Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Stretament 2018 Meps Vs Speed - 29-11
Загружено:
js14camaraОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Stretament 2018 Meps Vs Speed - 29-11
Загружено:
js14camaraАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
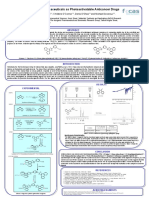
Comparing the high-throughput efficiency
of microextraction techniques, MEPS and µSPEed,
for the isolation of polyphenols from food matrices
José S. 1,2,*
Câmara , Natalia 3
Casado , Jorge 2
Pereira , Catarina L. 2
Silva , Rosa 2
Perestrelo , Isabel Sierra3
1CQM
– Centro de Química da Madeira, Universidade da Madeira, Campus da Penteada, 9020-105
2Faculdade de Ciências Exatas e Engenharia da Universidade da Madeira, Campus da Penteada, 9020-105 Funchal, Portugal
3Departamento de Tecnología Química y Energética, Tecnología Química y Ambiental, Tecnología Mecánica y Química Analítica, E.S.C.E.T, Universidad Rey Juan Carlos, C/ Tulipán s/n, 28933 Móstoles, Spain
INTRODUCTION RESULTS
In this study, microextraction by packed sorbent (MEPS) or micro solid Optimization of extraction parameters
phase extraction (μSPEed) coupled to UHPLC-PDA, were evaluated and
compared regarding their analytical performance or the extraction of
polyphenols from baby foods.
To achieve the highest extraction efficiency, the influential parameters type
of sorbent, the number of extraction cycles, the pH, the elution solvent
and the elution volume, were systematically optimized.
Method selectivity, linear dynamic range, limits of detection (LODs) and
quantification (LOQs), accuracy, precision, and extraction yields, were
determined and discussed for both techniques.
Experimental
EXPERIMENTAL
Design
Figure 2. Optimization of the best experimental conditions for MEPS and SPEed: selection of the best sorbent (A), optimal sample loading condition (B), best sample volume (C), optimum sample pH
0
(D) and best elution solvent (E) and respective optimal volume (F).
Step #1
Sorbent Step #2 Sealing MEPS
5 Activation activation Solvent
discarding
ring
Single
direction
flow
FLOW Check FLOW Check
Valve Valve
Frit MEPS
Open Closed
packed
bed
Step #3
Sorbent Step #4
10
Conditioning conditioning Solvent
discarding End plug
Figure 3. Representative chromatogram of real
Needle sample upon SPEed extraction and UPLC analysis
FLOW FLOW Analytical method validation
µSPEed Table 1. Validation parameters for the MEPS/UHPL-PDA and µSPEed/UHPLC-PDA analysis of the selected phenolic compounds..
15 Step #5 eVOL®
Analytical Method Validation Method Application
Sample Filtered
sample
Step #6
Unretained
XCHANGE® Phenolic compounds Extraction LDR
R 2 LOD LOQ Recovery Intra-day Inter-day Banana Apple
Multi-fruits Chicken, beef
with cereals & vegetables
syringe
Loading loading analytes
discarding
interface
technique (µg/mL) (µg/kg) (µg/kg) (%) precision precision
Conc. RSD Conc. RSD Conc. RSD Conc. RSD
MEPS 0.994 12.8 42.5 63 2.3 4.2 99 5.3 71 2.4 133 4.6 112 1.8
