Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ieep1a2 PDF
Загружено:
Lakhan KumarИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ieep1a2 PDF
Загружено:
Lakhan KumarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Appendix -II
Definitions and symbols of the seven base units of the International System of Units (SI)
Base Quantity Unit Symbol Definition
Length metre m The metre is the length of path
travelled by light in vacuum during
a time interval of 1/299 792 458* of
a second (17th CGPM, 1983).
Mass kilogram kg The kilogram is the unit of mass; it
is equal to the mass of the
international prototype of the
kilogram (3rd CGPM, 1901).
Time second s The second is the duration of
9192631770 periods of the radiation
corresponding to the transition
between the two hyperfine levels of
the ground state of the caesium-133
atom (13th CGPM, 1967).
Electric current ampere A The ampere is that constant current
which, if maintained in two straight
parallel conductors of infinite
length, of negligible circular cross-
section, and placed 1 metre apart
in vacuum, would produce between
these conductors a force equal to
2 × 10-7 Newton per metre of length
(9th CGPM, 1948).
Thermodynamic kelvin K The kelvin, unit of thermodynamic
temperature, is the fraction 1/
temperature
273.16 of the thermodynamic
temperature of the triple point of
water (13th CGPM, 1967).
Amount of substance mole mol The mole is the amount of
substance of a system which
contains as many elementary
entities as there are atoms in 0.012
kilogram of carbon-12. When the
mole is used, the elementary
entities must be specified and may
be atoms, molecules, ions,
electrons, other particles, or
specified groups of such particles
(14th CGPM, 1971).
Luminous intensity candela cd The candela is the luminous
intensity, in a given direction, of a
source that emits monochromatic
radiation of frequency 540 × 1012
hertz and that has a radiant
intensity in that direction of (1/683)
watt per steradian (16 th CGPM,
1979).
* 299 792 458 m/s is the velocity of light vacuum
D EFINITIONS AND S YMBOLS 181
Appendix -III
Elements, their Symbol, Atomic Number and
Molar Mass
Element Symbol Atomic Molar Element Symbol Atomic Molar
Number mass/ Number mass/
(g mol–1) (g mol–1)
Actinium Ac 89 227.03 Mercury Hg 80 200.59
Aluminium Al 13 26.98 Molybdenum Mo 42 95.94
Americium Am 95 (243) Neodymium Nd 60 144.24
Antimony Sb 51 121.75 Neon Ne 10 20.18
Argon Ar 18 39.95 Neptunium Np 93 (237.05)
Arsenic As 33 74.92 Nickel Ni 28 58.71
Astatine At 85 210 Niobium Nb 41 92.91
Barium Ba 56 137.34 Nitrogen N 7 14.0067
Berkelium Bk 97 (247) Nobelium No 102 (259)
Beryllium Be 4 9.01 Osmium Os 76 190.2
Bismuth Bi 83 208.98 Oxygen O 8 16.00
Bohrium Bh 107 (264) Palladium Pd 46 106.4
Boron B 5 10.81 Phosphorus P 15 30.97
Bromine Br 35 79.91 Platinum Pt 78 195.09
Cadmium Cd 48 112.40 Plutonium Pu 94 (244)
Caesium Cs 55 132.91 Polonium Po 84 210
Calcium Ca 20 40.08 Potassium K 19 39.10
Californium Cf 98 251.08 Praseodymium Pr 59 140.91
Carbon C 6 12.01 Promethium Pm 61 (145)
Cerium Ce 58 140.12 Protactinium Pa 91 231.04
Chlorine Cl 17 35.45 Radium Ra 88 (226)
Chromium Cr 24 52.00 Radon Rn 86 (222)
