Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Maxwell's Equations - Definition & Application - Video & Lesson Transcript PDF
Загружено:
Bright Tendai ChingwenaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Maxwell's Equations - Definition & Application - Video & Lesson Transcript PDF
Загружено:
Bright Tendai ChingwenaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
for Teachers for Schools for Working Scholars
1
Plans Courses Credit Degrees Schools Log In Sign Up Search Courses & Lessons
Physics: High School / Science Courses Next Lesson
Support
Maxwell's Equations: De nition & Application
Chapter 15 / Lesson 11 Transcript
Video Quiz Course Try it risk-free for 30 days
You are viewing lesson 11 in chapter 15 of the course:
Physics: High School
18 chapters | 212 lessons
Equation and Application
Ch 15. Magnetism in Physics
The Biot-Savart Law: De nition & Examples 6:19
Ampere's Law: De nition & Examples 5:58
Maxwell's Equations: De nition & Application 6:22
Go to Magnetism in Physics
Ch 16. Physics Lab Experiments:...
Next Lesson 3:36
Electrical Energy Storage of
Capacitors: Physics Lab
Change in Electric Current: Physics Lab 3:26
Add to Timeline Autoplay off Speed Normal 44K views
Building Series & Parallel Circuits: Physics Lab 4:01
Maitreyee
‘
The E ect of a Magnetic Field on Moving 3:07
Teacher Beautifully structured, analysed and Charges: Physics Lab
United States
explained. Easy to follow! Thank you
02/04/2018 The Photoelectric E ect: Physics Lab 3:21
Go to Physics Lab Experiments: Electricity
Create an account
Ch 17. Thermal Physics &...
Recommended Lessons and Courses for You
Related Lessons Related Courses
Gauss' Law: De nition & Faraday's Law of Ampere's Law: De nition & Displacement Current:
Examples Electromagnetic Induction: Examples De nition & Function
Equation and Application
Lesson Transcript
Instructor: David Wood
David has taught Honors Physics, AP Physics, IB Physics and general science courses. He has a Masters in
Education, and a Bachelors in Physics.
After watching this video, you will be able to explain what Maxwell's equations are, the basic principles behind each one, and
what bene ts they have led to in society. A short quiz will follow.
What Are Maxwell's Equations?
Maxwell's equations are a series of four partial di erential equations that describe the force of electromagnetism. They were
derived by mathematician James Clerk Maxwell, who rst published them in 1861 and in 1862. Individually, the four equations
are named Gauss' law, Gauss' law for magnetism, Faraday's law and Ampere's law. The equations look like this:
While using these equations involves integrating (calculus), we
can still talk about what each law represents conceptually, and
how they're used:
Gauss' law relates the distribution of electric charge to
the eld that charge creates. If you know the shape of
the object and, therefore, how the charge is distributed,
you can use Gauss' law to gure out an expression for
the electric eld. This is generally used when there's a
degree of symmetry, making the equation simpler.
Gauss' law for magnetism says that magnetic
monopoles do not exist. It's really more of a statement
than something we might use to derive expressions. Four Maxwell equations
Charges exist as positive or negative. But in magnetism,
whenever you have a south pole, you also have a north pole - there are no single, or monopoles, as yet discovered.
Faraday's law says that any change to the magnetic environment of a coil of wire will cause a voltage to be induced in the
coil. If the magnetic eld strength changes, or the magnet moves, or the coil moves, or the coil is rotated - any of these
things will create a voltage in the coil.
Ampere's law says that the magnetic eld created by an electric current is proportional to the size of that electric current,
with a constant of proportionality equal to the permeability of free space. Stationary charges produce electric elds,
proportional to the magnitude of that charge. But moving charges produce magnetic elds, proportional to the current
(the charge and movement).
Applications of Maxwell
The uses and applications of Maxwell's equations are just too many to count. By understanding electromagnetism we're able to
create images of the body using MRI scanners in hospitals; we've created magnetic tape, generated electricity, and built
computers. Any device that uses electricity or magnets is on a fundamental level built upon the original discovery of Maxwell's
equations.
