Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Qi Project Poster Template
Загружено:
api-4565373110 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
169 просмотров1 страницаОригинальное название
qi project poster template
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
169 просмотров1 страницаQi Project Poster Template
Загружено:
api-456537311Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
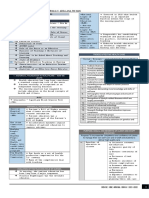
Mock a Fall - Save a Life
Maryum Abdul-Basir, Dennisha Fuller, George Johnson, Marshe’ Minor, and Kara Natividad
Bon Secours Memorial College of Nursing
Description of the Issue Analysis of the Issue Solution
Hypothesis: If healthcare staff members are provided with annual “falls training” in addition to semi-annual
Macro: ❖ Communication skills checks led by physical therapy, then the units will experience less falls overall.
● Fall injuries ranked top 20th most expensive medical conditions (CDC, 2016)
➢ Updating whiteboards
Evidence: The addition of a mock fall drill as a continuation of training would be beneficial to the reduction of
● Fall rate increased 30% since 2007 ➢ SBAR bedside report with patient involvement falls and improvement of staff knowledge and training. A study was conducted to increase confidence levels
● 30% of adults aged 65 and older fall each year ➢ Schmid score reassessment and emphasis in report and improve nursing performance during medical emergencies (Herbes & Heaser, 2016). For two years mock
● $50B in medical cost (Florence, 2017) ❖ Medication codes were conducted, and data was collected related to confidence levels and response times. The results
of the study indicated that nurses competence levels increased when given the opportunity to practice these
➢ Pharmacy consults for high-fall risk meds → narcotics, anti-convulsants,
○ 75% covered by Medicare and Medicaid essential skills, an increase improvement in nurses response time by 12%, and increased staff appreciation
anti-hypertensives, analgesics, sleep aids, etc. of the opportunity for hands-on practice with the equipment, reinforcing their knowledge and refining their
○ Average hospital cost for fall with injury: $30,000
➢ Evaluate medications and medication reconcilliation medical emergency skills (Herbers & Heaser, 2016, pg. 396).
● 700,000 -1,000,000 inpatient falls each year (AHRQ, 2013) ❖ Education/Training
Logistics: The increase in falls on the given units contribute to the overall desire for implementing better
○ 30-50% results in injury ➢ Reinforce patient education from admit date to discharge
plans for patient safety.
■ Toileting most common contributing factors ❖ Material
With the addition of mock falls there will be an increase in staff education. In order to accomplish this task,
➢ Decrease unneccesary material clutter in room per hourly rounds educational tools will be utilized for both new hires and current staff members.
■ 95% of hip fractures results from falls
➢ If patient is ambulating, disconnect and remove SCD sleeves from legs
● 7 fall deaths per hour by 2030 ❖ Equipment Currently offered:
➢ Continue to utilize volunteer services for equipment checks per each room ● Annual skills fair (chest tube management, PPE doning, glucose qualtity control, etc.)
Micro: ➢ Reinforce gait belt standard when getting a patient up and out of bed ● Online module completion (falls prevention module and assessment)
● St. Francis Hospital Performance Improvement Coordinator reports that the hospital experienced 128 inpatient
falls in the fiscal year of 2018
❖ Environmental
○ 27 falls on the Progressive Care Unit ➢ Environmental checks with hourly rounding: Additions:
PT mock fall trial/station with annual skills fair for all employees
■ 6 falls resulted in injury
○ 23 falls on the Orthopedic Unit Completion of all elements of hourly rounding: PT body ergonomics strengthening/training modifications for new hires
■ 12 falls resulted in injury
● $14,000 Joint Comission per fall with injury
➢ 5 p’s: personal needs (toileting), pain, position, possessions, proximity. Make Stakeholders:
sure to put an emphasis on addressing personal needs and toileting as it is one ● Hospital administration
of the major contributors to falls. During rounding making sure to complete ● Employees
environmental safety check to ensure patient’s room is free from clutter or items ○ Nursing staff
Root Cause that could contribute to falls. ○ Nursing administration
○ Nurse educators
■ Appropriate lighting for patient needs
○ Risk management/Falls champion
■ Ensure patient has all personal belongings accessible at the bedside
○ Physical Therapy
The Progressive Care Center and Orthopedic units at St. Francis have experienced ● An interview conducted on February 7, 2019 with nurses on the ● Patients
a significant amount of falls in the past fiscal year (FY’18). The units appear to lack Progressive Care Unit at St. Francis found that one contributing factor to
continual fall training for staff members and fails to enforce fall prevention education patient falls were “patient’s rooms are small and clutter easily.” Costs: - $36/HR - PT for 2hrs each day
to patients. This multifactorial presence emphasizes the need for continual review - Leadership facilitators for 2hrs (nurse educators)
and adaptation of current fall policies. - Equipment/Supplies (online module, poster board, mannequin, etc.)
