Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
1
Загружено:
kimchiarmy0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
12 просмотров4 страницыsadadsa
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документsadadsa
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
12 просмотров4 страницы1
Загружено:
kimchiarmysadadsa
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 4
1.
a solution is created by dissolving a
solute in a solvent at or near its
It is necessary to filter the solution boiling point. At this high
while still hot because according on temperature, the solute has a greatly
the principles of solubility, increased solubility in the solvent, so
a much smaller quantity of hot
compounds tend to be more soluble
solvent is needed than when the
in hot liquids, if you allowed it to solvent is at room temperature.
cool, the solute is no longer soluble When the solution is later cooled,
in the solvent and forms crystals of after filtering out insoluble impurities,
pure compound. the amount of solute that remains
dissolved drops precipitously. At the
Because some of the compounds cooler temperature, the solution is
will solidify and precipitate when the saturated at a much lower
solution is not hot. As a result the concentration of solute. The solute
compound will be collected as the that can no longer be held in solution
solid residue instead of the liquid forms purified crystals of solute,
filtrate. which can later be collected.
Recrystallization works only when
A hot filtration is generally used in
the proper solvent is used. The
some crystallization, when a solid
solute must be relatively insoluble in
contains impurities that are insoluble
the solvent at room temperature but
in the crystallization solvent. It is
much more soluble in the solvent at
also necessary in crystallization
higher temperature. At the same
when charcoal is used to remove
time, impurities that are present
highly colored impurities from a
must either be soluble in the solvent
solid, as charcoal is so fine that it
at room temperature or insoluble in
cannot be removed by decanting.
the solvent at a high temperature.
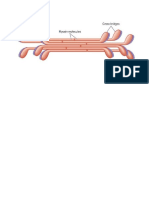
A filtration procedure called "hot I assume you are talking
gravity filtration" is used to separate
about recrystallisation, a
insoluble impurities from a hot
solution. Hot filtrations require fluted technique of purifcation of
filter paper and careful attention to solids.
the procedure to keep the apparatus A solvent is chosen which
warm but covered so that solvent will dissolve the compound of
does not evaporate. Hot gravity interest when hot but not
filtrations are no longer included in
cold, but not dissolve the
the routine procedures for the
impurity when hot or cold.
experiments in the organic chemistry
teaching labs. If you need to do such The mixture is taken up in
a filtration, read the procedure in the the minimum amount of hot
Handbook and consult your TA. solvent to dissolve all the
desired compound, filtered to
The principle behind recrystallization
is that the amount of solute that can remove the insoluble impurity
be dissolved by a solvent increases and then allowed to cool. On
with temperature. In recrystallization, cooling the purified desired
compound will crystallise out compound must be a solid at room
of solution. temperature. Recrystallization is
often used as a final clean-up step,
after other methods (such as
If you did not filter while hot,
extraction or column
then the solid which came chromatography) that are effective at
out of the cold solution would removing larger amounts of
still contain the insoluble impurities, but that do not raise the
impurities. purity of the final compound to a
You filter the solution to sufficiently high level.
remove the insoluble
In hot filtration, the impurity less
impurities. If not filtered hot,
soluble than the sample will remain
the solution might crystallize
on the filter paper.
quickly thus trapping the
insoluble impurities. The funnel has to be kept hot , to
Although the terms "crystallization" avoid crystallization on its stem .
and "recrystallization" are
sometimes used interchangeably,
they technically refer to different
processes. Crystallization refers to
the formation of a new, insoluble
product by a chemical reaction; this
product then precipitates out of the
reaction solution as an amorphous
solid containing many trapped
impurities. Recrystallization does not
involve a chemical reaction; the
crude product is simply dissolved
into solution, and then the conditions
are changed to allow crystals to re-
form. Recrystallization produces a
more pure final product. For this
reason, experimental procedures
that produce a solid product by
crystallization normally include a
final recrystallization step to give the
pure compound.