Cobalt Co 27 58.93 Rhenium Re 75 186.2
Copper Cu 29 63.54 Rhodium Rh 45 102.91
Curium Cm 96 247.07 Rubidium Rb 37 85.47
Dubnium Db 105 (263) Ruthenium Ru 44 101.07
Dysprosium Dy 66 162.50 Rutherfordium Rf 104 (261)
Einsteinium Es 99 (252) Samarium Sm 62 150.35
Erbium Er 68 167.26 Scandium Sc 21 44.96
Europium Eu 63 151.96 Seaborgium Sg 106 (266)
Fermium Fm 100 (257.10) Selenium Se 34 78.96
Fluorine F 9 19.00 Silicon Si 14 28.08
Francium Fr 87 (223) Silver Ag 47 107.87
Gadolinium Gd 64 157.25 Sodium Na 11 22.99
Gallium Ga 31 69.72 Strontium Sr 38 87.62
Germanium Ge 32 72.61 Sulphur S 16 32.06
Gold Au 79 196.97 Tantalum Ta 73 180.95
Hafnium Hf 72 178.49 Technetium Tc 43 (98.91)
Hassium Hs 108 (269) Tellurium Te 52 127.60
Helium He 2 4.00 Terbium Tb 65 158.92
Holmium Ho 67 164.93 Thallium Tl 81 204.37
Hydrogen H 1 1.0079 Thorium Th 90 232.04
Indium In 49 114.82 Thulium Tm 69 168.93
Iodine I 53 126.90 Tin Sn 50 118.69
Iridium Ir 77 192.2 Titanium Ti 22 47.88
Iron Fe 26 55.85 Tungsten W 74 183.85
Krypton Kr 36 83.80 Ununbium Uub 112 (277)
Lanthanum La 57 138.91 Ununnilium Uun 110 (269)
Lawrencium Lr 103 (262.1) Unununium Uuu 111 (272)
Lead Pb 82 207.19 Uranium U 92 238.03
Lithium Li 3 6.94 Vanadium V 23 50.94
Lutetium Lu 71 174.96 Xenon Xe 54 131.30
Magnesium Mg 12 24.31 Ytterbium Yb 70 173.04
Manganese Mn 25 54.94 Yttrium Y 39 88.91
Meitneium Mt 109 (268) Zinc Zn 30 65.37
Mendelevium Md 101 258.10 Zirconium Zr 40 91.22
The value given in parenthesis is the molar mass of the isotope of largest known half-life.
182 EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS
Вам также может понравиться
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresОт EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- NotesДокумент1 страницаNotesbsuma.jeevuОценок пока нет
- Definitions and Symbols of The Seven Base Units of The International System of Units (SI)Документ2 страницыDefinitions and Symbols of The Seven Base Units of The International System of Units (SI)AryanОценок пока нет
- Engineering Measurement-Basic and Derived UnitsДокумент8 страницEngineering Measurement-Basic and Derived UnitsJofel Dulguime SuanОценок пока нет
- SI UnitsДокумент2 страницыSI UnitsDiana DragomirescuОценок пока нет
- Units and MeasurementsДокумент16 страницUnits and MeasurementsKajol HОценок пока нет
- Adobe Scan 10 May 2021Документ8 страницAdobe Scan 10 May 2021AsdasdОценок пока нет
- SI Units & Their Symbols: Unit (Name) Unit (Symbol) Quantity (Name)Документ1 страницаSI Units & Their Symbols: Unit (Name) Unit (Symbol) Quantity (Name)Srini VasuluОценок пока нет
- SI Base UnitsДокумент11 страницSI Base UnitsHasan BashoriОценок пока нет
- 1st Puc Physics Chapter2-Units and Measurements Notes by U N SwamyДокумент16 страниц1st Puc Physics Chapter2-Units and Measurements Notes by U N Swamyashwinikumari bОценок пока нет
- 1 Puc Notes PDFДокумент185 страниц1 Puc Notes PDFbsuma.jeevuОценок пока нет
- As 7 Grandezas de Base Do SiДокумент1 страницаAs 7 Grandezas de Base Do SiventooesteОценок пока нет
- Tech Data PDFДокумент35 страницTech Data PDFymsyaseenОценок пока нет
