Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Intinsic PEEP, Gas Trapping and The Expiratory Hold Manoeuvre
Загружено:
Khairiyah MahalilОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Intinsic PEEP, Gas Trapping and The Expiratory Hold Manoeuvre
Загружено:
Khairiyah MahalilАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
This document was created by Alex Yartsev (dr.alex.yartsev@gmail.
com); if I have used your data or images and forgot to reference you, please email me.
Intrinsic PEEP(PEEPi), Gas Trapping and the expiratory hold manoeuvre
The EXPIRATORY BREATH HOLD manoeuvre to measure intrinsic PEEP
Intrinsic PEEP
Pressure Machine PEEP
The Physics of Intrinsic PEEP:
Airway opening pressure
Flow
Alveolar pressure
When you exhale,
airflow is driven by the difference between these two pressures.
Volume The difference is created by the elastic recoil of the lungs and
the chest wall.
The Expiratory breath Hold The flow of air out of the lungs is also resisted by the
If there is gas trapped in the alveoli, and expiration is not sufficient EXPIRATORY AIRWAY RESISTANCE
in clearing that gas out, a certain amount of positive pressure will
still be found in the lungs following expiration.
Typically, it takes 1.5 seconds to exhale a tidal breath.
This positive pressure is termed “intrinsic PEEP”
Things which increase intinsic PEEP are things which
An expiratory breath hold stops all flow in the airways; so you can - Impair elastic recoil
eliminate the expiratory airway resistance (the flow dependent o Emphysema
component of intrinsic PEEP). - Increase expiratory resistance
o Bronchospasm
Thus you are able to measure the “static PEEP”, the PEEP due to the o Airway collapse at the equal-pressure point
elastic recoil of the lungs putting pressure on the gas trapped inside them. (where intrathoracic pressure equals
GAS TRAPPING intrabronchial pressure)
VOLUME CONTROLLED ACV o
This is called “gas trapping”,
or Dynamic Hyperinflation.
The key issue is that
THERE IS NOT ENOUGH
Pressure
TIME FOR EXPIRATION.
The flow fails to reach zero; another breath has been
taken before the lungs have had a chance to empty. The solution to this problem is
Observe: it takes a while for the flow to reach
to increase the I:E ratio.
zero. This is a sign of airway obstruction, eg The patient needs more time
bronchospasm.
to exhale the volume.
o
Flow
Volume control target
Volume
With “Basic Assessment and Support in Intensive Care” by Gomersall et all as a foundation, I built using the humongous and canonical “Principles and Practice of Mechanical Ventilation” by Tobins et al – the 1442 page 2 nd edition
Вам также может понравиться
- Mechanical Ventilation GraphicsДокумент144 страницыMechanical Ventilation GraphicsSaddamОценок пока нет
- Lung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesОт EverandLung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesAlain JunodОценок пока нет
- Patient-Ventilator Dyssynchrony in The Intensive Care Unit A PracticalДокумент12 страницPatient-Ventilator Dyssynchrony in The Intensive Care Unit A PracticalBrenda Serrano LaraОценок пока нет
- Managing Coagulopathy ICUДокумент38 страницManaging Coagulopathy ICUMirabela Colac100% (1)
- A Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsОт EverandA Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes On Respiratory Physiology PDFДокумент33 страницыLecture Notes On Respiratory Physiology PDFMiles HuiОценок пока нет
- Basics of Ventilatory SupportДокумент43 страницыBasics of Ventilatory SupportAdhithya Bhat100% (1)
- Viscoelastic Tests of Clotting Function (TEG and ROTEM) - Deranged PhysiologyДокумент12 страницViscoelastic Tests of Clotting Function (TEG and ROTEM) - Deranged Physiologyhnzzn2bymdОценок пока нет
- Acute Severe Asthma Critical Care Management: Lokesh Tiwari Aiims PatnaДокумент53 страницыAcute Severe Asthma Critical Care Management: Lokesh Tiwari Aiims PatnaYohana SepthiyaОценок пока нет
- Aprv Power PointДокумент96 страницAprv Power PointAndi HidayatОценок пока нет
- Overview of Respiratory Failure & Use of Mechanical VentilationДокумент89 страницOverview of Respiratory Failure & Use of Mechanical VentilationsheharyarОценок пока нет
- LIGHT Pulmo Ventilation Sleep Apnea DR ConstantinoДокумент6 страницLIGHT Pulmo Ventilation Sleep Apnea DR ConstantinoMiguel Cuevas DolotОценок пока нет
