Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Circular Convolution
Загружено:
kshiИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Circular Convolution
Загружено:
kshiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CIRCULAR CONVOLUTION
Let us take two finite duration sequences x1(n) and x2(n), having integer length as
N. Their DFTs are X1(K) and X2(K) respectively, which is shown below -
Now, we will try to find the DFT of another sequence x3(n), which is given as X3(K)
X3(K)=X1(K)�X2(K) By taking the IDFT of the above we get
Comparison points
Linear Convolution
Circular Convolution
Shifting Linear shifting Circular shifting
Samples in the convolution result
N1+N2-1 Max(N1,N2)
Finding response of a filter
Possible Possible with zero padding
Methods of Circular Convolution Generally, there are two methods, which are adopted
to perform circular convolution and they are -
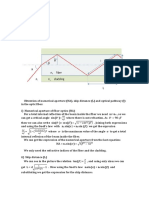
Concentric circle method, ? Matrix multiplication method. Concentric Circle Method
Let x1(n) and x2(n) be two given sequences. The steps followed for circular
convolution of x1(n) and x2(n) are: > Take two concentric circles. Plot N samples
of x1(n) on the circumference of the outer circle (maintaining equal distance
successive points) in anti-clockwise direction. > For plotting x2(n), plot N
samples of x2(n) in clockwise direction on the inner circle, starting sample placed
at the same point as 0th sample of x1(n). > Multiply corresponding samples on the
two circles and add them to get output. > Rotate the inner circle anti-clockwise
with one sample at a time. Matrix Multiplication Method Matrix method represents
the two given sequence x1(n) and x2(n) in matrix form. > One of the given sequences
is repeated via circular shift of one sample at a time to form a N X N matrix. >
The other sequence is represented as column matrix. > The multiplication of two
matrices give the result of circular convolution.
Вам также может понравиться
- Discrete Time Periodic Signals: N N X N XДокумент60 страницDiscrete Time Periodic Signals: N N X N XArshad KvОценок пока нет
- Fast Signal Processing Algorithms Week 3Документ58 страницFast Signal Processing Algorithms Week 3M Ali NaeemОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 DFT and FFTДокумент42 страницыUnit 4 DFT and FFThrrameshhrОценок пока нет
- Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)Документ22 страницыDiscrete Fourier Transform (DFT)Maheshwaran MahiОценок пока нет
- Digital Signal Processing (Lecture2) : Dr. Anumoy Ghosh Assistant Professor ECE DeptДокумент20 страницDigital Signal Processing (Lecture2) : Dr. Anumoy Ghosh Assistant Professor ECE DeptAyush SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- DSP Module 3Документ41 страницаDSP Module 3Ajay kumarОценок пока нет
- DFT FFT NotesДокумент41 страницаDFT FFT NotesManthan PandhareОценок пока нет
- HW9Документ2 страницыHW9Radhika AgarwalОценок пока нет
- DSP Unit 2Документ13 страницDSP Unit 220-403 TejashwiniОценок пока нет
- Discrete Fourier Transform Part 1Документ48 страницDiscrete Fourier Transform Part 1eloira1214Оценок пока нет
- Compute Linear Convolution Using DFTДокумент38 страницCompute Linear Convolution Using DFTAman SharmaОценок пока нет
- DFT and Digital Signal ProcessingДокумент19 страницDFT and Digital Signal ProcessingljjbОценок пока нет
- DSP 2 Marks Q&a1Документ38 страницDSP 2 Marks Q&a1shankarОценок пока нет
