Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Result:: Volume of Naoh 250 ML Volume of HCL 10 ML Volume of Ethyl Acetate 250 ML
Загружено:
mujahid alkolaibiОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Result:: Volume of Naoh 250 ML Volume of HCL 10 ML Volume of Ethyl Acetate 250 ML
Загружено:
mujahid alkolaibiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Result :
Volume of NaOH = 250 ml
Volume of HCl = 10 ml
Volume of ethyl acetate = 250 ml
Times (s) NaOH NaOH CA ∆CA ∆CA/ ∆t
( ml) (mol) (mol / L) (mol / L) (mol / L.s)
0.0 5.4 0.0005 0.046 -3*10-3 0.0002
10 5.7 0.0004 0.043 -8*10-3 0.00027
30 6.5 0.0004 0.035 -0.013 0.00029
50 7.8 0.0002 0.022
Times (s) ∆CA/ ∆t Ln (∆CA/ ∆t) Ln CA
(mol / L.s)
0.0 0.0 -3.079
10 0.0002 -8.517 -3.14655
30 0.00027 -8.217 -3.3524
50 0.00029 -8.1456 -3.817
Ln k = -3.079
K= 4.6*10-2 and the reaction is first order
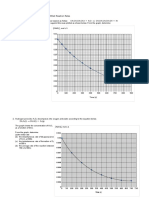
Conce of A with time
0.05
0.045
0.04
0.035
concen of A (mol /L)
0.03
0.025 Conce of A with time
0.02
0.015
0.01
0.005
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
time( S)
Discussion:
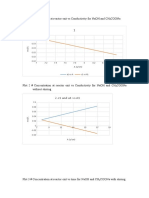
It can be cleary seen from the tables and results that as the time proceeds the two reactants the
amount of NaOH from the pure increase this is due to the fact that reactant NaOH in the the
reactor is consumed as time proceeds and so less amount of 0.01 M HCl is needed from 10 ml
HCl to end the reaction that is consume the remaining NaOH is needed (0.1 M) thus larger
amount of HCl will present and so more NaOH is needed from the pure to reach the end point.
The reaction between NaOH and acetate ethyl ( CH3COOC2H5 ) is completed winth in (120 sec)
so no more than 4 saple are needed since no NaOH is present.
Since ther is some strage reading in tableit was not satisfy the expect trend of reading it then
excluded from calculate to avoid the error that may be from personal error or from the
concentration of chemical used.
A plot of Ln (∆CA/ ∆t) Vs Ln CA was obtained , get a straight line with slope = 1.12 and
intercept ln k = -3.079 k= 4.6*10-2
Conclusion:
1. the reaction between NaOH and acetate ethyl ( CH3COOC2H5) is fast and can be ended
with in 120 sec based on250 ml NaOH and 250 ml of (CH3COOC2H5 ) and equal
concentration.
2. when the volume of NaOH from the buret equal HCl volume added , then the reaction is
complyted and no more samples are needed
3. the addition of distillation water to samples for titration doesn't affect the process and
results, it can be used since small volume are used for titration
4. the order of reaction is first order this dosent mean that bothe order of A and B are equal
but if it's the case then the reaction is called elementary reaction since a = 1 and b=0.0
which equal to the stiochmtry coefficient in the reaction
5. k ( which is the rate constant is found = 4.6*10-2
References:
1. Chemical process laboratory ,Dr .Khalil Alhalholi
2. Element of chemical reaction engineering, 4rd edition, H.scott Foglar
Sample calculation:
NAo dX/dt = -rA *V -rA = CA dX/dt = k CA ( 1 – x)
Ln (-rA ) = ln k = n ln( ∆CA/ ∆t )
- assume x is volume of HCl (0.1 M) consumed in NaOH reaction with HCl
- volume of HCl presented ( 10 – x ) ml after reaction
- volume of NaOH from pure = volume of HCl remaning
- fror example sample (2)
10-x = 5.7 x = 4.3
Mol of HCl = 4.3*0.1*10-3 = 4.3 *10-4 mole
Mole of NaOH = 4.3*10-4
CA = 4.3*10-4 / 10*10-3 = 0.043mol /l ater 15 sec
-∆CA/ ∆t = -( 0.043 - 0.046 ) / 15 = 0.0002mol/ L.s
k = 4.6*10-2
Вам также может понравиться
- Organic Chem Diels-Alder Reaction LabДокумент9 страницOrganic Chem Diels-Alder Reaction LabPryanka BalleyОценок пока нет
