Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Functions of the Major Cortical Lobes and Areas
Загружено:
carll0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
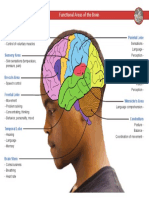
23 просмотров2 страницыThe cerebral cortex is divided into four main lobes - frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital - each containing cortical areas that serve specific functions. The frontal lobe contains areas for emotions, complex thought, speech production and motor control. The parietal lobe contains areas for somatosensation and processing of multisensory information. The temporal lobe contains areas for auditory processing and comprehension of language. The occipital lobe contains the primary visual cortex for detection of visual stimuli.
Исходное описание:
fx
Оригинальное название
cereb
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe cerebral cortex is divided into four main lobes - frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital - each containing cortical areas that serve specific functions. The frontal lobe contains areas for emotions, complex thought, speech production and motor control. The parietal lobe contains areas for somatosensation and processing of multisensory information. The temporal lobe contains areas for auditory processing and comprehension of language. The occipital lobe contains the primary visual cortex for detection of visual stimuli.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
23 просмотров2 страницыFunctions of the Major Cortical Lobes and Areas
Загружено:
carllThe cerebral cortex is divided into four main lobes - frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital - each containing cortical areas that serve specific functions. The frontal lobe contains areas for emotions, complex thought, speech production and motor control. The parietal lobe contains areas for somatosensation and processing of multisensory information. The temporal lobe contains areas for auditory processing and comprehension of language. The occipital lobe contains the primary visual cortex for detection of visual stimuli.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
FUNCTIONAL DIVISIONS OF THE CEREBRAL CORTEX
Lobe Cortical Area Function
Frontal Prefrontal cortex. Emotions, complex thought, problem solving.
Motor association cortex (premotor and supplementary cortex): Coordination of complex movement.
• Located in front of primary motor cortex, on lateral cortex (Brodmann area 6).
Primary motor cortex: Initiation of voluntary movement; receives sensory
• Located within precentral gyrus (Brodmann area 4). input from spinal cord and other cortical areas w/c
• Body parts represented in order along gyrus: legs on top, head at bottom. it uses to modify motor commands.
• Amount of body cortex representing bodypart is proportional in size to amount
of skill neededed for its movement (eg, cortical areas for hand movements are
much larger than those for trunk.)
Broca area – at inferior frontal gyrus, anterior to inferior end of motor cortex Production and articulation of speech.
(Brodmann areas 44 and 45 .)
Parietal Primary somatosensory cortex: Receives tactile information from the body.
• Located within postcentral gyrus (Brodmann areas 1, 2, 3).
• Body parts represented in order along gyrus: legs on top, head at bottom.
• Size of cortical receiving area for impulses from body part is proportional to the
number of receptors in that part (eg, cortical areas for hands are much larger than
those for trunk).
Sensory association cortex. Processing of multisensory information.
Temporal Auditory cortex: Detection of sound quality.
• Located in superior temporal lobe in sylvian fissure (Brodmann area 41).
Auditory association cortex. Complex processing of auditory information.
Wernicke area: Comprehension of language.
• Supramarginal and angular gyri and posterior part of superior temporal gyrus
(Brodmann area 22).
Lobe Cortical Area Function
Limbic system: Behavior (aggression, feeding, sexuality).
• Includes cingulate, parahippocampal, and subcallosal gyri; hippocampus; Emotions, olfaction, memory.
amygdale; dentate gyrus; subiculum; hypothalamus; basal ganglia. Autonomic responses (blood pressure, respiration).
• Papez circuit: closed circuit of the limbic system: hippocampus > fornix >
mamillary bodies > anterior nuclei of thalamus (mamillothalamic tract) >
cingulated cortex > hippocampus.
Occipital Visual cortex: occipital eye fields (Broadmann area 17). Detection of visual stimuli.
Visual association area overlaps posterioir parietal and temporal areas. Complex processing of visual information.
