Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Dysphagia Causes Jotting
Загружено:
Chinedu H. DuruАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Dysphagia Causes Jotting
Загружено:
Chinedu H. DuruАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Dysphagia causes jotting
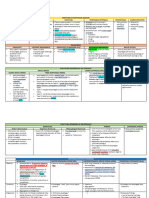
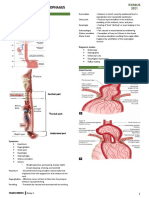
CAUSES OF DYSPHAGIA
NEUROMUSCULAR OBSTRUCTIVE
OROPHARYNGEAL CNS Tumours of
DYSPHAGIA - Bulbar (brainstem) paralysis – caused by - Tongue, buccal cavity, pharynx
cerebrovascular accidents, brainstem Inflammation
tumours, etc. - Stomatitis, tonsillitis,
- Parkinson’s dx pharyngitis, retropharyngeal
- Wilson dx abscess Ludwig’s angina; TB;
- Multiple sclerosis syphilis
PNS Plummer-Vinson syndrome = iron
- Poliomyelitis deficiency anaemia, dysphagia,
- Peripheral neuropathies caused by oesophageal stenosis, and atrophic
Diphtheria, Tetanus, DM, etc glossitis
Motor endplate
- Myasthenia gravis
Muscles of oropharynx -
- Dystrophy
- Myositis
- Metabolic myopathy (e.g. glycogen storage
dx, lipid storage dx)
Upper oesophageal sphincter disorders
- Incomplete relaxation (cricopharyngeal
Achalasia; oculopharyngeal muscular
dystrophy)
- Inadequate opening (cricopharyngeal bar;
Zenker diverticulum)
- Delayed relaxation (familiar dysautonomia)
OESOPHAGEAL Most common Congenital
DYSPHAGIA - Achalasia - Atresia; Stenosis; Webs; Rings
- Diffuse spasm of oesophagus (Schatski ring); Dysphagia
Others lucosuria
- Nutcracker oesophagus Acquired
- Hypertensive LES - Intraluminal - - Foreign body;
- Motility disorders 2ndary to – Scleroderma, Food obstruction
DM, Collagen dxos, & Chagas dx - Intramural - -
Tumours (including
oesophageal carcinoma);
Stricture (Corrosive stricture,
Inflammatory strictures caused
by Reflux oesophagitis or
GERD, Radiation oesophagitis,
foreign body);
Perforation
Diverticular dx – Zenker
diverticulum
Barret’s oesophagus
Plummer-Vinson syndrome
OESOPHAGO- Achalasia - Gastric carcinoma of cardia,
GASTRIC fundus or upper lesser curvature
DYSPHAGIA - Gastric volvulus
- Stricture
PARAOESOPHAGEAL - Sublingual dermoid
/ EXTRAMURAL - Cervical spine dx
DYSPHAGIA - Thyromegaly / Goitre
(Hashimoto’s thyroiditis)
- Lymphadenopathy (cervical or
mediastinal)
- Mediastinal tumour
- Left atrial enlargement
Oropharyngeal dysphagia
- @ the level of oropharynx
- @ the voluntary phase of swallowing
Oesophageal dysphagia
- @ oesophageal level
- @ involuntary phase of swallowing
Neuro-muscular dysphagia
- There is paralysis or weakness of the oropharyngeal or oesophageal muscles leading to Esophageal Motility Disorder
(EMD)
- Commonest cause of oropharyngeal dysphagia
Obstructive dysphagia
- Dysphagia due to Obstruction of the oesophagus by luminal, intramural and extramural lesions
Zenker diverticulum (pharyngoesophageal diverticulum)
- Most common diverticulum of the oesophagus
- a pulsion diverticulum developing between the inferior pharyngeal constrictor and the cricopharyngeus muscle.
