Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Print Me
Загружено:
IuliaNiculae0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
7 просмотров2 страницыPrint Me
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документPrint Me
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
7 просмотров2 страницыPrint Me
Загружено:
IuliaNiculaePrint Me
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
Print this document out and review it right before you take the test.
CCNA Cheat Sheet
Get in the mindset: Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link, Physical
ISDN Standards: E deals with telephone network standards (between ISDN devices), I deals with concepts
and terminology, Q deals with switching.
Learn the ISDN reference points:
TE1: Terminal Equipment type 1. This is the ISDN telephone, computer, ISDN FAX machine. Or whatever
it is that you've hooked up to the ISDN phone line.
<the wire between a TE1 and a NT2 is called reference point S>
TE2: Terminal Equipment type 2. This is the old analog telephone, old-style fax machine, modem. Or
whatever you used to hook up to the analog phone line. It can also be other communications equipment that
is handled by a TA (see below).
<the wire between a TE2 and a TA is reference point R>
TA: Terminal Adaptor. This lets old, TE2 stuff talk to the ISDN network. It also adapts other kinds of
equipment, like ethernet interfaces , to ISDN. It is typically called a POTS (Plain old Telephone system)
port.
<the wire between a TE2 an a NT2 is reference point S>
NT2: Network Termination type 2. In most homes, this won't exist. If you were a big company with your
own private telephone system, then this would be the guts of that telephone system.
<the wire between a NT2 and an NT1 is reference point T>
NT1: Network Termination type 1. This is the end of the line for the local phone company, and the
beginning of your house's phone network.
<the wire between a NT1 and the LT is reference point U>
LT: Line Termination. This is the physical connection to the phone company.
<the wire between a LT and the ET is reference point V>
ET: Exchange Termination. This is the local phone company's logical connection from your telephones to
"the phone network".
ISDN device may raise its priority level when all the other devices in the D channel have had a chance to
send a D message.
PRI circuit types: E1 uses CRC4 or no CRC4, T1 uses SF or ESF
Dialer-list is used to filter what traffic is interesting
IGRP and RIP are classful routing protocols
EIGRP, OSPF, and NLSP are not classful
You can have a maximum of 6 name servers.
You should avoid using more than 2 VLSMs on any network (according to Cisco)
LMI is autosensing after version 11.2 (remember the version #)
Cisco keywords for IPX Encapsulations
Ethernet II – keyword: ARPA
Ethernet 802.2 on Ethernet/Token Ring/FDDI – keyword: SAP
Ethernet 802.2 SNAP on Ethernet/Token Ring/FDDI – keyword: SNAP
Ethernet 802.3 (novell’s proprietary format) – keyword: novell-ether
How to setup an ISDN/Pri Interface on cisco 7500
Isdn switch-type switch-type
Controller t1 slot/port [or] Controller t1 number
Framing esf
Linecode b8zs
Pri-group [timeslots/range]
Enhanced Editing features: CTRL-A returns to the beginning of a line, CTRL-B is a backspace, CTRL H,
is a destructive backspace, CTRL-P cycles through the command history, CTRL-L reloads the previous
line, CTRL-K clears the line, ESC-B moves back one word at a time. Enhanced Editing is enabled by
default.
Вам также может понравиться
- Important Legal NoticeДокумент2 страницыImportant Legal NoticeIuliaNiculaeОценок пока нет
- Explanations and Answers For The Cisco ObjectivesДокумент23 страницыExplanations and Answers For The Cisco ObjectivesIuliaNiculaeОценок пока нет
- MCCA ProCredit 0813Документ19 страницMCCA ProCredit 0813IuliaNiculaeОценок пока нет
- Managementul Riscurilor BancareДокумент93 страницыManagementul Riscurilor BancareIuliaNiculaeОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Redseer Consulting Report On Vernacular LanguagesДокумент36 страницRedseer Consulting Report On Vernacular LanguagesMalavika SivagurunathanОценок пока нет
