Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Car
Загружено:
Simran Singh Kotla0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
59 просмотров2 страницыCar transport
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документCar transport
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
59 просмотров2 страницыCar
Загружено:
Simran Singh KotlaCar transport
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
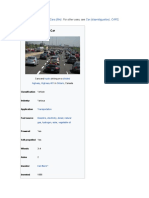
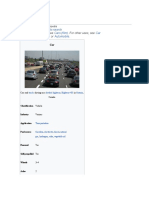
A car (or automobile) is a wheeled motor vehicle used
for transportation. Most definitions of car say they run
primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have
four tires, and mainly transport people rather than
goods.[2][3] Cars came into global use during the 20th
century, and developed economies depend on them. The
year 1886 is regarded as the birth year of the modern car
when German inventor Karl Benz patented his Benz
Patent-Motorwagen. Cars became widely available in the
early 20th century. One of the first cars that were
accessible to the masses was the 1908 Model T, an
American car manufactured by the Ford Motor Company.
Cars were rapidly adopted in the US, where they
replaced animal-drawn carriages and carts, but took much
longer to be accepted in Western Europe and other parts
of the world.
Cars have controls for driving, parking, passenger comfort
and safety, and controlling a variety of lights. Over the
decades, additional features and controls have been
added to vehicles, making them progressively more
complex. Examples include rear reversing cameras, air
conditioning, navigation systems, and in-car
entertainment. Most cars in use in the 2010s are propelled
by an internal combustion engine, fueled by
the combustion of fossil fuels. This causes air
pollution and also contributes to climate change and global
warming.[4] Vehicles using alternative fuels such
as ethanol flexible-fuel vehicles and natural gas
vehicles are also gaining popularity in some
countries. Electric cars, which were invented early in the
history of the car, began to become commercially
available in 2008.
There are costs and benefits to car use. The costs include
acquiring the vehicle, interest payments (if the car is
financed), repairs and maintenance, fuel, depreciation,
driving time, parking fees, taxes, and insurance.[5] The
costs to society include maintaining roads, land use, road
congestion, air pollution, public health, health care, and
disposing of the vehicle at the end of its life. Road traffic
accidents are the largest cause of injury-related deaths
worldwide.[6]
The benefits include on-demand transportation, mobility,
independence, and convenience.[7] The societal benefits
include economic benefits, such as job and wealth
creation from the automotive industry, transportation
provision, societal well-being from leisure and travel
opportunities, and revenue generation from the taxes. The
ability for people to move flexibly from place to place has
far-reaching implications for the nature of societies.[8] It
was estimated in 2014 that the number of cars was over
1.25 billion vehicles,[9] up from the 500 million of
1986.[10] The numbers are increasing rapidly, especially
in China, India and other newly industrialized countries.[11]
Вам также может понравиться
- Car Say They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have FourДокумент1 страницаCar Say They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have FourDerrick BaltimoreОценок пока нет
- Ethanol Flexible-Fuel VehiclesДокумент1 страницаEthanol Flexible-Fuel VehicleslatchanyananaОценок пока нет
- Citation NeededДокумент1 страницаCitation NeededDexterОценок пока нет
- Cars Came Into Global Use During The 20th Century, and Developed EconomiesДокумент5 страницCars Came Into Global Use During The 20th Century, and Developed EconomiestjasaОценок пока нет
