Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
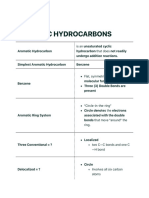
Experiment Number Test Performed Expected Positive Result Principle of Reaction Examples of Compounds That Provide Positive Results
Загружено:
Honami Tada0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
11 просмотров12 страницОригинальное название
ORGCHEM_TADA.docx
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
11 просмотров12 страницExperiment Number Test Performed Expected Positive Result Principle of Reaction Examples of Compounds That Provide Positive Results
Загружено:
Honami TadaАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 12
Experiment Test Performed Expected Positive Principle of Examples of
Number Result Reaction Compounds that
provide positive
results
7 Solubility in No Precipitation Miscibility is the
Concentrated H2SO4 property of liquids to
mix in all proportions,
therefore forming a Hexane
homogenous solution. Hexene
By contrast, substances Cyclohexane
are considered Toluene
immiscible if in any Benzene
proportion, they do not
form a solution. In
organic compounds, The
miscibility is determined
by the weight
percentage of the
hydrocarbon chain.
7 Ignition Test Presence of a yellow A flame test is an
flame or soot analytic procedure used
in chemistry to detect
the presence of certain Hexane
elements, primarily Hexene
metal ions, based on Cyclohexane
each element's Toluene
characteristic emission Benzene
spectrum. The color of
flames in general also
depends on
temperature; see flame
color.
7 Baeyer’s test Decolorization of a The Baeyer test for
purple solution and unsaturation is for Cyclohexene
formation of a brown determining the
precipitate. presence of carbon-
carbon double bonded
compounds, called
alkenes or carbon-
carbon trible bonded
compounds, called
alkyne bonds. An alkene
is replaced with a diol (a
compound with 2
hydroxy groups).
7 Bromine Test Decolorization of an In organic chemistry, the
orange solution bromine test is a
qualitative test for the
presence of Hexane
unsaturation (carbon-to- Hexane
carbon double or triple Cyclohexene
bonds) , phenols and Toluene
anilines. An unknown Benzene
sample is treated with a
small amount of
elemental bromine in an
organic solvent, being as
dichloromethane or
carbon tetrachloride.
7 Nitration Production of a yellow One of the most
globule or yellow oily important methods of Hexane
layer adding a nitrogen atom Hexane
to an already existing Cyclohexane
organic substrate is a Cyclohexene
reaction called nitration. Toluene
Nitration is the process Benzene
of adding a nitro group
(NO2) to a benzene ring.
7 Basic Oxidation positive result in the An oxidation-reduction
test leads to a violet (redox) reaction is a
solution (MnO4) or type of chemical
brown precipitate reaction that involves a Toluene
(MnO2) transfer of electrons
between two species.
Redox reactions are
common and vital to
some of
the basic functions of
life, including
photosynthesis,
respiration, combustion,
and corrosion or rusting.
8 Beilstein Test: Copper A positive test is The Beilstein test is a
Halide Test indicated by a green simple qualitative
flame caused by the chemical test for
formation of copper halides. A copper wire is
halide. cleaned and heated in a
Bunsen burner flame to n-butyl chloride
form a coating of Sec-butyl chloride
copper(II) oxide. It is Tert-butyl chloride
then dipped in the chlorobenzene
sample to be tested and
once again heated in a
flame. A positive test is
indicated by a green
flame caused by the
formation of a copper
halide. The test does not
detect
fluorine/fluorides.
8 Reactivity with Alcoholic slow formation of a A solution of ethanol
AgNO3 precipitate with some silver nitrate
added will provide the
weak nucleophile – the sec-butyl chloride
alcohol itself. A few tert-butyl chloride
drops of alkyl halide will chlorobenzene
be added. If an SN1
reaction occurs, the
alkyl halide will
dissociate to form a
carbocation, which will
then react with the
ethanol to form an
ether.
9 Solubility Test Turbid solution Miscibility is the N- Butyl
property of liquids to Benzene
mix in all proportions,
therefore forming a
homogenous solution.
By contrast, substances
are considered
immiscible if in any
proportion, they do not
form a solution. In
organic compounds, The
miscibility is determined
by the weight
percentage of the
hydrocarbon chain.
