Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Choosing The Right Assessment Tool
Загружено:
Perry FranciscoОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Choosing The Right Assessment Tool
Загружено:
Perry FranciscoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Choosing the Right Assessment Tools
(Based on Fulks, Janet, “Assessing Student Learning in Community Colleges”, Bakersfield College, 2004 obtained at
http://online.bakersfieldcollege.edu/courseassessment/Default.htm)
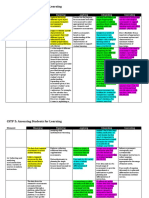
Examples of various assessment tools are included in the table below. It should be noted that the
categorizations may vary depending upon your perspective and the way in which you construct the assessment.
Bloom's level
K= Knowledge
Domain
Method Usage Type C= Comprehension
C= Cognitive
Tool D= Direct F= Formative A= Application Pros Cons
P= Psychomotor
I= Indirect S= Summative ASE= Analysis or
A= Affective
Synthesis or
Evaluation
Multiple D C F or S K, C easy to grade; reduces
Choice Exam If carefully objective assessment to
constructed ASE multiple choice
answers
Licensing D C S K, C, A easy to score and no authentic
Exams compare testing, may
outdate
Standardized D C S K, C, A? comparable heavily dependent
Cognitive between students on exposure to
Tests topics on test
Checklists D C, A, P F or S Variable very useful for skills can minimize large
or performances; picture and
students know interrelatedness;
exactly what is evaluation
missing feedback is
basically a yes/no -
present/absent -
without detail
Essay D C, A F or S K, C, A, ASE displays analytical time consuming to
and synthetic grade, can be
thinking well subjective
Case Study D C, A F or S K, C, A, ASE displays analytical creating the case is
and synthetic time consuming,
thinking well; dependent on
connects other student knowledge
knowledge to topic form multiple areas
Problem D C F or S K, C, A, ASE displays analytical difficult to grade
Solving and synthetic due to multiple
thinking well; methods and
authentic if real potential multiple
world situations are solutions
used
Oral Speech D C F or S Variable easily graded with difficult for ESL
K, C, A, ASE rubric; allows other students; stressful
students to see and for students; takes
learn what each course time; must
student learned; fairly grade course
connects general content beyond
education goals delivery
with discipline-
specific courses
Debate D C, A F or S K, C, A, ASE provides immediate requires good
feedback to the rubric; more than
student; reveals one evaluator is
thinking and ability helpful; difficult for
to respond based ESL students;
on background stressful for
knowledge and students; takes
critical thinking course time
ability
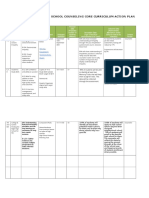
Bloom's level
K= Knowledge
Domain
Method Usage Type C= Comprehension
C= Cognitive
Tool D= Direct F= Formative A= Application Pros Cons
P= Psychomotor
I= Indirect S= Summative ASE= Analysis or
A= Affective
Synthesis or
Evaluation
Product D C, P, A F or S Variable students can must have clearly
Creation & K, C, A, ASE display skills, defined criteria and
Special knowledge, and evaluative
Reports abilities in a way measures; "the
that is suited to look" can not over-
them ride the content
Flowchart or D C F or S C, A, ASE displays original more difficult to
Diagram synthetic thinking grade, requiring a
on the part of the checklist or rubric
student; perhaps for a variety of
the best way to different answers;
display overall high difficult for some
level thinking and students to do on
articulation abilities the spot
Portfolios D C, P S Variable provides the Time consuming to
students with a grade; different
clear record of their content in portfolio
work and growth; makes evaluating
best evidence of difficult and may
