Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
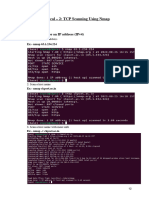
Port Scan
Загружено:
riaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Port Scan
Загружено:
riaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
PORT SCAN
Running a port scan on a network or server reveals which ports are open and listening
(receiving information), as well as revealing the presence of security devices such as
firewalls that are present between the sender and the target. This technique is known as
fingerprinting.
A port scan sends a carefully prepared packet to each destination port number.
The basic techniques that port scanning software is capable of include:
Vanilla– the most basic scan; an attempt to connect to all 65,536 ports one
at a time. A vanilla scan is a full connect scan, meaning it sends a SYN flag
(request to connect) and upon receiving a SYN-ACK (acknowledgement of
connection) response, sends back an ACK flag. This SYN, SYN-ACK, ACK
exchange comprises a TCP handshake. Full connect scans are accurate,
but very easily detected because full connections are always logged by
firewalls.
SYN Scan– Also referred to as a half-open scan, it only sends a SYN, and
waits for a SYN-ACK response from the target. If a response is received,
the scanner never responds. Since the TCP connection was not completed,
the system doesn’t log the interaction, but the sender has learned if the
port is open or not.
XMAS and FIN Scans– an example of a suite of scans used to gather
information without being logged by the target system. In a FIN scan, an
unsolicited FIN flag (used normally to end an established session) will be
sent to a port. The system’s response to this random flag can reveal the
state of the port or insight about the firewall. For example, a closed port
that receives an unsolicited FIN packet, will respond with a RST (an
instantaneous abort) packet, but an open port will ignore it. An XMAS scan
simply sends a set of all the flags, creating a nonsensical interaction. The
system’s response by can be interpreted to better understand the system’s
ports and firewall.
FTP Bounce Scan– allows for the sender’s location to be disguised by
bouncing the packet through an FTP server. This is also designed for the
sender to go undetected.
Sweep scan– pings the same port across a number of computers to
identify which computers on the network are active. This does not reveal
information about the port’s state, instead it tells the sender which systems
on a network are active. Thus, it can be used as a preliminary scan.
Вам также может понравиться
- Nmap Port Scanning TechniquesДокумент3 страницыNmap Port Scanning TechniquesAHMED MOHAMEDОценок пока нет
- Port Scanning: Ranveer Singh GehlotДокумент13 страницPort Scanning: Ranveer Singh GehlotRanveer Singh GehlotОценок пока нет
- Scanning:: TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)Документ12 страницScanning:: TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)Karthik MinnikantiОценок пока нет
- NMAPДокумент18 страницNMAPMuhammad AshfaqОценок пока нет
- Final Cyber Security Lab Manual Practical 1 To Practical 10Документ94 страницыFinal Cyber Security Lab Manual Practical 1 To Practical 10Satyam Parekh60% (5)
- Scanning & Enumeration: Module 3,4Документ6 страницScanning & Enumeration: Module 3,4naveen kumarОценок пока нет
- U A N L Facultad de Ciencias Fisico MatematicasДокумент5 страницU A N L Facultad de Ciencias Fisico MatematicasAzBlexxОценок пока нет
- Ceh Chap3 QuizletДокумент2 страницыCeh Chap3 QuizletlynnverbОценок пока нет
- Cain Abel: Snort and Nmap - Two Sides of The Same CoinДокумент8 страницCain Abel: Snort and Nmap - Two Sides of The Same CoinDavid51Оценок пока нет
- Nmap (Scan Type(s) ) (Options)Документ8 страницNmap (Scan Type(s) ) (Options)mrpessimist931Оценок пока нет
- Arp PoisoningДокумент12 страницArp PoisoningVishal MishraОценок пока нет
- Hacking Module 03Документ69 страницHacking Module 03Jitendra Kumar Dash100% (1)
- Port Scanning Techniques ReviewДокумент8 страницPort Scanning Techniques ReviewabcdefОценок пока нет
- Evaluation & Testing of Information AssetsДокумент10 страницEvaluation & Testing of Information AssetsMaksОценок пока нет