NOTE: Plummer-Vinson syndrome is a.k.a. Patterson-Kelly syndrome
Вам также может понравиться
- 1.3 DysphagiaДокумент37 страниц1.3 Dysphagiavk4bftgg2kОценок пока нет
- Lianne Beck, MD Assistant Professor Emory Family MedicineДокумент52 страницыLianne Beck, MD Assistant Professor Emory Family MedicineTauqeer IqbalОценок пока нет
- Throat PowerpointДокумент29 страницThroat Powerpointminci sensei100% (8)
- MED Diseases of The EsophagusДокумент4 страницыMED Diseases of The EsophagusJulie Anne AciertoОценок пока нет
- ThyroxineДокумент37 страницThyroxinedfdxgfcvhbОценок пока нет
- GI Sympt Mokhtar (2015)Документ85 страницGI Sympt Mokhtar (2015)Abdelrahman MokhtarОценок пока нет
- Surgery OSCE PDFДокумент26 страницSurgery OSCE PDFWisal Merghani100% (4)
- Electrolyte ChartДокумент3 страницыElectrolyte Chartsurviving nursing schoolОценок пока нет
- Thymus NeoplasiaДокумент3 страницыThymus NeoplasiaHimalaya AggarwalОценок пока нет
- Neuro-Onkologi: Bagian/SMF Saraf FK-UGM/RS Dr. Sardjito YogyakartaДокумент59 страницNeuro-Onkologi: Bagian/SMF Saraf FK-UGM/RS Dr. Sardjito YogyakartaNovasiska Indriyani HutajuluОценок пока нет
- Dysphagia: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasДокумент39 страницDysphagia: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasRaviОценок пока нет
- Long Case DysphagiaДокумент3 страницыLong Case DysphagiaNadia SalwaniОценок пока нет
- Sem 3 Medical Science b4 ExmДокумент2 страницыSem 3 Medical Science b4 ExmKelly YeowОценок пока нет
- Vincristine Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыVincristine Drug StudyNiziu BearsОценок пока нет
- Stridor Kabilan 150810151525 Lva1 App6892Документ31 страницаStridor Kabilan 150810151525 Lva1 App6892Aisha HassanОценок пока нет
- Dysphagia (Definition and Anatomy) : Muhammad Zaid Bin Zamri 135284Документ56 страницDysphagia (Definition and Anatomy) : Muhammad Zaid Bin Zamri 135284Nurul Najwa ZulkifliОценок пока нет
- 2012 The Patient History - Evidence Based Appoach-368-376 PDFДокумент9 страниц2012 The Patient History - Evidence Based Appoach-368-376 PDFJoseph AndradeОценок пока нет
- Congenital SyphilisДокумент3 страницыCongenital SyphilisLakshya J BasumataryОценок пока нет
- Gastrointestinal System: Symptomatology of TheДокумент85 страницGastrointestinal System: Symptomatology of TheAbdelrahman MokhtarОценок пока нет
- HomeworkДокумент2 страницыHomeworkpzmatias15Оценок пока нет
- Materi Dr. Muryanto - HemoroidsДокумент20 страницMateri Dr. Muryanto - HemoroidsAndria SaputraОценок пока нет
- Inv A Sion Pha Se: Rabies PatophysiologyДокумент1 страницаInv A Sion Pha Se: Rabies PatophysiologyRudelsa Agcolicol LangamanОценок пока нет
- RevisionДокумент67 страницRevisionPrasanna DeshiniОценок пока нет
- Disease Characteristics of The Pain Other Associated Symptoms Main Physical Findings Sonography Findings AdenomyosisДокумент2 страницыDisease Characteristics of The Pain Other Associated Symptoms Main Physical Findings Sonography Findings AdenomyosisaliyahОценок пока нет
- Git DisordersДокумент11 страницGit DisordersSara JosephОценок пока нет
- Upper GITДокумент13 страницUpper GITKiara Govender100% (1)
- Chest Wall Deformity and Pleural Diseases 2020Документ7 страницChest Wall Deformity and Pleural Diseases 2020Janna Trisha ApareceОценок пока нет
- Cpe Ecfvg Appendix of Common DiagnosesДокумент9 страницCpe Ecfvg Appendix of Common DiagnosesMayank Mj PatelОценок пока нет
- Trematodes (Flatworms)Документ6 страницTrematodes (Flatworms)Woo Rin ParkОценок пока нет
- E-Mental ScriДокумент30 страницE-Mental ScriGisselle Mildred PauloОценок пока нет
- Catatan Orthopedi AriefДокумент8 страницCatatan Orthopedi Ariefmiwer 765Оценок пока нет
- Inv A Sion Pha Se: Bill Julius Samuel G. Alferez BSN IiiДокумент1 страницаInv A Sion Pha Se: Bill Julius Samuel G. Alferez BSN IiiRudelsa Agcolicol LangamanОценок пока нет
