Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Dale Carnegie - How To Win Friends Influence People - Pocket (1990)
Загружено:
muruganaviatorОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Dale Carnegie - How To Win Friends Influence People - Pocket (1990)
Загружено:
muruganaviatorАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
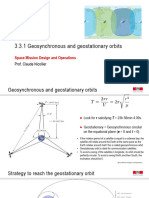
AE 240/338/415/713 Practice Session No.
11 –Advanced Orbital Manoeuvres
1. A spacecraft is in an elliptic orbit with perigee at 100 km altitude and apogee at 250 km
altitude above the Earth’s surface, having perigee argument of 30o. Determine the magnitude
and direction of velocity impulse needed at perigee to change the argument to 60o.
2. Determine the velocity impulses required for Hohmann transfer method for transfer of a
satellite from low Earth orbit of radius 1.03 RE to an orbit around moon with radius 60 RE.
Next perform the same manoeuvre by (1) first escaping to infinity on a parabola, (2) then
performing zero ‘∆v’ approach to the moon’s orbit on another parabola and (3) finally,
circularizing the moon’s orbit.
3. On launch the space shuttle does not directly inject into the final mission orbit, but the
main engine shutdown occurs when its apogee is at 100 km altitude and perigee at 30 km
altitude above Earth’s surface. Determine the velocity impulses necessary to (1) first transfer
it into an elliptic orbit with perigee at 100 km altitude and apogee at 250 km altitude and (2)
next circularize the orbit at 250 km altitude.
4. Determine the velocity impulses required for Hohmann transfer method for transfer of a
satellite from low Earth orbit of radius 1.03 RE to an orbit around moon with radius 60 RE.
Next perform the same manoeuvre by (1) first escaping to infinity on a parabola, (2) then
performing zero ‘∆v’ approach to the moon’s orbit on another parabola and (3) finally,
circularizing the moon’s orbit.
5. A low-thrust orbit-transfer vehicle is in a circular orbit with radius ‘a’, and is attempting to
change its inclination ‘i’. If the thrust profile is that A = -A for -90o < θ +90o and A = +A for
90o < θ < 270o, and is normal to the orbital plane, show that change in angular momentum
during one orbital cycle and associated incremental inclination change are;
a3 4a 2 A
∆H = 4 Aa qˆ; ∆i =
µ µ
6. A satellite with perigee of 552 km altitude and apogee of 2208 km altitude needs to make a
10o plane change when the spacecraft reaches its apogee. Determine the ‘∆V’ required for the
manoeuvre and compare it with the impulse required at perigee for performing the same
manoeuvre of plane change.
7. A satellite leaves a circular parking orbit around Earth, having initial inclination ‘i’, to
achieve a circular geosynchronous equatorial orbit, using Hohmann transfer method. The
required inclination change is done partly in the first change and remaining in the second
change. Determine the total velocity change needed to complete the orbit change. Also obtain
the optimal breakup of ∆i1 & ∆i2 that minimizes the total ∆V.
8. A geosynchronous satellite, over a period of one mean solar day, changes its orbit such that
while its apogee remains the same, perigee reduces by 1%. If the orbit is to be circularized at
the end of each day when sun is overhead only for 15 minutes, determine the size of the solar
sail that would achieve this objective.
Вам также может понравиться
- Assignment 3: Task #1 Has (10 Parts) That Corresponds To CLO # 2 For A Total of 30 PointsДокумент2 страницыAssignment 3: Task #1 Has (10 Parts) That Corresponds To CLO # 2 For A Total of 30 PointsWaqas AliОценок пока нет
- Space DynamicsДокумент4 страницыSpace DynamicsShubham ShekharОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Remote Sensing Orbital CharacteristicsДокумент30 страницIntroduction to Remote Sensing Orbital CharacteristicsSaurabh SinghОценок пока нет
- Assignment - 1Документ21 страницаAssignment - 1shoyeb ahmedОценок пока нет
- Orbital MechanicsДокумент103 страницыOrbital MechanicsJL1206Оценок пока нет
