Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Future Forms Will: Won't Be LL Rain LL Get
Загружено:
Andres MinguezaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Future Forms Will: Won't Be LL Rain LL Get
Загружено:
Andres MinguezaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
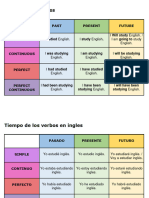
FUTURE FORMS
WILL
Lo utilizamos para predicciones o para expresar algo que acabamos de decidir
+ = Subject + WILL + Verb (infinitive)
- = Subject + WON’T / WILL NOT + Verb (infinitive)
¿ = Will + Subject + Verb (infinitive)
Contracciones= I’ll, You’ll, He’ll, She’ll, It’ll, We’ll, You’ll, They’ill
We won’t be ready.
Do you think it’ll rain this afternoon?
(The phone rings) I’ll get it.
BE GOING TO
Lo utilizamos para expresar decisiones que hemos tomado antes de hablar (intenciones) o
predicciones que estamos SEGUROS que van a ocurrir (hay pruebas)
+ = Subject + TO BE (present simple) + GOING TO + Verb (infinitive)
- = Subject + TO BE (Negative present simple) + GOING TO + Verb (infinitive)
? = TO BE (present simple) + Subject + GOING TO + Verb (infinitive)
Podemos contraer el verbo to be con el sujeto
EJEMPLO DE INTENCIÓN: I’m going to study Chemistry next year
EJEMPLO DE PREDICCIÓN CON PRUEBA: Oh look! It is going to rain!
PRESENT CONTINUOUS
Lo utilizamos para planes con otras personas, están fijados y normalmente decimos una hora
o momento exacto en el que van a ocurrir
+ = Subject + TO BE (present simple) + Verb (-ING)
- = Subject + TO BE (NEGATIVE present simple) + Verb (-ING)
? = TO BE (present simple) + Subject + Verb (-ING)
EJEMPLO: What are you doing this evening?
We aren’t doing anything tomorrow
DIFERENCIAS ENTRE BE GOING TO / PRESENT CONTINUOUS
DAISY: -Amy’s coming round at 3 pm. (= arrangement between Amy and Daisy)
I’m going to study at Cambridge University. (= Amy’s intention)
I’m going to clean my room tonight. (= intention)
I’m cleaning my room tonight. (not an arrangement)
Вам также может понравиться
- FUTURE SIMPLE TENSE and BE GOING TO10thДокумент2 страницыFUTURE SIMPLE TENSE and BE GOING TO10thJonathan SayayОценок пока нет
- Idiomas 2022Документ59 страницIdiomas 2022Alex ToledoОценок пока нет
- Will and Shall Are Modal Verbs. They Are Used With The Base Form of TheДокумент14 страницWill and Shall Are Modal Verbs. They Are Used With The Base Form of TheNga LêОценок пока нет
- On Ngu Phap Lop 9 Lan IIДокумент69 страницOn Ngu Phap Lop 9 Lan IIHa Tran100% (1)
- Tiempos VerbalesДокумент8 страницTiempos VerbalesClaudia Yanina GonzálezОценок пока нет
- Summary 5 Topic: Review Expressing Ideas in Future: General ExplanationДокумент4 страницыSummary 5 Topic: Review Expressing Ideas in Future: General ExplanationJaime G. MendozaОценок пока нет
- Be GointДокумент11 страницBe Gointjacobolizeth13Оценок пока нет
- Pre Interm A FUTURE TENSES 3BДокумент2 страницыPre Interm A FUTURE TENSES 3BRooh FernandezОценок пока нет
- Will B Goin ToДокумент8 страницWill B Goin Togendis raraОценок пока нет
- FutureДокумент26 страницFutureMariana BlancoОценок пока нет
- The 12 Principal TensesДокумент43 страницыThe 12 Principal TensesHa TranОценок пока нет
- Sometimes Often: Verb in Infinitive Read ForgetsДокумент15 страницSometimes Often: Verb in Infinitive Read ForgetsromОценок пока нет
- Simple Future TenseДокумент4 страницыSimple Future TenseGavrilla OliviaОценок пока нет
