Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Circulatory System
Загружено:
Tado0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
10 просмотров3 страницыThe circulatory system transports blood throughout the body using the heart, veins and arteries. Common diseases include angina which causes chest pain from reduced blood flow to the heart, myocardial infarction which is a severe blockage of blood to the heart muscle, leukemia which is cancer of the blood-forming tissues, stroke which occurs when blood supply to the brain is interrupted, hypertension which refers to high blood pressure, and atherosclerosis which is the buildup of plaque in the artery walls restricting blood flow. Emerging technologies help diagnose and treat these conditions, such as smart watches that monitor heart rate, implants that reduce stroke risk, and minimally invasive procedures to open blocked arteries.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
circulatory-system.docx
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe circulatory system transports blood throughout the body using the heart, veins and arteries. Common diseases include angina which causes chest pain from reduced blood flow to the heart, myocardial infarction which is a severe blockage of blood to the heart muscle, leukemia which is cancer of the blood-forming tissues, stroke which occurs when blood supply to the brain is interrupted, hypertension which refers to high blood pressure, and atherosclerosis which is the buildup of plaque in the artery walls restricting blood flow. Emerging technologies help diagnose and treat these conditions, such as smart watches that monitor heart rate, implants that reduce stroke risk, and minimally invasive procedures to open blocked arteries.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
10 просмотров3 страницыCirculatory System
Загружено:
TadoThe circulatory system transports blood throughout the body using the heart, veins and arteries. Common diseases include angina which causes chest pain from reduced blood flow to the heart, myocardial infarction which is a severe blockage of blood to the heart muscle, leukemia which is cancer of the blood-forming tissues, stroke which occurs when blood supply to the brain is interrupted, hypertension which refers to high blood pressure, and atherosclerosis which is the buildup of plaque in the artery walls restricting blood flow. Emerging technologies help diagnose and treat these conditions, such as smart watches that monitor heart rate, implants that reduce stroke risk, and minimally invasive procedures to open blocked arteries.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
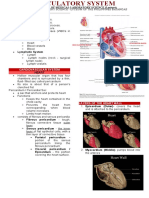
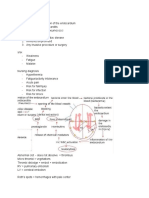
Circulatory System
a. Heart - bone marrow produces
- essential in the system abnormal white blood cells
- cardiac muscles for blood - may be acute (immature
distribution blood cells that can’t
b. Veins & Arteries function normally) or
- just as essential in the chronic (mature blood cells
system which produce too many or
- main site for blood too few)
transport & distribution - causes: previous cancer
treatment, genetic
disorders, smoking (acute
Diseases
myelogenous leukemia),
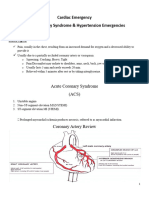
1. Angina Pectoris family history of leukemia
- angina = localized pain - symptoms: fever/chills,
- pectoris = relating to the fatigue, weakness, weight
chest loss, swollen lymph nodes,
- lack of blood flow to enlarged liver or spleen,
