Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
30 TOP SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODES Questions and Answers PDF SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODES Questions and Answers PDF
Загружено:
sanaullahОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
30 TOP SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODES Questions and Answers PDF SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODES Questions and Answers PDF
Загружено:
sanaullahАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Engineering interview questions,Mcqs,Objective Questions,Class
Notes,Seminor topics,Lab Viva Pdf free download. CIVIL | Mechanical | CSE |
EEE | ECE | IT | Chemical Online Quiz Tests for Freshers.
HOME Interview Questions MCQs *LAB VIVA CLASS NOTES SEMINAR TOPICS
ONLINE TEST SSC CGL GATE CAT
Home » SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODES Questions and
Answers » 30 TOP SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODES
Questions and Answers pdf
30 TOP SPECIAL PURPOSE
DIODES Questions and
Answers pdf
Posted on August 19, 2018 by engineer Leave a
comment
Ads by Google
Wire
Electrical Test Wound
Electronic Circuit
Mechanical Test Resistor
Basics of Electronics
setfuse.com
SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODES Questions and
Answers pdf :-
1. What is a zener diode?
SETfuse
Zener diode is a p-n junction diode specially designed for Under UL
operation in the breakdown region in reverse bias Certificating.
condition.
High Quality,
Value, Precision
2. Define what is zener voltage?
The voltage at which the zener diode breaks down is called
the zener voltage.
3. What is meant by the temperature coefficient?
OPEN
The effect of temperature on zener voltage is given in terms
of temperature coefficient which is defined as the
percentage change in nominal zener voltage for each
degree centigrade of change in junction temperature.
4. Define what happens to the series current , load
current and zener current when the dc input voltage of
a zener regulator increases?
Zener current and series current increases while the load
current remains unchanged.
Custo
5. Why is zener diode used as a voltage regulator?
Zener diode has the property of behaving like a dc battery
in ‘on’ state (i.e. when the voltage across the zener diode Engineering Questions
exceeds its zener voltage rating VZ) . In ‘on’ state , the Engineering Q…
voltage across zener diode remains constant until the 5.5K likes
voltage across it deops less than VZ . This property of zener
diode makes its use as a voltage regulator.
Like Page
6. Explain how zener diode maintains constant voltage
Be the first of your friends to like this
across the load?
Zener diode has the property of behaving like a dc battery Find us on Google Plus
in ‘on’ state. If the zener diode is shunted across the load RL
Engineering In
and the voltage across zener diode is more than the zener
Follow
voltage VZ then zener diode is on ‘on’ state , and any
variation in voltage across the zener diode due to 768 followers
variations either in supply voltage or in load resistance is
not able to change the output voltage. Thus zener diode
maintains voltage constant across the load.
7. Define what is tunnel diode?
Tunnel diode is a high conductivity two-terminal p-n
junction doped heavily (about 1,000 times higher than a
normal diode).
8. What is tunneling?
The mechanism of conduction in a semiconductor diode in
which charge carriers (possessing very little energy) punch
through a barrier directly instead of climbing over it is
called tunneling.
9. What are the applications of tunnel diodes?
Tunnel diodes are used as amplifiers, oscillators or
switching devices, being an exclusive high-frequency
component because of its very fast response inputs.
10. What is PIN diode?
PIN is composed of three sections with a high resistivity
intrinsic layer sandwiched between p and n regions. It
offers a variable resistance (decreasing with the increase in
the forward current) in the forward bias mode and infinite
resistance in the reverse bias mode.
SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODES Interview Questions and
Answers ::
11. What is a varactor diode?
A varactor diode is a specially fabricated p-n junction with
proper impurity concentration profile and operated under
reverse-biased mode so as to give a variable junction
capacitance.
12. Which device produces voltage variable capacitor?
How the voltage variable capacitance varies with the
change in voltage across it?
The varactor diode produces voltage variable capacitor.
The junction capacitance of a varactor diode varies
inversely as the square root of the reverse bias voltage in
case of alloyed junction and varies inversely as the cube
root of reverse bias voltage for diffuse junction.
