Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Sample PDP and HLR
Загружено:
gegeАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Sample PDP and HLR
Загружено:
gegeАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Test procedure
A PDP context activation is requested by the SS with the transaction identifier set to ’1’. The UE shall not
respond to this request.
A PDP context is then activated from the UE and accepted from SS. A deactivate message is then sent from the
SS with a different transaction identifier to the one used in the activate request message sent by the UE. The UE
shall reply with a SM STATUS message with cause #81 ’invalid transaction identifier value’ and transaction
identifier same as one used in deactivate message.
A modify message is then sent from the SS with a different transaction identifier to the one used in the activate
request message sent by the UE. The UE shall reply with a SM STATUS message with cause #81 ’invalid
transaction identifier value’ and transaction identifier same as one used in modify message.
A modify request message is then sent from the SS with transaction identifier equal to the one used in the
activate request message sent by the UE. The UE shall reply with a modify accept message.
Two invalid accept messages are then sent by the SS with T3380 seconds between them. After a further T3380
seconds a valid accept message is sent by the SS.
A deactivate message is then sent from the SS with the transaction identifier set to ’111’. The UE shall reply
with a SM STATUS message with transaction identifier set to ’111’.
A deactivate message is then sent from the SS with a different transaction identifier to the one used in the
activate request message sent by the UE. The UE shall reply with a SM STATUS message with cause #81
’invalid transaction identifier value’.
Three invalid modification messages are then sent to the UE in turn. The UE shall respond each time with a SM-
STATUS message with cause # 96 ”invalid mandatory information”.
The Home Location Register is a database within the Home Public Land Mobile Network.
1. It provides routing information for Mobile Terminated calls and Short Message Service. It is also
responsible for the maintenance of user subscription information.
2. This is distributed to the relevant VLR -Visitor Location Register or SGSN - Serving GPRS
Support Node through the attach process and mobility management procedures such as Location
Area and Routing Area updates.
3. HLR stores and manages all mobile subscriptions belonging to a specific operator. The HLR
is considered the most important database because it stores permanent data about subscribers,
including subscriber’s supplementary services, location information, and. authentication
parameters buys When a person a subscription, it is registered in the operator’s HLR.
4. The HLR can be implemented with the MSC/VLR or as a stand-alone database.
5. A HLR contains user information such as account information, account status, user
preferences, features subscribed to by the user, user’s current location, etc. The data stored in
HLRs for the different types of networks is similar but does differ in some details.
6. HLRs are used by the Mobile Switching Centers (MSCs) to originate and deliver arriving mobile
calls.
HLR Redundancy
When a single HLR fails, all subscribers with records in that HLR will not be able to roam or receive
calls. HLR Redundancy can prevent such a loss of subscriber activity. This feature is achieved by
having an additional HLR node for each HLR node in the network. HLR Redundancy provides
protection against disaster situations such as fire at an HLR site. At the same time, it will give
protection against Signalling failures towards an HLR and will also lower the lack of availability
caused by HLR restarts.
With this feature, the subscriber can make and receive calls even in disastrous situations like an
earthquake with little or no change in network continuity or functionality. The HLR Redundancy
feature, allows failure to be invisible to the network and the subscriber. A mated HLR is introduced
in such a way that subscribers and load are shared in normal operation, and when one HLR fails,
the other picks up all traffic normally routed to the pair.
2. VLR
A VLR is a database, similar to a HLR, which is used by the mobile network to temporarily hold
profiles of roaming users (users outside their home area). This VLR data is based on the user
information retrieved from a HLR. MSCs use a VLR to handle roaming users.
Database contains information about all mobile stations currently located in the MSC service area.
