Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CHAPTER 7 Elec3 Reviewer
Загружено:
Hazel Mosot0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
13 просмотров2 страницыreviewer
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документreviewer
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
13 просмотров2 страницыCHAPTER 7 Elec3 Reviewer
Загружено:
Hazel Mosotreviewer
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
CHAPTER 7: STRATEGIC LEADERSHIP Top management team - composed of the key individuals
who are responsible for selecting and implementing the
Strategic leadership- the ability to anticipate, envision, firm’s strategies.
maintain flexibility, and empower others to create strategic Heterogeneous top management team - composed of
change as necessary. individuals with different functional backgrounds,
Effective strategic leadership - a prerequisite to successfully experience, and education.
use the strategic management process. Figure 12.2 Factors Affecting Managerial Discretion
Effective strategic leadership has five major components:
1) Determining the firm’s strategic direction
2) Effectively managing the firm’s resource portfolio
3) Sustaining an effective organizational culture
4) Emphasizing ethical practices
5) Establishing balanced organizational controls.
Figure 12.1 Strategic Leadership and the Strategic Management Process
Internal managerial labor market - consists of a firm’s
opportunities for managerial positions and the qualified
employees within that firm.
External managerial labor market - the collection of
managerial career opportunities and the qualified people
who are external to the organization in which the
opportunities exist.
Figure 12.3 Effects of CEO Succession and Top Management Team
Composition on Strategy
Top-level management decisions influence the culture of
firms as well as how organizations are structured and how
goals are set and achieved.
Top-level managers - an important resource for firms to
develop and exploit competitive advantages
The primary factors that determine the amount of decision-
making discretion held by a manager are:
1) external environmental sources such as the industry
structure, the rate of market growth in the firm’s
primary industry, and the degree to which products
can be differentiated;
2) characteristics of the organization, including its size, Determining strategic direction - involves specifying the
age, resources, and culture image and character the firm seeks to develop over time
3) characteristics of the manager, including Core competencies - capabilities that serve as a source of
commitment to the firm and its strategic outcomes, competitive advantage for a firm over its rivals.
tolerance for ambiguity, skills in working with - Relate to an organization’s functional skills, such as
different people, and aspiration levels manufacturing, finance, marketing, and research
and development.
Competitive agility - an ability to act in a variety of disseminating the code of conduct to all
competitively relevant ways stakeholders to inform them of the firm’s ethical
Competitive speed - an ability to act quickly when facing standards and practices
environmental and competitive pressures developing and implementing methods and
Figure 12.4 Exercise of Effective Strategic Leadership procedures to use in achieving the firm’s ethical
standards
creating and using explicit reward systems that
recognize acts of courage
creating a work environment in which all people
are treated with dignity.
Organizational controls - formal, information based
procedures used by managers to maintain or alter patterns
in organizational activities.
Two organizational controls:
1) Financial control - focuses on short-term
financial outcomes
Training and development programs can provide the 2) Strategic control - focuses on the content of
means by which new strategic leaders are cultivated within strategic actions rather than their outcomes.
an organization. Balanced scorecard - a framework firms can use to verify that
they have established both strategic and financial controls to
Human capital - refers to the knowledge and skills of a firm’s assess their performance
entire workforce. - A tool that helps strategic leaders assess the
Social capital - involves relationships inside and outside the effectiveness of the controls.
firm that help the firm accomplish tasks and create value for Four perspectives are integrated to form the balanced
customers and shareholders. scorecard framework:
Organizational culture - consists of a complex set of 1. Financial - concerned with growth, profitability, and
ideologies, symbols, and core values that are shared risk from the shareholders’ perspective
throughout the firm and influence the way business 2. Customer - concerned with the amount of value
is conducted. customers perceive was created by the firm’s
Five dimensions characterize a firm’s entrepreneurial products
mind-set: 3. Internal business processes - with a focus on the
1) Autonomy – allows employees to take actions that priorities for various business processes that create
are free of organizational constraints and permits customer and shareholder satisfaction
individuals 4. Learning and growth - concerned with the firm’s
2) Innovativeness –reflects a firm’s tendency to engage effort to create a climate that supports change,
in and support new ideas, novelty, experimentation, innovation, and growth
and creative processes that may result in new Figure 12.5 Strategic Controls and Financial Controls in a Balanced
products, services, or technological processes. Scorecard Framework
3) Risk taking –reflects a willingness by employees and
their firm to accept risks when pursuing
entrepreneurial opportunities.