13. Define what is point contact diode?
Point connect diode consists of an n-type germanium or
silicon (preferably germanium) wafer about 1.25 mm suare
by 0.5 mm thick, one face of which is soldered to a metal
and the other face has a phosphor bronze or tungsten
spring pressed against it. Because of very low capacitance,
point contact diode is very much suitable for high freuency
applications (of the order of 10 GHz).
14. Define what is a step-recovery diode and why is it so
called ?
Step-recovery diode is a voltage-dependent variable
capacitor diode with graded doping profile (concentration
of charge carriers decreasing near the junction). Because of
step or sudden recovery from the reverse current ON to
reverse current OFF, it is called the step-recovery diode.
15. Define what is Schottky diode?
Schottky diode is uite different in construction from the
normal p-n junction diode. It has metal (such as gold, silver,
platinum , molybdenum, chrome or tungsten ) n one side
and n-type doped silicon on the other side of the junction. It
has no storage charge. The junction barrier is called the
Schottky barrier.
16. Why is Schottky diode called hot-carrier diode?
Since in forward bias operation of the Schottky diode, the
electrons on the n-side gains enough energy to cross the
junction and plunge into the metal with very large energy,
they are usually called into the metal with very large
energy, they are usually called hot carriers and the diode is
called hot-carrier diode.
17. Define what is back diode?
Back diode is similar to a tunnel diode except that
tunneling effect is large but only in the reverse direction.
This is also called a unilateral diode.
18. What are power diodes?
The power diodes are similar to p-n junction signal or low-
power diodes but have large power-, voltage-, and current-
handling capabilities than those of conventional p-n
junction diodes. Power diodes find many applications in
electronics and electrical engineering circuits.’
19. Why the current in power diode varies linearly
rather than exponentially with voltage?
The large magnitude of current in power diodes leads to
ohmic drop that hides the exponential part of the V-I
characteristic curve.
20. Define what is photodiode?
Photodiode is a two-terminal semiconductor p-n junction
diode device and is designed to operate with reverse bias.
21. How the current is reduced to zero in a photodiode?
The reverse saturation current I0 flowing through a
photodiode is reduced to zero by applying a forward bias
voltage of magnitude eual to barrier potential.
22. Photodiode is a photovoltaic device or a
photoconductive device or both?
Photodiode is a photovoltaic device as well as a
photoconductive device. When it is operated with a reverse
bias, it is photoconductive device and when operated
without the reverse bias, it is a photovoltaic device.
23. Define what is meant by LED?
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode.
24. What precautions are reuired to be observed in the
use of LEDs?
LEDs should neither be reverse-biased nor operated near
their maximum current rating. The leads of an LED should
never be bent closer than about 2 mm from the
encapsulation.
SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODES Interview Questions and
Answers pdf free download ::
Ads by Google
Electrical Test Electronic Circuit
Mechanical Test Basics of Electronics
LEAVE A REPLY
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment
Вам также может понравиться
- Analog Electronics PDFДокумент9 страницAnalog Electronics PDFDoan BaoОценок пока нет
- Capacitors MCQ & AnsДокумент6 страницCapacitors MCQ & AnsMMBDONОценок пока нет