- Assignment 10 Linear and Circular Convolution: April 3, 2019Документ5 страницAssignment 10 Linear and Circular Convolution: April 3, 2019Amar dattaОценок пока нет
- Circular Convolution DFT Linear ConvolutionДокумент15 страницCircular Convolution DFT Linear Convolutiondearprasanta6015Оценок пока нет
- DSP Projects Call 9952749533Документ84 страницыDSP Projects Call 9952749533setsindia3735Оценок пока нет
- Unit-4 - Kec503 DSP - 2023-24Документ34 страницыUnit-4 - Kec503 DSP - 2023-24shubhОценок пока нет
- Reviewof The Fourier TransformДокумент18 страницReviewof The Fourier Transformjamesyu100% (2)
- Questions & Answers On Discrete Fourier Transform - Properties and ApplicationsДокумент13 страницQuestions & Answers On Discrete Fourier Transform - Properties and Applicationskibrom atsbha50% (2)
- Exp 7Документ2 страницыExp 7SUBHRO ROYОценок пока нет
- DFT Chapter Guide for Digital Signal ProcessingДокумент50 страницDFT Chapter Guide for Digital Signal Processingmeseret sisayОценок пока нет
- DSP NoteДокумент7 страницDSP Notemohammed fakehОценок пока нет
- CYCLIC SIEVING, PROMOTION, AND TABLEAUXДокумент55 страницCYCLIC SIEVING, PROMOTION, AND TABLEAUXAnonymous UrVkcdОценок пока нет
- It1252 Digital Signal ProcessingДокумент22 страницыIt1252 Digital Signal ProcessingainugiriОценок пока нет
- DSP - Lab@4 TДокумент4 страницыDSP - Lab@4 Tjadhavbhavesh891Оценок пока нет
- Digital Signal Processing Important 2 Two Mark Question and Answer IT 1252Документ14 страницDigital Signal Processing Important 2 Two Mark Question and Answer IT 1252startedforfunОценок пока нет
- Convolution techniques for signal processingДокумент2 страницыConvolution techniques for signal processinguclabruintizedОценок пока нет
- Unit I - Discrete Fourier Transform Part - AДокумент10 страницUnit I - Discrete Fourier Transform Part - AindhuОценок пока нет
- FFT ComputationДокумент4 страницыFFT Computationjeyaseelan1982Оценок пока нет
- Directional Secant Method For Nonlinear Equations: Heng-Bin An, Zhong-Zhi BaiДокумент14 страницDirectional Secant Method For Nonlinear Equations: Heng-Bin An, Zhong-Zhi Baisureshpareth8306Оценок пока нет
- 3 Goertzel's AlgorithmДокумент41 страница3 Goertzel's Algorithmvidya_sagar826100% (1)
- DTFT ContinueДокумент51 страницаDTFT Continueraskal23Оценок пока нет
- Digital Signal Processing Lecture Notes - 22nov2010 - v4Документ11 страницDigital Signal Processing Lecture Notes - 22nov2010 - v4Thiagu RajivОценок пока нет
- The Sequence y (N) Is Obtained From IDFT of Y (K) - by Definition of IDFTДокумент28 страницThe Sequence y (N) Is Obtained From IDFT of Y (K) - by Definition of IDFTDrìftОценок пока нет
- DSP Fundamentals Lecture Note Set #21 The FFT: 1 Course AnnouncementsДокумент5 страницDSP Fundamentals Lecture Note Set #21 The FFT: 1 Course AnnouncementsZaid Al-AlshaikhОценок пока нет
- DSP QuestionДокумент1 страницаDSP Questionmadhuk2011Оценок пока нет
- Unit 3 - Discrete Fourier TransformДокумент62 страницыUnit 3 - Discrete Fourier Transformchandrani deyОценок пока нет
- Review of Discrete Fourier Transform: Cwliu@twins - Ee.nctu - Edu.twДокумент46 страницReview of Discrete Fourier Transform: Cwliu@twins - Ee.nctu - Edu.twhakkem bОценок пока нет
- FFT convolution stepsДокумент19 страницFFT convolution stepsAbishek RajeshОценок пока нет
- Eee 2429&eee2330-Assignments 1&2Документ2 страницыEee 2429&eee2330-Assignments 1&2Solomon KenОценок пока нет
