Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Oracle RAC Architecture
Загружено:
RiturajHarshАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Oracle RAC Architecture
Загружено:
RiturajHarshАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Oracle RAC Architecture
By Ahmed Baraka
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Objectives
In this lecture, you should learn how to describe the following:
• Oracle RAC hardware requirements
• Shared storage configuration options
• Oracle Grid Infrastructure components
• Oracle Clusterware network configuration
• Oracle RAC connectivity cycle
• Oracle RAC database files locations
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Oracle RAC History
• Oracle Parallel Server (OPS)
Oracle 6.2 on VAX/VMS.
• Oracle Real Application Cluster (RAC)
Oracle 9i
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Oracle RAC: Software Stack
• Oracle Grid Infrastructure
Clusterware
• Manage the whole cluster
• Monitor the availability of the resources
• Controls the resources startup order
• Can be programmed for user applications
ASM
• Oracle Database
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Oracle RAC Basic Architecture
Public Network
Private Network
Node 1 Node 2 Node n
Public IP Public IP Public IP
Virtual IP Virtual IP Virtual IP
Private Private Private
IP IP IP
ASM
Oracle ACFS or OCFS2
Shared Storage certified cluster file systems
NSF servers
Raw disks
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
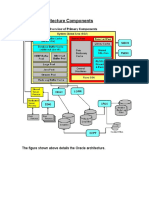
Oracle RAC Architecture Overview
• Every server that is part of the RAC is called node.
• Clients connect to the database through public network.
• Nodes connect to each other via private network (called
interconnect)
• Database datafiles are stored in shared storage.
• A RAC database has multiple instances. Every instance is
running in a single node.
• For a database to be available to the clients, at least one instance
should be up and running.
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Oracle RAC: Hardware Requirements
• Two or more servers
Similar hardware architecture and same OS
• Two Network cards installed into every node:
Public network: connected to the clients
Private network: interconnect network among the nodes
Redundant private interconnect configuration is highly recommended
• Shared storage
High speed storage network required, such as 16GbE FC
Redundant connections to the storage with multipathing configuration
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Oracle RAC: Memory Requirements
• If the same workload is kept on an instance, when migrating a
single-instance database to RAC, more memory is need:
10% more buffer cache
15% more shared pool
Memory used by ASM and Clusterware processes
• Memory consumed by client sessions will be distributed among
the instances
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Shared Storage Options
• ASM (the recommended option)
Volume manager and file system for Oracle Databases
More efficient for Oracle Databases
The only supported option with Oracle Standard Edition
• Oracle ACFS
Extends ASM functionality to support all files.
Provides: dynamic FS resizing, direct access to ASM DG, I/O parallelism
• OCFS2 (Oracle Cluster File System 2)
Open source general-purpose file system developed by Oracle
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Shared Storage Options (cont)
• Third-party Certified cluster file systems
Examples: Veritas Storage Foundation Cluster File System (SFCFS) for
Oracle RAC
• NFS Server
Only NFS protocol version 3 (NFSv3) is currently supported
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Oracle RAC: Engineered Systems
• Oracle Database Appliance (ODA)
Pros: tested for maximum performance, easy management
Cons: only two nodes
• Oracle Exadata Database Machine
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
About Oracle Grid Infrastructure
• Provide clustering features (clusterware) plus ASM
• It must be installed in its own, local home
• Usually owned by a dedicated OS user “grid”
• Cluster Ready Service (CRS) resources:
- ASM instances - SCAN listener
- ASM Diskgroup - database services
- Virtual IP (VIP) services - Oracle Net listener
- Single Client Access Name (SCAN) - Oracle Notification Service (ONS)
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
About Oracle Clusterware
• Requires shared storage to store:
Voting files for node membership
Oracle Clusterware Registry (OCR) for cluster configuration information
They must be saved in a high-redundant storage
• Further configuration data stored in two local files:
Oracle Local Registry (OLR): metadata for the local node
Grid Plug and Play (GPnP) profile: network profile and VD
• It used private interconnect network to carry the heartbeat
communication
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Oracle Clusterware
Configuration Data Distribution
Public Network
Node 1 Node 2 Node n
Grid Home Grid Home Grid Home
GPnP, GPnP, GPnP,
OLR OLR OLR
Shared Storage
Oracle Cluster Registry (OCR)
Voting files
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Clusterware: CRS Daemons and Services
Daemon/Ser Process Name Description
vice
CRS CRSD Start, stop, monitor, and failover operations on resources
CSS Service ocssd.bin Monitors the node membership in the cluster and updates the node
status information in VD
CSS Agent cssdagent Monitors, starts, and stops the CSS.