VLR contains temporary subscriber information needed by the MSC to provide service for visiting
Вам также может понравиться
- Clarinet Fingering ChartДокумент1 страницаClarinet Fingering ChartSuzannah LettsОценок пока нет
- Swift 4Документ86 страницSwift 4Freeman JacksonОценок пока нет
- PI OPC Clients PDFДокумент8 страницPI OPC Clients PDFrznajibОценок пока нет
- Mobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationОт EverandMobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- Summary of Andreas M. Antonopoulos, Olaoluwa Osuntokun & René Pickhardt's Mastering the Lightning NetworkОт EverandSummary of Andreas M. Antonopoulos, Olaoluwa Osuntokun & René Pickhardt's Mastering the Lightning NetworkОценок пока нет
- GSM Network ComponentsДокумент23 страницыGSM Network ComponentsShakeel AminОценок пока нет
- MAP Roaming Tutorial: EAAA Professional Services - KPI GenerationДокумент17 страницMAP Roaming Tutorial: EAAA Professional Services - KPI Generationrahulsingh_2998100% (1)
- Welcome All Trainees: Course No. 270 by Rajesh Suwalka Engineer (WMTDC)Документ29 страницWelcome All Trainees: Course No. 270 by Rajesh Suwalka Engineer (WMTDC)Rajesh Suwalka100% (1)
- Ui Ux Design Development ContractДокумент4 страницыUi Ux Design Development ContractPure One0% (1)
- HLR Redundancy DescriptionДокумент14 страницHLR Redundancy DescriptionKenny IsaacОценок пока нет
- Traffic CasesДокумент30 страницTraffic CasesNitin JainОценок пока нет
- airOS7 UMДокумент52 страницыairOS7 UMtravieso112Оценок пока нет
- GSM LectureДокумент26 страницGSM Lecturesamy gomaaОценок пока нет
- HLR BasicsДокумент13 страницHLR BasicsAyan Chakraborty75% (4)
- HLR Fe TutorialДокумент9 страницHLR Fe TutorialintorefОценок пока нет
- The Home Location RegisterДокумент2 страницыThe Home Location RegisterSamSameleviОценок пока нет
- Manage subscriber data with HLR databaseДокумент2 страницыManage subscriber data with HLR databaseSamSameleviОценок пока нет
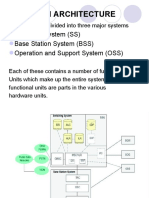
- GSM Architecture: Switching System (SS) Base Station System (BSS) Operation and Support System (OSS)Документ19 страницGSM Architecture: Switching System (SS) Base Station System (BSS) Operation and Support System (OSS)aimslifeОценок пока нет
- SS7 in Mobile Communication NetworkingДокумент5 страницSS7 in Mobile Communication Networkinggunasekaran.subramani3879Оценок пока нет
- Network Switching Subsystem Functions and ComponentsДокумент5 страницNetwork Switching Subsystem Functions and ComponentsMehboob AliОценок пока нет
- Operation and Maintenance CenterДокумент3 страницыOperation and Maintenance CenterRabia RindОценок пока нет
- Mobile Communication ThesisДокумент5 страницMobile Communication ThesisWaseem AhmedОценок пока нет
- Unit4 (Second Part)Документ15 страницUnit4 (Second Part)Sanju ShreeОценок пока нет
- VLR Overflow 1 PDFДокумент9 страницVLR Overflow 1 PDFpothiqueОценок пока нет
- GSM Network ArchitectureДокумент72 страницыGSM Network ArchitectureAkash Kumar100% (1)
- 16.functioning of HLRДокумент2 страницы16.functioning of HLRdeepak19m100% (1)
- Gateway Location Register Technical Report SummaryДокумент11 страницGateway Location Register Technical Report SummaryJuan CalfulcuraОценок пока нет
- HLR & VLR (Wireless and Mobile Network Architectures)Документ2 страницыHLR & VLR (Wireless and Mobile Network Architectures)Luciferr SatannОценок пока нет
- GSM Architecture: Project ReportДокумент40 страницGSM Architecture: Project ReportaadafullОценок пока нет
- Network Switching SubsystemДокумент35 страницNetwork Switching SubsystemmanthasaikarthikОценок пока нет
- Building Blocks and Services of 802.11 WLANsДокумент3 страницыBuilding Blocks and Services of 802.11 WLANsEneet Singh RanaОценок пока нет