4) Proactiveness –describes a firm’s ability to be a
market leader rather than a follower.
5) Competitive aggressiveness – a firm’s propensity to
take actions that allow it to consistently and
substantially outperform its rivals.
Strategic leaders can take several actions to develop
an ethical organizational culture. Examples of these
actions include:
establishing and communicating specific goals to
describe the firm’s ethical standards
continuously revising and updating the code of
conduct, based on inputs from people
throughout the firm and from other
stakeholders
Вам также может понравиться
- Glowing Light Bulb PowerPoint TemplatesДокумент44 страницыGlowing Light Bulb PowerPoint TemplatesEbtehal TamerОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1 - Strategic ManagementДокумент1 страницаLesson 1 - Strategic ManagementCzamille Rivera GonzagaОценок пока нет
- Group 7 ReportДокумент14 страницGroup 7 ReportJason SiaОценок пока нет
- Business PolicyДокумент9 страницBusiness PolicyHarlene Justine CalderonОценок пока нет
- Lecture in Business Policy 2Документ11 страницLecture in Business Policy 2Harlene Justine CalderonОценок пока нет
- Finals ReviewerДокумент6 страницFinals ReviewerDharnel Jude EpeОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1 - Strategic ManagementДокумент1 страницаLesson 1 - Strategic ManagementCzamille Rivera GonzagaОценок пока нет
- Final Module in Strategic ManagementДокумент34 страницыFinal Module in Strategic ManagementRaj RodrigoОценок пока нет
- Simplified Notes Strategic ManagementДокумент2 страницыSimplified Notes Strategic ManagementWakin PoloОценок пока нет
- CH 12 MBAДокумент25 страницCH 12 MBAGeorgia HolstОценок пока нет
- 3 - Corporate Strategy and Long Range Planning: Strategic Management LessonДокумент8 страниц3 - Corporate Strategy and Long Range Planning: Strategic Management LessonMich AlbaniaОценок пока нет
- Ional Behaviour Management - Assessment 1 - Jeremiah Cerdon (1) - TaggedДокумент15 страницIonal Behaviour Management - Assessment 1 - Jeremiah Cerdon (1) - Taggednaureen fatimaОценок пока нет
- MarketingДокумент27 страницMarketingM Kaleem AbidОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2: The Strategic-Management Model and SWOT Analysis Topic: Learning OutcomesДокумент40 страницLesson 2: The Strategic-Management Model and SWOT Analysis Topic: Learning OutcomesFritz CacatianОценок пока нет
- MGMT 1063 - Strama Module 2Документ14 страницMGMT 1063 - Strama Module 2Kay AbawagОценок пока нет
- p2 ReviewerДокумент4 страницыp2 ReviewerRyza Mae PringОценок пока нет
- Operational ManagementДокумент10 страницOperational Managementmitzie torranoОценок пока нет
- OTQM Midterm Quiz 1Документ3 страницыOTQM Midterm Quiz 1Yi ZaraОценок пока нет
- The Internal Audit: Chapter SixДокумент33 страницыThe Internal Audit: Chapter SixAbdullahОценок пока нет
- The Business Excellence JourneyДокумент32 страницыThe Business Excellence JourneyPuguh HariantoОценок пока нет
- SM - Notes 3Документ12 страницSM - Notes 3TC26COUNSELОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Notes Midterm 1Документ2 страницыChapter 1 Notes Midterm 1Kez MaxОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Management ReviewerДокумент2 страницыFundamentals of Management ReviewerJovzkieОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Strategic Human Resource ManagementДокумент26 страницChapter 2 Strategic Human Resource Managementenv.vrgОценок пока нет