growth and change require training;
over time; students bulky to manage
can display skills. depending on size
knowledge, and
abilities in a way
that is suited to
them; promotes
self-assessment
Exit Surveys D and I A S ASE provides good Likert scales limit
summative data; feedback, open-
easy to manage ended responses
data if Likert-scaled are bulky to
responses are used manage
Performance D C, P F or S Variable provides best stressful for
K, C, A, ASE display of skills and students; may take
abilities; provides course time; some
excellent students may take
opportunity for the evaluation very
peer review; hard - evaluative
students can statements must be
display skills. carefully framed
knowledge, and
abilities in a way
that is suited to
them
Capstone D C, P , A F orS ASE best method to focus and breadth
project or measure growth of assessment and
course overtime with understanding all
regards to a course the variables to
or program - produce
cumulative assessment results
are important; may
result in additional
course
requirements;
requires
coordination and
agreement on
standards
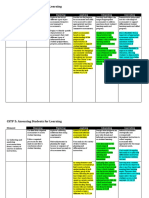
Bloom's level
K= Knowledge
Domain
Method Usage Type C= Comprehension
C= Cognitive
Tool D= Direct F= Formative A= Application Pros Cons
P= Psychomotor
I= Indirect S= Summative ASE= Analysis or
A= Affective
Synthesis or
Evaluation
Team Project D C, A F or S Variable connects general must fairly grade
K, C, A, ASE education goals individuals as well
with discipline- as team; grading is
specific courses slightly more
complicated;
student interaction
may be a challenge
Reflective D and I C, A S ASE provides invaluable must use evidence
self- ability to evaluate to support
assessment affective growth in conclusions, not
essay students just self-
opinionated
assessment
Satisfaction I C, P, A S C, A, ASE provides good respondents may
and indirect data; data be influenced by
Perception can be compared factors other than
Surveys longitudinally; can those being
be used to considered; validity
determine and reliability most
outcomes over a be closely watched
long period of time
Assessment Tool Checklist
1. Does the assessment adequately evaluate academic performance relevant to the desired outcome? (validity)
2. Does this assessment tool enable students with different learning styles or abilities to show you what they have
learned and what they can do?
3. Does the content examined by the assessment align with the content from the course? (Content validity)
4. Does this assessment method adequately address the knowledge, skills, abilities, behavior, and values
associated with the intended outcome? (Domain validity)
5. Will the assessment provide information at a level appropriate to the outcome? (Bloom’s)
6. Will the data accurately represent what the student can do in an authentic or real life situation? (Authentic
assessment)
7. Is the grading scheme consistent; would a student receive the same grade for the same work on multiple
evaluations? (Reliability)
8. Can multiple people use the scoring mechanism and come up with the same general score? (Reliability)
9. Does the assessment provide data that is specific enough for the desired outcomes? (alignment with outcome)
10. Is the assessment summative or formative - if formative does it generate diagnostic feedback to improve
learning?
11. Is the assessment summative or formative - if summative, is the final evaluation built upon multiple sources of
data? (AAHE Good practice)
12. If this is a summative assessment, have the students had ample opportunity for formative feedback and practice
displaying what they know and can do?
13. Is the assessment unbiased or value-neutral, minimizing an attempt to give desirable responses and reducing
any cultural misinterpretations?
