Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Answer:-Repeat Question
Загружено:
sumitsinha89Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Answer:-Repeat Question
Загружено:
sumitsinha89Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
DECEMBER 2018
EXAMINATION OF MARINE ENGINEER OFFICER
Function: Marine Engineering at Management Level
MARINE ENGINEERING KNOWLEDGE (MOTOR)
TIME ALLOWED - 3 HOURS
Instructions: -
1. Answer SIX questions only.
2. All Questions carry equal marks
3. Neatness in handwriting and clarity in expression carries
weightage
4. Illustration of an Answer with clear sketches /diagram
carries weightage
5. All unused pages of the answer script must be
cancelled out by two lines (X) across the page
6. Write the full question before attempting
to write the answer to same.
Q1. With reference to the main engine burning heavy fuel. Ship has
been asked to use low sulphur diesel oil, what are the problems
likely to be encountered and risks involved in continuous running of
main engine on such low sulphur fuels.
Answer:- Repeat question.
Q2. With respect to Air starting systems for 2 strokes diesel
engines;A. Sketch and describe Main engine starting air distributor.
B. List the safety devices and interlocks incorporated in main
engine air starting system and state the purpose of each.
Answer:- Repeat question.
Q3. Sketch and show all parts of a two-stroke engine stuffing box.
Describe the procedure of overhauling two stroke engine stuffing
box, without removing piston. All safety precautions to be
mentioned proper tools used for overhaul mentioned.
Answer:- Repeat question.
Q4. With respect to piston cooling in large two stroke marine
engines;
A. Briefly discuss the relative advantages and disadvantages of
oil and water for piston cooling. B. Sketch a piston for a large
two-stroke crosshead engines indicating the coolant flow. C.
State the causes of piston cracking and burning and how it can
be avoided.
Answer:- (A) .
Advantages :- * The specific heat of water is almost
twice the specific heat of oil and so the heat
carrying capacity of water is better and hence the
quantity of water in circulation is
The boiling point of water at about 3 to 4
bar is over 150 0C and that makes water a
safe fluid for cooling since it will never
reach its boiling point during circulation.
However this cannot be stated for oil since
being more volatile than water it flashes
into vapour even before it reaches its
boiling point.
Disadvantages:- water is prone to cause corrosion and
scale formation even with careful monitoring , whereas oil
has no corrosive qualities .
Considering these pros and cons it is now a
considered conclusion by engine builders to use water
for jacket cooling and oil for piston cooling .
In pistons the passages for the cooling medium
are smaller in cross section area than the passages in
the jackets and cylinder heads and that is the reason
for their considered preferences.
(B)
(C) The causes for piston cracking and burning are:
* The burning of the piston crown surface
is caused by flame impingement on the crown. This
can be avoided by maintaining the injectors in good
condition , especially the sprayer plate or sprayer cap
. If these are blocked or worn the penetration of the
atomised fuel is not uniform which makes the
effective holes penetration length longer and this leads
to flame impingement. The fuel pumps need to be
regularly monitored for their correct timing . Late
admission of fuel will lead to after burning of the fuel
which again causes burning of the crown surface.
Improper cooling of the piston leads to
formation of cracks on the piston body and this can
be avoided by maintaining the internal cooling
passages and surfaces clean. At regular intervals
especially during unit overhauls the piston cooling
surfaces must be made to soak in a paraffin or
kerosene for about 24 hours and then flushed with
clean kerosene . This will remove the accumulated
sludge and carbon residue from the internal surfaces.