- Genetics Dysmorphology in Pediatrics - MedicoNotesДокумент1 страницаGenetics Dysmorphology in Pediatrics - MedicoNotesJ KPОценок пока нет
- Esophageal DysphagiaДокумент3 страницыEsophageal Dysphagianevelle4667Оценок пока нет
- QuizletДокумент67 страницQuizletnaimОценок пока нет
- Diseases of Esophagus.Документ3 страницыDiseases of Esophagus.Isabel Castillo100% (2)
- Osmosis Esophageal Disease PDF Amm DR NotesДокумент13 страницOsmosis Esophageal Disease PDF Amm DR NotestajammalОценок пока нет
- Pedia - Intensive PhaseДокумент2 страницыPedia - Intensive Phasepasabay270Оценок пока нет
- Antihelmintic Drugs Humayunz CollectionДокумент2 страницыAntihelmintic Drugs Humayunz CollectionTatenda BrunoОценок пока нет
- A UGI (Blue Keyword Pyq)Документ3 страницыA UGI (Blue Keyword Pyq)Irsyad SiddeeqОценок пока нет
- MetoclopramideДокумент2 страницыMetoclopramideGinena BelarminoОценок пока нет
- Midterm (Ramadan Edition)Документ6 страницMidterm (Ramadan Edition)kpf42mcjgvОценок пока нет
- Presentacion GastrointestinalДокумент228 страницPresentacion GastrointestinalNb + XB = AVОценок пока нет
- Electrolyte ChartДокумент2 страницыElectrolyte ChartJenny Varghese100% (4)
- BIMC Update PresentationДокумент25 страницBIMC Update PresentationWahyuОценок пока нет
- Esophagus Lecture Fatima NEW 2015Документ31 страницаEsophagus Lecture Fatima NEW 2015Aileen EmyОценок пока нет
- Upper Gastrointestinal Congenital MalformationsДокумент8 страницUpper Gastrointestinal Congenital Malformationsaasingh7800Оценок пока нет
- Stenosis, Scleroma, TracheostomyДокумент22 страницыStenosis, Scleroma, Tracheostomysimi yОценок пока нет
- Esophageal Motility Disorders: DR / Hytham NafadyДокумент31 страницаEsophageal Motility Disorders: DR / Hytham NafadyRabie MeramОценок пока нет
- Approach To VomitingДокумент4 страницыApproach To VomitingShamen KohОценок пока нет
- DysphagiaДокумент2 страницыDysphagiaKimberlyLaw95Оценок пока нет
- Study Guide Exam 1 Know The Following Combining FormsДокумент2 страницыStudy Guide Exam 1 Know The Following Combining FormsRuth ChenОценок пока нет
- Etiologi Sesak Nafas (Dyspnea) - AlmaДокумент2 страницыEtiologi Sesak Nafas (Dyspnea) - AlmaAnonymous gvEtLsОценок пока нет
- Vasculitis: Disorder Vessels Pathology Presentation Test TX OtherДокумент3 страницыVasculitis: Disorder Vessels Pathology Presentation Test TX OthermcwnotesОценок пока нет
- Endocrine/ Metabolic Infectious/Inflammatory Neurological GastroentericДокумент1 страницаEndocrine/ Metabolic Infectious/Inflammatory Neurological Gastroentericjjj hhhОценок пока нет
- Dysphagia (ENT Posting)Документ36 страницDysphagia (ENT Posting)rajhiniОценок пока нет
- Uptodate: Chronic Kidney DiseaseДокумент13 страницUptodate: Chronic Kidney DiseaseAtiqah ShahОценок пока нет
- Cardio To C OgraphyДокумент6 страницCardio To C OgraphyChinedu H. DuruОценок пока нет
- Solutions - Iit-Jee-2011: Code: 2: Chemistry Paper - 1Документ5 страницSolutions - Iit-Jee-2011: Code: 2: Chemistry Paper - 1Chinedu H. DuruОценок пока нет
- Signs & Symptom of Shock: Hypovolemic Shock Septic Shock Cardiogenic Shock Neurogenic Shock Anaphylactic Head & NeckДокумент2 страницыSigns & Symptom of Shock: Hypovolemic Shock Septic Shock Cardiogenic Shock Neurogenic Shock Anaphylactic Head & NeckChinedu H. DuruОценок пока нет
- Anaesthesia JottingДокумент2 страницыAnaesthesia JottingChinedu H. DuruОценок пока нет
- MCQ CommДокумент5 страницMCQ CommChinedu H. DuruОценок пока нет
- Urethral Stricture DiseaseДокумент4 страницыUrethral Stricture DiseaseChinedu H. DuruОценок пока нет
- Traumatic: Urology Stuff Urethral Stricture DiseaseДокумент4 страницыTraumatic: Urology Stuff Urethral Stricture DiseaseChinedu H. DuruОценок пока нет