Вам также может понравиться
- Brain Lobes & FunctionsДокумент15 страницBrain Lobes & FunctionsAlyssa PangОценок пока нет
- VisibleBody Brain Ebook May2021Документ38 страницVisibleBody Brain Ebook May2021Sandra RubianoОценок пока нет
- l15 CerebrumДокумент31 страницаl15 CerebrumDr. Pinki RaiОценок пока нет
- L15 CerebrumДокумент27 страницL15 CerebrumEvilneko1Оценок пока нет
- Higher Center - Dr. BarbonДокумент5 страницHigher Center - Dr. BarbonMelissa SalayogОценок пока нет
- K8a Anatomi Sistem Saraf PusatДокумент87 страницK8a Anatomi Sistem Saraf Pusathartinissa vaniaОценок пока нет
- Neural Basis 5Документ24 страницыNeural Basis 5zainabbu2023Оценок пока нет
- 03 Lecture DPT 4 Neuroanatomy 'FUNCTION OF CEREBRAL HEMISPHERE' 'Part A'Документ48 страниц03 Lecture DPT 4 Neuroanatomy 'FUNCTION OF CEREBRAL HEMISPHERE' 'Part A'Farhan HaleemОценок пока нет
- CNS PR Copy LatestДокумент321 страницаCNS PR Copy LatestAnteneh TesfayeОценок пока нет
- YДокумент111 страницYNimra ArshadОценок пока нет
- Lesson1 Intro Sensory SystemsДокумент53 страницыLesson1 Intro Sensory SystemsLeoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ41 страницаChapter 5Reneilwe MoshidiОценок пока нет
- Brodmann's Classification of Cerebral Cortex AreasДокумент10 страницBrodmann's Classification of Cerebral Cortex Areasjake paulОценок пока нет
- Traumatic Brain InjuryДокумент15 страницTraumatic Brain InjuryAbbey Janine Mandapat Passi100% (3)
- Nervous System OverviewДокумент4 страницыNervous System OverviewEds SyОценок пока нет
- PBL Blok 6 - NEWДокумент28 страницPBL Blok 6 - NEWDiary SI CADOKОценок пока нет
- Neurological ConditionsДокумент43 страницыNeurological Conditionszm2h8hpsq8Оценок пока нет
- Cerebrum 2Документ67 страницCerebrum 2Syed Abdul BasitОценок пока нет
- Cortex Cerebri Structure and FunctionsДокумент48 страницCortex Cerebri Structure and FunctionsHeru Febriyadi KedokteranОценок пока нет
- Cerebral Cortex Functions and Memory AreasДокумент3 страницыCerebral Cortex Functions and Memory Areas22 - Fernandez, Lyza Mae D.Оценок пока нет
- Ilovepdf MergedДокумент65 страницIlovepdf Mergedrogegir407Оценок пока нет
- NCM 116 Lecture (Midterm) PDFДокумент11 страницNCM 116 Lecture (Midterm) PDFKimberly Ann Boricano100% (1)
- Draft Case 5Документ11 страницDraft Case 5Debbi YuniseraniОценок пока нет
- Review Cerebrum and Diencephalon AnatomyДокумент107 страницReview Cerebrum and Diencephalon AnatomyMuhammad Ilyas AhmadОценок пока нет
- Properties of Reflexes and Motor AreasДокумент72 страницыProperties of Reflexes and Motor AreasMdAbdulMateenОценок пока нет
- BrainДокумент46 страницBrainSantosh DeshmukhОценок пока нет
- Areas CerebraisДокумент30 страницAreas CerebraisLUIS VICENTE FerreiraОценок пока нет
- Brain Structure & FunctionДокумент34 страницыBrain Structure & Functionmaha abdallahОценок пока нет
- 17-03 Fundamentos Neuroanatómicos Del LenguajeДокумент27 страниц17-03 Fundamentos Neuroanatómicos Del LenguajeAngela Solar San MartínОценок пока нет
- CNS AnatomyДокумент27 страницCNS Anatomysam peligroОценок пока нет
- Cerebral CortexДокумент26 страницCerebral CortexAkila AkinsОценок пока нет
- The Limbic SystemДокумент2 страницыThe Limbic SystemLanaОценок пока нет
- Cerebral hemisphere anatomy and functionsДокумент83 страницыCerebral hemisphere anatomy and functionsAlokh Saha RajОценок пока нет
- Brain: DR Anil Sabharwal Mbbs - MD (Medicine)Документ77 страницBrain: DR Anil Sabharwal Mbbs - MD (Medicine)Chetan RathiОценок пока нет
- Neuroanatomy of the Central and Peripheral Nervous SystemДокумент88 страницNeuroanatomy of the Central and Peripheral Nervous SystemAchenk BarcelonistaОценок пока нет
- 10 - Brain Areas-1Документ7 страниц10 - Brain Areas-1علي. احمدОценок пока нет