- Discrete Fourier Transform and Signal Spectrum: Advance Digital Signal ProcessingДокумент40 страницDiscrete Fourier Transform and Signal Spectrum: Advance Digital Signal ProcessingSaad AlwashОценок пока нет
- A Basical Study On Two-Point Seismic Ray Tracing: Wenzheng Yang December 16, 2003Документ8 страницA Basical Study On Two-Point Seismic Ray Tracing: Wenzheng Yang December 16, 2003Ola OyekunleОценок пока нет
- Lab 6Документ12 страницLab 6Sujan HeujuОценок пока нет
- DSP Lab Sheet 2 PDFДокумент50 страницDSP Lab Sheet 2 PDFSreekrishna DasОценок пока нет
- Digital Signal Processing PROF. S. C. Dutta Roy Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Delhi Discrete Fourier Transform (D F T Cont.) Lecture-10Документ15 страницDigital Signal Processing PROF. S. C. Dutta Roy Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Delhi Discrete Fourier Transform (D F T Cont.) Lecture-10Sudha PatelОценок пока нет
- A Compressed Beamforming Framework For Ultrafast Ultrasound ImagingДокумент4 страницыA Compressed Beamforming Framework For Ultrafast Ultrasound ImagingDueОценок пока нет
- Computer Assisted Method For Proving Existence of Periodic OrbitsДокумент15 страницComputer Assisted Method For Proving Existence of Periodic OrbitsMohamad Ali AnsariОценок пока нет
- Lecture - 5Документ28 страницLecture - 5Joanna YahyaОценок пока нет
- Convolution & IDFT Part 6 PDFДокумент36 страницConvolution & IDFT Part 6 PDFAbishek RajeshОценок пока нет
- Maximum-Length Sequences ExplainedДокумент9 страницMaximum-Length Sequences ExplainedLucio BianchiОценок пока нет
- KorovkinДокумент10 страницKorovkinMurali KОценок пока нет
- Lecture 5Документ26 страницLecture 5Nanditha AОценок пока нет
- Exercise 3Документ4 страницыExercise 3JavierОценок пока нет
- Atomic Structure - JEE Mains PYQ 2020-2022Документ147 страницAtomic Structure - JEE Mains PYQ 2020-2022pankaj baidОценок пока нет
- Experiment-3: %linear Convolution Using Circular ConvolutionДокумент4 страницыExperiment-3: %linear Convolution Using Circular ConvolutionFAIZОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1Документ2 страницыAssignment 1RaghuОценок пока нет
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)От EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Оценок пока нет
- Linkedin Employee CountДокумент9 страницLinkedin Employee CountkshiОценок пока нет
- Manufacturing Raj Guj KshitijДокумент5 страницManufacturing Raj Guj Kshitijkshi100% (1)
- Yash - i5M&P - YASH KALA PGP 2021-23 BatchДокумент5 страницYash - i5M&P - YASH KALA PGP 2021-23 BatchkshiОценок пока нет
- Team 2 - Company DataДокумент30 страницTeam 2 - Company DatakshiОценок пока нет
- Jaya Ranjan: Female, 24 YearsДокумент1 страницаJaya Ranjan: Female, 24 YearskshiОценок пока нет
- Kolkata Alchemus Abdul WasimДокумент9 страницKolkata Alchemus Abdul WasimkshiОценок пока нет
- Ahmedabad ITES and Pharma Companies Contact ListДокумент6 страницAhmedabad ITES and Pharma Companies Contact ListkshiОценок пока нет
- Team 2 - Company DataДокумент30 страницTeam 2 - Company DatakshiОценок пока нет
- Declaration and Conduct AgreementДокумент1 страницаDeclaration and Conduct AgreementkshiОценок пока нет
- Book 1Документ1 страницаBook 1kshiОценок пока нет
- Book 1Документ1 страницаBook 1kshiОценок пока нет
- New Doc 2018-02-28Документ3 страницыNew Doc 2018-02-28kshiОценок пока нет
- Telecommunications May 2020 PDFДокумент39 страницTelecommunications May 2020 PDFkshiОценок пока нет
- Telecommunications May 2020 PDFДокумент39 страницTelecommunications May 2020 PDFkshiОценок пока нет