- Grammar Tenses ReportДокумент13 страницGrammar Tenses ReportAlberto Emiliano Montoya OlivoОценок пока нет
- Future Form PDFДокумент2 страницыFuture Form PDFMaylen FerminОценок пока нет
- Apuntes Gramática Inglés 1 EsoДокумент17 страницApuntes Gramática Inglés 1 EsoSara Iglesias100% (1)
- Future Forms Present Continuous, Be Going To, Will Won'tДокумент1 страницаFuture Forms Present Continuous, Be Going To, Will Won'tАнатоль БумберсОценок пока нет
- Simple Future Tense and Future Continuous TenseДокумент14 страницSimple Future Tense and Future Continuous TenseAlfi arintiaОценок пока нет
- Guided Discovery Future TensesДокумент2 страницыGuided Discovery Future TensesBillosОценок пока нет
- Tenses: Simple Present Tense, Simple Past Tense Simple Future TenseДокумент39 страницTenses: Simple Present Tense, Simple Past Tense Simple Future TensedeanisaОценок пока нет
- El Futuro: Will / Won'T - Be Going To - Present Continuous - Present SimpleДокумент12 страницEl Futuro: Will / Won'T - Be Going To - Present Continuous - Present SimpleZayra GomezОценок пока нет
- GrammarДокумент11 страницGrammarPedro MarsiОценок пока нет
- English TensesДокумент13 страницEnglish Tenseslog1alexОценок пока нет
- English Future Tenses: 1. Present Continuous For Future ArrangementsДокумент4 страницыEnglish Future Tenses: 1. Present Continuous For Future ArrangementsIsabel Garcia OrtizОценок пока нет
- Be Going To + Infinitive Present Continuous Will Back To IndexДокумент2 страницыBe Going To + Infinitive Present Continuous Will Back To IndexAndrei MarinОценок пока нет
- The Future - Infinitive of PurposeДокумент24 страницыThe Future - Infinitive of PurposeSusaku KururugiОценок пока нет
- Future Tenses Basic Grammar 13th 1A FixedДокумент31 страницаFuture Tenses Basic Grammar 13th 1A FixedungdoyieОценок пока нет
- Difference Between Will and Going ToДокумент3 страницыDifference Between Will and Going ToemilillaОценок пока нет
- Future TenseДокумент6 страницFuture TenseMuhammad Ibnu LaksonoОценок пока нет
- Study and Exercise Guide: Past SimpleДокумент6 страницStudy and Exercise Guide: Past SimpleHernán FelipeОценок пока нет
- Tense Indefinite Continuous Perfect Perfect Continuous: Presen TДокумент2 страницыTense Indefinite Continuous Perfect Perfect Continuous: Presen TBilal BhattiОценок пока нет
- Present Simple: Fact: Habit and Routine Schedule Feeling and EmotionsДокумент4 страницыPresent Simple: Fact: Habit and Routine Schedule Feeling and EmotionsKhim SoklengОценок пока нет
- TensesДокумент5 страницTensesYanina ChaileОценок пока нет
- GrammarДокумент25 страницGrammarPedro MarsiОценок пока нет
- Simple Future TenseДокумент8 страницSimple Future TenseIzad IdinОценок пока нет
- 3rd YearДокумент70 страниц3rd YearAndrea RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Present Simple (Verb Infinitive/s/) Present Continious (To Be+ Verb - Ing)Документ3 страницыPresent Simple (Verb Infinitive/s/) Present Continious (To Be+ Verb - Ing)Joselito hdОценок пока нет
- TensesДокумент7 страницTensesSdkanisius WatuagungОценок пока нет
- Going To - Will - Present ProgressiveДокумент8 страницGoing To - Will - Present ProgressiveNety HestiawatiОценок пока нет
- Conditional Sentence: Clause (Often Referred To As The If-Clause) and The ConsequenceДокумент12 страницConditional Sentence: Clause (Often Referred To As The If-Clause) and The ConsequencePuteri DamayantiОценок пока нет
