Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lte Questions and Answers
Загружено:
Raj RanjanОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lte Questions and Answers
Загружено:
Raj RanjanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Question-1: What is the difference between LTE FDD and LTE TDD?
Answer-1:The difference lies in the LTE frame structure in both the FDD and TDD versions ofthe LTE.
In FDD there will be pair of frequencies assigned in the downlink and uplink directionsand hence
transmissions from multiple subscribes can happen at the same time but on differentfrequencies as
mentioned. In TDD, one single frequency will be used at different time instants bymultiple subscriber
terminals (UEs). Both frame versions of LTE will have 1 ms sub-frameduration and 0.5 ms slot
duration.
Question-2: What is resource block in LTE?
Answer-2:LTE frame is divided based on time slots on time axis and frequency subcarrier
onfrequency axis. Resource block is the smallest unit of resource allocation in LTE system. It is
ofabout 0.5ms duration and composed of 12 subcarriers in 1 OFDM symbol. One time slot is equalto
7 OFDM symbols in normal cyclic prefix and 6 OFDM symbols in extended cyclic prefix.One full
resource block is equal to 12 subcarriers by 7 symbols in normal CP. Hence it consistsof total 84
time/frequency elements referred as resource elements in LTE network.
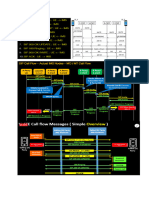
LTE Cell Search Procedure used by UE
A cell search procedure is used by the UE to acquire time and frequency
synchronization with a LTE cell and UE detects the physical layer Cell ID
(PCI) of that cell. Two cell search procedures in LTE: initial synchronization
and detecting neighbour cells in preparation for handover LTE uses a
hierarchical cell search scheme similar to WCDMA
Step-1: After being powered on, UE tunes the RF and attempts to measure
the wideband received power (RSSI) for specific frequencies (channels as
commanded by higher layer) over a set of supported frequency bands one
after another and ranks those cells based on signal strength.
Step-2: Then it uses downlink synchronization channels i.e. locally stored P-
SS and S-SS to correlate with received one. UE first finds the primary
synchronization signal (PSS) which is located in the last OFDM symbol of first
time slot of the first and 5th sub-frames This enables UE to be synchronized
on sub-frame level. Primary Synchronization Signal helps for Slot Timing
Detection and Physical Layer ID (0,1,2) detection.
Step-3:: secondary synchronization symbols are also located in the same sub-
frame of P-SS but in the symbol before P-SS. From secondary SS, UE is able
to obtain physical layer cell identity group number (0 to 167) It helps for Radio
Frame Timing detection, find Physical Layer Cell ID, cyclic prefix length
detection, FDD or TDD detection. The same is depicted in the LTE cell
search procedure figure below.
Step-4: Once UE knows the PCI for a given cell, it also knows the location of
cell Reference signals - which are used for channel estimation, cell selection /
reselection and handover procedures. After channel estimation using
RS(reference signal), MMSE equalization is performed to remove the effect of
channel impairment from the received symbols.
Вам также может понравиться
- LTE Interview Questions and AnswersДокумент19 страницLTE Interview Questions and AnswersSachin Patel100% (1)
- This LTE Tutorial Covers LTE Cell Search Procedure Used by UEДокумент5 страницThis LTE Tutorial Covers LTE Cell Search Procedure Used by UEPramod KumarОценок пока нет