Gallic acid 0.25 - 2
μSPEed 0.997 2.1 6.9 67 2.8 4.5 138 7.3 169 3.8 154 2.7 125 1.1
FLOW
FLOW
MEPS 0.998 1.0 3.3 77 3.3 3.1 48 6.8 48 5.2 - - - -
High Protocatechuic acid 0.10 - 1.5
μSPEed 0.993 2.3 7.6 85 1.6 3.4 109 2.8 50 3.9 - - - -
Pressure
MEPS 0.995 1.7 5.6 53 2.4 4.1 - - 815 2.2 569 2.6 194 3.1
Connection Chlorogenic acid 0.03 - 0.75
20 Step #7 μSPEed 0.990 2.5 8.3 77 2.6 3.2 - - 1790 1.4 1353 2.9 284 4.1
MeOH Sorbent MEPS 0.992 5.3 17.6 48 0.8 1.0 31.5 1.7 - - 43 3.1 31 5.1
Step #8 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid 0.10 - 2
Time
(min)
Elution loading Target Bed μSPEed
MEPS
0.999
0.995
5.1
7.1
17.1
23.8
52
81
1.5
3.2
3.3
3.3
37 4.1
153 3.7
-
469 1.8
- 44.7
293
1.9
3.3
30 4.1
-
analytes High Epicatechin 0.05 - 1.5
Micro μSPEed 0.993 3.8 12.6 93 2.3 3.7 294 2.9 565 2.4 416 3.6 -
elution Pressure
One-Way MEPS 0.992 2.1 7.2 71 2.1 2.5 67 2.6 32.6 2.3 64 3.8 65 3.3
Seal p-Coumaric acid 0.03 - 0.75
FLOW
FLOW
Valve μSPEed 0.996 1.4 4.6 67 2.7 4.8 63 5.5 31 2.6 60.3 1.4 71.5 1.3
Cartridge
MEPS 0.993 1.6 5.4 63 1.0 1.8 236 2.5 - - 365 2.2 112 3.7
Ferulic acid 0.01 - 0.95
μSPEed 0.992 1.6 5.2 86 1.1 1.9 307 3.8 - - 409 1.6 165 1.3
Figure 1. Experimental layout of the MEPS and SPEed extraction procedures using the semi-automatic eVol® syringe. MEPS 0.992 9.6 31.9 70 1.6 1.9 340 3.4 169 2.5 360 2.3 < LOQ -
Rutin 0.05 - 2
μSPEed 0.984 2.5 8.4 77 2.1 2.8 387 3.2 192 4.3 367 1.7 36.3 1.3
MEPS 0.997 1.8 5.9 83 2.6 2.8 - - - - - - - -
Parameters MEPS µSPEed Resveratrol
μSPEed
0.03 - 0.75
0.992 1.4 4.7 84 2.4 1.7 - - - - - - - -
MEPS 0.992 3.3 11.2 79 1.5 3.1 108 5.1 52 2.1 98 2.2 < LOQ -
C2, C8, C18, Sil, M1, PEP, PS-DVB/RP-NP, C18 Myricetin
μSPEed
0.03 - 0.75
0.998 2.8 9.2 96 2.2 4.8 179 3.1 74 2.9 161 3.3 < LOQ -
Sorbent type R-CX, DVB/HLB, SCX, R- PS-DVB/RP, PS- Naringenin
MEPS
0.05 - 1.5
0.992 10.0 33.3 93 1.0 3.5 128 3.2 61 3.0 285 5.7 148 5.4
μSPEed 0.992 7.8 26.1 91 1.4 4.1 104 4.3 65 4.9 307 4.4 147 1.6
AX, PGC, HyDRC DVB/SCX, PS-DVB/SAX MEPS 0.985 7.4 24.6 98 2.2 4.2 < LOQ - < LOQ - - < LOQ 110 6.4
Kaempferol 0.05 - 1.5
Sample cycles 3×, 5×, 10× μSPEed 0.980 13.6 45.2 97 1.8 3.1 < LOQ - 52 4.3 - < LOQ 71 3.1
Legend: LDR – linear dynamic range; R2 – correlation coefficient; LOD – limits of detection; LOQ – limits of quantification; ME – Matrix effect; RSD – relative standard deviation.
Sample volume (µL) 100, 250, 500 25, 50, 100
Elution volume (µL) 100, 150, 200 25, 50, 100
Elution solvent
pH
ACN, MeOH
2, 7, 10
CONCLUSIONS
MEPS and μSPEed, combined with UHPLC-PDA, were evaluated and compared to determine the most suitable
Chromatographic conditions (UPLC®-PDA)
extraction approach for the simultaneous quantification of 12 polyphenols in baby food products.
Mobile phase 0.1% Formic Acid/MeOH The proposed analytical approaches were successfully optimized and validated in terms of selectivity, linearity,
Column HSS T3 LOD, LOQ, accuracy and precision.