- Lecture 23: Port and Vulnerability Scanning, Packet Sniffing, Intrusion Detection, and Penetration TestingДокумент71 страницаLecture 23: Port and Vulnerability Scanning, Packet Sniffing, Intrusion Detection, and Penetration TestingUnsharp DevОценок пока нет
- Packet or Network SniffingДокумент56 страницPacket or Network SniffingRamadhani RaisОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3: Gathering Network and Host Information: Scanning and EnumerationДокумент14 страницChapter 3: Gathering Network and Host Information: Scanning and EnumerationBiff PocorobaОценок пока нет
- The SfPortscan ModuleДокумент13 страницThe SfPortscan ModuleDu CônОценок пока нет
- 3.scanning NetworkДокумент8 страниц3.scanning NetworkqwertyОценок пока нет
- OS FingerprintingДокумент6 страницOS Fingerprintingjose2985Оценок пока нет
- CSДокумент89 страницCSShubham DevganОценок пока нет
- Nmap With WiresharkДокумент19 страницNmap With WiresharkMoïse GuilavoguiОценок пока нет
- Dar Es Salaam Institute of Technology: Lab 3 ReportДокумент10 страницDar Es Salaam Institute of Technology: Lab 3 ReportJoel JohnОценок пока нет
- NmapДокумент17 страницNmapJavier Hevia MirandaОценок пока нет
- TCP in A NutshellДокумент5 страницTCP in A NutshellmuktakankshiОценок пока нет
- Ana Chanaba Robert HuyloДокумент18 страницAna Chanaba Robert HuyloAkshay ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- NMAP - Information GatheringДокумент6 страницNMAP - Information GatheringRockstar GmailОценок пока нет
- How SYN Scans Work and How to Use Nmap for Port ScanningДокумент1 страницаHow SYN Scans Work and How to Use Nmap for Port ScanningFrancis FinanОценок пока нет
- TCP Scanning Using NmapДокумент12 страницTCP Scanning Using Nmapprat jariwalaОценок пока нет
- 3 ScanningДокумент54 страницы3 ScanningChaimae MoussaouiОценок пока нет
- Nmap Commands Cheat SheetДокумент1 страницаNmap Commands Cheat SheetSaidu Haruna musaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 23Документ61 страницаLecture 233201313Оценок пока нет
- Port and Vulnerability Scanning Packet Sniffing Intrusion Detection and Penetration TestingДокумент60 страницPort and Vulnerability Scanning Packet Sniffing Intrusion Detection and Penetration TestingSree Saibaba Digital Advanced Network Pvt LtdОценок пока нет
- Ethical Hacking TipsДокумент26 страницEthical Hacking Tipskashyaprohith32Оценок пока нет
- Port MirroringДокумент17 страницPort MirroringKing DeedОценок пока нет
- Detection of Reflected Cross-Site Scripting AttackДокумент4 страницыDetection of Reflected Cross-Site Scripting AttackPankaj SahuОценок пока нет
- CH 02Документ42 страницыCH 02andrewiles88Оценок пока нет
- 3.scanning NetworkДокумент25 страниц3.scanning Networkripper.g5520Оценок пока нет
- NO Lecture23Документ61 страницаNO Lecture23Zxe IebОценок пока нет
- Cisco CCNA Security Module 6 (23 questions) 100Документ6 страницCisco CCNA Security Module 6 (23 questions) 100asvasОценок пока нет
- Perform An Experiment For Port Scanning With Nmap, Superscan or Any Other Equivalent SoftwareДокумент4 страницыPerform An Experiment For Port Scanning With Nmap, Superscan or Any Other Equivalent SoftwaresangeetadineshОценок пока нет
- Reto 4Документ5 страницReto 4pgn_pedroguillenОценок пока нет
- Command Sheet Cheat - NmapДокумент6 страницCommand Sheet Cheat - NmapEdgar FerreiraОценок пока нет
- Distributed Intrusion Detection: Mamata Desai (99305903) M.Tech.,CSE Dept, IIT BombayДокумент27 страницDistributed Intrusion Detection: Mamata Desai (99305903) M.Tech.,CSE Dept, IIT BombaydepdneoОценок пока нет
- Scanning Traffic Using WiresharkДокумент8 страницScanning Traffic Using WiresharkAshish BhangaleОценок пока нет
- Nmap Cheat SheetДокумент9 страницNmap Cheat Sheetrivigan888Оценок пока нет
- SniffingДокумент120 страницSniffingWoyОценок пока нет
- Port KnockingДокумент10 страницPort KnockingOktetОценок пока нет
- Ns Lab 2Документ4 страницыNs Lab 2Deepanshu SharmaОценок пока нет
- Nmap The Art of Port Scanning PDFДокумент6 страницNmap The Art of Port Scanning PDFJapari JaporaОценок пока нет
- KrutikShah CSS Exp8Документ13 страницKrutikShah CSS Exp8Krutik ShahОценок пока нет