- LTE UE ON ProcedureДокумент10 страницLTE UE ON ProcedureMani KandanОценок пока нет
- LTE Interview Questions and Answers EricssonДокумент32 страницыLTE Interview Questions and Answers Ericssonusmanghani8257Оценок пока нет
- Cell Reselection Procedures in LTE - LteencyclopediaДокумент4 страницыCell Reselection Procedures in LTE - LteencyclopediaDONALFYОценок пока нет
- LTE Everyday From MaddyДокумент50 страницLTE Everyday From MaddySultan JavedОценок пока нет
- LTE QuestionsДокумент4 страницыLTE QuestionsWill ACОценок пока нет
- Difference Between LTE FDD Vs TDD LTEДокумент25 страницDifference Between LTE FDD Vs TDD LTEmegi agusОценок пока нет
- Lte Initial Network CampingДокумент1 страницаLte Initial Network Campingsrinvas_107796724Оценок пока нет
- Read MoreДокумент9 страницRead MorecharantejaОценок пока нет
- Frame Structures in LTE-TDD and LTE-FDD: LauroДокумент4 страницыFrame Structures in LTE-TDD and LTE-FDD: Laurogourav_bhardwajОценок пока нет
- LTE Quick ReferenceДокумент30 страницLTE Quick ReferenceAnkur Samsung2Оценок пока нет
- LTE - TDD - Trame StructureДокумент29 страницLTE - TDD - Trame StructureArielОценок пока нет
- Cell Search Techniques in LTE PaperДокумент10 страницCell Search Techniques in LTE PaperManoj WanjariОценок пока нет
- Understanding Call Flow inДокумент19 страницUnderstanding Call Flow inBraj Bhushan100% (1)
- PSS and SSSДокумент2 страницыPSS and SSSAman DeepОценок пока нет
- 5G UE Power OnДокумент3 страницы5G UE Power OnVusal SuleymanovОценок пока нет
- LTE Interview1Документ5 страницLTE Interview1Uzair SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- LTE Interview Questions and AnswersДокумент25 страницLTE Interview Questions and Answersadnangulzar100% (6)
- Air InterfaceДокумент11 страницAir InterfaceBhosdiwale ChachaОценок пока нет
- Physicallayer by Pa1Документ3 страницыPhysicallayer by Pa1Pavan Kumar Reddy ChillaОценок пока нет
- Basic Call Flow in LTEДокумент14 страницBasic Call Flow in LTESadu TamaОценок пока нет
- Secondary Synchronization Signal in 5G New RadioДокумент6 страницSecondary Synchronization Signal in 5G New Radioyigit ozcanОценок пока нет
- Basic LTE Call Flow: LTE A Terminal Must Perform Certain StepsДокумент9 страницBasic LTE Call Flow: LTE A Terminal Must Perform Certain StepsAnonymous SuO1HHОценок пока нет
- LTE: LTE Cell Search Procedure - What Happens in LTE After Mobile Switch OnДокумент7 страницLTE: LTE Cell Search Procedure - What Happens in LTE After Mobile Switch Onzuhqasmi-1Оценок пока нет
- Lte 1Документ2 страницыLte 1Mohammad Salahuddin AzharОценок пока нет
- Questions With Answers Lte UpdatedДокумент51 страницаQuestions With Answers Lte UpdatedNuman KhanОценок пока нет
- Question 3Документ14 страницQuestion 3WaQas AhMadОценок пока нет
- LTE Frame Structure PDFДокумент3 страницыLTE Frame Structure PDFbalamuruganОценок пока нет
- Don't Forget PCFICH While Doing Physical Cell Identity (PCI) PlanningДокумент8 страницDon't Forget PCFICH While Doing Physical Cell Identity (PCI) PlanningPeterParker Spidy100% (1)
- 12 LTE Interview Questions and AnswersДокумент19 страниц12 LTE Interview Questions and AnswersAlex Umeaku100% (1)
- LTE Frame StructureДокумент5 страницLTE Frame StructureAnway MohantyОценок пока нет
- LTE Protocols & Signaling (Cell Search and Synchronization) - Day 4Документ7 страницLTE Protocols & Signaling (Cell Search and Synchronization) - Day 4maryam rahimluОценок пока нет
- Sip-Cell search-HO-frames Call FlowДокумент7 страницSip-Cell search-HO-frames Call FlowImran AslamОценок пока нет
- OpticsДокумент29 страницOpticsPuneet KumarОценок пока нет