- Topic 1 Basic Electronics - 00 V2.0Документ64 страницыTopic 1 Basic Electronics - 00 V2.0JENNIFER SERVOОценок пока нет
- Running (Test-1) EC 322 SensorsДокумент68 страницRunning (Test-1) EC 322 SensorsSaurabh MauryaОценок пока нет
- Current Electricity: Written WorkДокумент35 страницCurrent Electricity: Written WorkShaari KashaniОценок пока нет
- Digital Electronics: CT 304N Unit:1 Number Systems and CodesДокумент172 страницыDigital Electronics: CT 304N Unit:1 Number Systems and CodesLiyanshu patelОценок пока нет
- Active and Passive ComponentsДокумент2 страницыActive and Passive Componentssarsm56Оценок пока нет
- ELE-2213 Lecture-Notes2 201910 (Student Version)Документ144 страницыELE-2213 Lecture-Notes2 201910 (Student Version)Leads girlОценок пока нет
- MCQs General Unit IДокумент25 страницMCQs General Unit IN1234m100% (1)
- 4-Bit Parallel AdderДокумент39 страниц4-Bit Parallel AdderRajuОценок пока нет
- Digital Electronics NotesДокумент132 страницыDigital Electronics Notescute couplesОценок пока нет
- Taming TigerДокумент24 страницыTaming Tigerphu nongОценок пока нет
- Ee and Ece Important MCQ Pdf-Oscillators 1Документ6 страницEe and Ece Important MCQ Pdf-Oscillators 1sayed100% (1)
- MCQ 3,4Документ18 страницMCQ 3,4vijayalakshmiОценок пока нет
- Analog Electronics II, ECE-204: Chapter-1: Feedback ConceptsДокумент31 страницаAnalog Electronics II, ECE-204: Chapter-1: Feedback ConceptstsegayОценок пока нет
- EE 322 TransformersДокумент73 страницыEE 322 TransformersCedric BernardОценок пока нет
- Measuring Instruments & TransducersДокумент6 страницMeasuring Instruments & TransducersHarith Nawfel100% (1)
- MCQ Measurements and InstrumentationДокумент47 страницMCQ Measurements and Instrumentationeee2014.rvsОценок пока нет
- MCQДокумент99 страницMCQsangeetadineshОценок пока нет
- MCQ-Flip FlopДокумент11 страницMCQ-Flip Flop01ABHIGYAN MAJIОценок пока нет
- A. B. C. D.: Answer: Option B ExplanationДокумент10 страницA. B. C. D.: Answer: Option B ExplanationKuya KimОценок пока нет
- Transformer MCQsДокумент33 страницыTransformer MCQsKhan AaghaОценок пока нет
- Multiple Choice Questions ElectricianДокумент6 страницMultiple Choice Questions Electricianvijay100% (1)
- Diodes NotesДокумент27 страницDiodes Noteskhanjamil12Оценок пока нет
- Multiple Choice Questions and Answers On Semiconductor Diode - Electronics PostДокумент8 страницMultiple Choice Questions and Answers On Semiconductor Diode - Electronics PostDurga DeviОценок пока нет
- Sequential Circuits-Class NotesДокумент41 страницаSequential Circuits-Class NotessrisairampolyОценок пока нет
- Electrical Technology Volume I Basic Electrical EngineeringДокумент36 страницElectrical Technology Volume I Basic Electrical EngineeringsantoshpbkОценок пока нет
- Practice Set SSC-CGL TIER I PDFДокумент15 страницPractice Set SSC-CGL TIER I PDFmanuОценок пока нет
- Resistors, Capacitors and Inductors GuideДокумент5 страницResistors, Capacitors and Inductors GuideErwin AhmadОценок пока нет
- Logic Families MCQs SimpleДокумент8 страницLogic Families MCQs SimplebijukumargОценок пока нет
- Chapter14 Electric CurrentДокумент11 страницChapter14 Electric CurrenteltytanОценок пока нет
- Topicwise Mains Question Papers GSM1 From 2013 To 2019Документ29 страницTopicwise Mains Question Papers GSM1 From 2013 To 2019Vigneshwaran MuruganОценок пока нет
- Signals & Systems Lecture Overview: Time-Domain, Fourier, Z Transforms & Digital FiltersДокумент55 страницSignals & Systems Lecture Overview: Time-Domain, Fourier, Z Transforms & Digital FiltersWaqas Akram GondalОценок пока нет
- Free Study Materials & Career Guidance for Engineers, Doctors & MoreДокумент124 страницыFree Study Materials & Career Guidance for Engineers, Doctors & MoreaduveyОценок пока нет