Recrystallization is a method of
purifying a compound by removing
any impurities that might be mixed
with it. It works best when the
compound is very soluble in a hot
solvent, but very insoluble in the cold
version of the same solvent. The
2. What are the methods of inducing crystal
formation from solution?
liquid to evaporate (very
slowly)
a) increasing
The first thing is by
concentrations of the
"scratching" or rubbing
constituents until the
solubility constant the flask with a glass
conditions are reached. This rod or metal spatula. A
can be done by removing second tactic is the use
solvent, by adding one or of seed crystals. Taking
several constituents in just a few crystals from
concentrated form, or by
the previous crop and
changing the state of
putting them in your
constituents into the form
solution will promote the
that will cause
crystallization. growth of more crystals.
Often, it is enough to
b) providing nuclei for just stir the solution with
crystallization to avoid a spatula that has
formation of supersaturated touched some of the
solutions.
desired crystals.
reduce the volume of the
Supersaturated solutions hold more
solvent (boiling, solute than should be possible.
evaporation, low pressure) Hence they are very unstable.
There are a few ways to make the
solute crystallize:
add solvent which the
Put in a crystal of the solute.
solute is not soluble in, e.g. Sometimes any small particle, or
adding ethanol to water even dust, will do the trick.
precipitates some things Scratch the glass container (on the
inside)
A ferm knock or shake
cooling (and heating, when
the solubility of the
compound relies on the
presence of a dissolved gas
e.g. CaCO3 - limescale)
place a string in the
solution then allow the
Вам также может понравиться
- 1Документ1 страница1kimchiarmyОценок пока нет
- Karren T. Reyes Bsp1A: The Angel of Life (1895)Документ1 страницаKarren T. Reyes Bsp1A: The Angel of Life (1895)kimchiarmyОценок пока нет
- ScriptДокумент15 страницScriptkimchiarmyОценок пока нет
- Exercise 7 Data SheetДокумент1 страницаExercise 7 Data SheetkimchiarmyОценок пока нет
- Disaster ReflectionДокумент2 страницыDisaster ReflectionkimchiarmyОценок пока нет
- Disaster ReflectionДокумент2 страницыDisaster ReflectionkimchiarmyОценок пока нет
- 07 Handbook Unit2 Intercultural Communication Conflict ResolutionДокумент4 страницы07 Handbook Unit2 Intercultural Communication Conflict ResolutionkimchiarmyОценок пока нет
- February 2017 Lesson PlansДокумент1 страницаFebruary 2017 Lesson Plansapi-258725700Оценок пока нет
- Artificial Blood (Page 1)Документ1 страницаArtificial Blood (Page 1)kimchiarmyОценок пока нет
- Durian (Durio Zibethinus) As A Natural Aphrodisiac For MenДокумент2 страницыDurian (Durio Zibethinus) As A Natural Aphrodisiac For MenkimchiarmyОценок пока нет
- 123Документ8 страниц123kimchiarmyОценок пока нет
- Artificial Blood (Page 2)Документ2 страницыArtificial Blood (Page 2)kimchiarmyОценок пока нет
- Artificial Blood (Official Article)Документ2 страницыArtificial Blood (Official Article)kimchiarmyОценок пока нет
- Artificial BloodДокумент1 страницаArtificial BloodkimchiarmyОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- MWH S Water Treatment Principles and Design Third Edition - 2012 - Crittenden - Appendix C Physical Properties of WaterДокумент2 страницыMWH S Water Treatment Principles and Design Third Edition - 2012 - Crittenden - Appendix C Physical Properties of WaterbastianpurwaОценок пока нет