- Units and MeasurementДокумент4 страницыUnits and Measurementsonu kumarОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1. Units: Physics Is The Fundamental Laws of Nature, Which Simply Put, Are The Laws That Underlie AllДокумент10 страницLesson 1. Units: Physics Is The Fundamental Laws of Nature, Which Simply Put, Are The Laws That Underlie AllArianne PoleaОценок пока нет
- Chem101 Ho1Документ12 страницChem101 Ho1Jordan DingayanОценок пока нет
- UD Kinamatics NLMДокумент45 страницUD Kinamatics NLMSancia SamОценок пока нет
- 25 Apr 2022 PhysicsДокумент55 страниц25 Apr 2022 PhysicsA. SANDESHОценок пока нет
- Fundamental Physics "Unit and Quantity": Name: Citra Fatima Marsidi NIM: 19101105020 Study Program: PharmacyДокумент7 страницFundamental Physics "Unit and Quantity": Name: Citra Fatima Marsidi NIM: 19101105020 Study Program: PharmacyCitra MarsidiОценок пока нет
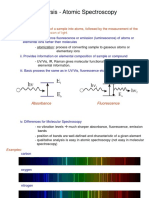
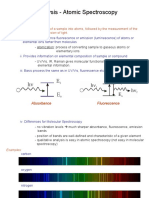
- Elemental Analysis - Atomic Spectroscopy: A) IntroductionДокумент32 страницыElemental Analysis - Atomic Spectroscopy: A) IntroductionAvinashОценок пока нет
- ASC 0304 Chapter2 Atomic Structure NHFДокумент14 страницASC 0304 Chapter2 Atomic Structure NHFLukhman Al AmeenОценок пока нет
- Tables of SI Units And: PrefixesДокумент4 страницыTables of SI Units And: PrefixesZUBER AHMEDОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3Документ36 страницLecture 3Seagal AsjaliОценок пока нет
- Chemical StructureДокумент92 страницыChemical StructureMaya HarrisОценок пока нет
- Manufactur 1 Technical DataДокумент48 страницManufactur 1 Technical DatajhonОценок пока нет
- CPC - 1 Chp. Lec.Документ17 страницCPC - 1 Chp. Lec.Latu BharaliОценок пока нет
- 7 SI Base SystemДокумент6 страниц7 SI Base SystemfamikuОценок пока нет
- Atomic Structure PDFДокумент42 страницыAtomic Structure PDFvijayОценок пока нет
- Atomic StructureДокумент42 страницыAtomic StructureSanjay PandeyОценок пока нет
- .Trashed 1702966746 1700327610640Документ48 страниц.Trashed 1702966746 1700327610640gno667533Оценок пока нет
- Heater Temperature Sensor Ti Nano-Disk Thermal Bridge: R V Rbe/MДокумент2 страницыHeater Temperature Sensor Ti Nano-Disk Thermal Bridge: R V Rbe/MTest EmailОценок пока нет
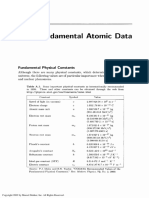
- Fundamental Atomic Data: Appendix AДокумент70 страницFundamental Atomic Data: Appendix AHJОценок пока нет
- Si Base UnitsДокумент1 страницаSi Base Unitsmattcutts1996Оценок пока нет
- Si UnitsДокумент3 страницыSi Unitsmouxritsa_83Оценок пока нет
- Stockbridge-Type Damper Effectiveness Evaluation: Part II-The Influence of The Impedance Matrix Terms On The Energy DissipatedДокумент8 страницStockbridge-Type Damper Effectiveness Evaluation: Part II-The Influence of The Impedance Matrix Terms On The Energy DissipatedServando LozanoОценок пока нет
- 21-02-24 em Waves DiscussionДокумент31 страница21-02-24 em Waves Discussionsrinivasa rao nallapaneniОценок пока нет
- Applied PhysicsДокумент16 страницApplied PhysicsEfraim BalingitОценок пока нет
- 48) Sistemul InternationalДокумент5 страниц48) Sistemul InternationalCosmin LTDAОценок пока нет
- Holt 2210Документ159 страницHolt 2210Masoud AliОценок пока нет