- Basic Electronics Lec-1Документ41 страницаBasic Electronics Lec-1world cup 2019Оценок пока нет
- KRL Institute of Technology, Kahuta: CIT-2 Year Subject: Digital & Industrial Electronics Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент7 страницKRL Institute of Technology, Kahuta: CIT-2 Year Subject: Digital & Industrial Electronics Multiple Choice QuestionsHamza MustafaОценок пока нет
- Objective Questions. Topic: Number System and CodesДокумент56 страницObjective Questions. Topic: Number System and Codesthejareddy14Оценок пока нет
- Digital Electronics Question BankДокумент34 страницыDigital Electronics Question Banksujithaa13100% (1)
- Basic Magnetism Concepts Explained in 25 QuestionsДокумент10 страницBasic Magnetism Concepts Explained in 25 QuestionsWinnie Jun ColangoyОценок пока нет
- Basic Electronics: Prepared By: Omair Khimani (10905)Документ22 страницыBasic Electronics: Prepared By: Omair Khimani (10905)Omair KhimaniОценок пока нет
- ADC and DAC Converters ExplainedДокумент5 страницADC and DAC Converters ExplainedMatthew AlexanderОценок пока нет
- Module2 (RESISTOR)Документ40 страницModule2 (RESISTOR)Marlon AranasОценок пока нет
- Digital Electronics Interview QuestionsДокумент5 страницDigital Electronics Interview QuestionsetasureshОценок пока нет
- Unit-1 8085Документ299 страницUnit-1 8085sujithОценок пока нет
- Number Systems and CodesДокумент37 страницNumber Systems and CodesSiva JiОценок пока нет
- Signals and SystemsДокумент42 страницыSignals and SystemsDeepa DhilipОценок пока нет
- Physics XII QP Set 1Документ10 страницPhysics XII QP Set 1meme MachineОценок пока нет
- Digital Q BankДокумент17 страницDigital Q BankMuhamad FaizalОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Diode ApplicationsДокумент22 страницыChapter 2 Diode ApplicationsDaNieL RuPErTOОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 QuizДокумент18 страницUnit 2 QuizkalpanadeviОценок пока нет
- DC Circuits MCQДокумент7 страницDC Circuits MCQcool yadavОценок пока нет
- Questions On DiodesДокумент40 страницQuestions On Diodeskibrom atsbha100% (1)
- MCQ LCR Circuits Master-1Документ14 страницMCQ LCR Circuits Master-1Deepak Choudhary DCОценок пока нет
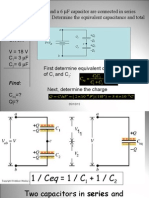
- Capacitor 2Документ31 страницаCapacitor 2Shaheer MirzaОценок пока нет
- Module 04 Electronics Fundamentals Aircraft License ComДокумент70 страницModule 04 Electronics Fundamentals Aircraft License ComMohamad Nadzmi100% (1)
- Registers and CountersДокумент6 страницRegisters and CountersgeethajeganОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 Transformer: Construction and WorkingДокумент20 страницUnit 3 Transformer: Construction and WorkingSamrudhi PatilОценок пока нет
- 30 Top Special Purpose Diodes Questions and Answers PDF Special Purpose Diodes Questions and AnswersДокумент3 страницы30 Top Special Purpose Diodes Questions and Answers PDF Special Purpose Diodes Questions and AnswersAmirSaeedОценок пока нет
- Special Purpose Diodes Questions and AnswersДокумент4 страницыSpecial Purpose Diodes Questions and AnswersSuresh LОценок пока нет
- Special Purpose Diodes Questions and AnswersДокумент3 страницыSpecial Purpose Diodes Questions and AnswersJohn CedrickОценок пока нет
- General knowledge MCQs with DetailsДокумент13 страницGeneral knowledge MCQs with DetailssanaullahОценок пока нет
- Civil Military RelationsДокумент13 страницCivil Military RelationsFaisal RanaОценок пока нет
- Computer Science Guess Papers 2017Документ7 страницComputer Science Guess Papers 2017engrsana ullahОценок пока нет
- CSS Cold War Origin, Causes and PhasesДокумент4 страницыCSS Cold War Origin, Causes and Phasessanaullah100% (1)
- Rivers of The World MCQs - World General Knowledge SeriesДокумент7 страницRivers of The World MCQs - World General Knowledge SeriessanaullahОценок пока нет
