Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
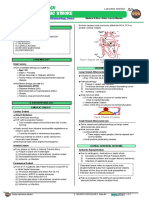
Cardiovascular Pathology: Hypertensive Retinopathy
Загружено:
Tom TsouОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cardiovascular Pathology: Hypertensive Retinopathy
Загружено:
Tom TsouАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cardiovascular Pathology
Name Definition
Hypertensive Emergency Severe hypertension with end-organ damage
(Usually exacerbation of Benign HTN)
- withdrawal of short-acting
antihypertensive drug (propranolol,
clonidine, beta-blockers)
- sympathomimetic drugs: cocaine,
amphetamine
- Pheochromocytoma
- Pre/eclampsia
End Organ Damage:
- Kidney renal failure/hematuria
- Heart Acute coronary syndrome (MI),
CHF w pulm. Edema, aortic dissection,
- Lungs Pulm. Edema
Clinical:
- Severe headache, visual disturbance,
altered mentation
Fundoscopy: Hypertensive Retinopathy
- Moderate: retinal hemorrhage, exudate,
cotton wool spots
- Severe: Papilledema
Acute Target: Organ Damage
- Brain
i) Stroke: lacunar infarct, intracerebral
& subarachnoid hemorrhage &
Hypertensive encephalopathy
- Heart & Blood Vessel
i) Acute Coronary Syndrome (MI)
ii) Acute LHF
iii) Aortic Dissection
- Kidney
i) Acute Hypertensive/Malignant
Nephrosclerosis
Hypertensive Urgency Severe hypertension in asymptomatic
WITHOUT ACUTE TARGET ORGAN DAMAGE
(asymp. HTN)
Fundoscopy: Moderate Hypertensive
Retinopathy (ie: no papilledema)
Requires different type of treatment
Essential (90-95%) Secondary (5-10%)
No single identifiable cause i) Renal Disease
1) Genetic Factors a. Renal Chronic Stenosis
(decreased glomerular flow & pressure
2) Reduced Renal Sodium Excretion in afferent arteriole – RENIN secretion
- ^ Fluid volume, CO & PR ^ BP by Juxtaglomerular cells)
3) Vasoconstrictive Influences Atherosclerosis
a. Environmental Factors (stress, - Elderly men (smoking, high
obesity, smoking etc.) cholesterol levels)
Fibromuscular Dysplasia
- Young female (string of beads)
- Focal stenosis & dilation
- Focal medial hyperplasia w
thickened fibromuscular ridges
adjacent
ii) Endocrine Disease
a. Pheochromocytoma
(nor/epinephrine)
iii) Vascular Disease
a. Coarctation of aorta
Effects of Hypertension on Heart
Increased systemic vascular resistance (afterload)
- Concentric Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (decreased LV Function)
- HTN accelerates atherosclerosis (^ Coronary Artery Disease)
i) ^ heart weight ( F >250 gm, M > 300 gm) -- ^ LV wall thickness (>1.5cm)
ii) Cardiohypertrophy
a. ^ cell size (diameter) & boxcar nuclei
iii) Interstitial Fibrosis (advanced)
iv) Heart Failure (cause of death)
Vascular Pathology in Essential Hypertension
Hyaline Arterio- & Arteriosclerosis “glass” HALLMARK OF BENIGN HYPERTENSION
- Thickening of wall of small muscular artery/arteriole
- Accum. Of pink, homogenous (hyaline) material
- Lumen narrowing & loss of underlying wall structure
Renal Pathology Hypertensive Nephrosclerosis/Benign Nephrosclerosis
- Hyaline arterio- & arteriosclerosis
Morphology
1) Glomerular sclerosis, hyalinization & tubular atrophy, arterial thickening, scattered
lymphocytic infiltrate
2) Advanced: small kidney w granular surface (preserved glomeruli) “granular contracted
kidney”
Clinical: Proteinuria chronic renal failure
Malignant (Acute Hypertensive) Nephrosclerosis
- Arteriolar & Glomerular Fibrinoid Necrosis
- Hyperplastic Arteriosclerosis
- Microinfarction & micro-hemorrhage (Flea Bitten Kidney)