- Brain Lobes and Their Functional AreasДокумент10 страницBrain Lobes and Their Functional AreasAdeel MasoodОценок пока нет
- Structure and Areas of Human BrainДокумент29 страницStructure and Areas of Human BrainPravallika JayarajuОценок пока нет
- 116 3maДокумент13 страниц116 3maalaisahmae02Оценок пока нет
- Neuro PDFДокумент8 страницNeuro PDFHira SheikhОценок пока нет
- A Guide To Brain AnatomyДокумент7 страницA Guide To Brain AnatomyPuppa AlexandraОценок пока нет
- Role of the BrainДокумент17 страницRole of the BrainfinikollinsОценок пока нет
- Neurologic NursingДокумент10 страницNeurologic NursingAllisson Beckers100% (1)
- Nervous SystemДокумент126 страницNervous SystemMuhammad IlhamОценок пока нет
- Clinical Neuroanatomy Part 1 (Original)Документ80 страницClinical Neuroanatomy Part 1 (Original)LEEОценок пока нет
- Cognitive Neuroscience. Anatomy of The BrainДокумент11 страницCognitive Neuroscience. Anatomy of The BrainKryzhel CuachonОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of the Brain and its LobesДокумент20 страницAnatomy of the Brain and its LobesStevent RichardoОценок пока нет
- Understanding How the Nervous System WorksДокумент34 страницыUnderstanding How the Nervous System WorksLailatuz ZakiyahОценок пока нет
- BrainanatomyДокумент48 страницBrainanatomySureshОценок пока нет
- Notes NeuroДокумент30 страницNotes NeuroKintanОценок пока нет
- Brain: (Rabbia Yousaf)Документ23 страницыBrain: (Rabbia Yousaf)Shafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniОценок пока нет
- PSYC 21 2022 Brain Structures - Short Edited - ForebrainДокумент3 страницыPSYC 21 2022 Brain Structures - Short Edited - ForebrainsdahjdhasjkdhaskdОценок пока нет
- Functional Areas of BrainДокумент1 страницаFunctional Areas of Brainsattya.nОценок пока нет
- Neurologic System Functions and StructuresДокумент9 страницNeurologic System Functions and StructuresBianx Flores DosdosОценок пока нет
- Module 3.3 Brain and BehaviorДокумент56 страницModule 3.3 Brain and BehaviorTrisha G.Оценок пока нет
- Functional Areas of Cerebral Cortex and Its Associated LesionsДокумент8 страницFunctional Areas of Cerebral Cortex and Its Associated Lesionsdrpankaj28Оценок пока нет
- BIOLOGICALДокумент4 страницыBIOLOGICALMehmet Enes TuranОценок пока нет
- Central Nervous System (CNS) Neuroanatomy &Документ26 страницCentral Nervous System (CNS) Neuroanatomy &Asaad JawedОценок пока нет
- Anat 1019 NeuroДокумент37 страницAnat 1019 NeurotakakamiseriaОценок пока нет
- Zoology 120: Visceral Effector Receptor Effect of Sympathetic Stimulation Effect of Parasympathetic Stimulation EyeДокумент2 страницыZoology 120: Visceral Effector Receptor Effect of Sympathetic Stimulation Effect of Parasympathetic Stimulation EyecarllОценок пока нет
- Zoology 120: Visceral Effector Receptor Effect of Sympathetic Stimulation Effect of Parasympathetic Stimulation EyeДокумент2 страницыZoology 120: Visceral Effector Receptor Effect of Sympathetic Stimulation Effect of Parasympathetic Stimulation EyecarllОценок пока нет
- Glycogen ExtractionДокумент1 страницаGlycogen ExtractioncarllОценок пока нет
- Glycogen ExtractionДокумент1 страницаGlycogen ExtractioncarllОценок пока нет
- Transport MechДокумент2 страницыTransport MechcarllОценок пока нет
- Skeleton MusclesДокумент4 страницыSkeleton MusclescarllОценок пока нет
- Isozyme Variation of Oreochromis Niloticus From Selected SitesДокумент4 страницыIsozyme Variation of Oreochromis Niloticus From Selected SitescarllОценок пока нет
- Generalized Bacteriophage Transduction in Serratia MarcescensДокумент3 страницыGeneralized Bacteriophage Transduction in Serratia MarcescenscarllОценок пока нет
- CCC 2Документ4 страницыCCC 2carllОценок пока нет
- 40 Fantastic Stories For Kids To Read in 2019Документ2 страницы40 Fantastic Stories For Kids To Read in 2019Nizam KakarОценок пока нет