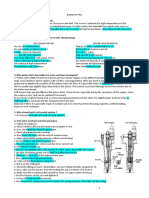
Q5. With respect to large two stroke crosshead main engines;
A. Sketch and describe a crosshead designed to prevent or
minimize bearing edge loading. B. State how the arrangement
describe a achieves its purpose. C. What would be an
acceptable range of bearing clearance for the top end bearing
and bottom end bearings of a large two-stroke marine diesel
engine
Answer:- (A)
The crosshead on a slow speed 2 stroke is a difficult bearing to lubricate effective
load is continually downward and because the con rod swings about the pin, chan
direction each stroke, true hydrodynamic lubrication cannot take place. Instead th
lubrication starts as boundary, and as the rubbing speed increases, a hydrodynami
built up. As the rubbing speed decreases the lubrication becomes boundary once
As engine powers and thus gas loads have increased, the difficulties
with achieving effective lubrication have increased. Larger pin
diameters have helped by increasing the linear rubbing speeds, and
the continuous lower bearing has reduced the loading/unit area.
The older forked type crosshead as found in earlier
engines (up to the mid 1980s) used various methods to
improve the lubrication of the crosshead. Oil grooves in
the lower bearings were used to distribute the oil. The
grooves in some cases extended to the edge of the
bearing, although with a reduced csa, to ensure a flow
of oil through the bearing.
THE MAN B&W MC ENGINE CROSSHEAD
The lower half of the bearing housing is formed by the
top end of the connecting rod. It supports the crosshead
pin over its entire length, the piston rod being bolted to
the top half of the crosshead pin through a cut out in
the bearing top half. Oil supply to the crosshead is via
a telescopic pipe from the main LO supply at a
pressure of about 2.5 bar.
The lower bearing shell (tin aluminium with overlay) has oil
grooves with machined wedges as shown in the diagram and
photo. The oil enters via the cut out channel in the centre. The
grooves extend right to the edges of the bearing to ensure a
flow of oil, thus cooling the bearing.
The lower half bearing extends to the full length of
the bearing so increasing the support area and
consequently the load/ unit area and with the high
pressure of the lub oil injected into the bearing a
stable hydrodynamic film is established
(C) The working clearances recommended are:
Top end ------------o.3 mm.
Bottom end------------0.5 mm ( allowed upto 0.65 mm)
Q6. State the probable engine defects and rectifying action needed
if the following conditions are
indicated on a single unit of a large two-stroke marine diesel
engine giving seven units. State any
additional information which might be of help in forming on
option
A. Increased exhaust temperatures.
B. Reduced exhaust temperature.
C. Reduction in jacket cooling water return temperature.
D. Increase in jacket cooling water return temperature.
Answer:-
(A) Increased exhaust temperatures are to be classified
as :
Higher than 450 0C may be attributed to leaky
exhaust valves caused by the valve seat and lid
partially burnt. The rectification is renewal of
the exhaust valve by A spare valve or
reconditioned valve.
Lower than 450 0C the defect may be
attributed to the injector/ fuel pump.
The suspected fuel pump needs to be
overhauled or renewed with a spare and
tested injector.
If the fuel pump is suspect it may be
causing after burning by late admission. The
fuel pump timing is to be checked and rectified
(B) Reduced Exhaust temperature :
In efficient combustion or no combustion caused
by defective injector or by loss of compression.
To make sure a compression card may be
taken to eliminate or confirm the loss of
compression. Loss of compression may be
attributed to broken rings or worn rings which
need to be renewed. If fuel injectors are
defective it needs to be renewed by spare
reconditioned injector
(C) Reduction in JCW return temperature:
Poor combustion. The reasons for poor
combustion and their rectification follows as
per (B).
Heavy scaling on the cooling surfaces of jacket
and cylinder head . This could lead to cracking
of cylinder head and /or liner and so the
cooling surfaces need descaling on an urgent
basis.
(D) Increase in JCW return temperature:
The liner or cylinder head may have developed
hair line cracks through which the products of
combustion are escaping into the cooling water.
Evidence of this could be found in the
expansion tank which will have small bubbles
rising in the water as seen from the sight
glass. Further confirmation can be had from
checking the flow of water through the vent
line led into the expansion tank. The flow will
be intermittent and signs of smoke can be
seen.