While using Maxwell's equations often involves calculus, there are simpli ed versions of the equations we can study. These
versions only work in certain circumstances, but can be useful and save a lot of trouble. Let's look at one of these - the simpli ed
version of Faraday's law.
As a reminder, Faraday's law says that any change to the magnetic environment of a coil of wire will cause a voltage to be
induced in the coil. And we can quantify those changes in a simple equation. Doing so gives you this equation below, where N is
the number of turns on the coil of wire, delta BA is the change in the magnetic eld times the area of the coil of wire, and delta t
is the time over which that change occurs.
This equation will give you the voltage produced in the coil. If
anything changes the values of B or A, a voltage will be
produced.
Example
Let's go through an example of how to use the simpli ed
version of Faraday's law. A coil of wire is placed in an external
magnetic eld of strength 0.1 teslas. The coil has 50 turns on
it, and a cross-sectional area of 0.05 meters squared. If the
eld strength is changed to 0.4 teslas gradually, over a period
of 3 seconds, what voltage will be induced in the coil of wire?
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account
Register to view this lesson
Are you a student or a teacher?
I am a student I am a teacher
Maxwell's Equations: De nition & Application Related Study Materials
Related Recently Updated Popular Explore Subjects
Browse by Courses Browse by Lessons
Science Courses The Hershey-Chase Experiment
Physics Courses Tools Used to Study Genes
Transferable Credit Courses The Evolution of Sexual Reproduction
Test Prep Courses How Ecological Factors Limit Population Growth
Credit by Exam Courses How Mitochondrial DNA & Ribosomal RNA Provide Molecular
Clocks
AP Biology Textbook
Quiz & Worksheet - How Animals & Humans Evolved
Honors Biology Textbook
Quiz & Worksheet - Animal Physiological Processes
Remedial Earth Science
Quiz & Worksheet - Male & Female Flower Components in
Chemistry: Credit Recovery Pollination
Fundamental Chemistry Quiz & Worksheet - Plant Life Cycles & Alternation of
Generations
High School Chemistry Textbook
Quiz & Worksheets - Plant Stems & Shoot Systems
Natural Sciences for Teachers: Professional Development
AP Physics 1 Linear Momentum: Homeschool Curriculum
Holt McDougal Modern Biology: Online Textbook Help
AP Physics 1 Motion: Homeschool Curriculum
Remedial Life Science
AP Physics 1 Oscillations: Homeschool Curriculum
Physics: Credit Recovery
AP Physics 1 Rotational Motion: Homeschool Curriculum
Anatomy & Physiology Textbook
AP Physics 1 Electrical Forces and Fields: Homeschool
8th Grade Life Science: Enrichment Program
Curriculum
Life Science Curriculum Resource & Lesson Plans
Create an account to start this course today
Create An Account
Try it risk-free for 30 days!
Explore our library of over 75,000 lessons
Search Search Courses & Lessons Browse Browse by subject
Products
Student Solutions
About Us
Blog
Support
Contact Support
Download the app
Get it on Google Play
Teacher Solutions Careers FAQ
Working Scholars
Study.com for Schools Get Your School Listed Site Feedback Working Scholars Bringing Tuition-Free
Get it on the App Store College to the Community
Working Scholars Solutions Teach For Us
Press Center
© copyright 2003-2019 Study.com. All other trademarks and copyrights are the property of their respective owners. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use Privacy Policy DMCA Notice ADA Compliance Honor Code For Students
Вам также может понравиться