- Hourly pay for healthcare member to attend mock trial skills fair
St. Francis fall policies
Timeline: Within one calendar year, the required educational modules and skills fair will be revised and
● Annual online fall prevention module References implemented for all direct care staff members.
● Use of preventative equipment Agency for healthcare research and quality (AHRQ) (2018). Preventing falls in hospitals. Retrieved from ● Initial training to be completed within one month of revised plan implementation.
● New staff orientation https://www.ahrq.gov/professionals/systems/hospital/fallpxtoolkit/index.html ● All training, including skills check off, to be completed within one month of completion of online module.
● “Stay with Me” policy
● Fall Prevention training Centers for disease control and prevention (CDC), National center for injury prevention and control. (2016). Data Collection:
● Dual RN/PCT hourly rounding responsibility Web-based inquiry query and reporting system (WISQARS). Retrieved from ● Fall rates collected by medical data analyst
https://www.cdc.gov/homeandrecreationalsafety/falls/fallcost.html. ○ 3 months - data analysis, 6 months - identify trends
● Fall Prevention whiteboards
● Collaborative bedside shift report ○ Per unit
Florence, C.,, Bergen, G., Atherly, A., Burns, E., Stevens, J., Drake, C. (2018). Medical Costs of Fatal and Nonfatal ○ Type and severity
Falls in Older Adults. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 66(4) 693-698. doi: 10.1111/jgs.15304 ● Outcomes
■ Staff compliance
Herbers, M. D., & Heaser, J. A. (2016). Implementing an in situ mock code quality improvement program. American ● Audits
journal of critical care,25(5), 393-399. doi:10.4037/ajcc2016583 ■ Employee surveys
● Do you feel more comfortable caring for patients at risk for falls?
● Are you better informed regarding the fall policy and protocols?
● Are you more capable of preventing falls on your unit?
■ Patient safety questionnaires scores (use of your RN w/ gait belt, use of grip socks/shoes every
time you got up, rationale for why
Вам также может понравиться
- Medical Education in Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine: Advanced Concepts and StrategiesОт EverandMedical Education in Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine: Advanced Concepts and StrategiesPatricia A. KritekОценок пока нет
- Poster Template 20191206Документ1 страницаPoster Template 20191206api-402050848Оценок пока нет
- Qi Project SaguarogroupДокумент15 страницQi Project Saguarogroupapi-708256548Оценок пока нет
- Qi Project SaguarogroupДокумент15 страницQi Project Saguarogroupapi-708278194Оценок пока нет
- Monachino 2019Документ7 страницMonachino 2019Wahyu HidayatОценок пока нет
- Poster Template 20191206Документ1 страницаPoster Template 20191206api-402053549Оценок пока нет
- Enhancing Patient Safety During Hand-Offs: Standardized Communication and Teamwork Using The SBAR' MethodДокумент3 страницыEnhancing Patient Safety During Hand-Offs: Standardized Communication and Teamwork Using The SBAR' MethodCantika SRОценок пока нет
- Energetic Modalities As A Self-Care Technique To Reduce Stress in Nursing StudentsДокумент8 страницEnergetic Modalities As A Self-Care Technique To Reduce Stress in Nursing StudentsManuel Antonio Santacruz BenavidesОценок пока нет
- Journal Homepage: - : IntroductionДокумент7 страницJournal Homepage: - : IntroductionIJAR JOURNALОценок пока нет
- Ulcers 4Документ5 страницUlcers 4Diego CastelblancoОценок пока нет
- Clinical Reasoning and Knowledge Management in Final Year Medical Students - The Role of Student-Led Grand RoundДокумент7 страницClinical Reasoning and Knowledge Management in Final Year Medical Students - The Role of Student-Led Grand RoundFranciscoОценок пока нет
- Nurs478 HealthcaredeliveryДокумент14 страницNurs478 Healthcaredeliveryapi-504371511Оценок пока нет
- Poster Template For Fall 2019Документ1 страницаPoster Template For Fall 2019api-485315684Оценок пока нет
- Collegian: Michelle Barakat-Johnson, Michelle Lai, Timothy Wand, Kathryn WhiteДокумент8 страницCollegian: Michelle Barakat-Johnson, Michelle Lai, Timothy Wand, Kathryn WhiteSUCHETA DASОценок пока нет
- Australasian Emergency Nursing Journal: Elise Grover, Joanne E. Porter, Julia MorphetДокумент6 страницAustralasian Emergency Nursing Journal: Elise Grover, Joanne E. Porter, Julia Morphetpuskesmas buloilaОценок пока нет