- Units and DimensionsДокумент22 страницыUnits and DimensionsGaurav NanheОценок пока нет
- Elemental Analysis - Atomic Spectroscopy: A) IntroductionДокумент40 страницElemental Analysis - Atomic Spectroscopy: A) IntroductionAree KabetoОценок пока нет
- NEET 2020 Answer Key For Set H3 by Allen KotaДокумент22 страницыNEET 2020 Answer Key For Set H3 by Allen Kotasenthil ganeshОценок пока нет
- Cosmic Ray Muons and The Muon LifetimeДокумент13 страницCosmic Ray Muons and The Muon Lifetimejohnsmith37758Оценок пока нет
- Background You Need To Know: 3.1 The AtomДокумент24 страницыBackground You Need To Know: 3.1 The AtomDuong AnhОценок пока нет
- Analytical Chem LecДокумент38 страницAnalytical Chem LecJulianne DimaguilaОценок пока нет
- ModernPhysics Exercise-4BДокумент3 страницыModernPhysics Exercise-4BBHBBSHWОценок пока нет
- MSE 102 Ch02 - 1Документ70 страницMSE 102 Ch02 - 1Mohammed AlbkiliОценок пока нет
- Nuclear Cheat SheetДокумент8 страницNuclear Cheat SheetM J RhoadesОценок пока нет
- 421-821-Chapter-8-10 FlameДокумент37 страниц421-821-Chapter-8-10 Flameعبير ال الحمدللهОценок пока нет
- 03nuclear SpectrosДокумент10 страниц03nuclear SpectrosMohamed AljamaeeОценок пока нет
- Nuclei Arihant CBSE ChapterwiseДокумент21 страницаNuclei Arihant CBSE ChapterwiseMRIDUL SINGH SOAMОценок пока нет
- Matter (Structure and Properties) BasicsДокумент3 страницыMatter (Structure and Properties) BasicsAnushka SinghОценок пока нет
- Elements of Mechanical Engineering: (1) Metric SystemДокумент8 страницElements of Mechanical Engineering: (1) Metric SystemSMIT PATELОценок пока нет
- CHP 23 Radioactive Decay StudentsДокумент24 страницыCHP 23 Radioactive Decay StudentsMuhammad Amin SuhaimiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2: Basic Concepts and Parameters of Plasma Physics: KT T T Ne NДокумент13 страницChapter 2: Basic Concepts and Parameters of Plasma Physics: KT T T Ne NRoy VeseyОценок пока нет
- Carbon Nano Tube by Ashwini Manohar ShriraoДокумент29 страницCarbon Nano Tube by Ashwini Manohar Shriraokapil1569Оценок пока нет
- 1001 Solved Problems in Electrical EngineeringДокумент814 страниц1001 Solved Problems in Electrical EngineeringRoselyn MatienzoОценок пока нет
- MCT1 Mass Spec PDFДокумент29 страницMCT1 Mass Spec PDFMohamed DahmaneОценок пока нет
- Chem 101 CH02 Ismail ANUДокумент82 страницыChem 101 CH02 Ismail ANUameer jomaОценок пока нет
- Nuclear Chemistry: Insert Picture From First Page of ChapterДокумент55 страницNuclear Chemistry: Insert Picture From First Page of ChapterJerson OceraОценок пока нет
- Class Xii Model Exam Marks:150 Computer Sciencetime:3HrsДокумент11 страницClass Xii Model Exam Marks:150 Computer Sciencetime:3HrsLakhan KumarОценок пока нет
- Bba PDFДокумент50 страницBba PDFLakhan KumarОценок пока нет
- Webdevelopmentintern PDFДокумент1 страницаWebdevelopmentintern PDFLakhan KumarОценок пока нет
- Web Development InternДокумент1 страницаWeb Development InternLakhan KumarОценок пока нет
- Analytical ChemistryДокумент79 страницAnalytical ChemistryDipeshBardoliaОценок пока нет
- Chem FM 3 Pre Tahossa - 20Документ4 страницыChem FM 3 Pre Tahossa - 20Mycovich MycoОценок пока нет