- Tendai B Chingwena. 2206assДокумент7 страницTendai B Chingwena. 2206assBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Magnetic OvenДокумент7 страницMagnetic OvenBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Bright Chingwena 174743T and Tichatonga Mudzingwa 174791TДокумент16 страницBright Chingwena 174743T and Tichatonga Mudzingwa 174791TBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Radio and TV Ass 1Документ4 страницыFundamentals of Radio and TV Ass 1Bright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- National University of Science and TechnologyДокумент7 страницNational University of Science and TechnologyBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1Документ6 страницAssignment 1Bright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- National University of Science and TechnologyДокумент8 страницNational University of Science and TechnologyBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Dear Student AffairsДокумент1 страницаDear Student AffairsBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- National University of Science and TechnologyДокумент11 страницNational University of Science and TechnologyBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Applied Sciences: Wireless Channel Models For Over-the-Sea Communication: A Comparative StudyДокумент32 страницыApplied Sciences: Wireless Channel Models For Over-the-Sea Communication: A Comparative StudyBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Microwave Devices Notes Agent 4743TДокумент4 страницыMicrowave Devices Notes Agent 4743TBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- MR Murauzi Final Exam PreparationДокумент1 страницаMR Murauzi Final Exam PreparationBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4: Understanding AM Transmitter Block Diagrams and CircuitsДокумент6 страницChapter 4: Understanding AM Transmitter Block Diagrams and CircuitsRainier RamosОценок пока нет
- Difference Between Linear Power Supply and Switched Mode Power Supply - Difference Between PDFДокумент1 страницаDifference Between Linear Power Supply and Switched Mode Power Supply - Difference Between PDFBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Applied Sciences: Wireless Channel Models For Over-the-Sea Communication: A Comparative StudyДокумент32 страницыApplied Sciences: Wireless Channel Models For Over-the-Sea Communication: A Comparative StudyBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Applied Sciences: Wireless Channel Models For Over-the-Sea Communication: A Comparative StudyДокумент32 страницыApplied Sciences: Wireless Channel Models For Over-the-Sea Communication: A Comparative StudyBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Delay 1Документ7 страницDelay 1Bright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- EMT 2 Marks and 16 Marks-Question BankДокумент30 страницEMT 2 Marks and 16 Marks-Question BankBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- What Is The Difference Between Linear Power Supply and SMPS I Need A Clear Explanation - Quora PDFДокумент1 страницаWhat Is The Difference Between Linear Power Supply and SMPS I Need A Clear Explanation - Quora PDFBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Difference Between Linear Power Supply and SMPS (With Comparison Chart) - Electronics Coach PDFДокумент1 страницаDifference Between Linear Power Supply and SMPS (With Comparison Chart) - Electronics Coach PDFBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Whole PDFДокумент263 страницыWhole PDFBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Customer Issues - Qos/Qoe As A Function of Customer Satisfaction and Retention - A Regulator'S Perspective Session 5 - ( (Day 1) )Документ6 страницCustomer Issues - Qos/Qoe As A Function of Customer Satisfaction and Retention - A Regulator'S Perspective Session 5 - ( (Day 1) )Bright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Ćuk Converter - Plexim PDFДокумент1 страницаĆuk Converter - Plexim PDFBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- U2 L7 Switching Limits PDFДокумент8 страницU2 L7 Switching Limits PDFBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Difference Between Linear Power Supply and SMPS (With Comparison Chart) - Electronics Coach PDFДокумент1 страницаDifference Between Linear Power Supply and SMPS (With Comparison Chart) - Electronics Coach PDFBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Topology Tutorial - Cuk ConverterДокумент1 страницаTopology Tutorial - Cuk ConverterBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- Questions & Answers On Maxwell EquationsДокумент20 страницQuestions & Answers On Maxwell Equationskibrom atsbha50% (2)