- Perceived Quality of Nursing Care and Patient EduДокумент9 страницPerceived Quality of Nursing Care and Patient EduLaras Adythia PratiwiОценок пока нет
- Presentation PosterДокумент1 страницаPresentation Posterapi-663253917Оценок пока нет
- Demeuse-Kirschling Colloquium Poster PresentationДокумент1 страницаDemeuse-Kirschling Colloquium Poster Presentationapi-512525946Оценок пока нет
- Conference PosterДокумент1 страницаConference Posterapi-340511808Оценок пока нет
- Physio Works in Falls Frailty Info LeafletДокумент2 страницыPhysio Works in Falls Frailty Info Leafletdan iacobОценок пока нет
- E047687 FullДокумент7 страницE047687 FullCesar GuevaraОценок пока нет
- NCM 102 Compilation M-FДокумент45 страницNCM 102 Compilation M-FIone ArnibalОценок пока нет
- Effectiveness-Matters-August-2014-Falls in HospitalsДокумент4 страницыEffectiveness-Matters-August-2014-Falls in HospitalsKibsJohnОценок пока нет
- 4001 EconДокумент31 страница4001 EconAngus LeungОценок пока нет
- Habib FallPreventionBundle 2019Документ37 страницHabib FallPreventionBundle 2019Saumya GeorgeОценок пока нет
- Improving Surgical Safety and Nontechnical Skills in Variable-Resource Contexts: A Novel Educational CurriculumДокумент8 страницImproving Surgical Safety and Nontechnical Skills in Variable-Resource Contexts: A Novel Educational CurriculumIsma WahyuniОценок пока нет
- Improving Patient Care Outcomes Through Better Delegation-Communication Between Nurses and Assistive PersonnelДокумент7 страницImproving Patient Care Outcomes Through Better Delegation-Communication Between Nurses and Assistive PersonneltasyaОценок пока нет
- International Wound Journal - 2019 - Gaspar - Effectiveness On Hospital Acquired Pressure Ulcers Prevention A SystematicДокумент16 страницInternational Wound Journal - 2019 - Gaspar - Effectiveness On Hospital Acquired Pressure Ulcers Prevention A SystematicErvin ArdiansahОценок пока нет
- Ebp-Charisse DuldulaoДокумент12 страницEbp-Charisse DuldulaoCharisse TaylanОценок пока нет
- Synthesis Final Presentation WeeblyДокумент18 страницSynthesis Final Presentation Weeblyapi-402053549Оценок пока нет
- Self-Reported Patient Safety Competence of Physical Therapy Interns Undergoing TelerehabilitationДокумент16 страницSelf-Reported Patient Safety Competence of Physical Therapy Interns Undergoing TelerehabilitationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Pressure Ulcers Nurses Knowledge PDFДокумент6 страницPressure Ulcers Nurses Knowledge PDFVar InderОценок пока нет
- EBP K3 INTER - DikonversiДокумент16 страницEBP K3 INTER - DikonversiMartha ChristinaОценок пока нет
- Coifman 2021Документ3 страницыCoifman 2021Mădălina Liliana PopОценок пока нет
- CRM 1Документ11 страницCRM 1nihalhabtiche135Оценок пока нет
- Henneman, 2007Документ6 страницHenneman, 2007aminОценок пока нет
- This Study Resource Was: Interprofessional Collaboration 2Документ5 страницThis Study Resource Was: Interprofessional Collaboration 2nirvanОценок пока нет
- Teaching Medical Students Clinical AnesthesiaДокумент8 страницTeaching Medical Students Clinical AnesthesiaSadhi RashydОценок пока нет
- AwarnesДокумент6 страницAwarnesnabilahbilqisОценок пока нет
- 2022 NaviauxДокумент6 страниц2022 NaviauxNursyazni SulaimanОценок пока нет
- Wocn-46-106 Australians KnowledgeДокумент7 страницWocn-46-106 Australians KnowledgeDAWITОценок пока нет
- Novice Nurse Support Group: A Pilot StudyДокумент21 страницаNovice Nurse Support Group: A Pilot Studyastor toОценок пока нет
- Anaesthesia 2004-59-166 HarmsДокумент8 страницAnaesthesia 2004-59-166 HarmsinoesienaОценок пока нет
- International Emergency Nursing: SciencedirectДокумент24 страницыInternational Emergency Nursing: SciencedirectRazak AbdullahОценок пока нет
- Transition Shock, Preceptor Support and Nursing Competency Among NewlyДокумент7 страницTransition Shock, Preceptor Support and Nursing Competency Among NewlyNurfadhila IlhamОценок пока нет
- Članak 18Документ14 страницČlanak 18InesCОценок пока нет
- SimulationДокумент9 страницSimulationKaren Joyce Costales MagtanongОценок пока нет
- Article ContentДокумент16 страницArticle ContentindahОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Ventilation Training During Graduate Medical Education: Perspectives and Review of The LiteratureДокумент13 страницMechanical Ventilation Training During Graduate Medical Education: Perspectives and Review of The LiteratureAbdullah MohdОценок пока нет