- 11 Math MCQsДокумент22 страницы11 Math MCQssanaullahОценок пока нет
- 4.1 The Special Situation of Landlocked CountriesДокумент3 страницы4.1 The Special Situation of Landlocked CountriessanaullahОценок пока нет
- Applied Physics - Underwater SoundsДокумент9 страницApplied Physics - Underwater SoundssanaullahОценок пока нет
- DC MOTORS: HOW THEY WORK AS GENERATORS & MOTORSДокумент7 страницDC MOTORS: HOW THEY WORK AS GENERATORS & MOTORSKelvin LiewОценок пока нет
- Applied Physics - Underwater SoundsДокумент9 страницApplied Physics - Underwater SoundssanaullahОценок пока нет
- Current Affairs MCQs from October and November 2020Документ56 страницCurrent Affairs MCQs from October and November 2020sanaullahОценок пока нет
- Current Affairs MCQs from October and November 2020Документ56 страницCurrent Affairs MCQs from October and November 2020sanaullahОценок пока нет
- Pak Study MCQs in PDF Part-1Документ19 страницPak Study MCQs in PDF Part-1Arshad Iqbal KhattakОценок пока нет
- Only Typing and Shorthand TestДокумент1 страницаOnly Typing and Shorthand TestSirajUlHaqОценок пока нет
- English Hints: List of Pre Xes: Learn New Words FasterДокумент7 страницEnglish Hints: List of Pre Xes: Learn New Words FastersanaullahОценок пока нет
- Restrict Users Access To C DriveДокумент4 страницыRestrict Users Access To C DrivesanaullahОценок пока нет
- 300 General Knowledge MCQ'SДокумент52 страницы300 General Knowledge MCQ'SArslan Shakir92% (25)
- Worlds Currents Affairs 1 To 50Документ48 страницWorlds Currents Affairs 1 To 50sanaullahОценок пока нет
- USA History PMSДокумент1 страницаUSA History PMSsanaullahОценок пока нет
- Sociology PMSДокумент1 страницаSociology PMSsanaullahОценок пока нет
- World General Knowledge MCQs (Solved) Geographical Epithets (Countries & Cities)Документ14 страницWorld General Knowledge MCQs (Solved) Geographical Epithets (Countries & Cities)sanaullahОценок пока нет
- Rivers of The World MCQs - World General Knowledge SeriesДокумент7 страницRivers of The World MCQs - World General Knowledge SeriessanaullahОценок пока нет
- Mock quiz sets on computer hardware and input devicesДокумент5 страницMock quiz sets on computer hardware and input devicessanaullahОценок пока нет
- 4.1 The Special Situation of Landlocked CountriesДокумент3 страницы4.1 The Special Situation of Landlocked CountriessanaullahОценок пока нет
- English Grammar Solved MCQs Sentence Completion (Prepositions)Документ3 страницыEnglish Grammar Solved MCQs Sentence Completion (Prepositions)Anonymous I2dHlfОценок пока нет
- CTBT Treaty Bans Nuclear TestsДокумент3 страницыCTBT Treaty Bans Nuclear TestssanaullahОценок пока нет
- Vertical Horizontal PDFДокумент8 страницVertical Horizontal PDFRj LegoreОценок пока нет
- Mock quiz sets on computer hardware and input devicesДокумент5 страницMock quiz sets on computer hardware and input devicessanaullahОценок пока нет
- Module 7: Memory Interfacing: Cs/Ece/Eee/Instr F241 - Microprocessor Programming & InterfacingДокумент4 страницыModule 7: Memory Interfacing: Cs/Ece/Eee/Instr F241 - Microprocessor Programming & InterfacingsanaullahОценок пока нет
- Trig All Proofs PDFДокумент9 страницTrig All Proofs PDFsanaullahОценок пока нет
- 1) Initial PagesДокумент7 страниц1) Initial Pagesapi-3784079100% (2)
- TechWeb E DL SiCДокумент88 страницTechWeb E DL SiC王政雄Оценок пока нет
- Module 9 Zener Diodes and ApplicationsДокумент34 страницыModule 9 Zener Diodes and ApplicationsGio AscanОценок пока нет
- CDBA220-HF Thru. CDBA2100-HF: SMD Schottky Barrier RectifiersДокумент4 страницыCDBA220-HF Thru. CDBA2100-HF: SMD Schottky Barrier Rectifierscatsoithahuong84Оценок пока нет