- W/o treatment acute renal failure
Hypertensive Encephalopathy
- When: BP: 240/140+ w neurologic (eg: Confusion)
o High BP dilation of small cerebral arteries/arterioles ^ permeability
Cerebral edema Raised intracranial pressure
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES)
o No focal lesion (ie: no brain infarct or hemorrhage)
- Progress to coma & death
Вам также может понравиться
- Aicardi’s Diseases of the Nervous System in Childhood, 4th EditionОт EverandAicardi’s Diseases of the Nervous System in Childhood, 4th EditionAlexis ArzimanoglouОценок пока нет
- Arterial Hypertension Eng PDFДокумент29 страницArterial Hypertension Eng PDFagustinaw1981Оценок пока нет
- Cardio Day 3 TemplateДокумент24 страницыCardio Day 3 TemplateMikeОценок пока нет
- Lecture 9Документ10 страницLecture 9Grafu Andreea AlexandraОценок пока нет
- Cardio I: Shock, CHF, HTN, ACS Cheat Sheet: by ViaДокумент3 страницыCardio I: Shock, CHF, HTN, ACS Cheat Sheet: by ViaMariana NannettiОценок пока нет
- Textbook Discussion On ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction - GicaroДокумент12 страницTextbook Discussion On ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction - GicaroJica Marie Bandiola GicaroОценок пока нет
- Pediatric StrokeДокумент43 страницыPediatric StrokePrachiti KarodeОценок пока нет
- Week 10 - Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, ArrhythmiaДокумент14 страницWeek 10 - Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, Arrhythmiashivani patel100% (1)
- Endocarditis: (Post Strep Infection)Документ8 страницEndocarditis: (Post Strep Infection)Eben Ezar Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Seminar On Management of StrokeДокумент54 страницыSeminar On Management of Stroke7762n9qsntОценок пока нет
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: Darpen Subhashbhai Mori Group 2, MD 3BДокумент13 страницHemorrhagic Stroke: Darpen Subhashbhai Mori Group 2, MD 3BDarpen MoriОценок пока нет
- hemiplegia دكتور عزونيДокумент4 страницыhemiplegia دكتور عزونيRaed AlhnaityОценок пока нет
- Pendukung StrokeДокумент202 страницыPendukung StrokeNovita DuffОценок пока нет
- Differential Diagnosis of StrokeДокумент2 страницыDifferential Diagnosis of StrokeAnonymous 7dsX2F8nОценок пока нет
- Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: HPI, Signs and Symptoms DVT: PEДокумент9 страницDeep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: HPI, Signs and Symptoms DVT: PETom MallinsonОценок пока нет
- Presenter: DR Edalia Facilitator: Prof AdamДокумент35 страницPresenter: DR Edalia Facilitator: Prof AdamUzma KhanОценок пока нет
- Reduced Renal Sodium Excretion: Forced Through A Narrow LumenДокумент5 страницReduced Renal Sodium Excretion: Forced Through A Narrow LumenFlowerОценок пока нет
- Management of Patientswith Complications From Heart DiseaseДокумент8 страницManagement of Patientswith Complications From Heart Diseasekristine keen buanОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular Dysfunction: (Patent Ductus Arteriosus)Документ6 страницCardiovascular Dysfunction: (Patent Ductus Arteriosus)Jc MacujaОценок пока нет
- Acute Ischemic Stroke: Etiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnostics, TreatmentДокумент7 страницAcute Ischemic Stroke: Etiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnostics, TreatmentAfrah AbdulОценок пока нет
- StrokeДокумент27 страницStrokeJASON KO CHIA SHENGОценок пока нет
- Stroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuДокумент20 страницStroke Hemoragik: Yuneldi Anwar Sps Departemen Neurologi FK UsuBrolie BarsebaОценок пока нет
- MCQ 1. Heart Sound Heart Sound S1 S2Документ7 страницMCQ 1. Heart Sound Heart Sound S1 S2Atirah AaОценок пока нет
- DR Imran Gafoor DR Ashok Anand Deptt of Ccem, Sir Gangaram Hospital, N.DelhiДокумент45 страницDR Imran Gafoor DR Ashok Anand Deptt of Ccem, Sir Gangaram Hospital, N.DelhiYoga YudhistiraОценок пока нет
- Neoplasm: - TermsДокумент125 страницNeoplasm: - Termsferina steffiОценок пока нет
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) : Pathogenesis RFДокумент5 страницCoronary Artery Disease (CAD) : Pathogenesis RFJennyu Yu100% (1)
- Introduction & Epidemiology Clinical Features: End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)Документ2 страницыIntroduction & Epidemiology Clinical Features: End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)Nikki VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- Hypertension +++Документ19 страницHypertension +++Mohamed Tarek El KwatehyОценок пока нет
- Materi 12 IMELS - Trombosis Emboli Paru, Iskemik Tungkai Akut - KritisДокумент64 страницыMateri 12 IMELS - Trombosis Emboli Paru, Iskemik Tungkai Akut - KritismaharyadyОценок пока нет
- Head Trauma: Yoon Seung-Hwan, M.DДокумент53 страницыHead Trauma: Yoon Seung-Hwan, M.Dilham darnoОценок пока нет
- Hemorrhagic StrokeДокумент57 страницHemorrhagic StrokefarhanomeОценок пока нет
- Hemorrhagic StrokeДокумент57 страницHemorrhagic StrokeAnonymous oEbVOEОценок пока нет
- Hypertension - PathologyДокумент4 страницыHypertension - PathologyFlowerОценок пока нет
- (Type The Documen T Title) : Jeffrey ConnorДокумент50 страниц(Type The Documen T Title) : Jeffrey ConnorJeffrey HingОценок пока нет
- Cvspa01 Hypertension and AthrosclerosisДокумент8 страницCvspa01 Hypertension and AthrosclerosisRobert So JrОценок пока нет
- Complications of Com: Dr. Ajay Manickam Junior Resident, Dept of Ent RG Kar Medical CollegeДокумент88 страницComplications of Com: Dr. Ajay Manickam Junior Resident, Dept of Ent RG Kar Medical CollegeRikizu Hobbies100% (1)
- Head Trauma: Yoon Seung-Hwan, M.DДокумент53 страницыHead Trauma: Yoon Seung-Hwan, M.DAhmed ZahranОценок пока нет
- Coronary Artery DiseaseДокумент3 страницыCoronary Artery DiseaseRitz CelsoОценок пока нет
- 4.18 Mankad Echo in Systemic DiseaseДокумент97 страниц4.18 Mankad Echo in Systemic DiseaseDiana_anca6Оценок пока нет
- Uptodate: Chronic Kidney DiseaseДокумент13 страницUptodate: Chronic Kidney DiseaseAtiqah ShahОценок пока нет
- Patho HypertensionДокумент30 страницPatho HypertensionMahmoud hilmyОценок пока нет
- Strokeppt 170720174010Документ95 страницStrokeppt 170720174010Venosha GunasekaranОценок пока нет
- Stroke Hemoragik: Dr. Rusli Dhanu, SP.S (K)Документ20 страницStroke Hemoragik: Dr. Rusli Dhanu, SP.S (K)BonitavanyОценок пока нет
- Stroke Hemoragik: Dr. Rusli Dhanu, SP.S (K)Документ20 страницStroke Hemoragik: Dr. Rusli Dhanu, SP.S (K)Lestari Amelia Adm100% (1)
- Hypertension: Nucleus Medical MediaДокумент17 страницHypertension: Nucleus Medical Mediakrish oswalОценок пока нет
- Meded Emq Revision Course Notes Set 1Документ44 страницыMeded Emq Revision Course Notes Set 1py siraОценок пока нет
- FINALS ch31Документ6 страницFINALS ch31Monica JubaneОценок пока нет
- Congenital Heart DefectsДокумент7 страницCongenital Heart DefectsJulia Rae Delos SantosОценок пока нет