- LIGHT Bronchiectasis Dr. ConstantinoДокумент5 страницLIGHT Bronchiectasis Dr. ConstantinoMiguel Cuevas DolotОценок пока нет
- Vasoplegic SyndromeДокумент41 страницаVasoplegic SyndromeFaizan Ahmad Ali100% (1)
- Asynchrony Consequences and ManagementДокумент17 страницAsynchrony Consequences and ManagementjuanОценок пока нет
- Principles and Practice of Pharmacology for AnaesthetistsОт EverandPrinciples and Practice of Pharmacology for AnaesthetistsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- A Simplified Treatment-Based Approach To TEG and ROTEMДокумент7 страницA Simplified Treatment-Based Approach To TEG and ROTEMCraigbud99Оценок пока нет
- APRVДокумент20 страницAPRVivanrom100% (1)
- Antibiotic Susceptibilities in Intensive Care: Gram Positive Gram NegativeДокумент2 страницыAntibiotic Susceptibilities in Intensive Care: Gram Positive Gram NegativeMai Anh NguyenОценок пока нет
- Flow LoopДокумент6 страницFlow LoopfarexОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary HypertensionДокумент26 страницPulmonary Hypertensionakoeljames8543Оценок пока нет
- Should We Use Driving Pressure To Set Tidal Volume? PDFДокумент7 страницShould We Use Driving Pressure To Set Tidal Volume? PDFYaxkin NikОценок пока нет
- Light Pulmo Cap Hcap DR LeeДокумент12 страницLight Pulmo Cap Hcap DR LeeMiguel Cuevas DolotОценок пока нет
- Ventilator Wave Form and InterpretationДокумент59 страницVentilator Wave Form and InterpretationArnab SitОценок пока нет
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesДокумент5 страницBreathing and Exchange of Gaseslpc4944Оценок пока нет
- Ards 2Документ7 страницArds 2LUCIBELLOT1Оценок пока нет
- Basic VentilationДокумент64 страницыBasic VentilationGBJ VisionОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary Artery HypertensionДокумент21 страницаPulmonary Artery HypertensionAzizi Abd RahmanОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Ventilation Handout - AllenhoДокумент23 страницыMechanical Ventilation Handout - AllenhoCarmen HerediaОценок пока нет
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Strategies for ManagementОт EverandCommunity-Acquired Pneumonia: Strategies for ManagementAntoni TorresРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- LIGHT Pneumonia Dr. ConstantinoДокумент6 страницLIGHT Pneumonia Dr. ConstantinoMiguel Cuevas DolotОценок пока нет
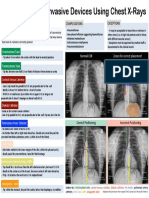
- Invasive Devices On CXRДокумент1 страницаInvasive Devices On CXRLaurensia Erlina NataliaОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary HTNДокумент51 страницаPulmonary HTNMuhammad HaekalОценок пока нет
- Pulsus ParadoxusДокумент2 страницыPulsus ParadoxusHassan.shehriОценок пока нет
- Evidence-Based Obstetric AnesthesiaОт EverandEvidence-Based Obstetric AnesthesiaStephen H. HalpernОценок пока нет
- Clinical Cases in Right Heart FailureОт EverandClinical Cases in Right Heart FailureLana TsaoОценок пока нет
- Basic Haemodynamic Monitoring - Brendan SmithДокумент86 страницBasic Haemodynamic Monitoring - Brendan SmithRhyno FebriyantoОценок пока нет
- PDF Heart FailureДокумент30 страницPDF Heart FailureNitya Manggala JayaОценок пока нет
- Review of HD Monitoring: DR Ghaleb Almekhlafi MD, SFCCM, EdicДокумент105 страницReview of HD Monitoring: DR Ghaleb Almekhlafi MD, SFCCM, EdicGHALEB A. Almekhlafi100% (1)
- Perioperative Medicine: Medical Consultation and Co-managementОт EverandPerioperative Medicine: Medical Consultation and Co-managementAmir K. JafferОценок пока нет
- Basic Principles of Mechanical VentilationДокумент34 страницыBasic Principles of Mechanical VentilationMohamed KorieshОценок пока нет
- VentilatorWebinar1-Prof YasserДокумент28 страницVentilatorWebinar1-Prof YasserShuaa AlabdulsalamОценок пока нет
- ICU One Pager NIPPVДокумент1 страницаICU One Pager NIPPVNicholas HelmstetterОценок пока нет
- Necrotizing PneumoniaДокумент7 страницNecrotizing PneumoniaMahdalenaSyahОценок пока нет
- How A Breath Is Delivered: OutlineДокумент16 страницHow A Breath Is Delivered: OutlineLesly Peinado TorresОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Ventilation Graphical Assessment: Mazen Kherallah, MD, MHA, FCCPДокумент30 страницMechanical Ventilation Graphical Assessment: Mazen Kherallah, MD, MHA, FCCPLuis LopezОценок пока нет
- Ventilator Graphics Recognition and Monitoring Made EasyДокумент38 страницVentilator Graphics Recognition and Monitoring Made EasyBA OngОценок пока нет