Q7. With reference to bridge control of a large slow
propulsion engine;
A. How starting and reversing achieved;
B. Investigate and proposal remedial action if the engine,
(i) fails to turn on air; (ii) turns on air but fails to fire on fuel;
(iii) fails to reverse.
Answer:- Repeat question.
Q8. With respect to scavenge fires in Large two stroke Marine
engines:
A. State the common causes of scavenge fires.
B. List the indication that a scavenge fire is in progress.
C. State the immediate action to be taken in the event of a
scavenge fire.
D. List with reasons the checks and precautions necessary
before an engine is put back
in to service following a scavenge fire.
Answer:- (a) The causes for scavenge fires are as follows.
(1) Excessive cylinder liner wear.
(2) Worn off and broken piston rings.
(3) Heavy accumulation of cylinder oil and carbon
residue in the scavenge space under piston caused
by over feed of cylinder lubrication.
The above three causes combined together make the
environment favourable for a fire which is caused by
the explosion flame passing through the piston rings
and lighting up the accumulated oil in the under
piston space and spreads by the continuous supply of
air under pressure.
(b) The symptoms of a fire are :
(1) continuous surging of the T/C due to the
increase of pressure in the scavenge space caused by
the burning oil-air mixture.
(2) If a pressure relief door is fitted it will
activate.
(3) In modern ships the particular unit scavenge
space temperature alarm will be activated.
(5) The paint around the scavenge trunking close
to the unit will appear burnt. and will feel hot on
touching.
(c) The actions to be taken are as follows:
(1)As soon as the temperature alarm is activated
rush to the scavenge trunk and confirm it is a
scavenge fire from any of the above mentioned
symptoms which will be observed..
(2) If scavenge space fire extinguishing system is
fitted, it should be operated.
(3)Inform the bridge and slow down the engine, and
inform C/E.
(4) Stop engines ,engage turning gear and keep turning
engine and operate the particular unit cylinder
lubricator manually continuing it till the space has
cooled..
If the weather is calm and there is no sign of
weather deteriorating for the next 18 hours, the unit
may be opened , piston withdrawn and rings renewed
as needed. Unit assembled in all respects and proceed
on voyage. Ensure that the scavenge space drains
under the unit are well cleared. Reduce the cylinder
lubrication feed to the particular unit if the feed rate
is high .Ensure the scavenge space drains are clear and
working.
If the weather is not good and likely to
deteriorate, then cut off the unit and run at a slower
RPM suitable to the conditions which are :
vibration free and a smokeless exhaust. Ensure
all working cylinders exhaust temperatures are within
their normal limits.
The unit should be opened and piston rings
renewed as soon as the weather improves.
Q9. With reference to turbocharger bearings:
A. Discuss the relative advantages and disadvantages of white
metal sleeve and ball
race bearings for turbocharger rotor support.
B. State with reasons how axial location of the rotor is
achieved.
C. Explain how the bearing are kept cool in service.
D. Indicate how the bearings are sealed from the atmosphere
and exhaust gas.
Answer:- White metal lined sleeve bearings are by far
more efficient than roller bearings provided the oil
clearances are correctly limited and the oil is flowing
in at a high pressure to form a good hydrodynamic
fluid film
The purpose of lubrication is two-fold:
TO conduct away the heat developed by friction.
To reduce the coefficient of friction .
Both these are achieved as follows:
The lub-oil has a viscosity for good flow
characteristics which carry away the heat at a
good rate and the viscosity is also suitable tio
sustain a good fluid film.
Roller bearings have rolling friction which
needs lubrication only to take away the heat
and hence the rolling friction is not reduced
because it needs the friction to turn with out
slipping. Roller bearings are therefore inferior to
sleeve bearing
The roller bearings are subject to impact
loading causing Brinelling of the races surfaces
and to prevent this the bearings are
resiliently mounted by resilient spring leaves
packed in the bearing assembly
(B) Axial location is achieved by the opposing
thrusts of the air inlet pressure and the
exhaust gas inlet pressure to the turbine.