- Switched Mode Power Supplies PDFДокумент1 страницаSwitched Mode Power Supplies PDFBright Tendai ChingwenaОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Topic One Introduction To ElectronicsДокумент22 страницыTopic One Introduction To ElectronicsBlueprint MihОценок пока нет
- Lab 1 - Lab 1 - Material Del Curso 6Документ3 страницыLab 1 - Lab 1 - Material Del Curso 6Eduardo CalleОценок пока нет
- Sem) /sec B Sub: Heat & Mass Transfer Sub Code: 120503Документ1 страницаSem) /sec B Sub: Heat & Mass Transfer Sub Code: 120503RohanОценок пока нет
- F.A.L. CONDUCIVE ENGINEERING REVIEW CENTERДокумент3 страницыF.A.L. CONDUCIVE ENGINEERING REVIEW CENTERRon Christian Pardilla RicohermosoОценок пока нет
- YU Classical Mechanics Course SyllabusДокумент6 страницYU Classical Mechanics Course SyllabusMark KaplanОценок пока нет
- Measurement of Atmospheric Pressure: 3.1 GeneralДокумент24 страницыMeasurement of Atmospheric Pressure: 3.1 GeneralAso SerwanОценок пока нет
- Incremental encoder data sheetДокумент1 страницаIncremental encoder data sheetbuva034Оценок пока нет
- App PDEДокумент83 страницыApp PDEbmandarОценок пока нет
- Ats 1 Afst Paper 1Документ14 страницAts 1 Afst Paper 1Aryan GuptaОценок пока нет
- Guia Physics, 10thДокумент6 страницGuia Physics, 10thEspinal Karla YohelyОценок пока нет
- BE Electrical Engg. High Voltage Engg. MCQS: Test LinkДокумент17 страницBE Electrical Engg. High Voltage Engg. MCQS: Test LinkSample UseОценок пока нет
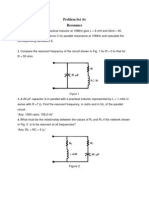
- ResonanceДокумент3 страницыResonanceBoules Atef0% (1)
- Drag of Conical Nose at Supersonic Speeds (Arthur Saw, EURECA 2013)Документ2 страницыDrag of Conical Nose at Supersonic Speeds (Arthur Saw, EURECA 2013)Arthur Saw Sher-QenОценок пока нет
- Caiga - Experiment 2Документ15 страницCaiga - Experiment 2Simon Mathew CaigaОценок пока нет
- Woodward Generator Load SensorДокумент30 страницWoodward Generator Load SensorRichard Lawrence100% (2)
- Relay and Protection Panel With SASДокумент145 страницRelay and Protection Panel With SASYash YadavОценок пока нет
- Illumination Basic Terms1Документ10 страницIllumination Basic Terms1Suraj SinghОценок пока нет
- Datasheet Diodo Zener 1n4148Документ1 страницаDatasheet Diodo Zener 1n4148Alan TorrezОценок пока нет
- Pre Commissioningchecklist 211027021204 - 2Документ150 страницPre Commissioningchecklist 211027021204 - 2nassarkiОценок пока нет
- ReactorprotectionДокумент39 страницReactorprotectionRK KОценок пока нет
- 1 Lac Intz Tank (Submition)Документ17 страниц1 Lac Intz Tank (Submition)Parth DaxiniОценок пока нет
- Lightning Protection Counter Test Equipment LightnДокумент4 страницыLightning Protection Counter Test Equipment LightnAndar ApriadiОценок пока нет
- Physics Student WorkbookДокумент511 страницPhysics Student WorkbookΚΩΝΣΤΑΝΤΙΝΟΣ ΠΑΠΑΪΩΑΝΝΟΥ100% (1)
- Navamathavan.r@vit - Ac.in: Dr. R. Navamathavan Physics Division School of Advanced Sciences (SAS)Документ24 страницыNavamathavan.r@vit - Ac.in: Dr. R. Navamathavan Physics Division School of Advanced Sciences (SAS)Somesh MuruganОценок пока нет
- Transformers: How They WorkДокумент4 страницыTransformers: How They WorkhiTxTHANOSОценок пока нет
- Generator Protection Class DefinedДокумент18 страницGenerator Protection Class Definedamitbharadwaj7Оценок пока нет
- Semiconductors: Physics Investigatory ProjectДокумент25 страницSemiconductors: Physics Investigatory ProjectSjssjsjsjjs100% (4)
- Assignment 3 - Ac CircuitДокумент3 страницыAssignment 3 - Ac CircuitDiptiben GanatraОценок пока нет
- How Planes Fly: Understanding Lift, Thrust, Drag and Weight in 40 CharactersДокумент1 страницаHow Planes Fly: Understanding Lift, Thrust, Drag and Weight in 40 CharactersbjsdkmlОценок пока нет