- Ventilator Weaning and Spontaneous Breathing Trials An Educational Review 2016Документ7 страницVentilator Weaning and Spontaneous Breathing Trials An Educational Review 2016Tarran PhagooОценок пока нет
- Understanding Mechanical Ventilation: Jennifer Zanni, PT, DSCPT Johns Hopkins HospitalДокумент52 страницыUnderstanding Mechanical Ventilation: Jennifer Zanni, PT, DSCPT Johns Hopkins HospitalDeepa BhattacharjeeОценок пока нет
- Basics of Chest X-RayДокумент44 страницыBasics of Chest X-RayvmamikonОценок пока нет
- Supraglottic Airway DevicesДокумент20 страницSupraglottic Airway DevicesZac CamannОценок пока нет
- Ventilator Management ProtocolДокумент9 страницVentilator Management ProtocolcrisdinasusenoОценок пока нет
- COPD Acute Management ABCDEДокумент11 страницCOPD Acute Management ABCDESSОценок пока нет
- Critical Thinking in Respiratory Care Practice PDFДокумент17 страницCritical Thinking in Respiratory Care Practice PDFFernando MorenoОценок пока нет
- Body Plethysmography AvneetДокумент54 страницыBody Plethysmography Avneetsalimtajamul100% (3)
- Parts of Speech AssignmentДокумент2 страницыParts of Speech Assignmentroyce542Оценок пока нет
- FleshLight Original FREE Stamina Training Unit Manual PDF EbookДокумент9 страницFleshLight Original FREE Stamina Training Unit Manual PDF Ebookfleshlight100% (1)
- Red Dog by Louis de Bernières Sample ChapterДокумент12 страницRed Dog by Louis de Bernières Sample ChapterRandomHouseAU83% (6)
- Brain Teasers 1Документ2 страницыBrain Teasers 1Starpiter80% (10)
- Excretory System of ChickenДокумент3 страницыExcretory System of ChickenAjikОценок пока нет
- MICRO Lecture 1 Introduction To Microbiology and Parasitology 1 PDFДокумент29 страницMICRO Lecture 1 Introduction To Microbiology and Parasitology 1 PDFJireh AcabalОценок пока нет
- Long Quiz 1 BiologyДокумент2 страницыLong Quiz 1 BiologyNonita Caracas CubiloОценок пока нет
- Pleno A Blok 22 (Abortus)Документ34 страницыPleno A Blok 22 (Abortus)Jesslyn HarapanОценок пока нет
- Histology of KidneyДокумент4 страницыHistology of KidneyIzzi FekratОценок пока нет
- Staff Training Slideshow 5-PestcontrolДокумент14 страницStaff Training Slideshow 5-PestcontrolJ NuchinОценок пока нет
- Dimensions of The DentureДокумент8 страницDimensions of The DentureetequetaquiОценок пока нет
- The Effect of Temperature On The Hatching Success of Brine ShrimpДокумент2 страницыThe Effect of Temperature On The Hatching Success of Brine ShrimptahamidОценок пока нет
- AttachmentДокумент15 страницAttachmentMamila TadОценок пока нет
- Biomechanics of RPD 1Документ9 страницBiomechanics of RPD 1Padmini ReddyОценок пока нет
- T: G A P: Ables Roups of Cupuncture OintsДокумент6 страницT: G A P: Ables Roups of Cupuncture OintsrikymediaОценок пока нет
- Dog GoldendoodleДокумент8 страницDog GoldendoodlejustasОценок пока нет
- English Language TriviaДокумент10 страницEnglish Language TriviaTrisha May Ara AnaretaОценок пока нет
- Pressure Groups in PoliticsДокумент66 страницPressure Groups in PoliticsRenzo de LeonОценок пока нет
- Hotel Taj Palace PresentationДокумент33 страницыHotel Taj Palace PresentationBhupesh KumarОценок пока нет
- What Is Hypotonic SolutionДокумент5 страницWhat Is Hypotonic SolutionC Six Nor AzwaniОценок пока нет
- Organization and Expression of Immunoglobulin GenesДокумент70 страницOrganization and Expression of Immunoglobulin Genesmicrokannan80% (5)
- Cleft Lip and PalateДокумент71 страницаCleft Lip and PalateMegha Sahni Grover75% (4)
- 2022 - 2023 Sunrise Sunset Tables Entire YearДокумент2 страницы2022 - 2023 Sunrise Sunset Tables Entire YearmartsОценок пока нет
- 2013 ENDOCRINE PHARMACOLOGY Word Notes PDFДокумент52 страницы2013 ENDOCRINE PHARMACOLOGY Word Notes PDFNicole Opao100% (4)
- Tibbit - A Playable Race For 5th EditionДокумент3 страницыTibbit - A Playable Race For 5th Editionsoudrack100% (5)
- Spellcaster #7Документ70 страницSpellcaster #7nispotulmiОценок пока нет
- Dichotomous KeynotesДокумент19 страницDichotomous KeynotesAnonymous vqO6zPОценок пока нет
- Една Кука Woollky Penguin Crochet Pattern by Babayaga EngДокумент4 страницыЕдна Кука Woollky Penguin Crochet Pattern by Babayaga EngDiana BozhilovaОценок пока нет
- ZOO 120 Laboratory ExperimentsДокумент17 страницZOO 120 Laboratory ExperimentsErica De Guzman100% (1)
- Who Should Pay The Animal Shelter Fine?: Small Bugs Big ChangesДокумент34 страницыWho Should Pay The Animal Shelter Fine?: Small Bugs Big Changescn_cadillacmiОценок пока нет