Flow rate 250 µL/min Nevertheless, the best performance was achieved with the μSPEed procedure since it exhibited higher extraction
potential towards the target analytes providing, in general, high recovery values and very low LODs and LOQs and
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS requiring less amount of sample and solvents.
Natalia Casado would like to thank the Rey Juan Carlos University for providing her a mobility grant to perform a pre-doctoral stay in the
CQM. This work was supported by FCT-Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (project PEst-OE/ QUI/UI0674/2013, CQM; Both extraction methods were used for the qualitative and quantitative determination of polyphenols from baby
SFRH/BD/97039/2013), and through Madeira 14-20 Program, project PROEQUIPRAM - Reforço do Investimento em Equipamentos e
food samples and constitute a promising tool to evaluate and improve the knowledge of the nutritional quality of
http://cqm.uma.pt
Infraestruturas Científicas na RAM (M1420-01-0145-FEDER-000008) and by ARDITI-Agência Regional para o Desenvolvimento da
Investigação Tecnologia e Inovação, through the project M1420-01-0145- FEDER-000005 -Centro de Química da Madeira -
CQM+(Madeira 14-20) and Project M1420-09-5369-FSE-000001 for the JAMP Post-Doctoral fellowship this kind of products
UID/QUI/
00674/2013
Вам также может понравиться
- Monitoring Protein Conformational Changes Using Fluorescent NanoantennasДокумент30 страницMonitoring Protein Conformational Changes Using Fluorescent NanoantennasAnahí TessaОценок пока нет
- Chemometrics in Pharmaceutical AnalysisДокумент11 страницChemometrics in Pharmaceutical AnalysisAngel GarciaОценок пока нет
- Svteehb - Institut Polyvalent Nanfah - Année Scolaire 20222023 - Probatoire Blanc N°1 - Classe PD CamerounДокумент4 страницыSvteehb - Institut Polyvalent Nanfah - Année Scolaire 20222023 - Probatoire Blanc N°1 - Classe PD CamerounPires NguepiaОценок пока нет
- Preferential Adsorption in Polymer/Solvent-l /solvent-2 Solutions Infrared SpectrosДокумент5 страницPreferential Adsorption in Polymer/Solvent-l /solvent-2 Solutions Infrared SpectrosShadowWing ShadowWingОценок пока нет
- V2 Student Copy A212 Spectroscopy Lab ManualДокумент17 страницV2 Student Copy A212 Spectroscopy Lab Manualkhadijahhannah2707Оценок пока нет
- Maripili Gutiérrez, Rafael Pardo, Marisol VegaДокумент1 страницаMaripili Gutiérrez, Rafael Pardo, Marisol VegaRafael PardoОценок пока нет
- Cuadro de Calificaciones Noveno SocialesДокумент4 страницыCuadro de Calificaciones Noveno Socialesyuma dvОценок пока нет
- Doc142 52 20283Документ1 страницаDoc142 52 20283Lilia Rosa Ibáñez SierrauyОценок пока нет
- Optimal Solubilization Screening Strategies For GST-Fusion Membrane ProteinsДокумент3 страницыOptimal Solubilization Screening Strategies For GST-Fusion Membrane ProteinsAsmaОценок пока нет
- Registro 2019 - 4to - PrimariaДокумент1 страницаRegistro 2019 - 4to - PrimariaJulio Cesar Fuentes PumaОценок пока нет
- Narag, Punzalan, SarmientoДокумент1 страницаNarag, Punzalan, SarmientoLoriene SorianoОценок пока нет
- TMP CE63Документ39 страницTMP CE63FrontiersОценок пока нет
- Notas TitoДокумент21 страницаNotas TitoVINICIO123Оценок пока нет
- RAHI 2008 Erin Nelson PosterДокумент1 страницаRAHI 2008 Erin Nelson PosterIanHerriottОценок пока нет
- Samar DCU Poster 2007Документ1 страницаSamar DCU Poster 2007Zainab altafОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 2Документ6 страницLab Report 2Jericho MaganaОценок пока нет