- Module 3 Chapter 4 6Документ23 страницыModule 3 Chapter 4 6Lyca FelicisimoОценок пока нет
- Strategic ImplementationДокумент25 страницStrategic ImplementationBeenay MaharjanОценок пока нет
- Strategic Management ReviewerДокумент3 страницыStrategic Management ReviewerJhon Vincent BaquiranОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Strategic ManagementДокумент7 страницIntroduction To Strategic ManagementAqiba Azhar 478Оценок пока нет
- MGT703 Topic 8Документ21 страницаMGT703 Topic 8Deepashni DeviОценок пока нет
- Strategic LradershipДокумент18 страницStrategic LradershipOlivethОценок пока нет
- Business Management 3 NOTES LCДокумент2 страницыBusiness Management 3 NOTES LCGraceОценок пока нет
- Organization and Management ReviewerДокумент3 страницыOrganization and Management ReviewerRoanaОценок пока нет
- CESMДокумент16 страницCESMgssgopi9_389290943Оценок пока нет
- Strategic Management ReviewerДокумент4 страницыStrategic Management ReviewerJah De DiosОценок пока нет
- Chapt 9 10 Strama ReviewerДокумент6 страницChapt 9 10 Strama Reviewerjessa suazoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ19 страницChapter 5Rochelle Esquivel ManaloОценок пока нет
- Strategic-Leadership Mina Balingkit DelacruzДокумент5 страницStrategic-Leadership Mina Balingkit DelacruzMelanie MinaОценок пока нет
- Strategic Management Note MBAДокумент27 страницStrategic Management Note MBAsadman100% (1)
- Strategic Management Part 6Документ9 страницStrategic Management Part 6aansh rajОценок пока нет
- Class Material of SMДокумент25 страницClass Material of SMPramila PaudelОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Strat ManДокумент6 страницChapter 1 - Strat ManHannah LegaspiОценок пока нет
- Functions and Skills of Management: Learning ObjectivesДокумент12 страницFunctions and Skills of Management: Learning ObjectivesananthaОценок пока нет
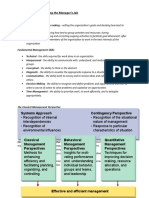
- CHAPTER 1: Understanding The Manager's Job: Systems Approach Contingency PerspectiveДокумент13 страницCHAPTER 1: Understanding The Manager's Job: Systems Approach Contingency PerspectiveNina ManginsayОценок пока нет
- LO Cheat SheetДокумент4 страницыLO Cheat Sheetkhaa91896Оценок пока нет
- Stratman NotesДокумент2 страницыStratman NotesWakin PoloОценок пока нет
- SM BBA PDUS UniversityДокумент15 страницSM BBA PDUS UniversityprofessorambrishОценок пока нет
- Business A Changing World Canadian 6Th Edition Ferrell Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFДокумент47 страницBusiness A Changing World Canadian 6Th Edition Ferrell Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFankledsisterlydaazg100% (12)
- Group 4 Internal AnalysisДокумент9 страницGroup 4 Internal AnalysisDarlene CruzОценок пока нет
- Business A Changing World Canadian 6th Edition Ferrell Solutions ManualДокумент26 страницBusiness A Changing World Canadian 6th Edition Ferrell Solutions Manualtamthuongw3wv100% (29)
- Stratman 1Документ5 страницStratman 1Riri CanezoОценок пока нет
- Derek F. Channon and Adrián A. Caldart: Mckinsey 7S ModelДокумент2 страницыDerek F. Channon and Adrián A. Caldart: Mckinsey 7S ModelBarış TunçbilekОценок пока нет
- PA 203 2nd Sem 2020 2021Документ105 страницPA 203 2nd Sem 2020 2021inshiraОценок пока нет
