Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Problem Set 3
Загружено:
Ced HernandezОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Problem Set 3
Загружено:
Ced HernandezАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Problem Set 1
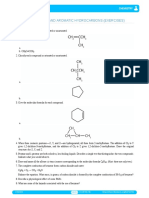
Draw the structural isomers of the following compounds: Problem Set 3
1. Draw the structures of 13 chain and position isomers of an alkene with the formula C6H12.
1. 9 isomers with the formula C7H16
2. Name the compounds you drew.
2. 8 isomers of C9H20 with 5 carbons in the longest chain
3. Which compound/s will exhibit geometric isomerism?
3. 11 isomers of C9H20 with 7 carbons in the longest chain
4. Draw the structures of the intermediates and the major products of the following reactions:
4. Isomer of C13H28 with the shortest possible longest chain of carbons
Include stereoisomers, if any.
5. 12 cyclic compounds of C6H12
a. (CH3)2C=CCH2CH3 + HCl
Name the compounds. b. 3,4-dimethyl3-heptene + HI
c. 2-methylbutene + H+, H2O
Using Newman projections, draw the most stable conformation of 2,2,4-trimethylpentane sighting
d. 3,5-diethyl-8-methyl-3-nonene + H+, H2O
through C3-C4.
e. 2-methyl-2-butene + Br2
Problem Set 2 f. Cis-2-butene + Br2
g. Cyclopentene + Br2
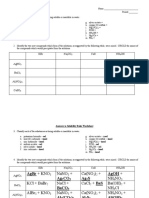
1. Predict the number of mono-chlorinated compounds from the reaction of each
C7H16 isomer with chlorine at high temperature.
Problem Set 4
2. Given 2,3-dimethylpentane, draw the structures of mono-chlorinated compounds
1. Draw the isomers of 6 alkynes with formula C6H10.
formed upon its reaction with chlorine in the presence of sunlight. Include 2. Name the compounds you drew.
stereoisomers, if any 3. Draw the I/TS and P. Include stereochemistry, if any.
3. Reactivity of halogens is as follows: F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > (I2). Chlorine is reactive and a. 1-pentyne + BH3 I/TS P + H2O2, OH- P
reacts with all free radical intermediates. Bromine, on the other hand, is selective b. 3-methyl-1,3-butadiene + HBr I/TS ↔ I/TS P
and reacts only with the most stable free radical intermediate. c. 1,3-cyclopentadiene + (1) O3 (2) Zn, HCl P
a. Draw the structure/s of mono-brominated compound/s upon the reaction of d. 1,3-pentadiyne + (1) O3 (2) Zn, HCl P
3-ethylpentane with bromine at high temperature. Include stereoisomers, if e. 2-butyne + H+, H2O I/TS P
f. Methylcyclohexene + KMnO4 (cold, alkaline) P
any.
g. (R) 3-methyl-2-pentene + MCPBA P + H2O P
b. Give the mechanism of the reaction.
h. 2,5-dimethyl-3-hexyne + 1 mole HCl I/TS P
4. Among the 12 cyclic compounds of C6H12:
i. 2-pentyne + 1 mole Br2 I/TS P
a. Which structures will exhibit geometric isomerism?
b. Which structures are chiral? Label the chiral carbons with *
Вам также может понравиться
- Hydrocarbon Answer KeyДокумент7 страницHydrocarbon Answer KeyVK CREATIONОценок пока нет
- Question Based On Name ReactionДокумент4 страницыQuestion Based On Name ReactionSelcouth elysianОценок пока нет
- Unsaturated and Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Section 1: Alkenes: Structures and NamesДокумент9 страницUnsaturated and Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Section 1: Alkenes: Structures and NamesAkhilesh SharmaОценок пока нет
- CHM207 TutorialДокумент3 страницыCHM207 Tutorialit's miaОценок пока нет
- Alkanes Practice ExercisesДокумент18 страницAlkanes Practice ExercisesAnonymousGodiswithyouОценок пока нет
- Name of The Molecule Molecular Formula Hybridization Type Bond Angle GeometryДокумент7 страницName of The Molecule Molecular Formula Hybridization Type Bond Angle GeometryKerala MekuriyaОценок пока нет
- XI Mid Term QPДокумент3 страницыXI Mid Term QPtechnical SiteОценок пока нет
- CH110 Tutorial SHEET 8 - Organic ChemistryДокумент10 страницCH110 Tutorial SHEET 8 - Organic ChemistryJames MukopaОценок пока нет
- Exercise AlkaneДокумент17 страницExercise Alkanerudi_zОценок пока нет
- AlkenaДокумент32 страницыAlkenaAdi Kurniawan EffendiОценок пока нет
- Chem52 Su13 PracticeExam1AДокумент11 страницChem52 Su13 PracticeExam1Aamarka01Оценок пока нет