- Calibration of Micropipettes: Test Methods and Uncertainty AnalysisДокумент16 страницCalibration of Micropipettes: Test Methods and Uncertainty Analysisrifki auliaОценок пока нет
- Bamboo Dyeing 2Документ5 страницBamboo Dyeing 2LoudetОценок пока нет
- NMR - Amali Kimia 4 (A231)Документ5 страницNMR - Amali Kimia 4 (A231)khadijahhannah2707Оценок пока нет
- Asuncion, Dennis M. NewДокумент4 страницыAsuncion, Dennis M. NewAllan Igbuhay100% (1)
- Notas Primer Período Química 11Документ1 страницаNotas Primer Período Química 11Karen ParraОценок пока нет
- 1551481-Agony From Into The Woods PDFДокумент7 страниц1551481-Agony From Into The Woods PDFSílvia PlanagumàОценок пока нет
- Polynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons by HPLCДокумент9 страницPolynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons by HPLCLuis VilchezОценок пока нет
- JNS AgriBiotech Vol 15 5Документ9 страницJNS AgriBiotech Vol 15 5HAJAR ZZОценок пока нет
- Aefs 12745Документ18 страницAefs 12745Jumadil AkhirОценок пока нет
- T 611 BlanqueadoresДокумент7 страницT 611 BlanqueadoresIvan ElgueraОценок пока нет
- 2009 Acores Acta CogumeloДокумент5 страниц2009 Acores Acta Cogumeloanugrah rajaОценок пока нет
- LACCB2018Документ1 страницаLACCB2018Alexandre OsmarОценок пока нет
- Summary of Grades: Potrero National High SchoolДокумент6 страницSummary of Grades: Potrero National High SchoolRosita C.CayananОценок пока нет
- LCGCEurope March2014 PDFДокумент70 страницLCGCEurope March2014 PDFPaolo PiccoliniОценок пока нет
- Paper 7Документ8 страницPaper 7ZomaОценок пока нет
- A Grande Aventura - Fichas de AvaliacaoДокумент33 страницыA Grande Aventura - Fichas de AvaliacaoSusana SilvaОценок пока нет
- Abdala Et Al 2002 J Vert Paleont 22Документ13 страницAbdala Et Al 2002 J Vert Paleont 22mioclaenusОценок пока нет
- Metacentric HeightДокумент9 страницMetacentric HeightNUR BADRINA NABILAH ZURIZALОценок пока нет
- Modified Electronic TOS v.1.0Документ26 страницModified Electronic TOS v.1.0Davy Manglicmot GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Paper FNCT 1Документ7 страницPaper FNCT 1vinit kumarОценок пока нет
- María Camila Daza, 201313554, Maria Alejandra Otavo, 201423279Документ6 страницMaría Camila Daza, 201313554, Maria Alejandra Otavo, 201423279camiladazcasОценок пока нет
- Environmental ManagementДокумент12 страницEnvironmental ManagementEngy Hisham MarwanОценок пока нет
- Method Epoch Last Accuracy Average Accuracy Best Accuracy Method Epochs Last Loss Average Loss Lowest LossДокумент3 страницыMethod Epoch Last Accuracy Average Accuracy Best Accuracy Method Epochs Last Loss Average Loss Lowest LosschamanthiОценок пока нет
- Técnica de Medición de Biomasa (Peso Seco, Conteo Directo)Документ6 страницTécnica de Medición de Biomasa (Peso Seco, Conteo Directo)JUAN DAVID GAMBOA MORENOОценок пока нет
- Linear Driving Force Model in Carbon Dioxide Capture by AdsorptionДокумент9 страницLinear Driving Force Model in Carbon Dioxide Capture by AdsorptionLong TranОценок пока нет
- Dark Ages: Sábado, 20/08/2022 CL 8000 12:40PMДокумент12 страницDark Ages: Sábado, 20/08/2022 CL 8000 12:40PMMarshall MatterОценок пока нет
- End Group 2Документ22 страницыEnd Group 2Sabha Khalid shafiqОценок пока нет
- GPA TP-12 - Liquid Densities of Ethane - Propane MixturesДокумент104 страницыGPA TP-12 - Liquid Densities of Ethane - Propane Mixturesheberth simancasОценок пока нет