The central diaphragm is provided with a
labyrinth gland which to some extent provides
axial support.
(c) Bearings are kept coolby the flow of oil
through the bearings. The oil in circulation is
further cooled in an oil cooler. In the Brown
Boveri T/C the oil is collected locally in its
sump and cooled by natural process since
thew heat extracted is not much.
(D) The bearings are sealed from the exhaust
gases and the air from the atmosphere by the
respective labyrinth gland seals.
Вам также может понравиться
- Part1 Q A Marine EngineerДокумент7 страницPart1 Q A Marine EngineerSamir Alshaar100% (1)
- Part1 Q A Marine Engineer PDFДокумент10 страницPart1 Q A Marine Engineer PDFturgut08Оценок пока нет
- Ek MotorДокумент32 страницыEk MotorAnshu BhushanОценок пока нет
- Parts FailureДокумент5 страницParts Failuremy generalОценок пока нет
- Cylinder Head, Exhaust Valve, ChainДокумент11 страницCylinder Head, Exhaust Valve, ChainAnakin Skywalker100% (1)
- Mek 2000 March 95 SR - No.2Документ2 страницыMek 2000 March 95 SR - No.2Bhupender RamchandaniОценок пока нет
- Motor 1Документ46 страницMotor 1Ganesh Anand100% (1)
- Mekm November 2022Документ18 страницMekm November 2022Chirag GuptaОценок пока нет
- 50 Questions and Answers For Marine Engineers Issue 1Документ10 страниц50 Questions and Answers For Marine Engineers Issue 1severo97100% (1)
- Scavenging & Supercharging Solution of DG Question Bank by Saidul Islam (Jahed) BMFA 35thДокумент8 страницScavenging & Supercharging Solution of DG Question Bank by Saidul Islam (Jahed) BMFA 35thkh al aminОценок пока нет
- 1Документ127 страниц1Rohan NaikОценок пока нет
- EparikshaДокумент2 страницыEparikshadkpushpdkОценок пока нет
- T-01-02 (Pasca) - ATT III - Operate Main and Auxiliary MachineryДокумент5 страницT-01-02 (Pasca) - ATT III - Operate Main and Auxiliary Machineryyudi jdxОценок пока нет
- Motor FinalДокумент72 страницыMotor FinalRamasamy100% (1)
- Fuel InjectorДокумент3 страницыFuel InjectorPar Nd Oo100% (3)
- MotorДокумент84 страницыMotorSarath Raghav100% (1)
- Singapore Polytechnic: MPA E-Assessment Guide For MEO COC 1/2Документ76 страницSingapore Polytechnic: MPA E-Assessment Guide For MEO COC 1/2naveen100% (1)
- Student's MdedhДокумент86 страницStudent's MdedhthomasdilirionОценок пока нет
- Training ManualДокумент135 страницTraining ManualVinithra Rajesh100% (1)
- Mot 13-11-99Документ11 страницMot 13-11-99Mobin GhariОценок пока нет
- Piston Oil CoolingДокумент3 страницыPiston Oil CoolingPranjyoti SaikiaОценок пока нет
- Lubricant System of Power PlantsДокумент12 страницLubricant System of Power PlantsPaulОценок пока нет
- QB 114462Документ15 страницQB 114462vasanthavananОценок пока нет
- 2013 Repeated Objective QuestionsДокумент50 страниц2013 Repeated Objective QuestionsTanawat SongkroaОценок пока нет
- Detect and Indentity The Cause of Machinery Ma-1Документ64 страницыDetect and Indentity The Cause of Machinery Ma-1sukarlem marsiahОценок пока нет
- Part3 Q A Marine EngineerДокумент10 страницPart3 Q A Marine Engineer12345Оценок пока нет
- Identifying Failure ModesДокумент4 страницыIdentifying Failure Modesayad60Оценок пока нет
- What Is Ovality of Auxiliary Engine Crank Pin?Документ62 страницыWhat Is Ovality of Auxiliary Engine Crank Pin?sumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- MAN B&W 6S50MC - Components DescriptionДокумент182 страницыMAN B&W 6S50MC - Components DescriptionHải Nguyễn Văn67% (3)