9 Lucas Test 1 unreactive The Lucas reagent is an
2 cloudy within 5-15 aqueous solution of
min, but some 2 fail to strong acid (HCl) and
react zinc chloride (ZnCl₂). The
3 cloudy instantly alcohol starting material
must be sufficiently sec-butyl alcohol
soluble in aqueous tert-butyl alcohol
environments for the
reaction to take place.
The reaction that occurs
in the Lucas test is an
SN1 nucleophilic
substitution. The acid
catalyst activates the OH
group of the alcohol by
protonating the oxygen
atom. The C-OH₂+
bond breaks to
generate the
carbocation, which in
turn reacts with the
chloride ion
(nucleophile) to
generate an alkyl halide
product.
9 Chromic Acid Test clear orange dark ppt The Chromic acid test
(Jones Oxidation) indicates 1° or 2° alcohol (Jones oxidation)
distinguishes primary
and secondary alcohols
from tertiary. Chromic Tert-butyl alcohol
acid will oxidize a Acetone
primary alcohol first to Acetophenone
an aldehyde and then to
a carboxylic acid and it
will oxidize a secondary
alcohol to a ketone.
Tertiary alcohols do not
react. The OH-bearing
carbon must have a
hydrogen atom
attached. Since the
carbon atom is being
oxidized in primary and
secondary, the orange
chromium Cr6+
ion is being reduced to
the blue-green Cr3+ ion.
9 2,4- Rapid appearance of a The 2,4-
dinitrophenylhydrazone thick precipitate Dinitrophenylhydrazone
Test test serves as a Acetaldehyde
derivative formation. n- butyraldehyde
Both aldehydes and benzaldehyde
ketones react with 2,4- acetophenone
dinitrophenylhydrazine acetone
to form a solid 2,4-
dinitrophenylhydrazone
(DNP) derivative. The
color of this derivative
can also provide useful
structural information. If
the solid is yellow, this
most often means that
the carbonyl group in
the unknown is
unconjugated. A
reddish-orange color
most likely means that
the carbonyl group is
conjugated. In a few
cases, compounds in
which the carbonyl
group is not conjugated
produce orange
precipitates. Simply
having a double bon or
phenyl group
somewhere in an
aldehyde or ketone does
not necessarily mean
that the carbonyl group
is conjugated. The
double bond must be
separated from the
carbonyl by one single
bond only. If the double
bond is further away, it
is isolated from the
carbonyl and not
conjugated with the
carbonyl.
9 Fehling’s Test reduction of the deep In Fehling’s test, the
blue solution of presence of
copper(II) to a red aldehydes and not
precipitate of insoluble ketones is detected by acetaldehyde
copper oxide reduction of the deep n-butyraldehyde
blue solution of copper benzaldehyde
(II)to muddy green
solution, and then form
a brick-red precipitate of
insoluble cuprous
oxide(Cu
2O). This test is
commonly used for
reducing sugars but is
known to be not specific
for aldehydes.
9 Tollen’s Silver Mirror Formation of a silver Tollens’ test, also known acetaldehyde
Test mirror as silver-mirror test, is
a qualitative laboratory
test used to distinguish
between and aldehyde and
a ketone. It exploits the fact
that aldehydes are readily
oxidized, whereas
ketones are not. Tollens’
test
uses a reagent known a
s Tollens’ reagent, which
is a colorless, basic, aqueous
solution containingsilver ions
coordinated to ammonia
[Ag(NH3)2+]. Tollens’
reagent oxidizes an
aldehyde into the
corresponding carboxylic
acid. The reaction
isaccompanied by the
reduction of silver ions in
Tollens’ reagent into
metallic silver, which, if
the test is carried out in a
clean glass test tube,forms
a mirror on the test
tube. Ketones are not
oxidized by the Tollens’
reagent, so
thetreatment of a
ketone with Tollens’
reagent in a
glass test tube does not
result in a silver mirror.
9 Iodoform Test yellow ppt only for R- The Iodoform test
CHOH-CH3 indicates the presence
of an aldehyde or
ketone in which one of
the groups directly Acetaldehyde
attached to the carbonyl Acetone
carbon is a methyl acetophenone
group. Such a ketone is
called a methyl ketone.