- Umts Spreading FactorДокумент8 страницUmts Spreading FactorSanthoshGampaОценок пока нет
- LTE Q&As VOL-1Документ78 страницLTE Q&As VOL-1Prabhat KumarОценок пока нет
- Throughput Calculation For Lte TDD and FDD Systems: December 2012Документ11 страницThroughput Calculation For Lte TDD and FDD Systems: December 2012Syachrul AmriefОценок пока нет
- Tutorial LTEДокумент13 страницTutorial LTEAngela BarrОценок пока нет
- Neighboring Cell Search Techniques For LTE Systems: CitationДокумент7 страницNeighboring Cell Search Techniques For LTE Systems: Citationacela3248Оценок пока нет
- MIB & SIB Nokia LTE PDFДокумент14 страницMIB & SIB Nokia LTE PDFDhiraj SinghОценок пока нет
- LTE Bit Rate CalculationДокумент36 страницLTE Bit Rate Calculationaidenpark100% (1)
- Lte Frame Structure - AbridgedДокумент7 страницLte Frame Structure - AbridgedAnudeep BhattacharyaОценок пока нет
- LTE / LTE-Advanced: Number of Cells and Protocol Stack: Follow-Up QuestionДокумент1 страницаLTE / LTE-Advanced: Number of Cells and Protocol Stack: Follow-Up QuestionZteTems OptОценок пока нет
- LTE and LTE Advanced Terminology - RF Wireless World TerminologyДокумент2 страницыLTE and LTE Advanced Terminology - RF Wireless World TerminologyAshutosh ShakyaОценок пока нет
- LTE PCI RSI Planning ToolДокумент38 страницLTE PCI RSI Planning ToolVarsan100% (1)
- 3G Documnet For InterviewДокумент5 страниц3G Documnet For InterviewTahir khan shinwariОценок пока нет
- LTE RF Interview Questions ShirazДокумент8 страницLTE RF Interview Questions Shirazadnangulzar0% (1)
- Cell Size ConfigurationДокумент7 страницCell Size ConfigurationSneha PavithranОценок пока нет
- LTE Fundamental ConceptsДокумент12 страницLTE Fundamental ConceptsAnonymous D9ShNMfVОценок пока нет
- Synchronous Optical NetworkДокумент5 страницSynchronous Optical Networkdeepaknath2200Оценок пока нет
- LTE Cell Search - White PaperДокумент22 страницыLTE Cell Search - White PaperpavansrinivasanОценок пока нет
- Overal LTE SequenceДокумент71 страницаOveral LTE SequenceFahim SayedОценок пока нет
- Physical ConfigurationДокумент6 страницPhysical Configurationਲਵਲੀਸ਼ ਕੁਮਾਰОценок пока нет
- KPI Introduction: Admin No CommentsДокумент4 страницыKPI Introduction: Admin No CommentsMustafa AliОценок пока нет
- Cell Selection Re SelectionДокумент40 страницCell Selection Re SelectionVishnu Kumar Jayswal100% (2)
- Practical Guide to LTE-A, VoLTE and IoT: Paving the way towards 5GОт EverandPractical Guide to LTE-A, VoLTE and IoT: Paving the way towards 5GОценок пока нет
- Qo SДокумент3 страницыQo SFrensel PetronaОценок пока нет
- Cell Radius in LTE PDFДокумент4 страницыCell Radius in LTE PDFse7en_csОценок пока нет
- LTE WhitePaperДокумент15 страницLTE WhitePaperfarrukhmohammedОценок пока нет
- Layer-3 Q&AДокумент2 страницыLayer-3 Q&ARaj RanjanОценок пока нет
- 11 17 1669-00-00ay 3d Ray Tracing and Network PerformanceДокумент23 страницы11 17 1669-00-00ay 3d Ray Tracing and Network PerformanceRaj RanjanОценок пока нет
- Gwan Mo 042712Документ22 страницыGwan Mo 042712kumaar1943Оценок пока нет
- 11 17 1669-00-00ay 3d Ray Tracing and Network PerformanceДокумент23 страницы11 17 1669-00-00ay 3d Ray Tracing and Network PerformanceRaj RanjanОценок пока нет
- C in Depth (2nd Ed.) (Srivastava 2009-06-30) PDFДокумент550 страницC in Depth (2nd Ed.) (Srivastava 2009-06-30) PDFAmal Dey73% (15)
- Lte Link BudgetДокумент71 страницаLte Link Budgetduttaamit219Оценок пока нет
- Model Tuning Process On Aircom AssetДокумент19 страницModel Tuning Process On Aircom AssetRaj Ranjan100% (1)
- Ip PlanningДокумент68 страницIp PlanningRaj RanjanОценок пока нет
- Planet EV 5.0 Create New SiteДокумент9 страницPlanet EV 5.0 Create New SiteRaj RanjanОценок пока нет