14. Are the intended uses for the assessment clear? (Grading, program review, both)
15. Have other faculty provided feedback?
16. Has the assessment been pilot-tested?
17. Has the evaluation instrument been normed?
18. Will the information derived from the assessment help to improve teaching and learning? (AAHE Good Practice)
19. Will you provide the students with a copy of the rubric or assignment grading criteria?
20. Will you provide the students examples of model work?
Вам также может понравиться
- Wii C Obj I Writing Course ObjectivesДокумент4 страницыWii C Obj I Writing Course Objectivesbilisuma sebokaОценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Sells 12Документ8 страницCSTP 5 Sells 12api-635588860Оценок пока нет
- 621 Tier 1 HR Action Plan TemplateДокумент2 страницы621 Tier 1 HR Action Plan Templateapi-584560790Оценок пока нет
- Performance Assessment Tasks for Teaching SubjectsДокумент5 страницPerformance Assessment Tasks for Teaching SubjectsReyna CarenioОценок пока нет
- Akhmad Dzaikra RamadhaniДокумент1 страницаAkhmad Dzaikra RamadhaniPearlОценок пока нет
- Assessing An AssessmentДокумент1 страницаAssessing An Assessmentapi-506656261Оценок пока нет
- Lessonplan 21Документ3 страницыLessonplan 21api-321658972Оценок пока нет
- Bloom's Taxonomy: A Classification of Educational ObjectivesДокумент3 страницыBloom's Taxonomy: A Classification of Educational ObjectivesRhea Blny MñgОценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Webster 5Документ9 страницCSTP 5 Webster 5api-622508187Оценок пока нет
- Ped 10 Module 1 Unit 1Документ13 страницPed 10 Module 1 Unit 1Barangay PamucutanОценок пока нет
- Lesson Observation Report: Teaching/Learning SituationДокумент8 страницLesson Observation Report: Teaching/Learning Situationapi-332045960Оценок пока нет
- Taxonomy Jhonnel L. Abadesa BCAED 2Документ2 страницыTaxonomy Jhonnel L. Abadesa BCAED 2Jhonnel L. AbadesaОценок пока нет
- CarlyhaberleДокумент4 страницыCarlyhaberleapi-507832305Оценок пока нет
- Quarter I Proposed Multimodal Assessment Strategy On Reflective Learning Using The IDEA Instructional ProcessДокумент3 страницыQuarter I Proposed Multimodal Assessment Strategy On Reflective Learning Using The IDEA Instructional ProcessGenna EstacioОценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Chaput 7 15 2023Документ8 страницCSTP 5 Chaput 7 15 2023api-678836671Оценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Feigin 4Документ11 страницCSTP 5 Feigin 4api-621922636Оценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Smiley 5Документ9 страницCSTP 5 Smiley 5api-534241952Оценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Reyes 09Документ10 страницCSTP 5 Reyes 09api-528997236Оценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Dow 5Документ8 страницCSTP 5 Dow 5api-414910309Оценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Kruki 5Документ11 страницCSTP 5 Kruki 5api-621898580Оценок пока нет
- Bus. Math DLL WK 2Документ3 страницыBus. Math DLL WK 2joeven manzoОценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Behrens 3Документ9 страницCSTP 5 Behrens 3api-571720796Оценок пока нет
- Differences between traditional and alternative assessmentsДокумент2 страницыDifferences between traditional and alternative assessmentsWENCY DELA GENTEОценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Stumfall 5Документ8 страницCSTP 5 Stumfall 5api-528157962Оценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Hayes 7Документ8 страницCSTP 5 Hayes 7api-302062949Оценок пока нет
- Compare and Contrast To Help Write A Compare and Contrast EssayДокумент6 страницCompare and Contrast To Help Write A Compare and Contrast Essayeva.benson100% (1)
- Assignment (Educ 119)Документ3 страницыAssignment (Educ 119)Mavill Joy CarreonОценок пока нет
- CSTP 5: Assessing Students For Learning: Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating InnovatingДокумент10 страницCSTP 5: Assessing Students For Learning: Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating InnovatingKaitlyn AprilОценок пока нет