CSS Monitor cssdmonitor It works with the CSS agent to provide data integrity in the
clusterware. Base on the CPU startvation or OS status, it may reboot
the node.
CTSS octssd.bin Maintains time synchronization among all the nodes in the cluster
EVM evmd.bin Publishes events to all the cluster nodes
ONS ons Manages the Fast Application Notification (FAN) events
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Clusterware: CRS Daemons and Services
(cont)
Daemon/Service Process Name Description
Oracle Agent oraagent Managing ohasd resources owned by oracle
Oracle Root Agent orarootagen Managing ohasd resources owned by root
Oracle ASM Managing the shared storage and disk volumes
Note: this list is not all the Clusterware processes.
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Oracle Clusterware Network Configuration
• Oracle Grid Naming Service (GNS)
A subdomain is delegated in the DNS server for the cluster
You only define the GNS server VIP in the DNS
DHCP is supported only in Linux systems
• Static Configuration:
No subdomain is delegated in the DNS server
All names and addresses are resolved by DNS:
• A SCAN name to resolve to three static IP addresses for the cluster
• A public and virtual IP names and addresses for each node
• A virtual IP name and address for each node
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Oracle Clusterware Network Configuration
(cont)
• Single Client Access Name (SCAN)
A domain name registered to at least one and up to three IP addresses,
either in DNS or GNS.
Must be used by the clients when connecting to the RAC database
• Node Virtual IP (VIP) is managed by the Clusterware:
Must be assigned to each node
Must be on the same subnet as the public IP address
Provides rapid failure notification and failover
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Oracle RAC Connectivity Cycle
Client
SCAN
SCAN Listener
Node 1 Node 2 Node n
Local Local Local
Listener Listener Listener
Instance 1 Instance 2 Instance 3
Shared Storage
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Oracle RAC Connectivity Cycle
Client
Steps:
1
Client requests connection
1 using a SCAN name and a
service name. The DNS or SCAN
GNS returns to the client on
of the SCNA IP addresses
SCAN Listener
Node 1 Node 2 Node n
Local Local Local
Listener Listener Listener
Instance 1 Instance 2 Instance 3
Shared Storage
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Oracle RAC Connectivity Cycle
Client
Steps:
Using a SCAN IP, the client
2
connects to a SCAN Listener 2
providing it with a service
name.
SCAN Listener
Node 1 Node 2 Node n
Local Local Local
Listener Listener Listener
Instance 1 Instance 2 Instance 3
Shared Storage
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Oracle RAC Connectivity Cycle
Client
Steps:
SCAN listener determines 3
3 which database instance hosts
the requested service and
routes the client to the local
listener on the node.
Node 1 Node 2 Node n
Local Local Local
Listener Listener Listener
Instance 1 Instance 2 Instance 3
Shared Storage
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Oracle RAC Connectivity Cycle
Client
Steps: 4
4 The local listener connects the
client to the local instance.
Node 1 Node 2 Node n
Local Local Local
Listener Listener Listener
Instance 1 Instance 2 Instance 3
Shared Storage
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Oracle RAC Database File
Locations
Public Network
Node 1 Node 2 Node n
Instance 1 Instance 2 Instance 3
DB Home DB Home DB Home
System and user datafiles
Undo tablespace per inst.
2 Redo G. per instance
Shared Storage
Control F., SPFILE, psswd f.