- Introduction Present ContinuousДокумент2 страницыIntroduction Present ContinuousMaría Cruz Rueda MesoneroОценок пока нет
- Present Simple TenseДокумент8 страницPresent Simple TenseGeorgiana BachrouchОценок пока нет
- Timpuri in EnglezaДокумент4 страницыTimpuri in EnglezaAnisoara SiminelОценок пока нет
- InglesДокумент20 страницInglesJesús RamsésОценок пока нет
- TOEFL Part III StructureДокумент65 страницTOEFL Part III StructurePatrick StevenОценок пока нет
- Tenses Present Tenses Tense FormДокумент5 страницTenses Present Tenses Tense FormnevremenaОценок пока нет
- FuturosДокумент6 страницFuturosSheila Palomares CamargoОценок пока нет
- Sentence: You Don't Study English at MEC EverydayДокумент16 страницSentence: You Don't Study English at MEC EverydayKhaidir KapaОценок пока нет
- Tiempos VerbalesДокумент6 страницTiempos VerbalesTeresa MiОценок пока нет
- Future FormsДокумент11 страницFuture FormsKaren Lorena GutierrezОценок пока нет
- Global AnglèsДокумент15 страницGlobal Anglèsu1994050Оценок пока нет
- Futuro Con WillДокумент5 страницFuturo Con Willfernanda muñoz rengifoОценок пока нет
- Estructuras y UsosverbalesДокумент7 страницEstructuras y UsosverbalesCarmen Ballester GamaОценок пока нет
- Present Simple: When, As Soon As, If, Even If, Unless, As Long AsДокумент7 страницPresent Simple: When, As Soon As, If, Even If, Unless, As Long AsYanina ChaileОценок пока нет
- 1A Word Order in QuestionsДокумент9 страниц1A Word Order in QuestionsLuis Antonio La Torre QuinteroОценок пока нет
- Muhammad Alauddin Nur, S.PD., GR.: Arranged byДокумент75 страницMuhammad Alauddin Nur, S.PD., GR.: Arranged byNo HikariОценок пока нет
- Tenses 1Документ23 страницыTenses 1Puspita IsnainiОценок пока нет
- 16 Tenses in English ALIAMSAH RITONGA DoДокумент9 страниц16 Tenses in English ALIAMSAH RITONGA Doindah pratiwiОценок пока нет
- Going To Future - 7r - ZapiskiДокумент4 страницыGoing To Future - 7r - ZapiskiAmelaОценок пока нет
- Discover Dublins Docklands 6PDL HRДокумент2 страницыDiscover Dublins Docklands 6PDL HRAndres MinguezaОценок пока нет
- The One With Chandler and Monica's Wedding: Enunciate by Spitting (FRIENDS: Season 7, Episode 23Документ3 страницыThe One With Chandler and Monica's Wedding: Enunciate by Spitting (FRIENDS: Season 7, Episode 23Andres MinguezaОценок пока нет
- Grammar SUMMARY NO Reglado 2Документ2 страницыGrammar SUMMARY NO Reglado 2Andres MinguezaОценок пока нет
- National Compliment DayДокумент4 страницыNational Compliment DayAndres MinguezaОценок пока нет
- Grammar SUMMARY NO Reglado 1 Resuumen2Документ1 страницаGrammar SUMMARY NO Reglado 1 Resuumen2Andres MinguezaОценок пока нет
- Dossier Navidad 4ESPA BДокумент34 страницыDossier Navidad 4ESPA BAndres MinguezaОценок пока нет
- 09 AdobePenToolCheatsheetДокумент1 страница09 AdobePenToolCheatsheetAndres MinguezaОценок пока нет
- Clark Tema 2Документ13 страницClark Tema 2Andres MinguezaОценок пока нет
- Ipad Digital Finger PaintingsДокумент5 страницIpad Digital Finger PaintingsAndres MinguezaОценок пока нет
- GrammarДокумент32 страницыGrammarAndres MinguezaОценок пока нет
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Mixed RephrasingДокумент14 страницMixed RephrasingAndres MinguezaОценок пока нет
- Comparison (Comparación)Документ12 страницComparison (Comparación)Andres MinguezaОценок пока нет
- Beware For I Am Fearless, and Therefore PowerfulДокумент1 страницаBeware For I Am Fearless, and Therefore PowerfulAndres MinguezaОценок пока нет