- Williams Landel Ferry - JACS55 PDFДокумент7 страницWilliams Landel Ferry - JACS55 PDFrishikeshmandawadОценок пока нет
- Energy Levels MS PDFДокумент3 страницыEnergy Levels MS PDFLoh Jun XianОценок пока нет
- PH6151 QuestionsДокумент2 страницыPH6151 Questionsvenkateswaran k.sОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer & ThermodynamicsДокумент194 страницыHeat Transfer & ThermodynamicsBetty Blue100% (1)
- SolidsNotes6 ElutriationДокумент7 страницSolidsNotes6 ElutriationRoberta BelazОценок пока нет
- Hopf Cole BrownДокумент21 страницаHopf Cole BrownRoberticoZeaОценок пока нет
- Sermaloy J Diffused Slurry Aluminide Coating: AdvantagesДокумент1 страницаSermaloy J Diffused Slurry Aluminide Coating: Advantagesbigsteve9088Оценок пока нет
- Types of Refrigerant Gas PresentationДокумент9 страницTypes of Refrigerant Gas PresentationTAIMOOR HUDAОценок пока нет
- Ansaldo Thomassen - Spare Parts (2014)Документ4 страницыAnsaldo Thomassen - Spare Parts (2014)guerrezОценок пока нет
- A Compressor Surge Control System: Combination Active Surge Control System and Surge Avoidance SystemДокумент7 страницA Compressor Surge Control System: Combination Active Surge Control System and Surge Avoidance SystemAbbas MohajerОценок пока нет
- PLate Impact Based On Johnson Cook ParametersДокумент33 страницыPLate Impact Based On Johnson Cook ParametersTaiwo OlasumboyeОценок пока нет
- Material Selection Notes 2Документ206 страницMaterial Selection Notes 2hschoi12Оценок пока нет
- Green Bipropellant Optimisation AOkninskiДокумент11 страницGreen Bipropellant Optimisation AOkninskiMariano SerranoОценок пока нет
- Guidelines On The Design of Floor For Vibration Due To Walking LoadsДокумент39 страницGuidelines On The Design of Floor For Vibration Due To Walking LoadsLeung LiangОценок пока нет
- 2021 Uzem Chemistry Ch09 - 2 Solubility and Complex-Ion EquilibriaДокумент102 страницы2021 Uzem Chemistry Ch09 - 2 Solubility and Complex-Ion EquilibriaErdem AltunОценок пока нет
- FEMA 451B Topic15-5a - Advanced Analysis Part1 Notes PDFДокумент85 страницFEMA 451B Topic15-5a - Advanced Analysis Part1 Notes PDFNivan RollsОценок пока нет
- Alloys, Melting PointДокумент2 страницыAlloys, Melting PointkieunkimОценок пока нет
- 4.convection Heat TransferДокумент26 страниц4.convection Heat TransferMohammed Zahran Mohammed Hashil Al HinaiОценок пока нет
- Linear Momentum and CollisionsДокумент2 страницыLinear Momentum and CollisionsAlex HuynhОценок пока нет
- Fluid DynamicsДокумент18 страницFluid DynamicsAngelica Losares100% (1)
- PVC PDFДокумент15 страницPVC PDFsrabon1059Оценок пока нет
- Carrier 50tcq 3 12TRДокумент118 страницCarrier 50tcq 3 12TRjack-bcОценок пока нет
- Nida Baig PPT PBДокумент7 страницNida Baig PPT PBShifa ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Lateral Earth PressureДокумент34 страницыLateral Earth PressureTimothy Charles YabutОценок пока нет
- P-Y Curves For Group PilesДокумент5 страницP-Y Curves For Group PilessatyaОценок пока нет
- TechNote - B008-20-Basic C-Shaped Wall Stud Behavior-WEBFINALДокумент6 страницTechNote - B008-20-Basic C-Shaped Wall Stud Behavior-WEBFINALsahanОценок пока нет
- SodaPDF-merged-Merging Result-2Документ258 страницSodaPDF-merged-Merging Result-2ermiasОценок пока нет
- Acoustics2 KKДокумент8 страницAcoustics2 KKAanchal BhartiyaОценок пока нет
- Steam Boiler Litt ReviewДокумент4 страницыSteam Boiler Litt ReviewToMem33% (3)