- Jovan Marjanovic Theory of Gravity MachinesДокумент10 страницJovan Marjanovic Theory of Gravity MachinesWilhelm HartmanОценок пока нет
- Dokumen - Tips - Curriculum Vitae Adrian Danar Wibisono 1Документ2 страницыDokumen - Tips - Curriculum Vitae Adrian Danar Wibisono 1Reo DeraОценок пока нет
- Larsen and Toubro RVNL Bid Document Rock Bolts PDFДокумент240 страницLarsen and Toubro RVNL Bid Document Rock Bolts PDFSubhash Kedia100% (1)
- Jce 70 2018 10 3 2437 enДокумент7 страницJce 70 2018 10 3 2437 enaaОценок пока нет
- DLP Sample Detailed Lesson PlanДокумент4 страницыDLP Sample Detailed Lesson PlanJaydie PalОценок пока нет
- Numerical Modeling of MHD Convective Heat and Mass Transfer in Presence of First-Order Chemical Reaction and Thermal RadiationДокумент20 страницNumerical Modeling of MHD Convective Heat and Mass Transfer in Presence of First-Order Chemical Reaction and Thermal Radiationmanasdutta3495Оценок пока нет
- Senthil Kumaran ResumeДокумент3 страницыSenthil Kumaran ResumeRamkumar SelvarajОценок пока нет
- A2 Accu-Flo Clamped Metal Pump: Engineering Operation MaintenanceДокумент28 страницA2 Accu-Flo Clamped Metal Pump: Engineering Operation MaintenanceThanh Nghị BùiОценок пока нет
- ME-341A - Heat and Mass TransferДокумент34 страницыME-341A - Heat and Mass TransferMukul ChandraОценок пока нет
- C-Zone SDN BHD: Price List Effective 10 AUG 2019Документ2 страницыC-Zone SDN BHD: Price List Effective 10 AUG 2019Cikgu AlОценок пока нет
- Building Applied Natural Language GenerationДокумент32 страницыBuilding Applied Natural Language Generationrat86Оценок пока нет
- User Manual For Soniclean Digital Benchtop Ultrasonic Cleaners 191013 PDFДокумент12 страницUser Manual For Soniclean Digital Benchtop Ultrasonic Cleaners 191013 PDFRafael GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Web UI Norox Neu PDFДокумент8 страницWeb UI Norox Neu PDFGovardhan RaviОценок пока нет
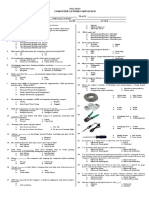
- Computer Systems Servicing: Pre-TestДокумент2 страницыComputer Systems Servicing: Pre-TestGerman Nueva Estrelles IIIОценок пока нет
- TIOut Brickwork 1Документ4 страницыTIOut Brickwork 1kevin smithОценок пока нет
- KNS2163 Week1Документ32 страницыKNS2163 Week1Nurul QurratuОценок пока нет
- Technical Service Bulletin (TSB) - VF7KFRHC8CS506525: 1. OriginДокумент3 страницыTechnical Service Bulletin (TSB) - VF7KFRHC8CS506525: 1. Originalexp50Оценок пока нет
- CPB 20104 Mass Transfer 2 UniKL MICET Experiment 1: Cooling TowerДокумент20 страницCPB 20104 Mass Transfer 2 UniKL MICET Experiment 1: Cooling TowerSiti Hajar Mohamed100% (6)
- LAPORAN PRAKTIK KERJA LAPANGAN - Id.enДокумент25 страницLAPORAN PRAKTIK KERJA LAPANGAN - Id.enAhmad JupriОценок пока нет
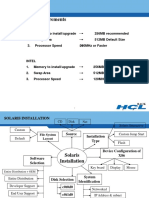
- Minimal Requirements: Solaris InstallationДокумент74 страницыMinimal Requirements: Solaris InstallationsrinivasОценок пока нет
- Office Automation & Attendance System Using IoTДокумент4 страницыOffice Automation & Attendance System Using IoTAnonymous kw8Yrp0R5rОценок пока нет
- Fpcroute User GuideДокумент34 страницыFpcroute User GuideJosé EireneОценок пока нет
- Schneider ElectricCahier Technique No. 199Документ36 страницSchneider ElectricCahier Technique No. 199Alda EnglandОценок пока нет
- Quectel MC60 at Commands Manual V1.2Документ262 страницыQuectel MC60 at Commands Manual V1.2Adimaro MontoyaОценок пока нет
- Grain Diameter (MM) Strength (Mpa) : 0.015 170 Mpa 0.025 158 Mpa 0.035 151 Mpa 0.050 145 MpaДокумент1 страницаGrain Diameter (MM) Strength (Mpa) : 0.015 170 Mpa 0.025 158 Mpa 0.035 151 Mpa 0.050 145 MpaTEBATSOОценок пока нет
- References:: 111 Richard Valantine, "Motor Control Electronics Handbook", 1998, ISBN 0-07-066810-8Документ30 страницReferences:: 111 Richard Valantine, "Motor Control Electronics Handbook", 1998, ISBN 0-07-066810-8rajeevОценок пока нет
- Outline Spesifikasi BPKPДокумент44 страницыOutline Spesifikasi BPKPnadyaОценок пока нет
- Doka Large Formwork User ManualДокумент21 страницаDoka Large Formwork User ManualNasir AryaniОценок пока нет
- AGE10503, Gas ProcessingДокумент34 страницыAGE10503, Gas ProcessingiranmortezaОценок пока нет