignment 1soumya0% (1)
- Thermo ExcerciseДокумент28 страницThermo ExcerciseAizel Jeong Aizel JeongОценок пока нет
- Thermo Quiz 1 (OAC)Документ4 страницыThermo Quiz 1 (OAC)SHUSWABHIT SHADANGIОценок пока нет
- Lecture 7 - Multiple Units (STUDENT COPY) - 1Документ23 страницыLecture 7 - Multiple Units (STUDENT COPY) - 1haqeemifarhanОценок пока нет
- Exercicio TermoДокумент1 страницаExercicio Termomcpe2793Оценок пока нет
- Universiti Malaysia Perlis: PPK Alam SekitarДокумент2 страницыUniversiti Malaysia Perlis: PPK Alam SekitarAiena AzlanОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics An Engineering Approach 8Th Edition Cengel Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFДокумент36 страницThermodynamics An Engineering Approach 8Th Edition Cengel Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFgeraldine.wells536100% (11)
- Thermodynamic (Sheet 1)Документ3 страницыThermodynamic (Sheet 1)Youssef AbbasОценок пока нет
- Thermo 5th Chap03P061Документ22 страницыThermo 5th Chap03P061IENCSОценок пока нет
- TD 1 Properties EnonceДокумент2 страницыTD 1 Properties EnonceLuc AusterОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics - هيرارح اكيمانيدДокумент16 страницThermodynamics - هيرارح اكيمانيدHafiz Mahar28Оценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics QuestionsДокумент6 страницThermodynamics QuestionsRОценок пока нет
- Problemas CompletosДокумент16 страницProblemas CompletosakksОценок пока нет
- Sheet 3 Solution 2012Документ35 страницSheet 3 Solution 2012jp2away68Оценок пока нет
- Rankine Cycle Diagram: K KG KJ K KG KJ Kpa S Kpa S S XДокумент16 страницRankine Cycle Diagram: K KG KJ K KG KJ Kpa S Kpa S S Xanon_166336005Оценок пока нет
- Gas Law PracticeДокумент5 страницGas Law PracticeKaly CantongОценок пока нет
- Tut 2Документ2 страницыTut 2GUNJAN MUDGALОценок пока нет
- Tarea III: - Answer: 224 VДокумент7 страницTarea III: - Answer: 224 VANDRES FELIPE AVILA TOROОценок пока нет
- Tut 2Документ2 страницыTut 2me21b105Оценок пока нет
- Master Complex Columns and Four Assumptions Problems 2020 Set - 5Документ7 страницMaster Complex Columns and Four Assumptions Problems 2020 Set - 5vikyappleОценок пока нет
- Moles&Gases 2345234Документ4 страницыMoles&Gases 2345234estellasr00Оценок пока нет
- Example 10B - 1 - Ideal Ammonia Vapor-Compression RefrigeratorДокумент22 страницыExample 10B - 1 - Ideal Ammonia Vapor-Compression RefrigeratorAshfaq Ali KhanОценок пока нет
- Pages From Thermodynamics (2) - 2Документ2 страницыPages From Thermodynamics (2) - 2hamid vahedil larijaniОценок пока нет
- HW 7 SolutionsДокумент9 страницHW 7 SolutionsDamien SolerОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Exercises 1 To 4Документ14 страницChapter 2 Exercises 1 To 4Rahmasari Nur SetyonoОценок пока нет
- Moles&Gases NewДокумент4 страницыMoles&Gases Newestellasr00Оценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics I P 04 PDFДокумент1 страницаThermodynamics I P 04 PDF黃羿傑Оценок пока нет
- Seed Sources For Florida Homegrown VegetablesДокумент6 страницSeed Sources For Florida Homegrown Vegetablesjimhale777Оценок пока нет
- Home Vegetable Garden Techniques - Hand Pollination of Squash and Corn in Small GardensДокумент4 страницыHome Vegetable Garden Techniques - Hand Pollination of Squash and Corn in Small Gardensjimhale777Оценок пока нет
- Florida Peach and Nectarine VarietiesДокумент17 страницFlorida Peach and Nectarine Varietiesjimhale777Оценок пока нет
- Heirloom Eggplant Varieties in FloridaДокумент6 страницHeirloom Eggplant Varieties in Floridajimhale777Оценок пока нет
- McBay, Aric - Tools For Gridcrash in The WakeДокумент52 страницыMcBay, Aric - Tools For Gridcrash in The WakeBill R Wilsberg100% (1)