- Leel, Llagas, MarasiganДокумент1 страницаLeel, Llagas, MarasiganLoriene SorianoОценок пока нет
- Matriz Calificaciones ECA 9 C 2022-2023 SEGUNDO QUIMESTRE PDFДокумент1 страницаMatriz Calificaciones ECA 9 C 2022-2023 SEGUNDO QUIMESTRE PDFJonnathan CastilloОценок пока нет
- Primer Informe de Minería y Medio AmbienteДокумент11 страницPrimer Informe de Minería y Medio AmbienteJean Pierre Riquez AcostaОценок пока нет
- Trabajos Individuales Trabajos Grupales PruebasДокумент1 страницаTrabajos Individuales Trabajos Grupales PruebasJahel SilvaОценок пока нет
- Poster INPPO 2021 Bruno KomazecДокумент1 страницаPoster INPPO 2021 Bruno KomazecBrunoОценок пока нет
- Development of An Animal-Component Free Electroporation and Recovery Formulation Using EX-CELL CHO Cloning MediumДокумент1 страницаDevelopment of An Animal-Component Free Electroporation and Recovery Formulation Using EX-CELL CHO Cloning MediumSAFC-GlobalОценок пока нет
- 2009 Dodge Ram 3500 SLT 6.7 ECMДокумент4 страницы2009 Dodge Ram 3500 SLT 6.7 ECMBastian CruzОценок пока нет
- David Paterson, Eun Jeong Kwak, Tanaya Bhowmick, Elizabeth Alexander, Jeff Loutit, Shu Zhang, Michael Dudley, Thomas J. WalshДокумент1 страницаDavid Paterson, Eun Jeong Kwak, Tanaya Bhowmick, Elizabeth Alexander, Jeff Loutit, Shu Zhang, Michael Dudley, Thomas J. WalshJuan Alonso Leon-AbarcaОценок пока нет
- In This Issue: Rev Chem Eng 2015 - Volume 31 - Issue 1Документ2 страницыIn This Issue: Rev Chem Eng 2015 - Volume 31 - Issue 1Filipe almeidaОценок пока нет
- BioPharm Intl March2018Документ54 страницыBioPharm Intl March2018ErikaОценок пока нет
- Asuncion, Dennis M. Copy 1Документ4 страницыAsuncion, Dennis M. Copy 1Allan IgbuhayОценок пока нет
- Lab Report CoverДокумент1 страницаLab Report CoverAmirul HazzmiОценок пока нет
- LabsheetallpeltonДокумент16 страницLabsheetallpeltonbronobodyОценок пока нет
- Tamil Lit SyllabusДокумент87 страницTamil Lit Syllabusmohandassn1970Оценок пока нет
- Higher Expression of Proline Dehydrogenase AlteredДокумент39 страницHigher Expression of Proline Dehydrogenase Alteredmichel.aug.silvaОценок пока нет
- Fruit That Ruins Gelatin: - Usually Soft and BrittleДокумент1 страницаFruit That Ruins Gelatin: - Usually Soft and Brittlejs14camaraОценок пока нет
- Cancer Registries in Four Provinces in Turkey: A Case Study: Research Open AccessДокумент8 страницCancer Registries in Four Provinces in Turkey: A Case Study: Research Open Accessjs14camaraОценок пока нет
- 0684 Autoimune DiseasesДокумент43 страницы0684 Autoimune Diseasesjs14camaraОценок пока нет
- Table 1Документ2 страницыTable 1js14camaraОценок пока нет
- B. Project Leader B1. Important Scientific Achievements of The Project LeaderДокумент2 страницыB. Project Leader B1. Important Scientific Achievements of The Project Leaderjs14camaraОценок пока нет
- 5CQM Meeting JAMPДокумент1 страница5CQM Meeting JAMPjs14camaraОценок пока нет
- Antioxidant and AntihypertensiveДокумент12 страницAntioxidant and Antihypertensivejs14camaraОценок пока нет
- Elena Ibañez EzequielДокумент1 страницаElena Ibañez Ezequieljs14camaraОценок пока нет
- William James, Gustav Fechner, and Early Psychophysics: Frontiers in Physiology October 2011Документ11 страницWilliam James, Gustav Fechner, and Early Psychophysics: Frontiers in Physiology October 2011Isaac KnarsОценок пока нет
- Pre TEST1 AnswerДокумент2 страницыPre TEST1 AnswerVal Daryl AnhaoОценок пока нет
- Lecture 4 - Principles of Experimental DesignДокумент23 страницыLecture 4 - Principles of Experimental DesignthinagaranОценок пока нет