- Space Mechanics by Lokesh KumarДокумент63 страницыSpace Mechanics by Lokesh Kumarloke116100% (1)
- Satellite Orbital ParametersДокумент30 страницSatellite Orbital ParametersNeil LewisОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Satellite Communications: Satellite LaunchingДокумент36 страницChapter 2 Satellite Communications: Satellite Launchingfadzlihashim87Оценок пока нет
- GYRO Key (Q - A)Документ10 страницGYRO Key (Q - A)Chirattakkattu HouseОценок пока нет
- Assignment Task 3 Answer PhysicsДокумент3 страницыAssignment Task 3 Answer PhysicsCallumОценок пока нет
- Calculating orbital trajectories using universal variables and perturbationsДокумент5 страницCalculating orbital trajectories using universal variables and perturbationsDarry BlanciaОценок пока нет
- 3.3. Special OrbitsДокумент18 страниц3.3. Special OrbitsVirginiaОценок пока нет
- SatComm Lec5Документ21 страницаSatComm Lec5ishac kayaОценок пока нет
- MA-101 ProjectДокумент14 страницMA-101 ProjectMohul KatyalОценок пока нет
- Satellite Communication: Topic: Orbit DynamicsДокумент18 страницSatellite Communication: Topic: Orbit DynamicsMohit SharmaОценок пока нет
- Unit I MechanicsДокумент83 страницыUnit I MechanicsHome SpaceОценок пока нет
- L19 InterPlanetДокумент15 страницL19 InterPlanetPrakashChouhanОценок пока нет
- 20ASE431A L10 O OM 4 Orbit ManeuversДокумент33 страницы20ASE431A L10 O OM 4 Orbit ManeuverssustainerspenОценок пока нет
- Aerospace Engineering Question BankДокумент9 страницAerospace Engineering Question BanksanjayОценок пока нет
- AS3050 - Assignment 3 - S-C Att Dyn - Orb MechДокумент2 страницыAS3050 - Assignment 3 - S-C Att Dyn - Orb MechSneakyRiderОценок пока нет
- Orbital Mechanics GuideДокумент17 страницOrbital Mechanics Guidevelan2745100% (1)
- Satellite Orbital MechanicsДокумент29 страницSatellite Orbital MechanicsmojammeljoyОценок пока нет
- Kepler's Laws: 1.2.1 Kepler's Law IntroductionДокумент6 страницKepler's Laws: 1.2.1 Kepler's Law IntroductionsubbuОценок пока нет
- UNIT 1 PPT Satellite CommunicationДокумент34 страницыUNIT 1 PPT Satellite Communicationselvi100% (1)
- Introduction To Astronautics: Sissejuhatus KosmonautikasseДокумент33 страницыIntroduction To Astronautics: Sissejuhatus Kosmonautikassegirithik14Оценок пока нет
- Orbital MechanicsДокумент33 страницыOrbital MechanicsKatleho Siyabonga ButheleziОценок пока нет
- EE 418, Lecture 2Документ6 страницEE 418, Lecture 2MMhammed AlrowailyОценок пока нет
- Circular MotionДокумент4 страницыCircular Motionryan valerioОценок пока нет
- Introduction To AstronauticsДокумент44 страницыIntroduction To AstronauticsUgur GuvenОценок пока нет
- Ec 8094 Satellite Communication - Course MaterialДокумент161 страницаEc 8094 Satellite Communication - Course Materialarun mОценок пока нет
- Orbit Transfers and Interplanetary TrajectoriesДокумент12 страницOrbit Transfers and Interplanetary Trajectoriesletter_ashish4444Оценок пока нет
- Eccentric Behavior of Nearly Frozen OrbitsДокумент13 страницEccentric Behavior of Nearly Frozen Orbitsdarin koblickОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Satellite OrbitsДокумент41 страницаIntroduction To Satellite OrbitsAngélica María Salazar Madrigal100% (1)
- Lec 1Документ43 страницыLec 1Yasmin HeppaОценок пока нет
- Satellite Orbits: Kepler's LawДокумент18 страницSatellite Orbits: Kepler's LawhelenОценок пока нет
- Look Angle DeterminationДокумент30 страницLook Angle DeterminationgantayatОценок пока нет
- Unit 1Документ11 страницUnit 1Anuja AnuОценок пока нет
- Orbital Mechanics and LaunchersДокумент53 страницыOrbital Mechanics and Launchersali70ymailОценок пока нет
- Pratt & Bostian - PPДокумент3 страницыPratt & Bostian - PPapi-26783388Оценок пока нет
- Planetary MotionДокумент7 страницPlanetary Motionsuhas048Оценок пока нет
- Lab II: Exploring Orbital Phenomena in the Earth-Moon SystemДокумент8 страницLab II: Exploring Orbital Phenomena in the Earth-Moon SystemAdolfo Ricardo Piminchumo SausaОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Satellite Communication Orbits and ParametersДокумент15 страницIntroduction to Satellite Communication Orbits and Parametersapollo eceОценок пока нет