- Ixan0010 PDFДокумент26 страницIxan0010 PDFBenito Rivera EdmundoОценок пока нет
- COM600S - Substation Automation, Analysis and Data ManagementДокумент52 страницыCOM600S - Substation Automation, Analysis and Data ManagementVamanОценок пока нет
- DCNДокумент133 страницыDCNSaroj patelОценок пока нет
- GE Renewal Parts: Contactor Model 17Cm53E10AДокумент3 страницыGE Renewal Parts: Contactor Model 17Cm53E10ARafael Dutil LucianaОценок пока нет
- GARRET PD 6500i User Manual ZONE 5-6 (ZONE 5 150+0%) : 3.5.20 RELAY Nio) Nic)Документ8 страницGARRET PD 6500i User Manual ZONE 5-6 (ZONE 5 150+0%) : 3.5.20 RELAY Nio) Nic)Felipe MejiasОценок пока нет
- Hybrid SCADA NetworksДокумент11 страницHybrid SCADA NetworksMarisela AlvarezОценок пока нет
- Dse850 Data SheetДокумент2 страницыDse850 Data SheetGeorge AniborОценок пока нет
- LaserДокумент6 страницLaserdianacmosquera23Оценок пока нет
- Xaar Datasheet ProtonДокумент2 страницыXaar Datasheet ProtonRicardo AmezcuaОценок пока нет
- Protecta: Normal and Emergency LightingДокумент4 страницыProtecta: Normal and Emergency LightingcharlnnmdОценок пока нет
- Fiber Optic Communications Fiber Optic Communications: EE4367 Telecom. Switching & TransmissionДокумент25 страницFiber Optic Communications Fiber Optic Communications: EE4367 Telecom. Switching & TransmissionnhatvpОценок пока нет
- Home Theater Onkyo HT-SR750Документ68 страницHome Theater Onkyo HT-SR750Vinicius MarcosОценок пока нет
- SRT 1F Equipment DetailsДокумент8 страницSRT 1F Equipment Detailsjcardenas55Оценок пока нет
- GD20-en V1.3 PDFДокумент122 страницыGD20-en V1.3 PDFjhonnyОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 RF Amplifier DesignДокумент50 страницLecture 2 RF Amplifier DesignVenkata Pradeep SangepuОценок пока нет
- Free Ebook WindmillДокумент10 страницFree Ebook Windmillwilliamd100% (7)
- DFGHJKL OijnbДокумент2 страницыDFGHJKL OijnbNea SandelОценок пока нет
- Compact Line Arrays Comparison PDFДокумент1 страницаCompact Line Arrays Comparison PDFJoanna NunezОценок пока нет
- Frontech User's Manual PDFДокумент9 страницFrontech User's Manual PDF06l01a0224Оценок пока нет
- En FM-Pro4, Pro4 3G DatasheetДокумент5 страницEn FM-Pro4, Pro4 3G DatasheetJoko PitoyoОценок пока нет
- ABB Surge Arrester MWK - Data Sheet 1HC0075865 E01 ABДокумент5 страницABB Surge Arrester MWK - Data Sheet 1HC0075865 E01 ABsriniОценок пока нет
- Admiral TG-2100A PTSM02Документ66 страницAdmiral TG-2100A PTSM02Jose LimónОценок пока нет
- 3m Filtrete Fap 04 SeriesДокумент10 страниц3m Filtrete Fap 04 SeriesJP anonymousОценок пока нет
- Jndal Power ResumeДокумент2 страницыJndal Power ResumeRahul Kumar YadavОценок пока нет
- V382 - 20 (00205363) - DecryptДокумент27 страницV382 - 20 (00205363) - Decryptleodias.souzaОценок пока нет
- Engine Control System 1. General: Engine - 2Tr-Fe Engine EG-31Документ32 страницыEngine Control System 1. General: Engine - 2Tr-Fe Engine EG-31Maxi SardiОценок пока нет
- Comparison Between Serial Adder and para PDFДокумент3 страницыComparison Between Serial Adder and para PDFvenkatОценок пока нет
- BigJoe S22Документ162 страницыBigJoe S22martinОценок пока нет
- Kamranmahar O3O4 1797633: 15. Which Type of Computers Uses The 8-Bit Code Called Ebcdic?Документ26 страницKamranmahar O3O4 1797633: 15. Which Type of Computers Uses The 8-Bit Code Called Ebcdic?AmirSaeedОценок пока нет
- EE124 Lecture 12 Source Follower Cascode Amplifier and Current Source Mar 9 Spring 2020 Annotated PDFДокумент13 страницEE124 Lecture 12 Source Follower Cascode Amplifier and Current Source Mar 9 Spring 2020 Annotated PDFSabeeq KarimОценок пока нет