- CarДокумент1 страницаCarinbawОценок пока нет
- Rise of Motorized VehiclesДокумент2 страницыRise of Motorized VehiclesMauyrОценок пока нет
- Recarch CarДокумент1 страницаRecarch CarBhupender AswalОценок пока нет
- მანქანა მაგარია ტოიოტა პრიუს ხოარ გადაობДокумент1 страницаმანქანა მაგარია ტოიოტა პრიუს ხოარ გადაობdachi apkhazavaОценок пока нет
- WkiДокумент1 страницаWkiAle IlovanОценок пока нет
- Modern Cars and Driving On An In, Canada: Trucks Expressway OntarioДокумент2 страницыModern Cars and Driving On An In, Canada: Trucks Expressway OntariosudinorangeОценок пока нет
- Car Doc: History of Cars from 1886 Model T to 1B Vehicles TodayДокумент5 страницCar Doc: History of Cars from 1886 Model T to 1B Vehicles Todaybluesparkles013Оценок пока нет
- Cars (Film) Car (Disambiguation) Cars Automobile: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orДокумент3 страницыCars (Film) Car (Disambiguation) Cars Automobile: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orAndrei SlabakovОценок пока нет
- Reference:WikipediaДокумент1 страницаReference:Wikipediagnoble30Оценок пока нет
- CarДокумент1 страницаCarSuryansh RajputОценок пока нет
- Jump To Navigationjump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orДокумент2 страницыJump To Navigationjump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orFrances camille TumbagaОценок пока нет
- FDFXДокумент1 страницаFDFXMahmoud Al NuaimiОценок пока нет
- CARSДокумент8 страницCARSRajbir SinghОценок пока нет
- CarДокумент1 страницаCarSzsbxbhxdhdhdОценок пока нет
- AutomobileДокумент1 страницаAutomobileschoolemail bellaОценок пока нет
- Accident Avoid Automatic Steering System Final ReportДокумент40 страницAccident Avoid Automatic Steering System Final ReportAlmubeenОценок пока нет
- A Car or Automobile Is A Motor Vehicle With WheelsДокумент2 страницыA Car or Automobile Is A Motor Vehicle With WheelsAlin VoicuОценок пока нет
- CarsДокумент2 страницыCarssaleha3695Оценок пока нет
- Safari - 08-Jun-2020 at 12:31 PM 3Документ1 страницаSafari - 08-Jun-2020 at 12:31 PM 3Santosh J Yadav's FriendОценок пока нет
- Jump To Navigation Jump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For The Country, See - For Other Uses, See,, orДокумент30 страницJump To Navigation Jump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For The Country, See - For Other Uses, See,, orLeonard IonutОценок пока нет
- The Evolution of CarsДокумент1 страницаThe Evolution of CarsmikkelОценок пока нет
- All About CarsДокумент16 страницAll About Carsapi-255581071Оценок пока нет
- For Other Types of Motorized Vehicles, See - For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See andДокумент4 страницыFor Other Types of Motorized Vehicles, See - For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See andewbОценок пока нет
- Car HistoryДокумент15 страницCar HistoryprakashОценок пока нет
- Etymology: Source - WikipediaДокумент3 страницыEtymology: Source - WikipediaWolfMensch1216Оценок пока нет
- Title The Automobile Revolution A JДокумент2 страницыTitle The Automobile Revolution A JromohacОценок пока нет
- Tata Motors 2012: Fuel and Propulision TechnologiesДокумент88 страницTata Motors 2012: Fuel and Propulision TechnologiesParth AggarwalОценок пока нет
- History of CarsДокумент21 страницаHistory of CarsGayle OmisolОценок пока нет
- Car ReviewДокумент3 страницыCar Reviewerwand21Оценок пока нет
- Cars Say That They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have FourДокумент9 страницCars Say That They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have FourShrinivas_shprОценок пока нет
- POM SC045 Study ReportДокумент6 страницPOM SC045 Study ReportRushikesh PatilОценок пока нет
- Everything You Need to Know About CarsДокумент5 страницEverything You Need to Know About CarsPawan KumarОценок пока нет
- The Evolution of AutomobilesДокумент2 страницыThe Evolution of Automobilesrjn46189nezidcomОценок пока нет