- MCS NotesДокумент3 страницыMCS Notesvijayadarshini vОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1-Basics of MNGT ModifiedДокумент39 страницChapter 1-Basics of MNGT ModifiedBahredin AbdellaОценок пока нет
- Reviewer - Module 1: 4. Implement StrategyДокумент3 страницыReviewer - Module 1: 4. Implement StrategyErika Mae LegaspiОценок пока нет
- Session 3 Organizational Alignment 7 S ModelДокумент5 страницSession 3 Organizational Alignment 7 S Modelshashwat shubhamОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER-9 MeДокумент2 страницыCHAPTER-9 MeHassan MarhoonОценок пока нет
- Strategic Management ReviewerДокумент6 страницStrategic Management Reviewersatriajea.faustino.eОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 NotesДокумент12 страницChapter 1 NotesIman NurainaОценок пока нет
- Activity 2 Part 1Документ2 страницыActivity 2 Part 1Hazel MosotОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Reviewer ELEC 3Документ3 страницыChapter 6 Reviewer ELEC 3Hazel MosotОценок пока нет
- Activity 1: Porter'S Five Forces Analysis: Soft Drink IndustryДокумент3 страницыActivity 1: Porter'S Five Forces Analysis: Soft Drink IndustryHazel MosotОценок пока нет
- 3.10 Pre-Operation Activities and Costs: Table 1 Estimated Cost of Development For The Mobile ApplicationДокумент5 страниц3.10 Pre-Operation Activities and Costs: Table 1 Estimated Cost of Development For The Mobile ApplicationHazel MosotОценок пока нет
- Activity 1Документ3 страницыActivity 1Hazel MosotОценок пока нет
- SkedДокумент1 страницаSkedHazel MosotОценок пока нет
- Activity 1Документ3 страницыActivity 1Hazel MosotОценок пока нет
- Management.: Chapter 2: Product, Process, and Schedule DesignДокумент4 страницыManagement.: Chapter 2: Product, Process, and Schedule DesignHazel MosotОценок пока нет
- Demo X and R ChartsДокумент3 страницыDemo X and R ChartsHazel MosotОценок пока нет
- Act. Prefi (U-Chart)Документ3 страницыAct. Prefi (U-Chart)Hazel MosotОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Facilities PlanningДокумент3 страницыChapter 1: Introduction To Facilities PlanningHazel MosotОценок пока нет
- Air PollutionДокумент2 страницыAir PollutionHazel MosotОценок пока нет
- Air Pollution SummaryДокумент2 страницыAir Pollution SummaryHazel MosotОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3: Flow System, Activity Relationships, and Space RequirementsДокумент2 страницыChapter 3: Flow System, Activity Relationships, and Space RequirementsHazel MosotОценок пока нет
- Act. Prefi (U-Chart)Документ3 страницыAct. Prefi (U-Chart)Hazel MosotОценок пока нет
- Demo X and R ChartsДокумент3 страницыDemo X and R ChartsHazel MosotОценок пока нет
- Act. Prefi (U-Chart)Документ3 страницыAct. Prefi (U-Chart)Hazel MosotОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Facilities PlanningДокумент3 страницыChapter 1: Introduction To Facilities PlanningHazel MosotОценок пока нет
- Le 1Документ2 страницыLe 1Hazel Mosot100% (2)
- Ie 223l WoodДокумент9 страницIe 223l WoodHazel MosotОценок пока нет
- PLC FormatДокумент38 страницPLC FormatHazel MosotОценок пока нет
- Waiting Lines (Class Problems) PDFДокумент20 страницWaiting Lines (Class Problems) PDFdreanichole100% (3)
- Shaping School Culture Case StudyДокумент7 страницShaping School Culture Case Studyapi-524477308Оценок пока нет