DB Home (not recommended)
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Oracle RAC Clusterware and
Database Stack Components
SCAN
Node x Node y
Grid Infrastructure Grid Infrastructure
VIP ASM VIP ASM
Dynamic Service Dynamic Service
SCAN Listener Local Listener SCAN Listener Local Listener
Interconnect
Database Home Database Home
Database Instance Database Instance
Shared Storage:
(OCR – Vote files) – (DB files)
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Summary
By the end of this lecture, you should have learnt how to describe
the following:
• Oracle RAC hardware requirements
• Shared storage configuration options
• Oracle Grid Infrastructure components
• Oracle Clusterware network configuration
• Oracle RAC connectivity cycle
• Oracle RAC database files locations
Oracl e© Database 12c RAC Adm i ni strati on – a course by Ahm ed Baraka
Вам также может понравиться
- Oracle 11g R1/R2 Real Application Clusters EssentialsОт EverandOracle 11g R1/R2 Real Application Clusters EssentialsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Oracle Database 11g - Underground Advice for Database Administrators: Beyond the basicsОт EverandOracle Database 11g - Underground Advice for Database Administrators: Beyond the basicsОценок пока нет
- DRBD-Cookbook: How to create your own cluster solution, without SAN or NAS!От EverandDRBD-Cookbook: How to create your own cluster solution, without SAN or NAS!Оценок пока нет
- Practicals Book DbaДокумент204 страницыPracticals Book Dbakomma_satish100% (1)
- Oracle Core DBAДокумент5 страницOracle Core DBAkrrishsoft071Оценок пока нет
- Data Guard - CheatsheetДокумент6 страницData Guard - CheatsheetRoshith Mele AreekkalОценок пока нет
- Benefits of RAC over Single Instance and Key ComponentsДокумент3 страницыBenefits of RAC over Single Instance and Key ComponentsOracleDBA2015100% (1)
- Useful Oracle RACДокумент11 страницUseful Oracle RACriadelidrissiОценок пока нет
- Rman DocumentДокумент11 страницRman Documentsantababu100% (2)
- RAC Important ConceptsДокумент96 страницRAC Important Conceptsrviswan100% (2)
- Oracle GoldenGate 11g GuideДокумент466 страницOracle GoldenGate 11g Guiderks441Оценок пока нет
- 1Z0 - 068 - Oracle Database 12c RAC and Grid Infrastructure AdministrationДокумент5 страниц1Z0 - 068 - Oracle Database 12c RAC and Grid Infrastructure Administrationkpratnaker0% (2)
- 1.2 Creating An Oracle 12c R2 Physical Standby RAC Database From A Primary RAC Database PDFДокумент21 страница1.2 Creating An Oracle 12c R2 Physical Standby RAC Database From A Primary RAC Database PDFShero Khan100% (1)
- Tcs Oracle DBA RacДокумент67 страницTcs Oracle DBA Racmail2petluri@gmail.com100% (1)
- Oracle 12c Upgrade High-level StepsДокумент23 страницыOracle 12c Upgrade High-level StepsKarthik ArvindОценок пока нет
- Senior Oracle DBA Interview QuestionsДокумент37 страницSenior Oracle DBA Interview QuestionsTikumusu Agborbesong100% (2)
- Oracle RAC DBA Training :DBA TechnologiesДокумент29 страницOracle RAC DBA Training :DBA TechnologiesDBA Technologies0% (1)
- Oracle RAC AdministrationДокумент26 страницOracle RAC AdministrationShivkumar Kurnawal100% (2)
- ORACLE Apps DBA ScriptsДокумент11 страницORACLE Apps DBA ScriptspankajksОценок пока нет
- Oracle DBA Interview Questions and AnswersДокумент20 страницOracle DBA Interview Questions and Answersramesh158100% (1)
- Top RAC Interview QuestionsДокумент10 страницTop RAC Interview QuestionsSiva KumarОценок пока нет
- Oracle RAC Interview Question and AnswersДокумент4 страницыOracle RAC Interview Question and Answerssherif adfОценок пока нет
- Installation Oracle RAC - AIXДокумент48 страницInstallation Oracle RAC - AIXHung NguyenОценок пока нет
- Job Description - Oracle DBAДокумент3 страницыJob Description - Oracle DBAJayendra Singh ChandelОценок пока нет
- The Basics of Oracle ArchitectureДокумент5 страницThe Basics of Oracle Architecturebhuvan_boseОценок пока нет