- Test 2 Take Home-ECV5601-Sem1-Yr2017-2018Документ4 страницыTest 2 Take Home-ECV5601-Sem1-Yr2017-2018Ilyas H. AliОценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Watkins 5Документ10 страницCSTP 5 Watkins 5api-528630304Оценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Pedue 7Документ10 страницCSTP 5 Pedue 7api-622185749Оценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Pedue 12Документ10 страницCSTP 5 Pedue 12api-622185749Оценок пока нет
- Lakewood School of Alabang Statistics and Probability Curriculum MapДокумент4 страницыLakewood School of Alabang Statistics and Probability Curriculum MapErick ConcepcionОценок пока нет
- Kahoot EvaluationДокумент2 страницыKahoot EvaluationDaniel BayerОценок пока нет
- SLOs, Bloom's Taxonomy, Cognitive, Psychomotor, and Affective DomainsДокумент5 страницSLOs, Bloom's Taxonomy, Cognitive, Psychomotor, and Affective DomainsEricka NavarreteОценок пока нет
- KG Observation 3Документ3 страницыKG Observation 3api-355958411Оценок пока нет
- Bloom TaxonomyДокумент3 страницыBloom TaxonomyAmirah HusnaОценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 TricomoДокумент9 страницCSTP 5 Tricomoapi-518371548Оценок пока нет
- What Is Bloom's Taxonomy and How Can You Use It To Create A TestДокумент1 страницаWhat Is Bloom's Taxonomy and How Can You Use It To Create A TestDhonna IdosoraОценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 HhakamiДокумент15 страницCSTP 5 Hhakamiapi-483659321Оценок пока нет
- Liesl Bryant Observation 1 November 3 2017Документ6 страницLiesl Bryant Observation 1 November 3 2017api-316733704Оценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Camburn 4Документ7 страницCSTP 5 Camburn 4api-556750285Оценок пока нет
- OBSERVATION SHE-WPS OfficeДокумент10 страницOBSERVATION SHE-WPS OfficejavaabbeОценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Fountain FinalДокумент10 страницCSTP 5 Fountain Finalapi-518367210Оценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Hyatt Sem 4Документ14 страницCSTP 5 Hyatt Sem 4api-529069079Оценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 - Reflection - Yellow and GreenДокумент10 страницCSTP 5 - Reflection - Yellow and Greenapi-529100008Оценок пока нет
- CurriculumactionplanfinalДокумент2 страницыCurriculumactionplanfinalapi-336685280Оценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Walker 12Документ10 страницCSTP 5 Walker 12api-636156921Оценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Sacks 5Документ10 страницCSTP 5 Sacks 5api-573207513Оценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Bernstein Semester 3Документ8 страницCSTP 5 Bernstein Semester 3api-483682821Оценок пока нет
- cstp5 Coggins 04Документ9 страницcstp5 Coggins 04api-518568920Оценок пока нет
- CSTP 5 Kaczmarek 12Документ8 страницCSTP 5 Kaczmarek 12api-528489480Оценок пока нет
- Concepts in Classroom Assessment Quiz: A C B C C D D B A C C B D D DДокумент1 страницаConcepts in Classroom Assessment Quiz: A C B C C D D B A C C B D D DBaluyut CabreraОценок пока нет
- CSTP 5: Assessing Students For Learning: Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating InnovatingДокумент10 страницCSTP 5: Assessing Students For Learning: Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating InnovatingKaitlyn AprilОценок пока нет
- CSTP 5: Assessing Students For Learning: Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating InnovatingДокумент9 страницCSTP 5: Assessing Students For Learning: Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating InnovatingKaitlyn MillerОценок пока нет
- Kaitlyn Phillips Us2Документ6 страницKaitlyn Phillips Us2api-309290535Оценок пока нет
- cstp5 CarminadiazalcarazДокумент9 страницcstp5 Carminadiazalcarazapi-573023941Оценок пока нет
- A Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasОт EverandA Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasОценок пока нет