heart (usually temporary) easy bleeding or bruising,
- may signify heart recurrent nosebleeds,
disorders excessive sweating, bone
- occurs with vomiting, pain or tenderness
neck, jaw or back
discomfort, and sweating 4. Stroke
- two types: stable (during - occurs when the blood
physical stress) & unstable supply to part of your brain
(severe – occurs at rest) is interrupted or reduced,
depriving brain tissue of
2. Myocardial Infarction oxygen and nutrients
- myo = muscle; cardial = - Ischemic Stroke: arteries
heart. to the brain become narrow
- infarction = obstruction or blocked
of blood - Hemorrhagic Stroke: blood
- severe obstruction of vessel in the brain leaks or
blood to heart muscle ruptures
- results to severe death of - causes: overweight or
muscle tissue obese, high cholesterol,
- causes: stress, obesity, diabetes, physical
lack of exercise & inactivity, heavy drinking &
underlying heart-related use of illicit drugs,
conditions obstructive sleep apnea,
personal or family history
3. Leukemia of stroke
- cancer of the body’s - symptoms: trouble with
blood-forming tissues speaking and understanding,
- white blood cells = seeing in one or both eyes,
infection fighters paralysis or numbness of the
face, arm or leg, & headache
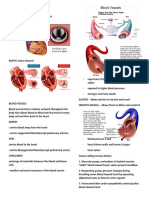
5. Hypertension
- greater force exerted by
the blood against the walls Technologies
of the blood vessels
- symptoms: headache, 1. Fat Attenuation Index
fatigue, chest pain & - measure the level of fat
difficulty breathing that restricts blood flow
- avoid sweets, salty and 2. Smart Watches
oily food - wearable technologies that
measure heart rate
6. Atherosclerosis - encourage physical
- buildup of plaque (fats, activity and allow for early
cholesterol and other detection
substances) in and on your 3. Watchman
artery walls, which can - permanent heart implant to
restrict blood flow. reduce the risk of stroke
- when plaques suddenly - designed to close off the
rupture, it can cause: left atrial appendage to
1. stroke (brain) keep stroke-causing blood
2. heart attack (heart) clots from escaping
4. Percutaneous Coronary
7. Aneurysms Intervention
- the enlargement of an
- procedure to open arteries
artery caused by weakness in
that are closed/blocked
the arterial wall
- non-surgical procedure
- aortic, cerebral and
that uses catheters to
peripheral aneurysms
narrow the arteries
- aneurysm rupture causes:
1. severe chest or back 5. Blood Pressure Monitor
pain - used to keep track with
2. angina: chest pain the force exerted by blood
that can lead to heart to the walls of the blood
attack vessel
3. sudden extreme head 6. Angioplasty and Stenting
ache if brain - opens a blocked vessel and
aneurysms lead to improve blood flow
subarachnoid 7. Cerebral Angiogram
hemorrhage (SAH) which - a diagnostic test that
is a stroke. uses an X-ray
- produces an image to find
blockages or other
abnormalities in the blood
vessels of your head and
neck
- safe and effective way to
diagnose and treat brain
abnormalities
- catheter is inserted in
the groin for the cerebral
angiogram
Вам также может понравиться
- First Aid For Colleges and Universities 1 Joseph J MistovichДокумент1 246 страницFirst Aid For Colleges and Universities 1 Joseph J Mistovich54633321100% (1)
- US - ASA Physical Status Classification Chart - V2Документ1 страницаUS - ASA Physical Status Classification Chart - V2Roberto PvetОценок пока нет
- University of The Immaculate Conception: ProteinДокумент13 страницUniversity of The Immaculate Conception: ProteinDams ZainalОценок пока нет