- Automotive Industry Analysis of Top CompaniesДокумент31 страницаAutomotive Industry Analysis of Top CompaniesSaif Muhammad AbdullahОценок пока нет
- INTRODUCTIONДокумент56 страницINTRODUCTIONkoolvansh692Оценок пока нет
- Wiki Loves Food - Wikipedia Photo Contest. Upload Pictures of Indian Food and Win PrizesДокумент24 страницыWiki Loves Food - Wikipedia Photo Contest. Upload Pictures of Indian Food and Win PrizesgadmaleОценок пока нет
- Promoting Lucas-TVS Filters: Understanding Decreasing SalesДокумент58 страницPromoting Lucas-TVS Filters: Understanding Decreasing SalesSourav Roy0% (1)
- Global Car Industry: A Brief HistoryДокумент3 страницыGlobal Car Industry: A Brief HistoryLillian KobusingyeОценок пока нет
- Natural SciencesДокумент13 страницNatural Sciencesxxmahnoor21Оценок пока нет
- The World of AutomobilesДокумент3 страницыThe World of AutomobilesAmogus MogusОценок пока нет
- How To Get Spanish Driving License EasilyДокумент3 страницыHow To Get Spanish Driving License EasilyDeangelo ParkhursterОценок пока нет
- Swot AnalysisДокумент12 страницSwot Analysispoonamy09Оценок пока нет
- Cars StudyДокумент2 страницыCars StudyFfkfj djdjfjОценок пока нет
- Cars and Trucks Driving On A Divided Highway, Highway 401 in Ontario, CanadaДокумент24 страницыCars and Trucks Driving On A Divided Highway, Highway 401 in Ontario, CanadaToday NewsОценок пока нет
- Literature ReviewДокумент4 страницыLiterature ReviewMuhammad Irfan Dogar100% (1)
- Scientific PaperДокумент9 страницScientific Paperapi-317125318Оценок пока нет
- Evolution of Cars Over 100 YearsДокумент1 страницаEvolution of Cars Over 100 YearsdiogoОценок пока нет
- Nama: Raina Fishecella Nim: C100220187: Transportation (Car)Документ1 страницаNama: Raina Fishecella Nim: C100220187: Transportation (Car)Farid AzisОценок пока нет
- CarsДокумент2 страницыCarsda. f1tnessОценок пока нет
- The Evolution of Muscle CarsДокумент15 страницThe Evolution of Muscle Carsvishal HarshОценок пока нет
- Page SemiДокумент39 страницPage SemiBallon DopeОценок пока нет
- My Research On CarsДокумент1 страницаMy Research On Carsjohn williamsОценок пока нет
- Citation NeededДокумент8 страницCitation NeededJayantYadavОценок пока нет
- Everything You Need to Know About CarsДокумент8 страницEverything You Need to Know About CarsJayantYadavОценок пока нет
- CarДокумент2 страницыCarSimran Singh KotlaОценок пока нет
- "Aeroplane" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, See and .: Airplane (Disambiguation) Aeroplane (Disambiguation)Документ2 страницы"Aeroplane" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, See and .: Airplane (Disambiguation) Aeroplane (Disambiguation)Simran Singh KotlaОценок пока нет
- This Is A DocumentДокумент1 страницаThis Is A DocumentSimran Singh KotlaОценок пока нет
- This Is A Bjhsdguehgfhebfjefjheuhf Frjghrejngrengr Grengjrngrngnrigrigor Nbciwhyvc FurgnirnrmgrДокумент1 страницаThis Is A Bjhsdguehgfhebfjefjheuhf Frjghrejngrengr Grengjrngrngnrigrigor Nbciwhyvc FurgnirnrmgrSimran Singh KotlaОценок пока нет
- Document 1Документ1 страницаDocument 1Simran Singh KotlaОценок пока нет
- Document 1Документ1 страницаDocument 1Simran Singh KotlaОценок пока нет
- This Is A Blank Document: Thank YouДокумент1 страницаThis Is A Blank Document: Thank YouSimran Singh KotlaОценок пока нет
- GEOGRAPHY PROJECT ON 5 TYPES OF POLLUTIONДокумент12 страницGEOGRAPHY PROJECT ON 5 TYPES OF POLLUTIONKelly MerieОценок пока нет
- Pollution in The PhilippinesДокумент1 страницаPollution in The PhilippinesKrausty IceОценок пока нет
- Cete 43 PDFДокумент25 страницCete 43 PDFSupravat KarmakarОценок пока нет
- Update On USP 797Документ16 страницUpdate On USP 797Alsaid ElewahОценок пока нет
- Environments Key Terms Matching ExerciseДокумент2 страницыEnvironments Key Terms Matching Exerciselisa langstonОценок пока нет
- Green Chemistry SyllabusДокумент2 страницыGreen Chemistry SyllabusAvigyan Mitra100% (1)