- GSM Architecture: Support System For GSM NetworksДокумент5 страницGSM Architecture: Support System For GSM NetworksHarini RahulОценок пока нет
- Mobile NetworkingДокумент6 страницMobile NetworkingPalanivel Rajan SОценок пока нет
- Basic Knowledge About Radio Network: Viettel Networks Corporation - O0oДокумент34 страницыBasic Knowledge About Radio Network: Viettel Networks Corporation - O0ovilaphong vongphachithОценок пока нет
- Mobile Switching Center Functions and ComponentsДокумент1 страницаMobile Switching Center Functions and ComponentsnuurОценок пока нет
- GSM SystemДокумент13 страницGSM Systemiamhridoy74Оценок пока нет
- Human - Computer Interaction ComputerДокумент18 страницHuman - Computer Interaction ComputerVipul VeramОценок пока нет
- ZXUN USPP Theoretical Basic-Interface Protocol-Interfaces and ServicesДокумент61 страницаZXUN USPP Theoretical Basic-Interface Protocol-Interfaces and Serviceskaijage kishekyaОценок пока нет
- Authentication Protocols in Wireless Communications ExaminedДокумент10 страницAuthentication Protocols in Wireless Communications ExaminedShilpa MaratheОценок пока нет
- Brief Introduction To 2GДокумент4 страницыBrief Introduction To 2GMajed ImadОценок пока нет
- DT DocumentsДокумент10 страницDT DocumentsSobaan ArshadОценок пока нет
- Global System For Mobile Communication (GSM)Документ6 страницGlobal System For Mobile Communication (GSM)RobertoОценок пока нет
- VolteДокумент15 страницVolteAakriti MahteОценок пока нет
- Basic Knowledge For CDMA SystemДокумент42 страницыBasic Knowledge For CDMA SystemSanjay GiriОценок пока нет
- WINET Haas Lin 1998 09Документ8 страницWINET Haas Lin 1998 09Chakravarthi ChittajalluОценок пока нет
- Introduction to GSM Network ComponentsДокумент8 страницIntroduction to GSM Network ComponentsWeedhat Utol UyoОценок пока нет
- GSM Mobility ManagementДокумент6 страницGSM Mobility ManagementRodjean SimballaОценок пока нет
- Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliДокумент66 страницGlobal System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliMuhammadwaqasnaseemОценок пока нет
- ZXUN USPP(HLR) Interfaces and Services OverviewДокумент65 страницZXUN USPP(HLR) Interfaces and Services Overviewkaijage kishekyaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To GSMДокумент5 страницIntroduction To GSMalaa_muneer2005Оценок пока нет
- GSM and Lte NotesДокумент6 страницGSM and Lte NotesSubhransu patraОценок пока нет
- Flare Network and FLR Token GuideДокумент9 страницFlare Network and FLR Token GuideM. Istiawan NurpratamaОценок пока нет
- An Example of SS7 - Global Cellular Network InteroperabilityДокумент3 страницыAn Example of SS7 - Global Cellular Network InteroperabilityKrishanu ModakОценок пока нет
- How To Determine The Location of A Mobile Subscriber: Sergey PuzankovДокумент3 страницыHow To Determine The Location of A Mobile Subscriber: Sergey PuzankovMisterAto MaisonОценок пока нет
- HLR Basic Concepts: Main Function of Hlr/AucДокумент7 страницHLR Basic Concepts: Main Function of Hlr/AucionwiratamaОценок пока нет
- Network Switching SubsystemДокумент35 страницNetwork Switching Subsystemprtp_y8618Оценок пока нет
- MM Location Update PresentationДокумент23 страницыMM Location Update Presentationmrcin26Оценок пока нет
- A Broad Assessment of Data Migration Practice in Network Communication IndustriesДокумент6 страницA Broad Assessment of Data Migration Practice in Network Communication IndustriesInternational Journal of Engineering and TechniquesОценок пока нет