- Histology Krok 1Документ103 страницыHistology Krok 1Ridhan SinghОценок пока нет
- Sofia Margarita M. NicolasДокумент11 страницSofia Margarita M. NicolasSofia MandacОценок пока нет
- Notes StrokeДокумент7 страницNotes Stroke202213Оценок пока нет
- Cerebrovascular AccidentДокумент21 страницаCerebrovascular AccidentCJОценок пока нет
- 1cardiovascular System DisordersДокумент13 страниц1cardiovascular System DisordersArvin MalondrasОценок пока нет
- Maintenance and Continuity of Life: QuestionsДокумент10 страницMaintenance and Continuity of Life: QuestionsAFRINA BATRISYIA BINTI MOHD WAFI MoeОценок пока нет
- Neurology ?Документ49 страницNeurology ?drxghamdiОценок пока нет
- CVAДокумент13 страницCVAAmlan jyoti thanapatiОценок пока нет
- Nurul Ilmi Hajar (PO.71.3.201.14.1.130) Nurul Khabliana (PO.71.3.201.14.1.131)Документ27 страницNurul Ilmi Hajar (PO.71.3.201.14.1.130) Nurul Khabliana (PO.71.3.201.14.1.131)Nurulilmi hajarОценок пока нет
- Neurologic Emergencies 2 MergedДокумент71 страницаNeurologic Emergencies 2 MergedDanica FrancoОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology: Cardiovascular SystemДокумент20 страницPharmacology: Cardiovascular SystemCheryl OrtizОценок пока нет
- Heart Muscle Shortness of Breath Tired Swelling of The Legs Heart Failure Irregular Heart Beat Fainting Sudden Cardiac DeathДокумент6 страницHeart Muscle Shortness of Breath Tired Swelling of The Legs Heart Failure Irregular Heart Beat Fainting Sudden Cardiac DeathSachin DwivediОценок пока нет
- 10.6 Health Issues Related To Cardiovascular SystemДокумент10 страниц10.6 Health Issues Related To Cardiovascular Systemwienna1987Оценок пока нет
- Coronary Artherosclerosis - ACS and MIДокумент5 страницCoronary Artherosclerosis - ACS and MIAila HinlogОценок пока нет
- Stroke 1Документ51 страницаStroke 1fatmaabdelazizОценок пока нет
- Lec 3 - Circulatory SystemДокумент9 страницLec 3 - Circulatory SystemJewel Jehd AlegriaОценок пока нет
- Power Point IHDДокумент143 страницыPower Point IHDnur syafiqah kamaruzamanОценок пока нет
- Cardiac EmergencyДокумент34 страницыCardiac EmergencyRima HannaniОценок пока нет
- Cerebrovascular Accident ReportДокумент16 страницCerebrovascular Accident ReportAngelu Gabrielle CastroОценок пока нет
- BugguДокумент16 страницBuggusudeepminz15Оценок пока нет
- Heart DiseasДокумент2 страницыHeart Diseasapi-349043985Оценок пока нет
- Hemorrhagic StokeДокумент6 страницHemorrhagic StokeeimОценок пока нет
- Agni LP Stoke HimorogikДокумент16 страницAgni LP Stoke HimorogikagnydwiОценок пока нет
- Disorders of The Circulatory SystemДокумент19 страницDisorders of The Circulatory Systemistep100% (1)
- Textbook Discussion On ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction - GicaroДокумент12 страницTextbook Discussion On ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction - GicaroJica Marie Bandiola GicaroОценок пока нет
- Ischemic Stroke - 3B5Документ77 страницIschemic Stroke - 3B5Aireen Grace GilosОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Pathophysiology of Ischemic Heart Ischemic Heart Disease DiseaseДокумент6 страницPathophysiology of Pathophysiology of Ischemic Heart Ischemic Heart Disease DiseaseYudo PrabowoОценок пока нет
- PPW 3rd CasestudyДокумент31 страницаPPW 3rd Casestudyfebie pachecoОценок пока нет
- Cerebrovascular Accident: Reporter: John Marlo R. OlaybarДокумент18 страницCerebrovascular Accident: Reporter: John Marlo R. Olaybarkuro hanabusaОценок пока нет
- Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)Документ37 страницIschemic Heart Disease (IHD)Yowan SusantiОценок пока нет
- Cardiology DR - Ahmed MowafyДокумент150 страницCardiology DR - Ahmed MowafyMohamed AlsaabОценок пока нет
- CVS NotesДокумент26 страницCVS NotesKelly YeowОценок пока нет
- Atherosclerosis: The Acute, Chronic, Recovery and Prevention StagesДокумент11 страницAtherosclerosis: The Acute, Chronic, Recovery and Prevention StagesLutfi HakimОценок пока нет
- Circulatory SystemДокумент6 страницCirculatory SystemchelliОценок пока нет
- Bio Cardiovascular DiseasesДокумент11 страницBio Cardiovascular DiseasesSoon ElaineОценок пока нет
- KUL 8 Stroke Nursing ManagementДокумент45 страницKUL 8 Stroke Nursing ManagementErina NopiyantiОценок пока нет
- SUBarachnoid HemorrhageДокумент4 страницыSUBarachnoid Hemorrhagekhadzx100% (2)
- Cardiovascular Problems: An Excerpt From Our Book, The Natural Remedies EncyclopediaДокумент12 страницCardiovascular Problems: An Excerpt From Our Book, The Natural Remedies Encyclopediarhimineecat71Оценок пока нет
- Cardiac Sheet: Personal HistoryДокумент7 страницCardiac Sheet: Personal HistorySyximsh FPОценок пока нет
- CPT OSCE Reviewer: I, III, V: Case #1Документ19 страницCPT OSCE Reviewer: I, III, V: Case #1manideepreddyОценок пока нет
- Brain-Attack or Stroke or Cerebrovascular-AccidentДокумент29 страницBrain-Attack or Stroke or Cerebrovascular-AccidentMission JupiterОценок пока нет
- Stroke 21 AДокумент10 страницStroke 21 AD/Badr Saleh Al jabryОценок пока нет
- Cardiovacular SystemДокумент44 страницыCardiovacular SystemHimanshuОценок пока нет
- Cardivascular Deseases and Diabetes MellitusДокумент38 страницCardivascular Deseases and Diabetes MellitusYu QingОценок пока нет
- Angina PectorisДокумент10 страницAngina Pectorissantoshd99Оценок пока нет
- Medical Disorders of The CNS, CvaДокумент46 страницMedical Disorders of The CNS, CvaMalueth AnguiОценок пока нет
- Acute Coronary, Angina Pectoris and Myocardial InfractionДокумент26 страницAcute Coronary, Angina Pectoris and Myocardial Infractionabeer alzhoorОценок пока нет
- Lec 3 Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemДокумент40 страницLec 3 Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemAzkaZulfiqarОценок пока нет
- Stroke (Encephalitis/Meningitis) Trauma Kepala Trauma Medulla SpinalisДокумент61 страницаStroke (Encephalitis/Meningitis) Trauma Kepala Trauma Medulla SpinalisUmar MukhtarОценок пока нет
- Med Surg BundleДокумент82 страницыMed Surg BundleThe Treasure ChestОценок пока нет
- Non-Communicable Diseases and Physical InactivityДокумент37 страницNon-Communicable Diseases and Physical InactivityMiles MontinolaОценок пока нет
- Lec 3 - Circulatory SystemДокумент8 страницLec 3 - Circulatory SystemJewel Jehd AlegriaОценок пока нет
- Admitting Conference: Abejo, Jerika D. Bona, Henry JR.Документ38 страницAdmitting Conference: Abejo, Jerika D. Bona, Henry JR.Henry BonaОценок пока нет
- Medical-Surgical Nursing: Primary Brain TumorДокумент20 страницMedical-Surgical Nursing: Primary Brain TumorYejiОценок пока нет
- 32 Critical IllnessДокумент5 страниц32 Critical Illnessgurusid09Оценок пока нет
- The Circulatory SystemДокумент25 страницThe Circulatory SystemEduardson PHОценок пока нет
- MSN - EndocarditisДокумент6 страницMSN - EndocarditisDanica AluraBalguaОценок пока нет
- 3 Heart FailureДокумент8 страниц3 Heart FailureAudrey Ann AcobОценок пока нет
- Disease of Nervous System Lect 2Документ62 страницыDisease of Nervous System Lect 2Monirul IslamОценок пока нет