- Recycling Research On International StudentДокумент11 страницRecycling Research On International StudentAbdelrazaq Al-JazaziОценок пока нет
- GreenLearner LEED Standards Study GuideДокумент3 страницыGreenLearner LEED Standards Study GuidesyampkОценок пока нет
- The CPV Valley Energy Center - 2013 RFPДокумент103 страницыThe CPV Valley Energy Center - 2013 RFP2rQiTPh4KnОценок пока нет
- 29 Multiple Choice Questions MCQs With Answers On "Environmental Legislatio PDFДокумент10 страниц29 Multiple Choice Questions MCQs With Answers On "Environmental Legislatio PDFArun modiОценок пока нет
- Mathematics, Science and Technology - Module 2Документ3 страницыMathematics, Science and Technology - Module 2Allysa Jean Tadlongan Alajan100% (2)
- Education Region III Tests Climate ChangeДокумент6 страницEducation Region III Tests Climate ChangeLiezl SabadoОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Environmental Project Engineer in Charleston SC Resume Eugene SantosДокумент3 страницыMechanical Environmental Project Engineer in Charleston SC Resume Eugene SantosEugeneSantosОценок пока нет
- On-Board Diagnostics II (OBDII) : Light-Duty Vehicle Emission Related Inspection and Maintenance (I/M) ProgramsДокумент92 страницыOn-Board Diagnostics II (OBDII) : Light-Duty Vehicle Emission Related Inspection and Maintenance (I/M) ProgramsmaxmicrosОценок пока нет
- Beth Dry Electrostatic PrecipitatorДокумент12 страницBeth Dry Electrostatic PrecipitatorDheagilang07Оценок пока нет
- (Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 1) Eric Lichtfouse (Auth.), Eric Lichtfouse (Eds.)-Organic Farming, Pest Control and Remediation of Soil Pollutants_ Organic Farming, Pest Control and Remediation of sДокумент416 страниц(Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 1) Eric Lichtfouse (Auth.), Eric Lichtfouse (Eds.)-Organic Farming, Pest Control and Remediation of Soil Pollutants_ Organic Farming, Pest Control and Remediation of sCesar Diaz Barrios100% (1)
- Multiple-Choice Test Chapter 22: Humans and The Environment: 1 A B C D 2 A B C D 3 A B C D 4 A B C D 5 A B C DДокумент2 страницыMultiple-Choice Test Chapter 22: Humans and The Environment: 1 A B C D 2 A B C D 3 A B C D 4 A B C D 5 A B C DsybejoboОценок пока нет
- Passive-Voice-Environment - 14654 (1) (6.8.2021)Документ2 страницыPassive-Voice-Environment - 14654 (1) (6.8.2021)Phương Nguyễn HàОценок пока нет
- Handling of Barley and Malt SpillagesДокумент2 страницыHandling of Barley and Malt SpillagesrememberОценок пока нет
- Emotions, Environment, GoalsДокумент22 страницыEmotions, Environment, GoalsMohamed ChaouichОценок пока нет
- Health COTДокумент24 страницыHealth COTSarah A. DavidОценок пока нет
- Apple and Tomato Peelings As Water PurifierДокумент7 страницApple and Tomato Peelings As Water Purifiermeshin yuОценок пока нет
- Misamis Occidental Plans to Protect Aquamarine ResourceДокумент8 страницMisamis Occidental Plans to Protect Aquamarine ResourcejelosalisaliОценок пока нет
- SDS - Alkyd Topcoat - Marine - Protective - English (Uk) - United Kingdom - 12300 - 25.06.2012Документ13 страницSDS - Alkyd Topcoat - Marine - Protective - English (Uk) - United Kingdom - 12300 - 25.06.2012manbkkОценок пока нет
- Campus STP DesignДокумент6 страницCampus STP DesignHarish LakshminarayananОценок пока нет
- AAANoise PollutionДокумент3 страницыAAANoise PollutionOnur BenerОценок пока нет
- Human Impact Station ActivityДокумент9 страницHuman Impact Station ActivityShayОценок пока нет
- Pollution Prevention in Offshore Oil and Gas Operations: Opportunities and ImplementationДокумент15 страницPollution Prevention in Offshore Oil and Gas Operations: Opportunities and ImplementationjanОценок пока нет
- Msds PDFДокумент6 страницMsds PDFYuNa YoshinoyaОценок пока нет
- Abstract Fahad Riaz 034Документ13 страницAbstract Fahad Riaz 034Saim TufailОценок пока нет