- KK Mid Semi 1Документ26 страницKK Mid Semi 1chikondikosamu24Оценок пока нет
- Set 4 PSPM Dk024Документ7 страницSet 4 PSPM Dk024anis fazilaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry 123S Oregon State University Worksheet 9 Notes Dr. Richard NafshunДокумент11 страницChemistry 123S Oregon State University Worksheet 9 Notes Dr. Richard NafshunuwuОценок пока нет
- Tutorial Letter 203/1/2016: General Chemistry 1BДокумент22 страницыTutorial Letter 203/1/2016: General Chemistry 1BLeigh MakanОценок пока нет
- Organic MenuДокумент18 страницOrganic MenuelishamahubiОценок пока нет
- Unit 16 LP02PS - Alkane Structural IsomersДокумент19 страницUnit 16 LP02PS - Alkane Structural IsomersP.Vidur VarshanОценок пока нет
- ch16 Blackman2e Answers Odd QuestionsДокумент23 страницыch16 Blackman2e Answers Odd QuestionsCarlosE.NeriОценок пока нет
- Hydrocarbon 1Документ6 страницHydrocarbon 1VK CREATIONОценок пока нет
- Target TestДокумент6 страницTarget TestKritika DalalОценок пока нет
- Solutions With Gradings: 39 Austrian Chemistry Olympiad National CompetitionДокумент16 страницSolutions With Gradings: 39 Austrian Chemistry Olympiad National CompetitionGerel BayrmagnaiОценок пока нет
- Exercise: AlkaneДокумент17 страницExercise: AlkaneHenerita RayОценок пока нет
- II PUCmid Term 23Документ4 страницыII PUCmid Term 23Varun. B. CОценок пока нет
- # of Carbons Name Formula (C: AP Chemistry Chapter 22 - Organic ChemistryДокумент5 страниц# of Carbons Name Formula (C: AP Chemistry Chapter 22 - Organic ChemistryChemist Mohamed MohyОценок пока нет
- Chemistry QP5Документ5 страницChemistry QP5Jinendra UvarajОценок пока нет
- 13.E: Unsaturated and Aromatic Hydrocarbons (Exercises)Документ3 страницы13.E: Unsaturated and Aromatic Hydrocarbons (Exercises)KiEl GlorkОценок пока нет
- Chem 1Документ16 страницChem 1sabina halОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Sma 2: FINAL EXAM SEM-2 2013/2014Документ3 страницыChemistry Sma 2: FINAL EXAM SEM-2 2013/2014Arda RahmainiОценок пока нет
- Question 808498Документ3 страницыQuestion 808498Vaibhav AjsjsiuxgxОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryДокумент92 страницыIntroduction To Organic ChemistryAmmaarah PatelОценок пока нет
- 1-2. Hidrokarbon (Alkana, Alkuna, Alkena)Документ56 страниц1-2. Hidrokarbon (Alkana, Alkuna, Alkena)Rizky OktaviaОценок пока нет
- 10 ChemistryДокумент5 страниц10 Chemistrykavita07mehroliaОценок пока нет
- XI-Chemistry Chapter Test-13-HydrocarbonsДокумент4 страницыXI-Chemistry Chapter Test-13-Hydrocarbonscakof67215Оценок пока нет
- MCQ Exam#1Документ3 страницыMCQ Exam#1roxyОценок пока нет
- Section A: Solution Term 2 Test Class 12 - ChemistryДокумент5 страницSection A: Solution Term 2 Test Class 12 - ChemistryPANKAJ GOURОценок пока нет
- 12 Nomenclature Formula Sheets QuizrrДокумент11 страниц12 Nomenclature Formula Sheets QuizrrInertiaОценок пока нет
- 3.1.1 Naming Practice QuestionsДокумент33 страницы3.1.1 Naming Practice QuestionsAyaan RaufОценок пока нет
- 13 General Organic Chemistry Formula Sheets QuizrrДокумент22 страницы13 General Organic Chemistry Formula Sheets QuizrrInertiaОценок пока нет
- Chem Set 1Документ6 страницChem Set 1ALOK RANJANОценок пока нет
- CHE 232 Test 1 2015 AnsДокумент12 страницCHE 232 Test 1 2015 AnsBONOLO RANKOОценок пока нет
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 NotesДокумент16 страницSPM Chemistry Form 5 NotesHongYu Hui100% (4)
- Chep202 QPДокумент5 страницChep202 QPshamiksha dОценок пока нет
- IB Questionbank - Topic20 - MarkchemeДокумент87 страницIB Questionbank - Topic20 - MarkchemeMagdaОценок пока нет
- LATIHAN SOAL PTS GANJIL KimiaДокумент1 страницаLATIHAN SOAL PTS GANJIL Kimiadiahutami347Оценок пока нет
- Test No-4 Hydrocarbon - Key PDFДокумент3 страницыTest No-4 Hydrocarbon - Key PDFNaveen KumarОценок пока нет
- 11 Chemistry23 24sp 01Документ13 страниц11 Chemistry23 24sp 01AbhishekОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ46 страницChapter 1c4.arsyadОценок пока нет
- Alkane Neet DPPДокумент2 страницыAlkane Neet DPPYogita GОценок пока нет
- Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesДокумент10 страницAlkanes Alkenes AlkynesPanda Boy100% (2)
- Tutorial Letter 203/2/2017: General Chemistry 1BДокумент18 страницTutorial Letter 203/2/2017: General Chemistry 1BLeigh MakanОценок пока нет
- Ch-4 Carbon and Its Compounds - 3 Marker QuestionsДокумент2 страницыCh-4 Carbon and Its Compounds - 3 Marker QuestionsArshita KarayatОценок пока нет
- Sy Chemistry Q. Bank Sem 1 2023-24Документ7 страницSy Chemistry Q. Bank Sem 1 2023-24Kia AsherОценок пока нет
- Organic 14 2Документ11 страницOrganic 14 2Lojy BasetОценок пока нет
- Organic ChemistryДокумент10 страницOrganic ChemistrylovelykissОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry Mock Exam (ANSWER KEY)Документ7 страницOrganic Chemistry Mock Exam (ANSWER KEY)k.talle039Оценок пока нет
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Strained Organic Molecules: Organic Chemistry: A Series of Monographs, Vol. 38От EverandStrained Organic Molecules: Organic Chemistry: A Series of Monographs, Vol. 38Оценок пока нет
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersОценок пока нет
- Carbon Nanomaterials for Advanced Energy Systems: Advances in Materials Synthesis and Device ApplicationsОт EverandCarbon Nanomaterials for Advanced Energy Systems: Advances in Materials Synthesis and Device ApplicationsWen LuОценок пока нет
- Sds NДокумент6 страницSds NCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- FefeДокумент4 страницыFefeCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- FefefeДокумент4 страницыFefefeCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- FefeДокумент5 страницFefeCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- FefeДокумент4 страницыFefeCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- FefeДокумент3 страницыFefeCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- NKKДокумент3 страницыNKKCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- New Text DocumentДокумент10 страницNew Text DocumentCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- DFDДокумент3 страницыDFDCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- JNLДокумент5 страницJNLCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- JMMNLДокумент2 страницыJMMNLCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- The Effects of School-Based Management in The Philippines: Policy Research Working Paper 5248Документ29 страницThe Effects of School-Based Management in The Philippines: Policy Research Working Paper 5248Ced HernandezОценок пока нет
- EfeДокумент18 страницEfeCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- New Text DffsocumentДокумент15 страницNew Text DffsocumentCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- DepedДокумент4 страницыDepedCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- Chem Lab CitationДокумент1 страницаChem Lab CitationCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- S EfeДокумент1 страницаS EfeCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- Periodic Trends OrganizerДокумент1 страницаPeriodic Trends Organizerself_21Оценок пока нет
- Solubility Table Worksheet PDFДокумент2 страницыSolubility Table Worksheet PDFCed Hernandez100% (1)
- AlalsfДокумент6 страницAlalsfCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- UcspДокумент2 страницыUcspCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- Churcs Vs TaxДокумент9 страницChurcs Vs TaxCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- Geo QuizДокумент46 страницGeo QuizCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- Solubility Rules Worksheet - AnswersДокумент1 страницаSolubility Rules Worksheet - AnswersCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- Global 20170307 Philippines Case StudyДокумент64 страницыGlobal 20170307 Philippines Case StudyCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- Supervision Practices of School Principals: Reflection in ActionДокумент11 страницSupervision Practices of School Principals: Reflection in ActionCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- Management of Supervisory Work: Reforming School Supervision For Quality ImprovementДокумент29 страницManagement of Supervisory Work: Reforming School Supervision For Quality ImprovementCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- Read Me!!!!Документ1 страницаRead Me!!!!MichaelNeferОценок пока нет