- CCC 2Документ4 страницыCCC 2carllОценок пока нет
- Practical Histology:) Motor Neurone Disease (MNDДокумент5 страницPractical Histology:) Motor Neurone Disease (MNDعلي حسين عودة العلياويОценок пока нет
- X Study Material Final ModifiedДокумент317 страницX Study Material Final Modifieddevisree100% (1)
- Mapping Bedah Saraf ICUДокумент1 страницаMapping Bedah Saraf ICUDessy FarwasОценок пока нет
- Tetanus Case StudyДокумент41 страницаTetanus Case StudyFAt Ty100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Conceptualizing Abnormal Psychology PDFДокумент67 страницChapter 2 Conceptualizing Abnormal Psychology PDFGabriel Jeremy OrtegaОценок пока нет
- 1st SemДокумент158 страниц1st SemSana chaudharyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 29 The Nervous SystemДокумент64 страницыChapter 29 The Nervous SystemAugustus Czar De LeonОценок пока нет
- Nervous System Part 1Документ11 страницNervous System Part 1Mariel AbatayoОценок пока нет
- QUIZ 1-Sci10-Nervous-SystemДокумент1 страницаQUIZ 1-Sci10-Nervous-SystemMarife GuadalupeОценок пока нет
- Disc Vis Lobe Front Et Tempo PDFДокумент12 страницDisc Vis Lobe Front Et Tempo PDFMarina MaatoukОценок пока нет
- Nervous System Structure and FunctionsДокумент46 страницNervous System Structure and FunctionssureshdassОценок пока нет
- Nervous System Examination SynopsisДокумент26 страницNervous System Examination Synopsisaarti chandeОценок пока нет
- Coordination and Control Chapter QuestionsДокумент19 страницCoordination and Control Chapter QuestionsUmme AbdullahОценок пока нет
- Spasticity NeurologyДокумент10 страницSpasticity NeurologySamuel BodoarcaОценок пока нет
- The BrainДокумент6 страницThe Brainapi-3996004350% (1)
- Biology Worksheet G10Документ4 страницыBiology Worksheet G10meОценок пока нет
- Your Brain and Nervous System ExplainedДокумент34 страницыYour Brain and Nervous System ExplainedAlmiah Alfarouk100% (1)
- 21 - Peripheral Nervous SystemДокумент16 страниц21 - Peripheral Nervous Systembhavikrao7605Оценок пока нет
- Nervous + Animal DiversityДокумент7 страницNervous + Animal DiversityMaisonette MichОценок пока нет
- Science-6 - PT - Q-2Документ7 страницScience-6 - PT - Q-2Erwin AcebucheОценок пока нет
- Cerebrovascular Accident: Causes, Risks & TreatmentДокумент53 страницыCerebrovascular Accident: Causes, Risks & TreatmentJulia Salvio50% (2)
- Brain Brief Right Brain-Left Brain FinalДокумент2 страницыBrain Brief Right Brain-Left Brain FinalGlaiza Leigh AgonoyОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Acute Coma and Disorders of ConsciousnessДокумент20 страницPathophysiology of Acute Coma and Disorders of ConsciousnessNeo YustindraОценок пока нет
- The Brilliance of The BrainДокумент5 страницThe Brilliance of The Brainapi-219083677Оценок пока нет
- This Study Resource Was: PHYSIOLOGY 451/551 Examination I Monday, September 26, 2005Документ9 страницThis Study Resource Was: PHYSIOLOGY 451/551 Examination I Monday, September 26, 2005ggfdsas sffddfОценок пока нет
- Neuroanatomy & PhysiologyДокумент44 страницыNeuroanatomy & PhysiologyKarina MawarnursaviraОценок пока нет
- AP Psych Anatomy The Brain - Coloring Worksheet - Visual MapДокумент2 страницыAP Psych Anatomy The Brain - Coloring Worksheet - Visual MapTiffany GallinaОценок пока нет
- Neurological AssessmentДокумент47 страницNeurological AssessmentMangayarkarasi Chandrakasan100% (4)
- Psychology An Exploration Canadian 1st Edition Ciccarelli Test BankДокумент26 страницPsychology An Exploration Canadian 1st Edition Ciccarelli Test BankWilliamBeckymce100% (30)
- MIDTERM Pilar College Anatomy Physiology Final EditДокумент41 страницаMIDTERM Pilar College Anatomy Physiology Final EditYeona BaeОценок пока нет