In the Iodoform test, the
sample is allowed to
react with a mixture of
iodine and base.
Hydrogens alpha to a
carbonyl group are
acidic and will react with
base to form the anion,
which then reacts with
iodine in this way to
form the triiodo
compound, which the
reacts with more base
to form the carboxylic
acid salt plus iodoform,
a yellow precipitate.
Formation of a yellow
precipitate therefore
indicates the presence
of a methyl group
directly attached to the
carbonyl. The
mechanism of the
iodoform reaction is
that of alpha-
halogenation of a
carbonyl compound
under basic conditions,
followed by nucleophilic
displacement of the
resulting triiodomethyl
group by hydroxide.
10 Hydrolysis of Acid The positive visible Acid halides,
Derivatives (Acyl halides result is the turbidity of anhydrides, esters, and Acetyl Chloride
and Acid anhydrides) the substance and its amides are all acyl
warming effect due to compounds of the
the presence of HCl general structure. These
compounds are also
known as acid
derivatives, because
historically they were
first derived from
carboxylic acids.
10 Hydrolysis of Acid plastic balloon-like odor Esters are of utmost Ethyl Acetate
Derivatives (Esters) importance to the
fragrance and flavoring
industry. The sweet
odors of fruits and
perfumes are usually
results of volatile esters.
10 Hydrolysis of Acid red litmus paper into Amides are found Benzamide
Derivatives (Amides) blue, an indication of throughout
presence of a basic biochemistry. It is the
substance amide group that
defines enzyme
structure, which in turn
defines us.
10 Alcoholysis: Schotten- strong plastic balloon- a reaction that occurs Acetic acid
Baumann Reaction like odor between an organic Acetyl Chloride
(Acetic Acid) molecule and an alcohol
of some sort, like when
tert-butyl chloride
reacts with methanol to
give methyl tert-butyl
ether as the product.
10 Aminolysis: Anilide white precipitate with is any chemical reaction Acetyl chloride
Formation (Acyl halides an oily layer in which a molecule is Acetic anhydride
and Acid anhydrides) split into two parts by
reacting with a molecule
of ammonia or an
amine. Another
common example is the
reaction of a primary
amine or secondary
amine with a carboxylic
acid or with a carboxylic
acid derivative to form
an amide. This reaction
is widely used,
especially in the
synthesis of peptides.
On the simple addition
of an amine to a
carboxylic acid, a salt of
the organic acid and
base is obtained.
10 Hydroxamic Acid Test Deep burgundy color Hydroxamic acids are Ethyl acetate
usually prepared from
either esters or acid
chlorides by a reaction
with hydroxylamine
salts.
Вам также может понравиться
- Hard and Soft Acids and Bases Principle in Organic ChemistryОт EverandHard and Soft Acids and Bases Principle in Organic ChemistryРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- The Chemistry and Biochemistry of Plant Hormones: Recent Advances in PhytochemistryОт EverandThe Chemistry and Biochemistry of Plant Hormones: Recent Advances in PhytochemistryV. C. RunecklesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Experient Number Test Performed Expected Positive Result Principle OF Reaction Examples of Coumpounds That Give Positive ResultsДокумент10 страницExperient Number Test Performed Expected Positive Result Principle OF Reaction Examples of Coumpounds That Give Positive ResultsErika EnriquezОценок пока нет
- Expt 7 Classification Tests For HydrocarbonsДокумент10 страницExpt 7 Classification Tests For Hydrocarbonssean goОценок пока нет
- Chemistry 120.1 - Organic Chemistry Laboratory Laboratory ReportДокумент3 страницыChemistry 120.1 - Organic Chemistry Laboratory Laboratory Reportkat katОценок пока нет