- Rate of Reaction of Sodium Thiosulphate and HCLДокумент7 страницRate of Reaction of Sodium Thiosulphate and HCLmudasir elahi0% (2)
- Conclusion ReportДокумент10 страницConclusion ReportleenzalalОценок пока нет
- Adsorption of Acetic Acid On Charcoal SurfaceДокумент3 страницыAdsorption of Acetic Acid On Charcoal SurfaceDrGaurav Rajput100% (1)
- Victoria Junior College Atoms, Molecules & Stoichiometry Tutorial (2015) Level 1-3 QuestionsДокумент18 страницVictoria Junior College Atoms, Molecules & Stoichiometry Tutorial (2015) Level 1-3 QuestionsJonathanNgОценок пока нет
- Experiment 2 - SAPONIFICAATION OF ETHYL ACETATE AND SODIUM HYDROXIDE IN CSTRДокумент18 страницExperiment 2 - SAPONIFICAATION OF ETHYL ACETATE AND SODIUM HYDROXIDE IN CSTRIzzaimRedzaОценок пока нет
- Lab 4 - 555Документ12 страницLab 4 - 555ZawanahОценок пока нет
- ReviewerДокумент43 страницыReviewerTiffany LiuОценок пока нет
- Objective:: Feed Tanks Batch ReactorДокумент5 страницObjective:: Feed Tanks Batch Reactorfareeha saeedОценок пока нет
- Experiment No: 6: Feed Tanks Batch ReactorДокумент5 страницExperiment No: 6: Feed Tanks Batch Reactorfareeha saeedОценок пока нет
- Chemical Reaction Rate and Order DeterminationДокумент15 страницChemical Reaction Rate and Order DeterminationAhmed ZakariaОценок пока нет
- Results and CalculationsДокумент5 страницResults and CalculationsGriezmann HaziqОценок пока нет
- Rate Reaction Lloaana 2020Документ8 страницRate Reaction Lloaana 2020Lloaana 12Оценок пока нет
- Calibration Curve ConductivityДокумент8 страницCalibration Curve Conductivitynur athilahОценок пока нет
- Solution Mix TuresДокумент6 страницSolution Mix TuresTengku AshrafОценок пока нет
- Conduct IV I DadДокумент7 страницConduct IV I DadEder E. AguilarОценок пока нет
- T2 - E5-Phase Transfer CatalystДокумент14 страницT2 - E5-Phase Transfer Catalystabhisheknemade9765Оценок пока нет
- CSTR 40 L Result Plus Conc, Recommendation, AnalysisДокумент8 страницCSTR 40 L Result Plus Conc, Recommendation, AnalysisFea MeenОценок пока нет
- Analisis Pembahasan Laju ReaksiДокумент11 страницAnalisis Pembahasan Laju ReaksiLia Yuli KusumaОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 2Документ2 страницыTutorial 2EreenОценок пока нет
- Results CSTR BaruДокумент6 страницResults CSTR Baruridzuwan rahimiОценок пока нет
- NCHE312Документ11 страницNCHE312Charmaine MoyoОценок пока нет
- Assignment 3Документ4 страницыAssignment 3Yi Hong LowОценок пока нет
- CHEM 154 PROBLEM SET 1 - Chemical Kinetics - September 2018Документ1 страницаCHEM 154 PROBLEM SET 1 - Chemical Kinetics - September 2018AlyssaRamosОценок пока нет
- CRE Lab ManualДокумент32 страницыCRE Lab ManualAABID SHAIK100% (1)
- Tutorial 1 Buffers - AnswersДокумент10 страницTutorial 1 Buffers - AnswersVõThịCẩmNhungОценок пока нет
- Discussion Batch SaponificationДокумент4 страницыDiscussion Batch SaponificationSuria Seri SulyanaОценок пока нет
- Jadavpur University: Reaction Engineering LaboratoryДокумент21 страницаJadavpur University: Reaction Engineering LaboratoryshantanuОценок пока нет
- Benzoic_Acid experimentДокумент7 страницBenzoic_Acid experimentShivani SinghОценок пока нет
- Co4: Effect of Concentration On Rate of Reaction: ObjectivesДокумент2 страницыCo4: Effect of Concentration On Rate of Reaction: ObjectivesSebastian Genesis ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Plots For Exp1Документ4 страницыPlots For Exp1Mohammed AlmoriseyОценок пока нет
- 01 - Ans To Stoichiometry Supplemtary QN - 2012Документ5 страниц01 - Ans To Stoichiometry Supplemtary QN - 2012caspersoongОценок пока нет
- Safonification conductometrically SS-13062021 uploadДокумент3 страницыSafonification conductometrically SS-13062021 uploadNerdОценок пока нет