- Satellite CommunicationsДокумент202 страницыSatellite CommunicationsSachin Korgaonkar50% (2)
- More On Orbits: R MV R M GM R GM VДокумент2 страницыMore On Orbits: R MV R M GM R GM Vdarin2carrОценок пока нет
- Satellite Communication LECTURE NOTESДокумент202 страницыSatellite Communication LECTURE NOTESSindhu Velayudham100% (1)
- Mid Sem Questions With SolutionsДокумент5 страницMid Sem Questions With SolutionsAakansha SuchittaОценок пока нет
- Mid Sem QuestionsДокумент1 страницаMid Sem QuestionsAakansha SuchittaОценок пока нет
- Orbital MechanicsДокумент47 страницOrbital Mechanicsrvanande21Оценок пока нет
- Orbital Mechanics and LaunchersДокумент42 страницыOrbital Mechanics and LaunchersidrishshaikОценок пока нет
- Unit IiДокумент36 страницUnit Iipradnya patilОценок пока нет
- Orbital Mechanics in Class JigsawДокумент4 страницыOrbital Mechanics in Class JigsawabdishОценок пока нет
- PH 103 Fall 2008:, Fourth Week Uniform Circular MotionДокумент6 страницPH 103 Fall 2008:, Fourth Week Uniform Circular MotionAli AhmadОценок пока нет
- AE2014 Introduction To AstronauticsДокумент4 страницыAE2014 Introduction To AstronauticsStefan LacatusuОценок пока нет
- Gyro Theory by Capt. Sirajul MuneerДокумент8 страницGyro Theory by Capt. Sirajul Muneeramalunni147Оценок пока нет
- Module1 - Satellite Communication VTU 7th SemДокумент127 страницModule1 - Satellite Communication VTU 7th Semrohan gowdaОценок пока нет
- Topic 7 GravitationДокумент43 страницыTopic 7 GravitationfrazatasОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSОценок пока нет
- Manned Mars Landing: Presentation to the Space Task Group - 1969От EverandManned Mars Landing: Presentation to the Space Task Group - 1969Оценок пока нет
- TheBritishEmpire 10061087 PDFДокумент264 страницыTheBritishEmpire 10061087 PDFmuruganaviatorОценок пока нет
- Bhakti Shastri Slokas Important-VersesДокумент12 страницBhakti Shastri Slokas Important-Versesnik250890Оценок пока нет
- MG HislifeandtimesДокумент572 страницыMG HislifeandtimesRajesh RanjanОценок пока нет
- C. J. Van Vliet - The Coiled Serpent (1939)Документ470 страницC. J. Van Vliet - The Coiled Serpent (1939)muruganaviator100% (1)
- Characteristics of The Residual Stress Distributio PDFДокумент7 страницCharacteristics of The Residual Stress Distributio PDFmuruganaviatorОценок пока нет
- Offshore Pipe Lines Complete DetailsДокумент4 страницыOffshore Pipe Lines Complete DetailsmuruganaviatorОценок пока нет
- 7.surface Energy and The Contact of Elastic Solids 1971 PDFДокумент14 страниц7.surface Energy and The Contact of Elastic Solids 1971 PDFmuruganaviatorОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13Документ4 страницыChapter 13muruganaviatorОценок пока нет
- A Textbook of Agronomy - B. Chandrasekaran Et Al - 2010 - (New Age)Документ856 страницA Textbook of Agronomy - B. Chandrasekaran Et Al - 2010 - (New Age)José Pedro Casagrande Trentín100% (1)
- Stress Functions ChoiceДокумент4 страницыStress Functions ChoiceAnonymous JJaNDZoОценок пока нет
- English PDFДокумент223 страницыEnglish PDFmuruganaviatorОценок пока нет
- Plate and Shell PDFДокумент77 страницPlate and Shell PDFJamshid PishdadiОценок пока нет
- (Studies in Corpus Linguistics) Sandra Götz-Fluency in Native and Nonnative English Speech-John Benjamins Publishing Company (2013) PDFДокумент263 страницы(Studies in Corpus Linguistics) Sandra Götz-Fluency in Native and Nonnative English Speech-John Benjamins Publishing Company (2013) PDFmuruganaviatorОценок пока нет
- Feel The Fear and Do It AnywayДокумент7 страницFeel The Fear and Do It AnywaymuruganaviatorОценок пока нет
- 2015 2017 BooklistДокумент13 страниц2015 2017 BooklistGezimОценок пока нет
- Tamil Catalogue 2014 15Документ14 страницTamil Catalogue 2014 15EaswaranОценок пока нет
- 3 CF 5Документ4 страницы3 CF 5muruganaviatorОценок пока нет
- Kakan A4 PDFДокумент176 страницKakan A4 PDFmuruganaviatorОценок пока нет