- LAID BACK - Sunshine ReggaeДокумент16 страницLAID BACK - Sunshine ReggaePablo ValdezОценок пока нет
- Meter BaseДокумент6 страницMeter BaseCastor JavierОценок пока нет
- Module ConnectionsДокумент16 страницModule ConnectionsHemilton Cheng Modulos100% (1)
- Two Gentlemen of VeronaДокумент13 страницTwo Gentlemen of Veronavipul jainОценок пока нет
- VC++ Splitter Windows & DLLДокумент41 страницаVC++ Splitter Windows & DLLsbalajisathyaОценок пока нет
- Clasificacion SpicerДокумент2 страницыClasificacion SpicerJoseCorreaОценок пока нет
- Timothy L. Mccandless, Esq. (SBN 147715) : Pre-Trial Documents - Jury InstructionsДокумент3 страницыTimothy L. Mccandless, Esq. (SBN 147715) : Pre-Trial Documents - Jury Instructionstmccand100% (1)
- Articles About Gossip ShowsДокумент5 страницArticles About Gossip ShowssuperultimateamazingОценок пока нет
- V.S.B Engineering College, KarurДокумент3 страницыV.S.B Engineering College, KarurKaviyarasuОценок пока нет
- Determination of Royalty Rates For Trademarks and BrandsДокумент31 страницаDetermination of Royalty Rates For Trademarks and BrandsNicole EstefanieОценок пока нет
- Generator Faults and RemediesДокумент7 страницGenerator Faults and Remediesemmahenge100% (2)
- S1-TITAN Overview BrochureДокумент8 страницS1-TITAN Overview BrochureصصОценок пока нет
- Bruce and The Spider: Grade 5 Reading Comprehension WorksheetДокумент4 страницыBruce and The Spider: Grade 5 Reading Comprehension WorksheetLenly TasicoОценок пока нет
- Awake! - 1964 IssuesДокумент769 страницAwake! - 1964 Issuessirjsslut100% (1)
- Class XI Economics 2011Документ159 страницClass XI Economics 2011Ramita Udayashankar0% (1)
- 18 Month QuestionnaireДокумент6 страниц18 Month QuestionnaireAnnie AbreuОценок пока нет
- CV - Cover LetterДокумент2 страницыCV - Cover LetterMoutagaОценок пока нет
- PHP Listado de EjemplosДокумент137 страницPHP Listado de Ejemploslee9120Оценок пока нет
- Task 1: Choose The Present Simple, The Present Continuous, The PresentДокумент5 страницTask 1: Choose The Present Simple, The Present Continuous, The PresentAlexandra KupriyenkoОценок пока нет
- Sound Culture: COMS 350 (001) - Winter 2018Документ12 страницSound Culture: COMS 350 (001) - Winter 2018Sakshi Dhirendra MishraОценок пока нет
- Phase/State Transitions of Confectionery Sweeteners: Thermodynamic and Kinetic AspectsДокумент16 страницPhase/State Transitions of Confectionery Sweeteners: Thermodynamic and Kinetic AspectsAlicia MartinezОценок пока нет
- SurrealismДокумент121 страницаSurrealismLaurence SamonteОценок пока нет
- Miraculous MedalДокумент2 страницыMiraculous MedalCad work1Оценок пока нет
- B. Complete The Following Exercise With or Forms of The Indicated VerbsДокумент4 страницыB. Complete The Following Exercise With or Forms of The Indicated VerbsLelyLealGonzalezОценок пока нет
- Bank ATM Use CasesДокумент12 страницBank ATM Use Casessbr11Оценок пока нет
- The Organization of PericentroДокумент33 страницыThe Organization of PericentroTunggul AmetungОценок пока нет
- Net 2020Документ48 страницNet 2020Krishan pandeyОценок пока нет
- SMTP/POP3/IMAP Email Engine Library For C/C++ Programmer's ManualДокумент40 страницSMTP/POP3/IMAP Email Engine Library For C/C++ Programmer's Manualadem ademОценок пока нет
- LEGO Group A Strategic and Valuation AnalysisДокумент85 страницLEGO Group A Strategic and Valuation AnalysisRudmila Ahmed50% (2)