- Experiment 1 Lab ReportДокумент7 страницExperiment 1 Lab ReportChaapi KimОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 1: Obtention o Fan Acid-Base Titration Curve: Sabela Teixeira Taboada Sabela - Teixeira@rai - Usc.esДокумент7 страницTutorial 1: Obtention o Fan Acid-Base Titration Curve: Sabela Teixeira Taboada Sabela - Teixeira@rai - Usc.esSabela TeixeiraОценок пока нет
- Acid hydrolysis of methyl acetateДокумент4 страницыAcid hydrolysis of methyl acetateLala GulОценок пока нет
- CSTR Reactor Design for Lactic Acid ProductionДокумент18 страницCSTR Reactor Design for Lactic Acid Productionنزار خيرОценок пока нет
- Gazi University Chemical Reaction Engineering ProblemsДокумент4 страницыGazi University Chemical Reaction Engineering ProblemsJerson Mendoza CОценок пока нет
- Kinetics, ThiosulfateДокумент4 страницыKinetics, ThiosulfateJUNEIL CLEMENCIO SUAREZОценок пока нет
- Absorption of CO2 Using NaOH TitrationДокумент3 страницыAbsorption of CO2 Using NaOH TitrationTaslinОценок пока нет
- Calculation & Discussion PFR CHE506Документ9 страницCalculation & Discussion PFR CHE506Wahyuningsih YuniОценок пока нет
- Gas Liquid AbsorptionДокумент9 страницGas Liquid AbsorptionShashwat OmarОценок пока нет
- Lab Report Experiment 1 and 2 - K2G7Документ11 страницLab Report Experiment 1 and 2 - K2G7Divagar SivaselvamОценок пока нет
- Back TitrationДокумент15 страницBack TitrationAnis NasuhaОценок пока нет
- LAb Report 7Документ3 страницыLAb Report 7Faisal MumtazОценок пока нет
- APPENDIX C ComputationsДокумент9 страницAPPENDIX C ComputationsNicole Anne BorromeoОценок пока нет
- Drills For An A CHM096Документ20 страницDrills For An A CHM096Aiman FitryОценок пока нет
- Conductance of SolutionДокумент6 страницConductance of SolutionHatmylifeОценок пока нет
- 5 Solution Stoichiometry (S)Документ11 страниц5 Solution Stoichiometry (S)Mr TanОценок пока нет
- 8 - RTD in A CSTRДокумент7 страниц8 - RTD in A CSTRsansayana100% (1)
- CSTR 40 LiterДокумент13 страницCSTR 40 LiterNikMuhammadIzzatОценок пока нет
- Post-Lab Exercise 3Документ2 страницыPost-Lab Exercise 3nickeita blairОценок пока нет
- Ideal CSTR SizingДокумент16 страницIdeal CSTR SizingChuka OmeneОценок пока нет
- Reaction KineticsДокумент15 страницReaction KineticsSadiaShoaibОценок пока нет
- Chemical Reaction Engineering Lab ExperimentsДокумент21 страницаChemical Reaction Engineering Lab ExperimentsBHOWMICK PATIDAR 15BCH00850% (1)
- Equilibrium Lab ReportДокумент3 страницыEquilibrium Lab ReportJustin G-Hood Jung100% (2)
- Experiment 4Документ2 страницыExperiment 4Tola PtolaОценок пока нет
- Post Lab Report FinalДокумент8 страницPost Lab Report FinalerizaОценок пока нет
- Solvolysis of Salt of A Weak Acid and Weak BaseДокумент11 страницSolvolysis of Salt of A Weak Acid and Weak BaseNitty MeYa100% (1)
- CHE 113 Final Exam ReviewДокумент15 страницCHE 113 Final Exam ReviewSrynnEОценок пока нет
- Fludisedbed Raw DataДокумент2 страницыFludisedbed Raw Datamujahid alkolaibiОценок пока нет
- Fluidization ReportДокумент11 страницFluidization Reportmujahid alkolaibiОценок пока нет
- Fluidization ReportДокумент11 страницFluidization Reportmujahid alkolaibiОценок пока нет
- 6th Week PlantДокумент6 страниц6th Week Plantmujahid alkolaibiОценок пока нет
- 4.1.2, 4.1.3 Exam QuestionsДокумент9 страниц4.1.2, 4.1.3 Exam QuestionsHyder OmarОценок пока нет
- Alkyl Halides: R-X (X F, CL, BR, I)Документ40 страницAlkyl Halides: R-X (X F, CL, BR, I)ranjit singh randhawaОценок пока нет
- Reaction Mechanism by Ashish Mishra @JEEBookPDFsДокумент21 страницаReaction Mechanism by Ashish Mishra @JEEBookPDFsMrinmay Dev SarmaОценок пока нет
- Rate Equation for Bromine and Nitrogen(II) Oxide ReactionДокумент22 страницыRate Equation for Bromine and Nitrogen(II) Oxide ReactionDarasimi OlasopeОценок пока нет