- Echo Heart FailureДокумент82 страницыEcho Heart FailureJing CruzОценок пока нет
- MedicalДокумент3 страницыMedicalNicole WilliamОценок пока нет
- Refreshing Shock: Pembimbing: Dr. Fauzi Abdillah Susman, SP - An, MSC Disusun Oleh: Achmad Reza SyamsuladeДокумент14 страницRefreshing Shock: Pembimbing: Dr. Fauzi Abdillah Susman, SP - An, MSC Disusun Oleh: Achmad Reza SyamsuladeSam.Оценок пока нет
- Maternal Cardiac ArrestДокумент28 страницMaternal Cardiac ArrestTruelly ChanantaОценок пока нет
- Neuro-Onkologi: Bagian/SMF Saraf FK-UGM/RS Dr. Sardjito YogyakartaДокумент59 страницNeuro-Onkologi: Bagian/SMF Saraf FK-UGM/RS Dr. Sardjito YogyakartaNovasiska Indriyani HutajuluОценок пока нет
- Neuro NotesДокумент54 страницыNeuro Notesmed s100% (1)
- Cardiology-4 HTNДокумент16 страницCardiology-4 HTNMahmoud RamadanОценок пока нет
- Kuliah Kriris HTДокумент29 страницKuliah Kriris HTDiska irmadhaniОценок пока нет
- Medicine Revision - Neurology TableДокумент10 страницMedicine Revision - Neurology TableUnomoshОценок пока нет
- Week 1 Notes - Ncmb312Документ3 страницыWeek 1 Notes - Ncmb312Leighanne Clyve FerrerОценок пока нет
- Lecture 8Документ7 страницLecture 8Grafu Andreea AlexandraОценок пока нет
- Brain OdemaДокумент2 страницыBrain OdemaMohamed Nasreldin HamdoonОценок пока нет
- Correct Answer:: Alcohol Acetaldehyde Acetic AcidДокумент5 страницCorrect Answer:: Alcohol Acetaldehyde Acetic AcidTom TsouОценок пока нет
- NA DNA Tech 2Документ36 страницNA DNA Tech 2Tom TsouОценок пока нет
- Med. Interview QuestionsДокумент58 страницMed. Interview QuestionsdarkmagicdrakeОценок пока нет
- NA Control of Cell VolumeДокумент28 страницNA Control of Cell VolumeTom TsouОценок пока нет
- Scapular Region and Spinal Cord LabДокумент24 страницыScapular Region and Spinal Cord LabdarkmagicdrakeОценок пока нет
- ECG Workshop PreviewДокумент25 страницECG Workshop PreviewTom TsouОценок пока нет
- Gene Expression 2 Regulation: Slide 1Документ20 страницGene Expression 2 Regulation: Slide 1darkmagicdrakeОценок пока нет
- An Breast and PectoralisДокумент36 страницAn Breast and PectoralisTom TsouОценок пока нет
- NA Risk Calc in MendelianДокумент34 страницыNA Risk Calc in MendelianTom TsouОценок пока нет
- NA Risk Calc in MendelianДокумент34 страницыNA Risk Calc in MendelianTom TsouОценок пока нет
- NA Inguinal and ScrotumДокумент52 страницыNA Inguinal and ScrotumTom TsouОценок пока нет
- NA Risk Calc in MendelianДокумент47 страницNA Risk Calc in MendelianTom TsouОценок пока нет
- Dissection Abd WallДокумент59 страницDissection Abd WallTom TsouОценок пока нет
- Dissection Supracolic & InfracolicДокумент44 страницыDissection Supracolic & InfracolicTom TsouОценок пока нет
- Path of HypertensionДокумент52 страницыPath of HypertensionTom TsouОценок пока нет
- NA Abdomen AnatomyДокумент123 страницыNA Abdomen AnatomyTom TsouОценок пока нет
- Stress & Effects On Heart PDFДокумент33 страницыStress & Effects On Heart PDFTom TsouОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular Pathology: Hypertensive RetinopathyДокумент7 страницCardiovascular Pathology: Hypertensive RetinopathyTom TsouОценок пока нет
- Basics of ECG Pre-Workshop: Dr. Nancy Selfridge Chair, Department of Clinical Medicine Semester 4 2019Документ43 страницыBasics of ECG Pre-Workshop: Dr. Nancy Selfridge Chair, Department of Clinical Medicine Semester 4 2019Tom TsouОценок пока нет
- Lipoprotein MetabolismДокумент41 страницаLipoprotein MetabolismTom TsouОценок пока нет