- Evstigneev 2011Документ6 страницEvstigneev 2011Khrisna MahendraОценок пока нет
- Classification Test For HydrocarbonsДокумент6 страницClassification Test For HydrocarbonsHeather GutierrezОценок пока нет
- Canales - Chem120.1 - Exercise No. 8Документ2 страницыCanales - Chem120.1 - Exercise No. 8Jamaica canalesОценок пока нет
- AaasdДокумент5 страницAaasdmaeallysa07Оценок пока нет
- 120lab Report 8aДокумент4 страницы120lab Report 8aValerie Mae Librero AreñoОценок пока нет
- Chem 111 LabДокумент7 страницChem 111 LabAira Lene ManaysayОценок пока нет
- Sion Orgchemlab4 PDFДокумент6 страницSion Orgchemlab4 PDFshellОценок пока нет
- Test Purpose Reagent Used Principle/Purpose of Reagent ResultДокумент5 страницTest Purpose Reagent Used Principle/Purpose of Reagent ResultAldren BeliberОценок пока нет
- Formal Report. Experiment 7: Classification Test For HydrocarbonsДокумент6 страницFormal Report. Experiment 7: Classification Test For Hydrocarbonsdemichosantos100% (6)
- Hydrocarbons: The First Family: Exercise 6Документ8 страницHydrocarbons: The First Family: Exercise 6Gagay Villamor CañeteОценок пока нет
- This Study Resource Was: Organic ChemistryДокумент4 страницыThis Study Resource Was: Organic ChemistryCLAUDETTE CLYDE GUERREROОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Experiment 2Документ7 страницChemistry Experiment 2Alexa Ysabel LiwagОценок пока нет
- Experiment 7 - Classification Tests For HydrocarbonsДокумент10 страницExperiment 7 - Classification Tests For HydrocarbonsDanielle De GuzmanОценок пока нет
- Exp 5Документ7 страницExp 5Dennisse San JoseОценок пока нет
- Classification Tests For Hydrocarbons Formal Report PDF FreeДокумент5 страницClassification Tests For Hydrocarbons Formal Report PDF FreeWavingOceansОценок пока нет
- Chem 120.1 Laboratory Report No. 8Документ2 страницыChem 120.1 Laboratory Report No. 8JM BoylesОценок пока нет
- Aromatic HydrocarbonsДокумент3 страницыAromatic Hydrocarbonsmihai_bors_01Оценок пока нет
- 9 2024 245 CH 9 Aromatics Lecture STUDENTДокумент36 страниц9 2024 245 CH 9 Aromatics Lecture STUDENTdingdong19690Оценок пока нет
- Relative Rates EAS Aromatic CompoundsДокумент2 страницыRelative Rates EAS Aromatic CompoundsKateОценок пока нет
- Class Notes 24-Jan-2021 (3)Документ7 страницClass Notes 24-Jan-2021 (3)JJ PrakashОценок пока нет
- Organic Qualitative Analysis Identifies BenzaldehydeДокумент33 страницыOrganic Qualitative Analysis Identifies BenzaldehydeStores Ac0% (1)
- Experimental 1 ReportДокумент7 страницExperimental 1 Reportjeremy jasonОценок пока нет
- MT1 - BIOCHEM - LAB - MT - EXP2 - Test Summary PDFДокумент1 страницаMT1 - BIOCHEM - LAB - MT - EXP2 - Test Summary PDF12 ABMJonica Iris BolinaОценок пока нет
- Benzene and Aromatic Compounds: Physical and Chemical Principles Organic and Biochemistry 14Документ2 страницыBenzene and Aromatic Compounds: Physical and Chemical Principles Organic and Biochemistry 14Apple ChemОценок пока нет
- ARENES AND PHENOLS (Autosaved)Документ85 страницARENES AND PHENOLS (Autosaved)dodoОценок пока нет
- REDICALESДокумент14 страницREDICALESmalaver528Оценок пока нет
- Huckel's Rule and Aromatic CompoundsДокумент16 страницHuckel's Rule and Aromatic CompoundsOfudje Edwin AndrewОценок пока нет
- Determination of Keto-Enol Equilibrium Constants and The Kinetic Study of The Nitrosation Reaction of Â-Dicarbonyl CompoundsДокумент9 страницDetermination of Keto-Enol Equilibrium Constants and The Kinetic Study of The Nitrosation Reaction of Â-Dicarbonyl CompoundsabcdefОценок пока нет
- Chem II Lab Report 1 - RXN of HydrocarbonsДокумент10 страницChem II Lab Report 1 - RXN of HydrocarbonsTHASVIN OFFICIAL NETWORKОценок пока нет