- Catalysis and Macrokinetics PDFДокумент32 страницыCatalysis and Macrokinetics PDFRicardoMR_14Оценок пока нет
- Applied Chemistry (MS-133) : Cannizzaro Reaction With Complete MechanismДокумент5 страницApplied Chemistry (MS-133) : Cannizzaro Reaction With Complete MechanismHammad RazaОценок пока нет
- Study Guide 2Документ4 страницыStudy Guide 2Orçun AtasevenОценок пока нет
- Limiting ReactantsДокумент18 страницLimiting ReactantsEmerlyn Panganiban100% (1)
- Chapter 7 - HaloalkanesДокумент13 страницChapter 7 - HaloalkanesPatricia ChongОценок пока нет
- Reaction of First Order: Chemical KineticsДокумент15 страницReaction of First Order: Chemical Kineticsrishabh mishraОценок пока нет
- Desconexión de Grupo Parte 2Документ29 страницDesconexión de Grupo Parte 2Johanna GalanОценок пока нет
- CH 6 - Organic ReactionsДокумент18 страницCH 6 - Organic Reactionskevincai96Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 9: Inverse Response and Time Delay Systems: Department of Chemical Engineering I.I.T. Bombay, IndiaДокумент8 страницLecture 9: Inverse Response and Time Delay Systems: Department of Chemical Engineering I.I.T. Bombay, IndiaPreeti KumariОценок пока нет
- Wolff Kishner Reduction - MECHДокумент2 страницыWolff Kishner Reduction - MECHbaskhemОценок пока нет
- CHEMISTRY 12 – ACTIVATION ENERGIESДокумент3 страницыCHEMISTRY 12 – ACTIVATION ENERGIESAlicias YongОценок пока нет
- Che 326 Lecture NotesДокумент155 страницChe 326 Lecture Noteswinifred ekpoОценок пока нет
- Synthesis of (+) - Camptothecin: Organic Chemistry: Technology: National Chemical Laboratory, Pune 411008, India E-MailДокумент5 страницSynthesis of (+) - Camptothecin: Organic Chemistry: Technology: National Chemical Laboratory, Pune 411008, India E-Mailevsgoud_goudОценок пока нет
- Aldehydes and Ketones PDFДокумент28 страницAldehydes and Ketones PDFAniruddha KawadeОценок пока нет
- Important Questions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Important Questions - Learn CBSEДокумент40 страницImportant Questions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Important Questions - Learn CBSErithimukulaОценок пока нет
- Chemical KineticsДокумент52 страницыChemical KineticsSai Sasivardhan GampaОценок пока нет
- Venpure Chemo PDFДокумент4 страницыVenpure Chemo PDFFernando J. Correa DelgadoОценок пока нет
- Types of Catalysts Speed Up ReactionsДокумент9 страницTypes of Catalysts Speed Up ReactionsJohn Rene DalidaОценок пока нет
- Equilibria (Equilibrium) : Physical Equilibrium Chemical EquilibriumДокумент5 страницEquilibria (Equilibrium) : Physical Equilibrium Chemical EquilibriumPrashant BhandariОценок пока нет
- Kinetic investigations of CO disproportionation on Fe catalystДокумент4 страницыKinetic investigations of CO disproportionation on Fe catalystSchfranzenОценок пока нет
- Subject Chemistry: Paper No and Title 9 Organic Chemistry-III Module No and Title 35 Ene Reaction Module Tag CHE - P9 - M35Документ11 страницSubject Chemistry: Paper No and Title 9 Organic Chemistry-III Module No and Title 35 Ene Reaction Module Tag CHE - P9 - M35DeadpoolОценок пока нет
- Reactor Design Report: Types of Reactors and Kinetic AnalysisДокумент30 страницReactor Design Report: Types of Reactors and Kinetic AnalysisAhmed YounisОценок пока нет
- Latihan 3 Enzyme KineticsДокумент4 страницыLatihan 3 Enzyme KineticsAesyah FadhilahОценок пока нет
- Electrophilic Addition of Hydrogen HalidesДокумент16 страницElectrophilic Addition of Hydrogen HalidesDk Hazra HadzryaОценок пока нет
- Aliphatic Nucleophilic Substitution ReactionsДокумент12 страницAliphatic Nucleophilic Substitution ReactionsDhanaswamy Ilangeswaran100% (6)