- Norde1979 A Modified Forward I-V Plot For Schottky Diodes With High Series ResistanceДокумент3 страницыNorde1979 A Modified Forward I-V Plot For Schottky Diodes With High Series Resistanceचन्द्रभाल सिंहОценок пока нет
- DIODO SCHOTTKY - Bat54 - Series - Wte PDFДокумент5 страницDIODO SCHOTTKY - Bat54 - Series - Wte PDFAntonio C MangifestaОценок пока нет
- Etat de L'art Et Prospectives Sur Les Composants de Puissance Grand GapДокумент16 страницEtat de L'art Et Prospectives Sur Les Composants de Puissance Grand GapkmcablacОценок пока нет
- Designing Schottky Diodes for Pulse CompressionДокумент7 страницDesigning Schottky Diodes for Pulse CompressionJesús MartínezОценок пока нет
- 30 Top Special Purpose Diodes Questions and Answers PDF Special Purpose Diodes Questions and AnswersДокумент3 страницы30 Top Special Purpose Diodes Questions and Answers PDF Special Purpose Diodes Questions and AnswersAmirSaeedОценок пока нет
- Estadry D-Type DBДокумент12 страницEstadry D-Type DBcharleselitb92Оценок пока нет
- Adapter Ac DCДокумент13 страницAdapter Ac DCAnderson OliveiraОценок пока нет
- Studies of Znse and Indium Tin Oxide Based Thin Film Schottky Barriers and Hetero Junctions For Their Electrical and Optical PropertiesДокумент263 страницыStudies of Znse and Indium Tin Oxide Based Thin Film Schottky Barriers and Hetero Junctions For Their Electrical and Optical PropertiesSumbitchalihaОценок пока нет
- Vishal Subbiah VДокумент20 страницVishal Subbiah VanyaarajeshОценок пока нет
- D10SC4M: ShindengenДокумент11 страницD10SC4M: ShindengensОценок пока нет
- Semiconductor Diode: Name: Gabriel, Marielle M. Student #: 2018103210Документ15 страницSemiconductor Diode: Name: Gabriel, Marielle M. Student #: 2018103210Elle GabrielОценок пока нет
- Max17126 Max17126a PDFДокумент34 страницыMax17126 Max17126a PDFVukica IvicОценок пока нет
- FDMC8200SДокумент12 страницFDMC8200Sdreyes3773Оценок пока нет
- Sic Appli-EДокумент89 страницSic Appli-EKrishna KumarОценок пока нет
- Lucas Semiconductors and Organic Semiconductor CapacitorsДокумент15 страницLucas Semiconductors and Organic Semiconductor CapacitorsBeny StephenОценок пока нет
- Extraction of Schottky Diode Parameters From Forward Current-Voltage CharacteristicsДокумент4 страницыExtraction of Schottky Diode Parameters From Forward Current-Voltage CharacteristicsChandu KakarlaОценок пока нет
- Data SheetДокумент2 страницыData SheetselocaОценок пока нет
- Wireless Mobile Charging Using Microwave RectennasДокумент12 страницWireless Mobile Charging Using Microwave RectennasReshmainduОценок пока нет
- Product Selection Guide: Ween SemiconductorsДокумент20 страницProduct Selection Guide: Ween SemiconductorsIosef Nee-MeОценок пока нет
- Bill of Materials - Design 1 Pre-Made Rectifier and Load Balancing Circuit Component Details Qty Price Per PC AmountДокумент6 страницBill of Materials - Design 1 Pre-Made Rectifier and Load Balancing Circuit Component Details Qty Price Per PC AmountHikaru HitachiinОценок пока нет
- Features Descriptio: LTC485 Low Power RS485 Interface TransceiverДокумент12 страницFeatures Descriptio: LTC485 Low Power RS485 Interface TransceiverSidumisile SikhosanaОценок пока нет
- Special Semiconductor DevicesДокумент40 страницSpecial Semiconductor DevicesJairus OnkwaniОценок пока нет
- Infineon 8CLJQ045 DataSheet v01 - 01 ENДокумент5 страницInfineon 8CLJQ045 DataSheet v01 - 01 ENjulio cardosoОценок пока нет
- 1N5819G Schottky Barrier DiodeДокумент4 страницы1N5819G Schottky Barrier DiodeHannan HannanОценок пока нет
- D12S60-Infineon Diode Schottky PDFДокумент8 страницD12S60-Infineon Diode Schottky PDFHưng HQОценок пока нет
- Fabrication of TransistorsДокумент10 страницFabrication of TransistorsDurga PrasathОценок пока нет