- Admin - CebuДокумент11 страницAdmin - CebuPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- 360 Feedback from SupportZebraДокумент4 страницы360 Feedback from SupportZebraPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Session 1 NotesДокумент5 страницSession 1 NotesPerry Francisco100% (1)
- Exit Interview ReportДокумент11 страницExit Interview ReportPerry Francisco100% (1)
- Top Level Reason Second Level ReasonДокумент3 страницыTop Level Reason Second Level ReasonPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- MELCHORA CABANAS, Plaintiff-Appelleevs - FRANCISCO PILAPIL, Defendant-Appellant (58 SCRA 94, July 25, 1974) FactsДокумент2 страницыMELCHORA CABANAS, Plaintiff-Appelleevs - FRANCISCO PILAPIL, Defendant-Appellant (58 SCRA 94, July 25, 1974) FactsPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Employee tenure and attrition dataДокумент6 страницEmployee tenure and attrition dataPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Philippine Government vs Monte de Piedad BankДокумент2 страницыPhilippine Government vs Monte de Piedad BankPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Employee tenure and attrition dataДокумент6 страницEmployee tenure and attrition dataPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Philippine Government vs Monte de Piedad BankДокумент2 страницыPhilippine Government vs Monte de Piedad BankPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Top Level Reason Second Level ReasonДокумент3 страницыTop Level Reason Second Level ReasonPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- PVTA Exempt from Overtime PayДокумент2 страницыPVTA Exempt from Overtime PayClaudine Christine A. VicenteОценок пока нет
- PDEA Application Requirements: Documents NeededДокумент1 страницаPDEA Application Requirements: Documents NeededPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Philippine Government vs Monte de Piedad BankДокумент2 страницыPhilippine Government vs Monte de Piedad BankPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- PVTA Exempt from Overtime PayДокумент2 страницыPVTA Exempt from Overtime PayClaudine Christine A. VicenteОценок пока нет
- Security and Maintenance SupervisorДокумент2 страницыSecurity and Maintenance SupervisorPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- PVTA Exempt from Overtime PayДокумент2 страницыPVTA Exempt from Overtime PayClaudine Christine A. VicenteОценок пока нет
- ABC Analysis1234Документ30 страницABC Analysis1234Asfa JaVedОценок пока нет
- Missing Employee RecordsДокумент56 страницMissing Employee RecordsPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Activity ProposalДокумент4 страницыActivity ProposalPerry Francisco100% (1)
- Facilitation Plan EthicsДокумент3 страницыFacilitation Plan EthicsPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- SANTACRUZAN ScoresheetДокумент2 страницыSANTACRUZAN ScoresheetPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- SANTACRUZAN ScoresheetДокумент2 страницыSANTACRUZAN ScoresheetPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Activity Proposal Heartily Yours! Date: February 14, 2018 ObjectivesДокумент3 страницыActivity Proposal Heartily Yours! Date: February 14, 2018 ObjectivesPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Santacruzan 2019 Flowers of May ProgramДокумент2 страницыSantacruzan 2019 Flowers of May ProgramPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- HR Activities Mother's Day 2017Документ2 страницыHR Activities Mother's Day 2017Perry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- PROPOSAL HR Activity Santacruzan 2019Документ5 страницPROPOSAL HR Activity Santacruzan 2019Perry Francisco0% (1)
- Santacruzan Flowers ContestДокумент2 страницыSantacruzan Flowers ContestPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Visual Communications Analyst IДокумент2 страницыVisual Communications Analyst IPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Visual Communications SupervisorДокумент2 страницыVisual Communications SupervisorPerry FranciscoОценок пока нет