- Oracle9i Database - Advanced Backup and Recovery Using RMAN - Student GuideДокумент328 страницOracle9i Database - Advanced Backup and Recovery Using RMAN - Student Guideacsabo_14521769Оценок пока нет
- Exadata AdminДокумент6 страницExadata AdminabidouОценок пока нет
- EDB High Availability Scalability v1.0Документ23 страницыEDB High Availability Scalability v1.0Paohua ChuangОценок пока нет
- Step by Step Installation of Oracle EBS R12.2Документ38 страницStep by Step Installation of Oracle EBS R12.2Prasad KaruturiОценок пока нет
- RAC - CheatsheetДокумент5 страницRAC - CheatsheetBhavesh ThakkarОценок пока нет
- Oracle Goldengate Hands-On Tutorial: Version Date: 1 Oct, 2012 EditorДокумент115 страницOracle Goldengate Hands-On Tutorial: Version Date: 1 Oct, 2012 EditorTolulope AbiodunОценок пока нет
- Advanced RAC TroubleshootingДокумент121 страницаAdvanced RAC TroubleshootingdrummerrОценок пока нет
- Oracle Database Security PDFДокумент43 страницыOracle Database Security PDFChidi OkerekeОценок пока нет
- Apply Rolling PSU Patch in Oracle Database 12c RAC EnvironmentДокумент6 страницApply Rolling PSU Patch in Oracle Database 12c RAC EnvironmentNarayan AdhikariОценок пока нет
- Oracle LibraryCacheInternals JulianDykeДокумент66 страницOracle LibraryCacheInternals JulianDyketssr2001Оценок пока нет
- Exadata Migration: Chris BradhamДокумент34 страницыExadata Migration: Chris BradhamAl Wall100% (1)
- RMAN Interview Questions From GeekinterviewДокумент10 страницRMAN Interview Questions From Geekinterviewrviswan100% (2)
- CRSCTL Commands in Oracle RACДокумент8 страницCRSCTL Commands in Oracle RACMaheboob MahebОценок пока нет
- Module 1 - Oracle ArchitectureДокумент34 страницыModule 1 - Oracle ArchitecturePratik Gandhi100% (1)
- Oracle DBA Interview QuestionsДокумент16 страницOracle DBA Interview QuestionsfkhalidОценок пока нет
- Oracle Asm QuestionsДокумент2 страницыOracle Asm QuestionsdbareddyОценок пока нет
- Schema Refresh Steps On Same Database PDFДокумент8 страницSchema Refresh Steps On Same Database PDFG.R.THIYAGU ; Oracle DBA100% (3)
- Oracle RMAN Interview QuestionsДокумент3 страницыOracle RMAN Interview QuestionsdbareddyОценок пока нет
- Oracle Database Performance and TuningДокумент69 страницOracle Database Performance and TuningSraVanKuMarThadakamalla100% (1)
- Oracle Cache Fusion Private Inter Connects and Practical Performance Management Considerations in Oracle RacДокумент25 страницOracle Cache Fusion Private Inter Connects and Practical Performance Management Considerations in Oracle RacKrishna8765Оценок пока нет
- Oracle Dataguard Interview QuestionsДокумент6 страницOracle Dataguard Interview QuestionsPranabKanojiaОценок пока нет
- Oracle Exadata Pocket ReferenceДокумент4 страницыOracle Exadata Pocket ReferenceNawab ShariefОценок пока нет
- Oracle DBA Interview Q&AДокумент58 страницOracle DBA Interview Q&Aaorya100% (1)
- How To Make Resume As Fresher Oracle DBA Myths-Mysteries-MemorableДокумент7 страницHow To Make Resume As Fresher Oracle DBA Myths-Mysteries-Memorablesriraam6Оценок пока нет
- APPS DBA Interview Questions - Oracle DBAДокумент39 страницAPPS DBA Interview Questions - Oracle DBAalex aguilarОценок пока нет
- Oracle ShardingДокумент43 страницыOracle ShardinghariprasathdbaОценок пока нет
- Oracle Export - Import - Data Pump Interview QuestionsДокумент4 страницыOracle Export - Import - Data Pump Interview QuestionsCherrie Ann Bautista Domingo-DilleraОценок пока нет
- Oracle RAC ArchitectureДокумент24 страницыOracle RAC ArchitectureSHAHID FAROOQОценок пока нет
- Database Architecture Oracle DbaДокумент41 страницаDatabase Architecture Oracle DbaImran ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Oracle DBA Interview QuestionsДокумент24 страницыOracle DBA Interview QuestionsGanesh.am93% (30)
- FND Load ScriptsДокумент4 страницыFND Load ScriptsManas Ranjan SahooОценок пока нет
- Global License Manager User GuideДокумент36 страницGlobal License Manager User GuideTaushif AlimОценок пока нет
- Essay in Auditing in CIS EnvironmentДокумент3 страницыEssay in Auditing in CIS EnvironmentPaul VaronaОценок пока нет