- Function 4BДокумент55 страницFunction 4BSiva PrakasamОценок пока нет
- Operate Main Andauxiliary Machineryand Associatedcontrol Systems-1-1-2Документ21 страницаOperate Main Andauxiliary Machineryand Associatedcontrol Systems-1-1-2Rio AryaОценок пока нет
- Marine Engineering Knowledge (Motor) All CollectionДокумент16 страницMarine Engineering Knowledge (Motor) All CollectionTapan KhandelwalОценок пока нет
- Mot03 03 1400Документ8 страницMot03 03 1400Mobin GhariОценок пока нет
- 03-04-2014 Motor 1Документ14 страниц03-04-2014 Motor 1Pankaj PooniaОценок пока нет
- Func 4B&6Документ58 страницFunc 4B&6Aswin MohanОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент88 страницUntitledGaurav GairolaОценок пока нет
- Jawaban PropulsiДокумент35 страницJawaban PropulsiyandaОценок пока нет
- Class 4 Written QuestionsДокумент12 страницClass 4 Written QuestionsSachinMarkoseОценок пока нет
- Basic GT EngineДокумент22 страницыBasic GT EngineabuhurairamunirОценок пока нет
- Section A: Justin Kallicharan 90422 Part 1Документ6 страницSection A: Justin Kallicharan 90422 Part 1Justin KallicharanОценок пока нет
- Combustion Process in SI Engines: What Is Combustion and Conditions Necessary To Be Done ?Документ45 страницCombustion Process in SI Engines: What Is Combustion and Conditions Necessary To Be Done ?ashenafi tesfayeОценок пока нет
- Ekm QB Jan 2010 Apr 2016Документ34 страницыEkm QB Jan 2010 Apr 2016Amit Kumar NarayanОценок пока нет
- Motor FinalДокумент109 страницMotor FinalStabin MathewОценок пока нет
- Bashar Sir FAQДокумент92 страницыBashar Sir FAQMehedy MasudОценок пока нет
- License Help For Canadian Engineers1Документ49 страницLicense Help For Canadian Engineers1chans117Оценок пока нет
- c6 PDFДокумент118 страницc6 PDFAnjaana PrashantОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент5 страницUntitledmalikiauОценок пока нет
- DG MotorДокумент213 страницDG MotorMehedy MasudОценок пока нет
- Mekm October 2022Документ14 страницMekm October 2022Chirag GuptaОценок пока нет
- Class III EKG 2Документ3 страницыClass III EKG 2Mahesh Bansode100% (1)
- Meo Class 4 Oral QuestionsДокумент174 страницыMeo Class 4 Oral QuestionsAshok KumarОценок пока нет
- UniKL MIAT Ignition System QuizДокумент6 страницUniKL MIAT Ignition System Quizmellon3duwenОценок пока нет
- Maintanance and Repairof Shipword MachineryДокумент58 страницMaintanance and Repairof Shipword MachineryBahtera Adi50% (2)
- 11 - Appendix (July 2009) PDFДокумент7 страниц11 - Appendix (July 2009) PDFValeriy DomashenkoОценок пока нет
- MEP ME Crank Pin Bearing OHДокумент30 страницMEP ME Crank Pin Bearing OHSuhas KassaОценок пока нет
- Plymouth and Chrysler-built cars Complete Owner's Handbook of Repair and MaintenanceОт EverandPlymouth and Chrysler-built cars Complete Owner's Handbook of Repair and MaintenanceОценок пока нет
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitОт EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitОценок пока нет
- Dual+fuel+engines (GI and LGI) PDFДокумент45 страницDual+fuel+engines (GI and LGI) PDFRamprabu ChandrasekarОценок пока нет
- Crankcase Insp AeДокумент4 страницыCrankcase Insp Aesumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- AFF Question1Документ81 страницаAFF Question1sumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- Air in Reefer SystemДокумент1 страницаAir in Reefer Systemsumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- Imo Conventions & CodesДокумент102 страницыImo Conventions & CodesIlgar KarimovОценок пока нет