- HEC Scholarship DetailsДокумент1 страницаHEC Scholarship DetailsDr AliОценок пока нет
- Netflix Business Model Canvas Highlights Key StrategiesДокумент1 страницаNetflix Business Model Canvas Highlights Key StrategiesNemo SecretОценок пока нет
- AGBT05-18 Guide To Bridge Technology Part 5 Structural DraftingДокумент73 страницыAGBT05-18 Guide To Bridge Technology Part 5 Structural DraftingyasОценок пока нет
- PVG 32 BobinasДокумент64 страницыPVG 32 BobinasSaul CastañedaОценок пока нет
- Metabolic AdaptationДокумент17 страницMetabolic AdaptationMozil Fadzil KamarudinОценок пока нет
- Health Care Facilities and Medical Gas and VacuumДокумент27 страницHealth Care Facilities and Medical Gas and VacuumStephen TabiarОценок пока нет
- SAP Localization TurkeyДокумент30 страницSAP Localization TurkeybenhzbОценок пока нет
- Biomedical Anna 27Документ30 страницBiomedical Anna 27Manoj GuruОценок пока нет
- Syllabus For Undergraduate Course in History (Bachelor of Arts Examination)Документ26 страницSyllabus For Undergraduate Course in History (Bachelor of Arts Examination)Rojalin Mishra0% (1)
- Toyota TVIP System ProgrammingДокумент11 страницToyota TVIP System Programmingcheerios353Оценок пока нет
- Hurdle TechnologyДокумент26 страницHurdle TechnologyPradeep Kumar93% (14)
- Cast StudyДокумент5 страницCast StudyFrancisco Rodriguez0% (3)
- Alpha Arbutin As A Skin Lightening Agent: A Review: April 2021Документ11 страницAlpha Arbutin As A Skin Lightening Agent: A Review: April 2021Atika HapsatiОценок пока нет
- Conceptualizing Wellbeing in The Workplace: Stefania de SimoneДокумент5 страницConceptualizing Wellbeing in The Workplace: Stefania de SimoneMariaP12Оценок пока нет
- 9701 s02 ErДокумент14 страниц9701 s02 ErHubbak KhanОценок пока нет
- Nature-Based+tourism+and+biodiversity+conservation+in+protected+areas +philippine+contextДокумент17 страницNature-Based+tourism+and+biodiversity+conservation+in+protected+areas +philippine+contextRene John Bulalaque EscalОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Differential Amplifiers by Muhammad Irfan Yousuf (Peon of Holy Prophet (P.B.U.H) )Документ133 страницыAnalysis of Differential Amplifiers by Muhammad Irfan Yousuf (Peon of Holy Prophet (P.B.U.H) )Sohail YousafОценок пока нет
- Closed Loop Speed Control of a DC Motor Lab ManualДокумент9 страницClosed Loop Speed Control of a DC Motor Lab ManualnatashaОценок пока нет
- Preliminary Examination EvidenceДокумент5 страницPreliminary Examination EvidenceRA MlionОценок пока нет
- FDA AssignДокумент9 страницFDA AssignZhainna SilvestreОценок пока нет
- 2007 128Документ168 страниц2007 128Walter Morales NeyreОценок пока нет
- Tools and MaterialsДокумент71 страницаTools and MaterialsMahardikaОценок пока нет
- Wall-Mounted King Shell Temperature and Humidity Transmitter User ManualДокумент6 страницWall-Mounted King Shell Temperature and Humidity Transmitter User ManualTrung Trần HữuОценок пока нет
- Salesforce CRMДокумент22 страницыSalesforce CRMkrishna_mf01Оценок пока нет
- ADANI POWER LIMITED: POWERING INDIA'S GROWTH WITH A 2030 OUTLOOKДокумент26 страницADANI POWER LIMITED: POWERING INDIA'S GROWTH WITH A 2030 OUTLOOKAnonymous V4jDKjUR6Оценок пока нет
- BE Semester-VIII (Civil Engineering) Question Bank (Design of Steel Structures)Документ2 страницыBE Semester-VIII (Civil Engineering) Question Bank (Design of Steel Structures)Suresh RajuОценок пока нет
- Hse Plan Rev01Документ71 страницаHse Plan Rev01Lovedeep SinghОценок пока нет
- B777 Fuel SystemsДокумент0 страницB777 Fuel Systemsandrinjo100% (3)
- ToLiss AirbusA321 V1.0.3 TutorialДокумент103 страницыToLiss AirbusA321 V1.0.3 TutorialMarc CerveraОценок пока нет
- Make Versus Buy Sample CalculationsДокумент2 страницыMake Versus Buy Sample CalculationsRobert CocklerОценок пока нет