- Qi ProjectДокумент1 страницаQi Projectapi-663860143Оценок пока нет
- Out 7Документ6 страницOut 7hikmat pramajatiОценок пока нет
- Best practices to reduce readmissions for seniorsДокумент6 страницBest practices to reduce readmissions for seniorsAnnold ochiezyОценок пока нет
- Perioperative ERAS Approach Defining The Role of Desflurane - Slide Deck FinalДокумент69 страницPerioperative ERAS Approach Defining The Role of Desflurane - Slide Deck FinalHelmiHassanОценок пока нет
- The role of patient care teams in chronic disease managementДокумент4 страницыThe role of patient care teams in chronic disease managementIndah SundariОценок пока нет
- Safe Patient HandlingДокумент2 страницыSafe Patient Handlingapi-3697326Оценок пока нет
- Wong2022 Article CriticalCareUltrasoundДокумент3 страницыWong2022 Article CriticalCareUltrasoundA. RaufОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S0260691719300668 MainДокумент8 страниц1 s2.0 S0260691719300668 Mainruby susmawatiОценок пока нет
- Interruptions Then and Now - Impact On Nurses' Clinical Reasoning, Emotions, and Medication SafetyДокумент7 страницInterruptions Then and Now - Impact On Nurses' Clinical Reasoning, Emotions, and Medication SafetyCONSTANZAОценок пока нет
- Acad Med 2016 BermanДокумент6 страницAcad Med 2016 BermanGariana MarridoОценок пока нет
- Importance of Client Education in HealthcareДокумент14 страницImportance of Client Education in HealthcareTrina Joy Domantay75% (4)
- BSN Portfolio Final AnalysisДокумент3 страницыBSN Portfolio Final Analysisapi-456537311Оценок пока нет
- Maryum Abdul Skills ChecklistДокумент6 страницMaryum Abdul Skills Checklistapi-456537311Оценок пока нет
- Maryum Abdul Portofolio ResumeДокумент1 страницаMaryum Abdul Portofolio Resumeapi-456537311Оценок пока нет
- Running Head: Integrative Literature Review 1Документ20 страницRunning Head: Integrative Literature Review 1api-456537311Оценок пока нет
- Call To Serve Post Reflection AssignmentДокумент3 страницыCall To Serve Post Reflection Assignmentapi-456537311Оценок пока нет
- Hospital Nurse Staffing and Quality of Care, Agency For Healthcare Research and Quality Archive, 2017)Документ2 страницыHospital Nurse Staffing and Quality of Care, Agency For Healthcare Research and Quality Archive, 2017)api-456537311Оценок пока нет
- Running Head: Senior Personal Philosophy Paper 1Документ10 страницRunning Head: Senior Personal Philosophy Paper 1api-456537311Оценок пока нет
- Paf-Karachi Institute of Economics & Technology Spring - 2021Документ3 страницыPaf-Karachi Institute of Economics & Technology Spring - 2021Basic Knowledge Basic KnowledgeОценок пока нет
- Instrument Installation Checklist Êîíò Îëüíàß Âåäîìîñòü Óñòàíîâêè Êîíò Îëüíî-Èçìå Èòåëüíûõ Ï Èáî ÎâДокумент2 страницыInstrument Installation Checklist Êîíò Îëüíàß Âåäîìîñòü Óñòàíîâêè Êîíò Îëüíî-Èçìå Èòåëüíûõ Ï Èáî ÎâAdrianОценок пока нет
- Elsie Kundai Mapeto Final DraftДокумент74 страницыElsie Kundai Mapeto Final DraftAnonymous yEPScmhs2qОценок пока нет
- Distillation TypesДокумент34 страницыDistillation TypesJoshua Johnson100% (1)
- Form 16 - IT DEPT Part A - 20202021Документ2 страницыForm 16 - IT DEPT Part A - 20202021Kritansh BindalОценок пока нет
- Local and Global TechnopreneursДокумент25 страницLocal and Global TechnopreneursClaire FloresОценок пока нет
- Circuit Breaker GalilioДокумент34 страницыCircuit Breaker GalilioMoaz KhursheedОценок пока нет
- How To Knit SocksДокумент10 страницHow To Knit SocksHolly Robles100% (1)
- Full Cases of Legal FormsДокумент15 страницFull Cases of Legal FormsEllen Glae DaquipilОценок пока нет
- History of US Medical Device RegulationДокумент7 страницHistory of US Medical Device RegulationHector Tinoco GarciaОценок пока нет
- Message From The Chairman: Section On International and Comparative AdministrationДокумент12 страницMessage From The Chairman: Section On International and Comparative AdministrationBrittany KeeganОценок пока нет
- Analog To Digital Converters (ADC) : A Literature Review: and Sanjeet K. SinhaДокумент9 страницAnalog To Digital Converters (ADC) : A Literature Review: and Sanjeet K. SinhaRyu- MikaОценок пока нет