- Determine Elements in Organic CompoundsДокумент6 страницDetermine Elements in Organic CompoundsBianca Chellyne AguilarОценок пока нет
- Classification Tests For HydrocarbonsДокумент8 страницClassification Tests For HydrocarbonsAnna Donato60% (5)
- Organic ChemДокумент4 страницыOrganic ChemCherry GalamitonОценок пока нет
- Experiment No. 8 HydrocarbonsДокумент7 страницExperiment No. 8 HydrocarbonsMa Jessa DuntingОценок пока нет
- chp9Документ1 страницаchp9M. ABDUR REHMANОценок пока нет
- Classification Tests Reveal Hydrocarbon PropertiesДокумент5 страницClassification Tests Reveal Hydrocarbon PropertiesKyle Guzman100% (1)
- Reaction of Alkenes and Alkynes For StudentsДокумент53 страницыReaction of Alkenes and Alkynes For StudentsGlen MangaliОценок пока нет
- Experiment No. 2 PhenolsДокумент3 страницыExperiment No. 2 PhenolsChristine MarcellanaОценок пока нет
- BTech Sem-III Unit-5 (Part-1)Документ20 страницBTech Sem-III Unit-5 (Part-1)sytriuОценок пока нет
- Chem Lab ReviewerДокумент2 страницыChem Lab ReviewerMaria Angelica PescadorОценок пока нет
- JEE MAINS - VOL - IV General Organic Chemistry MechanismsДокумент28 страницJEE MAINS - VOL - IV General Organic Chemistry MechanismsvramaanuОценок пока нет
- Chem 120.1 (R141) - Group2, Exercise 7&8Документ8 страницChem 120.1 (R141) - Group2, Exercise 7&8Jerwin JavierОценок пока нет
- Aromaticity: Aliphatic Alicyclic AromaticДокумент14 страницAromaticity: Aliphatic Alicyclic AromaticSourav DasОценок пока нет
- Alkene: The "Double Bonds" in A Benzene Ring Do Not React Like OthersДокумент18 страницAlkene: The "Double Bonds" in A Benzene Ring Do Not React Like OthersPenny LowОценок пока нет
- Classification Tests For Hydrocarbons Formal-ReportДокумент5 страницClassification Tests For Hydrocarbons Formal-ReportKristineAnneMabansagОценок пока нет
- Aromatic Compounds and Benzene StructureДокумент5 страницAromatic Compounds and Benzene StructureAbigail P. ARANGGAОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry Naming GuideДокумент26 страницOrganic Chemistry Naming GuideHarsh OthayothОценок пока нет
- Lecture-14 2Документ46 страницLecture-14 2nadimОценок пока нет
- 5all Organic TestДокумент1 страница5all Organic TestJaya SinghОценок пока нет
- Benzene and Its Derivatives: Key QuestionsДокумент58 страницBenzene and Its Derivatives: Key QuestionsBrian GichanaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 chm207Документ1 страницаChapter 2 chm207MIZUKI JIROОценок пока нет
- 12th Chemistry PracticalДокумент2 страницы12th Chemistry Practicalsuriya kumarОценок пока нет
- 152 Sample-ChapterДокумент5 страниц152 Sample-ChapterUnnati SinariОценок пока нет
- Experiment N0. 3 - Structural Effects On ReactivityДокумент2 страницыExperiment N0. 3 - Structural Effects On ReactivityVida HumadasОценок пока нет
- Aromatic HydrocarbonДокумент31 страницаAromatic HydrocarbonCamille Solana100% (1)
- Year 12 Chemistry SOLДокумент3 страницыYear 12 Chemistry SOLHansika SamudralaОценок пока нет
- GCE Chemistry Data Booklet Issue 2Документ35 страницGCE Chemistry Data Booklet Issue 2purityplus89% (9)
- Le 3000 Sostanze Controverse Che Neways Non UtilizzaДокумент122 страницыLe 3000 Sostanze Controverse Che Neways Non UtilizzaGiorgio FerracinОценок пока нет
- To Study The Production of Biodiesel Future FuelДокумент12 страницTo Study The Production of Biodiesel Future FuelAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Optimization of Biodiesel (MOME) Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM)Документ7 страницOptimization of Biodiesel (MOME) Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM)vinitdubeОценок пока нет