- Meshing Introduction v81 601 PDFДокумент18 страницMeshing Introduction v81 601 PDFpsychoachilles11314Оценок пока нет
- Feel The Fear and Do It AnywayДокумент35 страницFeel The Fear and Do It AnywaymuruganaviatorОценок пока нет
- Tamil Baby NamesДокумент24 страницыTamil Baby NamesmuruganaviatorОценок пока нет
- .Creating A Hunger Driven Smartphone Market by XiaomiДокумент6 страниц.Creating A Hunger Driven Smartphone Market by XiaomimuruganaviatorОценок пока нет
- Wahlberg WilleДокумент33 страницыWahlberg WillemuruganaviatorОценок пока нет
- Kirsch ProblemДокумент8 страницKirsch ProblemmuruganaviatorОценок пока нет
- Wahlberg WilleДокумент33 страницыWahlberg WillemuruganaviatorОценок пока нет
- MUHURTA by BV - RAMANДокумент109 страницMUHURTA by BV - RAMANattikka100% (8)
- Kamarajar Books BibliographyДокумент38 страницKamarajar Books Bibliographymuruganaviator0% (1)
- Mathematica Workshop 2016Документ2 страницыMathematica Workshop 2016muruganaviatorОценок пока нет
- Terrain Awareness and Warning Systems-TAWS: Buyer's GuideДокумент8 страницTerrain Awareness and Warning Systems-TAWS: Buyer's GuideDanielОценок пока нет
- Practices Test 3Документ4 страницыPractices Test 3Văn phú NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Bontorin 2016Документ9 страницBontorin 2016Keyla MaydeeОценок пока нет
- 1 2 5 A AerodynamicforcesДокумент2 страницы1 2 5 A Aerodynamicforcesapi-325609547Оценок пока нет
- NASA Space Shuttle STS-113 Press KitДокумент111 страницNASA Space Shuttle STS-113 Press KitOrion2015Оценок пока нет
- Astronomy NotebookДокумент50 страницAstronomy NotebookChaiat5Оценок пока нет
- EASA Part 66 Mechanical ModulesДокумент3 страницыEASA Part 66 Mechanical ModulesCharbel SayyarОценок пока нет
- Sungrazing COMETSДокумент116 страницSungrazing COMETSOscar GómezОценок пока нет
- Aircraft Manuf Materials (Composites)Документ12 страницAircraft Manuf Materials (Composites)Abhilash HotaОценок пока нет
- Beechcraft Model 18 - WikipediaДокумент21 страницаBeechcraft Model 18 - Wikipediafw190a40% (1)
- Blackhawk EPIC XPR Series BrochureДокумент3 страницыBlackhawk EPIC XPR Series Brochurealbucur100% (1)
- A 318Документ213 страницA 318Paul Dan PribacОценок пока нет
- Giriraj Himachal NewspaperДокумент12 страницGiriraj Himachal NewspaperSahil vermaОценок пока нет
- 10 Future Inventions Everyones Been Waiting ForДокумент10 страниц10 Future Inventions Everyones Been Waiting Forapi-234509659Оценок пока нет
- Airborne TrailblazerДокумент244 страницыAirborne Trailblazerapi-3819355Оценок пока нет
- Retell LectureДокумент2 страницыRetell LecturemohamadОценок пока нет
- Quick quiz on discovering the universeДокумент2 страницыQuick quiz on discovering the universebinduОценок пока нет
- NASA - sp8032 - Space Vehicle Design Criteria - Buckling of Thin Walled Double Curved Shells PDFДокумент37 страницNASA - sp8032 - Space Vehicle Design Criteria - Buckling of Thin Walled Double Curved Shells PDFNasos MasourasОценок пока нет
- YBBNДокумент48 страницYBBNzacklawsОценок пока нет
- Key Stage 3 Ks3 ScienceДокумент36 страницKey Stage 3 Ks3 Sciencerubini_m100% (1)
- Three Stages of Prediction: Yoga, Period, Double TransitДокумент5 страницThree Stages of Prediction: Yoga, Period, Double Transitsubbupisipati100% (1)
- Re-entry Vehicle Design and Aerodynamic PrinciplesДокумент17 страницRe-entry Vehicle Design and Aerodynamic PrinciplesAkshat JaniОценок пока нет
- Topic: Remote Sensing Platforms: Dr. Md. NazimДокумент17 страницTopic: Remote Sensing Platforms: Dr. Md. NazimShubham sinhaОценок пока нет
- SCIENCE 4th RatingДокумент34 страницыSCIENCE 4th RatingMichael Joseph Santos100% (3)
- XB 70 PDFДокумент16 страницXB 70 PDFKIRU SILVIUОценок пока нет
- Apollo 7 PAO Commentary TranscriptДокумент1 158 страницApollo 7 PAO Commentary TranscriptBob AndrepontОценок пока нет
- S-13 Rocket - WikipediaДокумент2 страницыS-13 Rocket - WikipediasorinartistuОценок пока нет
- 606877main - FS 2011 11 057 JSC Astro - TRNGДокумент1 страница606877main - FS 2011 11 057 JSC Astro - TRNGElaineAmaralОценок пока нет