- What is GSM? Everything You Need to KnowДокумент15 страницWhat is GSM? Everything You Need to KnowSwapnarekha NarravulaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To GSM: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communications)Документ12 страницIntroduction To GSM: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communications)Anuj KuradeОценок пока нет
- Communications 3Документ4 страницыCommunications 3jydee033Оценок пока нет
- Chapter # 1Документ51 страницаChapter # 1Chea SovongОценок пока нет
- BSC Call SetupДокумент1 страницаBSC Call SetupgegeОценок пока нет
- GSM CallДокумент1 страницаGSM CallgegeОценок пока нет
- Soft/Softer/Inter RNC HO Addition, Dedicated Channel: No Yes NoДокумент2 страницыSoft/Softer/Inter RNC HO Addition, Dedicated Channel: No Yes NoSamSameleviОценок пока нет
- GprsДокумент1 страницаGprsgegeОценок пока нет
- The Visitor Location RegisterДокумент1 страницаThe Visitor Location RegistergegeОценок пока нет
- The Visitor Location RegisterДокумент1 страницаThe Visitor Location RegistergegeОценок пока нет
- SPCC DocumentationДокумент33 страницыSPCC DocumentationKumar Dzhunushaliev100% (1)
- Tugas MultiДокумент33 страницыTugas MultiQi Nam WowwhstanОценок пока нет
- NGÂN HÀ BTEC-CO1 - LUẬN VĂNДокумент23 страницыNGÂN HÀ BTEC-CO1 - LUẬN VĂNNgân HàОценок пока нет
- 1 1 115 - GLO-Safer - Cities - For - Girls-Block - by - Block-Report-Final-IO-Engl-March19Документ48 страниц1 1 115 - GLO-Safer - Cities - For - Girls-Block - by - Block-Report-Final-IO-Engl-March19Jodel PierreОценок пока нет
- Brazil State of Mobile Experience Report - June 2021Документ21 страницаBrazil State of Mobile Experience Report - June 2021Bruno EnriqueОценок пока нет
- SEO GuideДокумент3 страницыSEO GuideHimal GhimireОценок пока нет
- Upso Search ResultsДокумент5 страницUpso Search ResultsMustika Dwi SusilowatiОценок пока нет
- Moving to New CampusДокумент2 страницыMoving to New CampusDehan YahatugodaОценок пока нет
- Lab1: Learning About Switches: 1 ObjectivesДокумент4 страницыLab1: Learning About Switches: 1 ObjectivesPrinoОценок пока нет
- Econometrics IntroductionДокумент41 страницаEconometrics IntroductionRay Vega LugoОценок пока нет
- Pharma Marketing Management Unit 2 Notes @trickpharmacyДокумент13 страницPharma Marketing Management Unit 2 Notes @trickpharmacySherkhan Saifi100% (1)
- ConjuguemosДокумент4 страницыConjuguemosapi-259709613Оценок пока нет
- Dashboard - Central Attendance - FAQДокумент3 страницыDashboard - Central Attendance - FAQsureesicОценок пока нет
- Pitman Shorthand Book PDFДокумент3 страницыPitman Shorthand Book PDFHamza SulehriaОценок пока нет
- GA Doa crossword puzzle vocabulary and shoppingДокумент6 страницGA Doa crossword puzzle vocabulary and shoppingkarensОценок пока нет
- Download Introduction to Probability Theory PDFДокумент7 страницDownload Introduction to Probability Theory PDFSubb kumstОценок пока нет
- Airtel Case StudyДокумент2 страницыAirtel Case StudyPathikrit GuhaОценок пока нет
- Finding A FamilyДокумент4 страницыFinding A FamilyDaniela De Alba StevensonОценок пока нет
- StormWatch UserGuideДокумент24 страницыStormWatch UserGuidejpibaseОценок пока нет
- Alcplus2 Idu ManagerДокумент286 страницAlcplus2 Idu Managerberroteranj100% (1)
- ABM Fundamentals of ABM 1 CGДокумент5 страницABM Fundamentals of ABM 1 CGMaria Angelica BermilloОценок пока нет
- Release-notes-anyconnect-3.1.12020Документ34 страницыRelease-notes-anyconnect-3.1.12020Emanuel JanssonОценок пока нет
- E-Commerce Hybrid Recommendation SystemДокумент3 страницыE-Commerce Hybrid Recommendation Systemvamsi karnatapuОценок пока нет
- APA 7th. Ed. Refs Examples 2023Документ9 страницAPA 7th. Ed. Refs Examples 2023Patrícia DordioОценок пока нет
- Internship Presentation SampleДокумент24 страницыInternship Presentation SampleVineet AnandОценок пока нет