- Fuel: J,..,krmt!'ot.Документ15 страницFuel: J,..,krmt!'ot.sahidОценок пока нет
- Fuel Info: List of ContentsДокумент23 страницыFuel Info: List of Contentssumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- What Is Ovality of Auxiliary Engine Crank Pin?Документ62 страницыWhat Is Ovality of Auxiliary Engine Crank Pin?sumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- 2 Tracing The Number 2 Worksheet 1Документ1 страница2 Tracing The Number 2 Worksheet 1sumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- Exit Exm-ChemcoДокумент3 страницыExit Exm-Chemcosumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Symbology 102 - Understanding Basic Fluid Power SchematicsДокумент3 страницыHydraulic Symbology 102 - Understanding Basic Fluid Power Schematicssumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Symbology 102 - Understanding Basic Fluid Power SchematicsДокумент3 страницыHydraulic Symbology 102 - Understanding Basic Fluid Power Schematicssumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Symbology 206 - Motors and ActuatorsДокумент4 страницыHydraulic Symbology 206 - Motors and Actuatorssumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- How Do Relief Valves WorkДокумент2 страницыHow Do Relief Valves Worksumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Symbology 206 - Motors and ActuatorsДокумент4 страницыHydraulic Symbology 206 - Motors and Actuatorssumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Symbology 201 - Industrial Directional Valves PDFДокумент5 страницHydraulic Symbology 201 - Industrial Directional Valves PDFsumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- Oil Spill KitДокумент8 страницOil Spill Kitnqt14283Оценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Symbology 201 - Industrial Directional Valves PDFДокумент5 страницHydraulic Symbology 201 - Industrial Directional Valves PDFsumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Symbology 205 - Hydraulic Pumps PDFДокумент5 страницHydraulic Symbology 205 - Hydraulic Pumps PDFsumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- Common Interview Questions: 1. "Tell Me A Little About Yourself... "Документ2 страницыCommon Interview Questions: 1. "Tell Me A Little About Yourself... "sumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- Cylinder Outlet Tempera-Ture Vs Turbocharger Turbine Inlet TemperatureДокумент2 страницыCylinder Outlet Tempera-Ture Vs Turbocharger Turbine Inlet TemperatureAmiyaОценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Symbology 205 - Hydraulic Pumps PDFДокумент5 страницHydraulic Symbology 205 - Hydraulic Pumps PDFsumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- Bunker Calculation Excel SheetДокумент1 страницаBunker Calculation Excel Sheetsumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- Bunker Calculation Excel SheetДокумент1 страницаBunker Calculation Excel Sheetsumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- Synch Motor Application PDFДокумент1 страницаSynch Motor Application PDFsumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- MEO Class 2 QuestionДокумент2 страницыMEO Class 2 Questionsumitsinha8950% (2)
- ABB ADVAC Circuit Breaker Manual PDFДокумент51 страницаABB ADVAC Circuit Breaker Manual PDFsumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- PID by UKДокумент58 страницPID by UKsumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- Synch Motor Application PDFДокумент1 страницаSynch Motor Application PDFsumitsinha89Оценок пока нет