- Catalysis in Organic Chemistry (1922) - Sabbatier PDFДокумент442 страницыCatalysis in Organic Chemistry (1922) - Sabbatier PDFbabithyОценок пока нет
- Stoichiometry Review 1Документ27 страницStoichiometry Review 1mostafa barakat100% (1)
- Encyclopedia of Textile Finishing PDFДокумент2 777 страницEncyclopedia of Textile Finishing PDFFERNANDO JOSE NOVAES100% (1)
- IAL Chemistry Unit 4 Reactions SummaryДокумент12 страницIAL Chemistry Unit 4 Reactions SummarySilmaSubahHoqueОценок пока нет
- Certificate of Analysis for Glycerin Lot 185433Документ4 страницыCertificate of Analysis for Glycerin Lot 185433Rizma IrsyadОценок пока нет
- Specification of Essential Oil Obtained From Lindera Neesiana (Wall. Ex Nees) KurzДокумент4 страницыSpecification of Essential Oil Obtained From Lindera Neesiana (Wall. Ex Nees) KurzKhilendra Gurung100% (2)
- Vidyamandir Classes: Organic Chemistry RevisionДокумент66 страницVidyamandir Classes: Organic Chemistry Revisionansh guptaОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 - Chemistry Lab 3 - Esterification With Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids Sem 1 16-17Документ2 страницыUnit 2 - Chemistry Lab 3 - Esterification With Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids Sem 1 16-17kelon scottОценок пока нет
- Reduction Agents Organic ChemistryДокумент55 страницReduction Agents Organic ChemistryvgvijuОценок пока нет
- Kinetics of Esterification Reaction Using Ion-Exchange Resin CatalystДокумент6 страницKinetics of Esterification Reaction Using Ion-Exchange Resin CatalystsumitОценок пока нет
- Esterification Reactor Special DesignДокумент21 страницаEsterification Reactor Special Designmohamedche88100% (7)
- Classification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesДокумент4 страницыClassification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesAJ Pasciolco50% (2)
- Handouts in BiochemДокумент46 страницHandouts in BiochemJobeth MurcillosОценок пока нет
- Synthesis and Applications of Boronic Acid-Containing Polymers: From Materials To MedicineДокумент23 страницыSynthesis and Applications of Boronic Acid-Containing Polymers: From Materials To MedicineJack RenОценок пока нет
- Niger Delta Post UtmeДокумент19 страницNiger Delta Post UtmeDelight DelightОценок пока нет
- الكيمياء العضويةالمرحلة الثالثة PDFДокумент398 страницالكيمياء العضويةالمرحلة الثالثة PDFAbdala Al-MawlaОценок пока нет
- Pro DrugsДокумент46 страницPro DrugsAditya KotamrajuОценок пока нет
- Jonson Matthey-Davy TechnologiesДокумент4 страницыJonson Matthey-Davy Technologiesjuan carlosОценок пока нет
- Montmorillonite Clay CatalystДокумент14 страницMontmorillonite Clay CatalystAshutosh BhaveОценок пока нет
- Multistep Lab ReportДокумент10 страницMultistep Lab Reportapi-508753814Оценок пока нет
- Development of Ketonic Resin by Polymeri PDFДокумент9 страницDevelopment of Ketonic Resin by Polymeri PDFkhizer iqbalОценок пока нет
- Chapter 21. Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution ReactionsДокумент20 страницChapter 21. Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions張湧浩Оценок пока нет
- Methyl Palmitate/Oleate Product SheetДокумент2 страницыMethyl Palmitate/Oleate Product SheetYassine LemsyehОценок пока нет
- Yr 11 Chemistry Exam NotesДокумент13 страницYr 11 Chemistry Exam NotesadfknaljhОценок пока нет
- notesG11Week1 1Документ24 страницыnotesG11Week1 1Damonte HenryОценок пока нет
- Lamellarins: Isolation, Activity, and Synthesis from Marine SourcesДокумент26 страницLamellarins: Isolation, Activity, and Synthesis from Marine SourcesJESUS DAVID BOLA‹O JIMENEZОценок пока нет