- MEDICAL PATHOLOGIES - CardiovascularДокумент6 страницMEDICAL PATHOLOGIES - Cardiovascularngachangong victorineОценок пока нет
- Postpartum Eclampsia or PreeclampsiaДокумент11 страницPostpartum Eclampsia or PreeclampsiaAnonymous l6Q1ROq2Оценок пока нет
- Iferika JR Histology Slide Compilation-1Документ197 страницIferika JR Histology Slide Compilation-1ikembachinomso06Оценок пока нет
- Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO)Документ4 страницыBranch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO)Mahmoud Ahmed MahmoudОценок пока нет
- CARDIOVASCULAR EXAMINATION Human DiseaseДокумент4 страницыCARDIOVASCULAR EXAMINATION Human DiseaseVictoria MedfordОценок пока нет
- Defibrillator Sync TestingДокумент4 страницыDefibrillator Sync TestingYahya SalemОценок пока нет
- برزنتيشن المدكلДокумент15 страницبرزنتيشن المدكلHuhgg VgctОценок пока нет
- Circresaha 119 312617Документ14 страницCircresaha 119 312617Andrianna NastasyaОценок пока нет
- Diabetes in PregnancyДокумент62 страницыDiabetes in Pregnancykapil khanalОценок пока нет
- Choose Only One Best AnswerДокумент10 страницChoose Only One Best AnswerMuhammad Farrukh ul Islam100% (1)
- Medical Requirement: Director General DirectivesДокумент33 страницыMedical Requirement: Director General DirectivesChiu ChernОценок пока нет
- OmerДокумент33 страницыOmerNoor Hasan WaheedОценок пока нет
- Polyneuritis Medical Appendix (Polyneuropathy, Multiple Neuritis, Multiple Symmetrical Peripheral Neuritis)Документ4 страницыPolyneuritis Medical Appendix (Polyneuropathy, Multiple Neuritis, Multiple Symmetrical Peripheral Neuritis)Chideraa FloveraОценок пока нет
- AnaphylaxisДокумент22 страницыAnaphylaxischitra gayenОценок пока нет
- Finals Ha Lec Heart and Neck Vessel, Peripheral Vascular Systems, Assessing The AbdomenДокумент8 страницFinals Ha Lec Heart and Neck Vessel, Peripheral Vascular Systems, Assessing The AbdomenNel joy PaurilloОценок пока нет
- Alterations in Genitourinary and Reproductive System - 3rd UEДокумент13 страницAlterations in Genitourinary and Reproductive System - 3rd UEBeyaaa GingoyonОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент19 страницDrug StudyArmie Joy Embat CariazoОценок пока нет
- 1st Prof 10 Years (2022)Документ58 страниц1st Prof 10 Years (2022)Sandip RoyОценок пока нет
- Insulin, Oral Hypoglycaemic Agents, GlucagonДокумент63 страницыInsulin, Oral Hypoglycaemic Agents, GlucagonBhavesh kunvarОценок пока нет
- CH 07 The Skeletal SystemДокумент78 страницCH 07 The Skeletal SystemHappy SharmaОценок пока нет
- Secondary Stroke PreventionДокумент54 страницыSecondary Stroke PreventionHùng Phạm Lý ChíОценок пока нет
- Clinical Case of A Patient With Aortic Periprosthetic InfectionДокумент4 страницыClinical Case of A Patient With Aortic Periprosthetic InfectionAthenaeum Scientific PublishersОценок пока нет
- Journal Homepage: - : IntroductionДокумент9 страницJournal Homepage: - : IntroductionIJAR JOURNALОценок пока нет
- Emergency Drugs: Drug Classification USE Stock Dose Nursing ConsiderationДокумент4 страницыEmergency Drugs: Drug Classification USE Stock Dose Nursing Considerationrhennifer100% (1)
- Inhibitors of AngiotensinДокумент37 страницInhibitors of AngiotensinBoyu GrtrОценок пока нет
- IJCD 2017 Know Your Instrument GuideДокумент106 страницIJCD 2017 Know Your Instrument GuideYarina Nathaly Pilco RomanОценок пока нет
- External Markers of Congenital Heart DiseaseДокумент1 страницаExternal Markers of Congenital Heart DiseaseSrinivas DhangarОценок пока нет