- Pharm of HypertensionДокумент89 страницPharm of HypertensionTom TsouОценок пока нет
- Death & DyingДокумент28 страницDeath & DyingTom TsouОценок пока нет
- Lipoprotein MetabolismДокумент41 страницаLipoprotein MetabolismTom TsouОценок пока нет
- Lipoprotein MetabolismДокумент41 страницаLipoprotein MetabolismTom TsouОценок пока нет
- FOB Price (Free On Board) - What Is FOB PriceДокумент3 страницыFOB Price (Free On Board) - What Is FOB PriceFarooq BhuttaОценок пока нет
- Marathi 3218Документ11 страницMarathi 3218Nuvishta RammaОценок пока нет
- State of Cyber-Security in IndonesiaДокумент32 страницыState of Cyber-Security in IndonesiaharisОценок пока нет
- SweetPond Project Report-2Документ12 страницSweetPond Project Report-2khanak bodraОценок пока нет
- Process Recording Template 1Документ5 страницProcess Recording Template 1api-584340241Оценок пока нет
- 08 - Case Law-Unknown Case Law ListДокумент28 страниц08 - Case Law-Unknown Case Law ListNausheen100% (1)
- Milton Friedman - The Demand For MoneyДокумент7 страницMilton Friedman - The Demand For MoneyanujasindhujaОценок пока нет
- Training ReportДокумент61 страницаTraining ReportMonu GoyatОценок пока нет
- KELY To - UE Section B Writing Topics 1989-2010Документ16 страницKELY To - UE Section B Writing Topics 1989-2010Zai MaОценок пока нет
- APLN - Audit Report 2018Документ133 страницыAPLN - Audit Report 2018Dini DesvarhozaОценок пока нет
- Ligutan V CA (Full Text)Документ15 страницLigutan V CA (Full Text)Yaz CarlomanОценок пока нет
- Islamic StudyДокумент80 страницIslamic StudyWasim khan100% (1)
- 10ca Contract Manual 2005Документ4 страницы10ca Contract Manual 2005Kavi PrakashОценок пока нет
- Poli TipsДокумент83 страницыPoli TipsJoyae ChavezОценок пока нет
- CCP Motivation Letter 2022Документ3 страницыCCP Motivation Letter 2022mohammed ahmed0% (1)
- DMДокумент12 страницDMDelfin Mundala JrОценок пока нет
- Auditing Unit - 5 by Anitha RДокумент16 страницAuditing Unit - 5 by Anitha RAnitha RОценок пока нет
- 02-Case Study ESSS - Milestone 01 Scope DefinitionДокумент10 страниц02-Case Study ESSS - Milestone 01 Scope Definition3LIX 311Оценок пока нет
- Hazing in The PhilippinesДокумент24 страницыHazing in The PhilippinesEdz Votefornoymar Del Rosario100% (2)
- Organzational Climate On InnoationДокумент23 страницыOrganzational Climate On Innoationlucky prajapatiОценок пока нет
- Management Decision Case: Restoration HardwaДокумент3 страницыManagement Decision Case: Restoration HardwaRishha Devi Ravindran100% (5)
- People vs. Chingh - GR No. 178323 - DigestДокумент1 страницаPeople vs. Chingh - GR No. 178323 - DigestAbigail TolabingОценок пока нет
- Community-Based Health Planning Services: Topic OneДокумент28 страницCommunity-Based Health Planning Services: Topic OneHigh TechОценок пока нет
- Internship ReportДокумент44 страницыInternship ReportRAihan AhmedОценок пока нет
- Philippine Law A Tapestry of Justice and HeritageДокумент2 страницыPhilippine Law A Tapestry of Justice and HeritageKaren Faith MallariОценок пока нет
- Managing Transaction ExposureДокумент34 страницыManaging Transaction Exposureg00028007Оценок пока нет
- Hispanic Heritage MonthДокумент2 страницыHispanic Heritage Monthapi-379690668Оценок пока нет
- Amazon Go ReportДокумент3 страницыAmazon Go ReportkatyaОценок пока нет
- Complete ES1 2023 Vol1Документ334 страницыComplete ES1 2023 Vol1Chandu SeekalaОценок пока нет
- Fashion OrientationДокумент7 страницFashion OrientationRAHUL16398Оценок пока нет