- AdminD5Paulette Rourke Supervision and EvaluatДокумент16 страницAdminD5Paulette Rourke Supervision and EvaluatCed HernandezОценок пока нет
- Ex. 7Документ3 страницыEx. 7Liza Mae NeisОценок пока нет
- CHEM111 Aromatic HydrocarbonsДокумент32 страницыCHEM111 Aromatic HydrocarbonsKharl Roei SalvadorОценок пока нет
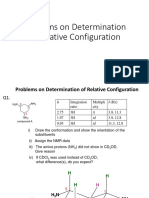
- Problems and Answers On Determination of Relative Configuration-02-8-2023Документ6 страницProblems and Answers On Determination of Relative Configuration-02-8-2023Solomon DereseОценок пока нет
- Acc Chem Res 2008 Hiyama-Denmark Coupling ReviewДокумент14 страницAcc Chem Res 2008 Hiyama-Denmark Coupling Reviewsleekboy25Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 12 Aldehyde & KetonesДокумент10 страницChapter 12 Aldehyde & KetonesForzen flamesОценок пока нет
- OXIdation and REDuction CompleteДокумент81 страницаOXIdation and REDuction CompleteMateen AliОценок пока нет
- HGJJHДокумент4 страницыHGJJHsugindavidrajОценок пока нет
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Chem2125.103.11f Taught by Sergio Cortes (Scortes)Документ7 страницUT Dallas Syllabus For Chem2125.103.11f Taught by Sergio Cortes (Scortes)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupОценок пока нет
- F0 XG 4 Z XGC H8 QN SDTy XW8Документ49 страницF0 XG 4 Z XGC H8 QN SDTy XW8Jatin PathakОценок пока нет
- Experiment No. 2 CarbohydratesДокумент5 страницExperiment No. 2 CarbohydratesZheldinan Nicole CruzОценок пока нет
- Practical 4Документ7 страницPractical 4Penjejak AwanОценок пока нет
- General Properties of CarbohydratesДокумент3 страницыGeneral Properties of CarbohydratesShine GatilloОценок пока нет
- Midterm Examination Organic ChemistryДокумент4 страницыMidterm Examination Organic ChemistryMichael Padilla EsmallaОценок пока нет
- Alkane Dehydrocyclization MechanismДокумент74 страницыAlkane Dehydrocyclization MechanismStefany CОценок пока нет
- Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones: Hydrogen Transfer Redox ReactionsДокумент20 страницReduction of Aldehydes and Ketones: Hydrogen Transfer Redox ReactionsDhewi LayОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes 13 - Esters88Документ4 страницыLecture Notes 13 - Esters88Surendra RamkissoonОценок пока нет
- Activity Biological MoleculesДокумент3 страницыActivity Biological MoleculesJapet AlcaideОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7a Lecture Slides PDFДокумент117 страницChapter 7a Lecture Slides PDFjoseph changОценок пока нет
- Boyles Resume 2015Документ19 страницBoyles Resume 2015David BoylesОценок пока нет
- ChemistryДокумент44 страницыChemistryRUPAMОценок пока нет
- Solid-Supported Synthesis of Oligomeric BioconjugatesДокумент38 страницSolid-Supported Synthesis of Oligomeric Bioconjugateskuala1982Оценок пока нет
- Experiment No 14Документ4 страницыExperiment No 14rathod karanОценок пока нет
- Amines: Organic Chemistry, 5Документ56 страницAmines: Organic Chemistry, 5kevin C. ZuritaОценок пока нет
- Alkanes PDFДокумент15 страницAlkanes PDFAnkitBanerjee100% (1)
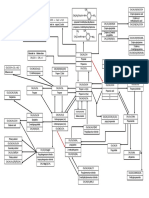
- Mind Map of Organic Chemistry: Ethanoate Ion TriiodomethaneДокумент1 страницаMind Map of Organic Chemistry: Ethanoate Ion TriiodomethanethomasОценок пока нет
- Functional Group NamesДокумент21 страницаFunctional Group NamesAdine RaissaОценок пока нет
- Alkane Alkene AlkyneДокумент99 страницAlkane Alkene AlkyneNelvianaОценок пока нет
- Chemical Resistance Selection Chart For Protective GlovesДокумент2 страницыChemical Resistance Selection Chart For Protective GlovesSaad QaiserОценок пока нет
- CHO For PKK 5203Документ51 страницаCHO For PKK 5203serang87Оценок пока нет
- Chem 215 Myers: The Suzuki ReactionДокумент10 страницChem 215 Myers: The Suzuki ReactionRajathi YadavОценок пока нет