- Hach DR900 Handheld Colorimeter Instruction ManualДокумент19 страницHach DR900 Handheld Colorimeter Instruction ManualLuis Enrique Vilca EspinozaОценок пока нет
- Assignment 3Документ10 страницAssignment 3Anjani Kunwar100% (1)
- CR-IR346/348CL Service Manual Performance CheckДокумент16 страницCR-IR346/348CL Service Manual Performance Checklabel engineering companyОценок пока нет
- AS400 Command DSPДокумент158 страницAS400 Command DSPAdi FangОценок пока нет
- HADR Installation On SAP ASE 16.0 For SAP NetWeaver ABAP With Single PASДокумент24 страницыHADR Installation On SAP ASE 16.0 For SAP NetWeaver ABAP With Single PASVitlenОценок пока нет
- Automatic Memory Management (AMM) On 11g & 12c Document 443746.1Документ9 страницAutomatic Memory Management (AMM) On 11g & 12c Document 443746.1Alexander SuarezОценок пока нет
- Performance Task in Ict 9Документ6 страницPerformance Task in Ict 9Spongie BobОценок пока нет
- Module 5 B4A Sample Login Program Using Database SQLite Browser - Puppycode BlogДокумент11 страницModule 5 B4A Sample Login Program Using Database SQLite Browser - Puppycode Blogmarcelo19750000100% (1)
- Computer Security: Principles and Practice: Chapter 5: Malicious SoftwareДокумент35 страницComputer Security: Principles and Practice: Chapter 5: Malicious SoftwareHarihara Gopalan SОценок пока нет
- Universiti Kuala Lumpur: Assessment Brief and Verification Cover SheetДокумент12 страницUniversiti Kuala Lumpur: Assessment Brief and Verification Cover SheetNaim NizamОценок пока нет
- A UNIX Primer: David A. Clarke Saint Mary's University, Halifax NS, CanadaДокумент22 страницыA UNIX Primer: David A. Clarke Saint Mary's University, Halifax NS, Canadazx1500Оценок пока нет
- Code of Practice For Concrete Structures For The Storage of Líquids NZS 3106-1986Документ79 страницCode of Practice For Concrete Structures For The Storage of Líquids NZS 3106-1986Josué Azurín RendichОценок пока нет
- Question No 1:: Implement The Above Algorithms in Java Language. Use Proper Indentation and Comments in Your CodeДокумент5 страницQuestion No 1:: Implement The Above Algorithms in Java Language. Use Proper Indentation and Comments in Your CodeTAHREEM FATIMAОценок пока нет
- ER To Relational Schema TranslationДокумент35 страницER To Relational Schema TranslationSarmadОценок пока нет
- 2 Art-Gallary-synopsisДокумент4 страницы2 Art-Gallary-synopsisKeerthi Vasan LОценок пока нет
- Launchpad Configuration PDFДокумент50 страницLaunchpad Configuration PDFShyamОценок пока нет
- User, S ManualДокумент64 страницыUser, S ManualTRITRONIX INDUSTRIAL SOLUTIONОценок пока нет
- Vivid S60N Brochure-2Документ1 страницаVivid S60N Brochure-2Quan NguyenngocОценок пока нет
- 2013 Cse - IV Sem ResultsДокумент143 страницы2013 Cse - IV Sem ResultsSaravanan VAОценок пока нет
- Construction Manual Standard Drawings PDFДокумент172 страницыConstruction Manual Standard Drawings PDFAshley DooshОценок пока нет
- Emailreceipt VerizonДокумент1 страницаEmailreceipt VerizonMichel GandhiОценок пока нет
- Engineering Drawing Textbook Intro by N D BhattДокумент11 страницEngineering Drawing Textbook Intro by N D BhattAizaz Shamshad100% (1)
- MEMORY AND DATA TYPESДокумент43 страницыMEMORY AND DATA TYPESMark Israel SantosОценок пока нет
- Installing AIA On An Oracle SOA Suite Cluster DeploymentДокумент37 страницInstalling AIA On An Oracle SOA Suite Cluster DeploymentAbhay KumarОценок пока нет
- Comandos de Referencia ZyxelДокумент384 страницыComandos de Referencia ZyxelJose Vergara SoberanisОценок пока нет
- 3D PRINTER USER GUIDE - A Complete Step by Step User Manual For Understanding The Fundamentals of 3D Printing, How To Maintain and Troubleshoot Common DifficultiesДокумент49 страниц3D PRINTER USER GUIDE - A Complete Step by Step User Manual For Understanding The Fundamentals of 3D Printing, How To Maintain and Troubleshoot Common DifficultiesSzeghalmi Attila80% (5)
- Designer & Creative Director Lambert AnaniasДокумент1 страницаDesigner & Creative Director Lambert AnaniasAsh A'sОценок пока нет