- Diarrhoeal Diseases: A Seminar Presentation by (Renal Unit) Medical Students DATE: December 2013Документ43 страницыDiarrhoeal Diseases: A Seminar Presentation by (Renal Unit) Medical Students DATE: December 2013Chinedu H. DuruОценок пока нет
- Metronidazole: Antibiotic Class: Antimicrobial SpectrumДокумент4 страницыMetronidazole: Antibiotic Class: Antimicrobial SpectrumChinedu H. DuruОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology Course OutlineДокумент2 страницыPharmacology Course OutlineChinedu H. DuruОценок пока нет
- Immunopathology: Normal Immune ResponseДокумент13 страницImmunopathology: Normal Immune ResponseChinedu H. DuruОценок пока нет
- Gastroenterology - Jaundice PDFДокумент2 страницыGastroenterology - Jaundice PDFMonica J Ortiz PereiraОценок пока нет
- Hepatology MRCP1Документ87 страницHepatology MRCP1Raouf Ra'fat SolimanОценок пока нет
- S3 CP2 Liver Disease TestДокумент4 страницыS3 CP2 Liver Disease Test2013SecBОценок пока нет
- Acute AbdomenДокумент48 страницAcute Abdomenjwan ahmedОценок пока нет
- Ulcerative Colitis Homeopathic Treatment PDFДокумент3 страницыUlcerative Colitis Homeopathic Treatment PDFhomeo pathyОценок пока нет
- Abdominal ExaminationДокумент25 страницAbdominal ExaminationASAP teleОценок пока нет
- Ocluzie Intestinala Prin Stenoza Extrinseca de Colon TransversДокумент8 страницOcluzie Intestinala Prin Stenoza Extrinseca de Colon TransversClaudia DanielaОценок пока нет
- Approach To Acute AbdomenДокумент50 страницApproach To Acute AbdomenAndie ArrОценок пока нет
- Fissure Treatment in MumbaiДокумент4 страницыFissure Treatment in MumbaiSambit ClinicОценок пока нет
- Penerapan Akupresur Pada Titik P6: Terhadap Emesis Gravidarum Pada Ibu Hamil Trimester 1Документ7 страницPenerapan Akupresur Pada Titik P6: Terhadap Emesis Gravidarum Pada Ibu Hamil Trimester 1Rizkia AuliaОценок пока нет
- DR Pradeep Jain Fortis Hospital DelhiДокумент21 страницаDR Pradeep Jain Fortis Hospital DelhiJessica RochaОценок пока нет
- Mrcs HepatobiliaryДокумент40 страницMrcs HepatobiliaryAdebisiОценок пока нет
- PR BleedДокумент20 страницPR BleedCathy KayОценок пока нет
- Acute AbdomenДокумент31 страницаAcute AbdomenTriono AssamsulОценок пока нет
- Abdominal PainДокумент12 страницAbdominal PainGeeza Gem VicencioОценок пока нет
- Acute CholangitisДокумент9 страницAcute CholangitisMike GОценок пока нет
- GastritisДокумент17 страницGastritisSri Wahyuni HarliОценок пока нет
- Pancreatic AbscessДокумент23 страницыPancreatic Abscessapi-196413370% (2)
- Gastritis. Ulcer DiseaseДокумент60 страницGastritis. Ulcer DiseaseShambhu AshokОценок пока нет
- Bologna Guidelines For Diagnosis and ManagementДокумент20 страницBologna Guidelines For Diagnosis and ManagementTony HardianОценок пока нет
- GI BleedingДокумент37 страницGI BleedingAnamul MasumОценок пока нет
- La Cirrhose Alcoolique: Aspects Épidémiologiques, Diagnostiques Et ÉvolutifsДокумент3 страницыLa Cirrhose Alcoolique: Aspects Épidémiologiques, Diagnostiques Et ÉvolutifsLoic MCОценок пока нет
- Acute AbdomenДокумент14 страницAcute AbdomenSaha DirllahОценок пока нет
- Illness Script For IbsДокумент2 страницыIllness Script For Ibsapi-466626583Оценок пока нет
- Ileus ObstructionДокумент22 страницыIleus ObstructionfitrahОценок пока нет
- 9 Assessment of Gastrointestinal Function and Management of Gastrointestinal DisordersДокумент61 страница9 Assessment of Gastrointestinal Function and Management of Gastrointestinal DisordersNoor MajaliОценок пока нет
- Pediatrics - Baby Emesis PDFДокумент2 страницыPediatrics - Baby Emesis PDFDaniel FischerОценок пока нет
- 25 Common Surgical ConditionsДокумент3 страницы25 Common Surgical ConditionsMu AbОценок пока нет
- Adenoma Velloso y ApendicitisДокумент4 страницыAdenoma Velloso y ApendicitisLuis MenesesОценок пока нет
- Dyspepsia GastritisДокумент80 страницDyspepsia GastritisSoumya Ranjan PandaОценок пока нет