- Rr321801 Non Ferrous Extractive MetallurgyДокумент4 страницыRr321801 Non Ferrous Extractive MetallurgySrinivasa Rao GОценок пока нет
- Acido Citrico Jiangsu Guoxin UnionДокумент1 страницаAcido Citrico Jiangsu Guoxin UnionCalidad JuacopanОценок пока нет
- Arrangement of The Periodic TableДокумент4 страницыArrangement of The Periodic TableDanielleОценок пока нет
- Coursebook Answers: Self-Assessment QuestionsДокумент1 страницаCoursebook Answers: Self-Assessment QuestionslizОценок пока нет
- Elements Compounds MixturesДокумент16 страницElements Compounds Mixturesmajji satishОценок пока нет
- Combined Chemistry Booklet 3Документ24 страницыCombined Chemistry Booklet 3api-422428700Оценок пока нет
- Inorganic Lab ManualДокумент17 страницInorganic Lab ManualEvs GoudОценок пока нет
- US2989448Документ3 страницыUS2989448Jakin RookОценок пока нет
- Cat Grease 5% MolyДокумент2 страницыCat Grease 5% MolycatoeraleifОценок пока нет
- Periodic TableДокумент28 страницPeriodic TablegajenraoОценок пока нет
- Classification of Steels: M S A EДокумент27 страницClassification of Steels: M S A Emuhammad irfanОценок пока нет
- O Level Chem OCR Papers With AnswersДокумент8 страницO Level Chem OCR Papers With AnswersZeneonОценок пока нет
- Not CR or CR (II) .: A2-Level Chemistry Unit 5.3 (Transition Metal Chemistry) Mark Scheme For Sample QuestionsДокумент5 страницNot CR or CR (II) .: A2-Level Chemistry Unit 5.3 (Transition Metal Chemistry) Mark Scheme For Sample QuestionsJake RobinsonОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 - The Chemistry of Engineering Materials MetalsДокумент18 страницUnit 3 - The Chemistry of Engineering Materials MetalsNiña Viaña BinayОценок пока нет
- Balancing Equations PacketДокумент5 страницBalancing Equations Packetapi-298247873Оценок пока нет
- UTS Kimia - Dwi Perdana - 1301455Документ6 страницUTS Kimia - Dwi Perdana - 1301455syarif_rokhmatОценок пока нет
- D-Block Elements: Short Answer QuestionsДокумент11 страницD-Block Elements: Short Answer QuestionsMahesh Babu100% (1)
- B216 Acid Neutralization With LimeДокумент18 страницB216 Acid Neutralization With Limeespirito2009100% (1)
- Chapter 5 The Periodic Law Notes and SlidesДокумент15 страницChapter 5 The Periodic Law Notes and Slidesapi-406028290Оценок пока нет
- Flame Test PracДокумент2 страницыFlame Test PracJimBeanz75% (12)
- Welding of Ni Alloy-IraqДокумент17 страницWelding of Ni Alloy-Iraqkhairy2013Оценок пока нет
- MABU - HCC 2022-SpecДокумент2 страницыMABU - HCC 2022-SpecDUANJUNXIОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To Chemistry: Rizal Technological UniversityДокумент5 страницAn Introduction To Chemistry: Rizal Technological UniversityThañeza Mae PeraОценок пока нет
- Transmission Glycol TestДокумент2 страницыTransmission Glycol TestRasoolKhadibiОценок пока нет
- Amalgam With Recent AdvancesДокумент56 страницAmalgam With Recent AdvancesSourav Ghosh100% (1)
- Effect of Metal Coupling On Rusting of Iron: Chemistry Project FileДокумент14 страницEffect of Metal Coupling On Rusting of Iron: Chemistry Project FilePrashant Pandey100% (3)
- Sodium Hypochloriteincompatibility ChartДокумент1 страницаSodium Hypochloriteincompatibility ChartpcubeОценок пока нет