- Product Specifications Product Specifications: SBNHH SBNHH - 1D45C 1D45C - SR SRДокумент6 страницProduct Specifications Product Specifications: SBNHH SBNHH - 1D45C 1D45C - SR SRjorgeerestrepoОценок пока нет
- S141 Advanced DSP-based Servo Motion ControllerДокумент8 страницS141 Advanced DSP-based Servo Motion ControllersharkeraОценок пока нет
- Encyclopedia of Big Data PDFДокумент338 страницEncyclopedia of Big Data PDFAmit Singh0% (1)
- Supply Chain Analysis of PRAN GroupДокумент34 страницыSupply Chain Analysis of PRAN GroupAtiqEyashirKanakОценок пока нет
- 1920s Irish Crochet Lace Edging OriginalДокумент8 страниц1920s Irish Crochet Lace Edging OriginalLaura HortopanuОценок пока нет
- IBP Cable and Pressure Transducers IncavДокумент6 страницIBP Cable and Pressure Transducers Incaveng_seng_lim3436Оценок пока нет
- Group7 Sula Wine IBДокумент16 страницGroup7 Sula Wine IBFenny ShahОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Review QuestionsДокумент5 страницChapter 4 Review Questionschiji chzzzmeowОценок пока нет
- SWOT Analysis of Standard Chartered BankДокумент4 страницыSWOT Analysis of Standard Chartered BankparthОценок пока нет
- United International University: Post Graduate Diploma in Human Resource Management Course TitleДокумент20 страницUnited International University: Post Graduate Diploma in Human Resource Management Course TitleArpon Kumer DasОценок пока нет
- Alabama Tenants HandbookДокумент26 страницAlabama Tenants HandbookzorthogОценок пока нет
- Dollar ReportДокумент26 страницDollar ReportNirati AroraОценок пока нет
- Fund Flow StatementДокумент17 страницFund Flow StatementPrithikaОценок пока нет
- Unsettling Definitions of QualДокумент8 страницUnsettling Definitions of QualJIANING ZHUОценок пока нет
- Lim Tong Lim v. Philippine Fishing Gear Industries IncДокумент2 страницыLim Tong Lim v. Philippine Fishing Gear Industries IncIhna Alyssa Marie SantosОценок пока нет
- Platinum Plans Phils. Inc Vs Cucueco 488 Scra 156Документ4 страницыPlatinum Plans Phils. Inc Vs Cucueco 488 Scra 156Anonymous b7mapUОценок пока нет
- Basic Terms of AccountingДокумент24 страницыBasic Terms of AccountingManas Kumar Sahoo100% (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityОт EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (19)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityОт EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedОт EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (78)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossОт EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОт EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОценок пока нет
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionОт EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (403)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (42)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosОт Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (207)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsОт EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeОт EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeОценок пока нет
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsОт EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsОт EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (169)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaОт EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryОт EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (44)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessОт EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (328)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.От EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (110)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingОт EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsОт EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (722)
- Summary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedОт EverandSummary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (11)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerОт EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (392)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- Secure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimeОт EverandSecure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (18)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)