- TCP Flags ExplainedДокумент1 страницаTCP Flags ExplainedVishal PatelОценок пока нет
- Copy of CS_Pr2Документ24 страницыCopy of CS_Pr2muskanbandariaОценок пока нет
- Firewall Interview Questions AsaДокумент3 страницыFirewall Interview Questions AsaRakesh Rakee0% (1)
- SniffingДокумент11 страницSniffingSenthil NathanОценок пока нет
- Phase 2Документ39 страницPhase 2Tarik AmezianeОценок пока нет
- Port ScanningДокумент21 страницаPort ScanningP.VEERABRAHMAMОценок пока нет
- 11 2PortScanningДокумент10 страниц11 2PortScanningmano2116Оценок пока нет
- AWS Core Services Quiz Review 80Документ3 страницыAWS Core Services Quiz Review 80Honor VenkiОценок пока нет
- (Indoneisa) UAT WAN-optimization 20140721Документ3 страницы(Indoneisa) UAT WAN-optimization 20140721Andi MYusufОценок пока нет
- CLI Command Guide For 24 Gbps NT 3HH04416EBAATCZZA01 PDFДокумент3 190 страницCLI Command Guide For 24 Gbps NT 3HH04416EBAATCZZA01 PDFalguialОценок пока нет
- Hub Based Network Configuration GuideДокумент162 страницыHub Based Network Configuration Guidedinesh_rhlОценок пока нет
- SD-WAN & VeloCloudДокумент18 страницSD-WAN & VeloCloudignatiuslowОценок пока нет
- VOIPДокумент262 страницыVOIPMirza Zaheer AhmedОценок пока нет
- Arista 4.17.2F ManualДокумент2 428 страницArista 4.17.2F ManualSon Tran Hong NamОценок пока нет
- 9 - Introduction To Network LayerДокумент28 страниц9 - Introduction To Network LayerDjangoОценок пока нет
- L4 Networking Newps401: Switching LU3. Describe Basic Switching Concepts and ConfigurationДокумент23 страницыL4 Networking Newps401: Switching LU3. Describe Basic Switching Concepts and ConfigurationIhirwe Shidy MegnyОценок пока нет
- 5.2.1.7 Lab - Viewing The Switch MAC Address TableДокумент4 страницы5.2.1.7 Lab - Viewing The Switch MAC Address TableЯрослав Алексеев33% (3)
- Solution: Wireshark Lab: DNSДокумент7 страницSolution: Wireshark Lab: DNSPhong LêОценок пока нет
- Comandos Ccna SecurityДокумент26 страницComandos Ccna SecurityRobtech opsОценок пока нет
- Virtual Net PDFДокумент590 страницVirtual Net PDFMohammed Akram AliОценок пока нет
- Dante Information For Network AdministrationДокумент2 страницыDante Information For Network Administrationjohn BronsonОценок пока нет
- Arbor Networks Help - Ports Used by SPДокумент4 страницыArbor Networks Help - Ports Used by SPuser userОценок пока нет
- Report by Team 11 Leader TASK 12 16th AugДокумент32 страницыReport by Team 11 Leader TASK 12 16th AuganjusnairОценок пока нет
- Hackers Information by Buddhax iEFДокумент20 страницHackers Information by Buddhax iEFIsrael a CatalunyaОценок пока нет
- Learners Guide - SightlineTMS DDOS UserAdmin Course (v1.9 - r9.3.5)Документ574 страницыLearners Guide - SightlineTMS DDOS UserAdmin Course (v1.9 - r9.3.5)ridha80Оценок пока нет
- Lab 5.4.1 Implementing EIGRPДокумент4 страницыLab 5.4.1 Implementing EIGRPAjith PathiranaОценок пока нет
- Lab2 - Static Routing-eNSPДокумент22 страницыLab2 - Static Routing-eNSPJosaf BustilloОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Explore The Network: Instructor MaterialsДокумент65 страницChapter 1: Explore The Network: Instructor Materialsalienarandas123100% (1)
- Data Communication Transport Layer Session 5: by Pruthvi Kumar K RДокумент47 страницData Communication Transport Layer Session 5: by Pruthvi Kumar K RMADHAN KUMAR SОценок пока нет
- ZXCTN 9000 MML Configuration Guide (IPv4 Routing) V2.08.32 enДокумент227 страницZXCTN 9000 MML Configuration Guide (IPv4 Routing) V2.08.32 entaipm100% (1)
- Sip LogДокумент23 страницыSip LogaprilОценок пока нет
- Ccnpv7.1 Switch Lab 10-2 Securing Vlans StudentДокумент9 страницCcnpv7.1 Switch Lab 10-2 Securing Vlans StudentFatin Nabilah RahmanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7ccnaДокумент32 страницыChapter 7ccnaashenafi animawОценок пока нет
- '''Engr - Muhammad Sohail Khan - CVДокумент6 страниц'''Engr - Muhammad Sohail Khan - CVSai Kyaw HtikeОценок пока нет
- Module Quiz - Data Link LayerДокумент3 страницыModule Quiz - Data Link LayerMaz PozankОценок пока нет
- TorrentsДокумент2 страницыTorrentsLorie Gail Calamayan0% (1)
- Packet Tracer 6 Lab Network ManagementДокумент3 страницыPacket Tracer 6 Lab Network ManagementkhomsavanhОценок пока нет