- Vacc Interruptor PDFДокумент40 страницVacc Interruptor PDFkhandelwalaОценок пока нет
- Diesel Engines and Their Fuels 2009Документ9 страницDiesel Engines and Their Fuels 2009Merrel RossОценок пока нет
- 2002 KX250 Race TuningДокумент4 страницы2002 KX250 Race TuningKidKawie100% (1)
- ECU AnnalysisДокумент6 страницECU AnnalysisAchmad AminОценок пока нет
- Vortec Manual de Serviço 7743365 Engine Manual 4.3 A, B, C, D, EДокумент262 страницыVortec Manual de Serviço 7743365 Engine Manual 4.3 A, B, C, D, Egm_santos197323088% (8)
- Merge File Sample Problems PDFДокумент42 страницыMerge File Sample Problems PDFArgielJohn LlagasОценок пока нет
- ATV 250 ManualДокумент223 страницыATV 250 ManualDavid PootОценок пока нет
- LO Analysis InterpretationДокумент36 страницLO Analysis InterpretationPatrickОценок пока нет
- Wisconsin Robin EY28partsДокумент40 страницWisconsin Robin EY28partsglsmith100Оценок пока нет
- Energies 15 07948 v2Документ20 страницEnergies 15 07948 v2FurqanОценок пока нет
- Lecture No.12 Compressible FluiddocxДокумент15 страницLecture No.12 Compressible Fluiddocxseif elsaieОценок пока нет
- Deutz Fahr TCD 2012 2V Engine Service Repair ManualДокумент17 страницDeutz Fahr TCD 2012 2V Engine Service Repair ManuallaopaodunОценок пока нет
- 2az-Fe Diagnostic Trouble Code ChartДокумент6 страниц2az-Fe Diagnostic Trouble Code ChartEdi Farnando100% (3)
- Tugas 1 Ananda Jaka Kelana 21138011Документ9 страницTugas 1 Ananda Jaka Kelana 21138011Rover CraftОценок пока нет
- GT125 250 Service ManualДокумент0 страницGT125 250 Service ManualJeferson SilvaОценок пока нет
- Engine Misfire, Runs Rough or Is UnstableДокумент4 страницыEngine Misfire, Runs Rough or Is UnstableAdolfo Dario Saavedra0% (1)
- Citycom.300: Service ManualДокумент270 страницCitycom.300: Service ManualFabio FОценок пока нет
- Combustion & Combustion Chamber Design: Lecture-5 by Zewdie Alemayehu Automotive Engineering December 2021Документ68 страницCombustion & Combustion Chamber Design: Lecture-5 by Zewdie Alemayehu Automotive Engineering December 2021ahmed jemalОценок пока нет
- 100 OctaneДокумент18 страниц100 Octanedunmunro100% (1)
- Gas Turbine LabДокумент5 страницGas Turbine LabKin Wai HongОценок пока нет
- Sym Joyride 125 - 150 - 200 (EN)Документ203 страницыSym Joyride 125 - 150 - 200 (EN)manualsym56% (9)
- Coil Press Machine CP-400Документ6 страницCoil Press Machine CP-400Mikhail YudhiantaraОценок пока нет
- Mercedes Benz M272 EngineДокумент28 страницMercedes Benz M272 EngineJijo Mercy100% (2)
- Volvo Penta Tamd63a-72j-A Instruction BookДокумент124 страницыVolvo Penta Tamd63a-72j-A Instruction BookJonathan Efrain100% (3)
- 14.09.2023 - Chapter 1 - Introduction To IC EnginesДокумент70 страниц14.09.2023 - Chapter 1 - Introduction To IC EnginesAditya RatleyОценок пока нет
- Scania DC16 The Evolving V-8 DieselДокумент8 страницScania DC16 The Evolving V-8 DieselAbcОценок пока нет
- ICE - UNIT V - Important QuestionsДокумент5 страницICE - UNIT V - Important QuestionsaravindОценок пока нет
- 8FG (D) U15-32, 8FGCU20-32 Repair Manual Supplement CU066Документ227 страниц8FG (D) U15-32, 8FGCU20-32 Repair Manual Supplement CU066Nguyễn Huỳnh ĐứcОценок пока нет
- ProjectДокумент44 страницыProjectewmdoОценок пока нет
- FYP Complete ReportДокумент70 страницFYP Complete ReportKaleem Furqan Ahmed100% (1)
- Volvo Fh16mainДокумент34 страницыVolvo Fh16mainArizioNeto50% (2)