- Francis Bacon - BiographyДокумент7 страницFrancis Bacon - BiographytomsillimoottilОценок пока нет
- Investigatory Project 2014Документ2 страницыInvestigatory Project 2014Vasquez Mico100% (1)
- Individual Project Instructions - 5aДокумент1 страницаIndividual Project Instructions - 5aIkhram JohariОценок пока нет
- Ei Pack RnewsДокумент5 страницEi Pack RnewsvujoОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics-I (ME321) : Dr. Ali Turab JafryДокумент22 страницыFluid Mechanics-I (ME321) : Dr. Ali Turab Jafryqaps lrkОценок пока нет
- 0001-MBA-Business Statistics-Week 12 Choosing Right Statistical Test-10!06!2023-SV1Документ97 страниц0001-MBA-Business Statistics-Week 12 Choosing Right Statistical Test-10!06!2023-SV1seyon sithamparanathanОценок пока нет
- Math 221 Week 1 QuizДокумент10 страницMath 221 Week 1 QuizFrankie AliОценок пока нет
- Discrete Probability Example: Yields An OutcomeДокумент3 страницыDiscrete Probability Example: Yields An OutcomeSia Ping ChongОценок пока нет
- Validasi AzadirachtinДокумент12 страницValidasi Azadirachtinbella puteriОценок пока нет
- Stats Lesson Plan - Desmos ActivityДокумент3 страницыStats Lesson Plan - Desmos Activityapi-383918624Оценок пока нет
- Business StatisticsДокумент3 страницыBusiness StatisticsRashida ArshadОценок пока нет
- Labmanual For MbaДокумент23 страницыLabmanual For MbarhariharancseОценок пока нет
- Educational Technology - The Fourth Educational RevolutionДокумент7 страницEducational Technology - The Fourth Educational RevolutionGopuОценок пока нет
- Makalah B.indonesiaДокумент19 страницMakalah B.indonesiaSasi HanilaОценок пока нет
- Regression Analysis - WikipediaДокумент10 страницRegression Analysis - WikipediaalejojgОценок пока нет
- A Study On Psychological Characteristics of Players in Different Positional Play in HockeyДокумент28 страницA Study On Psychological Characteristics of Players in Different Positional Play in HockeyPRAJINIKUMARОценок пока нет
- Simple Regression QuizДокумент6 страницSimple Regression QuizKiranmai GogireddyОценок пока нет
- Question Text: Answer Saved Marked Out of 1.00Документ16 страницQuestion Text: Answer Saved Marked Out of 1.00Danica Vetuz100% (2)
- Nutrition and The Anthropology of FoodДокумент22 страницыNutrition and The Anthropology of FoodSandhya MohanОценок пока нет
- Darke and Dahl 2003Документ11 страницDarke and Dahl 2003Fas RrabaОценок пока нет
- Research Paradigms - Qualitative Research and Action Research - Tables and Graphic OrganizersДокумент11 страницResearch Paradigms - Qualitative Research and Action Research - Tables and Graphic OrganizersYamith J. Fandiño100% (1)
- Modelling and Simulation of Dynamic Behaviour in Crushing PlantДокумент66 страницModelling and Simulation of Dynamic Behaviour in Crushing Plantmas26amin3465Оценок пока нет
- Methods of Research Chapter 3Документ10 страницMethods of Research Chapter 3Cherry Mae L. Villanueva100% (3)
- Pages From SPSS For BeginnersДокумент58 страницPages From SPSS For BeginnersWaqas NadeemОценок пока нет
- Activity 7, Assessment 7Документ10 страницActivity 7, Assessment 7Shey FuentesОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 Correlation and RegressionДокумент10 страницChapter 9 Correlation and RegressionAnonymous mIBVSEОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Variance: Testing Equality of Means Across GroupsДокумент7 страницAnalysis of Variance: Testing Equality of Means Across GroupsMuraliManoharОценок пока нет