Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Restrictive Orifice - Method 1: Rough Method Provided Originally in An Article in Chemical Engineering Magazine
Загружено:
alvinchuanОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Restrictive Orifice - Method 1: Rough Method Provided Originally in An Article in Chemical Engineering Magazine
Загружено:
alvinchuanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Thin plate orifice
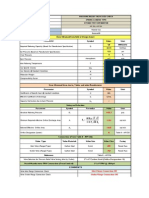
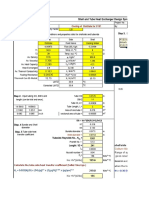
RESTRICTIVE ORIFICE ---- Method 1 Low-Moderate P
Rough method provided originally in an article in Chemical Engineering magazine tb/bore diameter = 0.93
P2/P1 = 0.05 Thin plate, no choked flow.
Calculation not applicable: refer to Kirk-Cunningham method.
P1: Method assumes, implicitly, that gas is ideal gas mixture or perfect gas.
D1: 7 Qg/SQRT( ∆P(P1 +P2)/(2SgT1) 1/5 Flow through a thin plate is never choked flow. For this to apply, the ratio of tb/bore
D2: D = X X (tp/0.125)
8 diameter must be < 6. (Reference: pg. 13.22, Richard Miller's "Flow Measurement
5440 Engineering Handbook," 3rd ed., McGraw Hill, 1996. Page 13-22 refers to the work
of Cunningham (1951) and Ward-Smith (1979).
Kirk-Cunningham applies when P2<0.63P1. Cunningham showed that choked flow
(critical, i.e., M =1 @ throat) does not occur for thin orifice plates.
D, inches; Qg, gas flow in SCFH (60 F, 1 atm); DP, P1, P2, psia; Sg = Mg/Mair Line Size tp,mm
T1, R; tp, plate thickness. 0.5 1.5
0.75 1.5
Qg: 250 SCFH @ 60 F, 1 atm Complete Property Sheet 1 1.5
∆P = 57.00 Tr = 2.51 from sheet 1.5 2
P1: 60 psig Pr = 0.11 2 2.5
P2: 3 psi Using initial properties @ 3 3
Mw: 17 P1, T1 4 3 Using table from
Sg = 0.59 manual allowed 6 3 Fluor specification:
T: 100 deg. F k = 1.28 8 6 "Flange Type
Plate Rate 300 300, 600# ANSI 10 6 Restrictive Orifice"
tp = 2.50 mm From Fluor table 12 6
Z: 1.00 0.98 Calculated using virial equations 14 9
D1, nom: 2.00 in. Sch.: 80 16 9
18 12
Sat. Curve Test: 0.749 Test: OK Abbott Equations are acceptable 20 12
Hot Gas Test: 0.433 Saturated Area 24 16
B1 = 0.135 Pr/Tr = 0.044 Z = 1.00
B0 = -0.014
Pcf = 40.98 psig Choked Flow - for thick plate D2 = 0.106 in. Beta = 0.055
1 of 1 Lemont, Illinois ORF1/RO1
Вам также может понравиться
- Ejercicio 246 PSV438 RESUELTOДокумент2 страницыEjercicio 246 PSV438 RESUELTOHumberto Ivan Gonzales TapiaОценок пока нет
- Gas Line Pressure LossesДокумент4 страницыGas Line Pressure Lossesyash saragiyaОценок пока нет
- Liquid Orifice SizingДокумент4 страницыLiquid Orifice SizingrmaganОценок пока нет
- Condensate Line SizingДокумент2 страницыCondensate Line SizingAnonymous oVRvsdWzfBОценок пока нет
- Level Transmitter CalculationДокумент9 страницLevel Transmitter Calculationsr322Оценок пока нет
- Pressure DropДокумент4 страницыPressure Dropmartin.rubenОценок пока нет
- Pump (English) TemplateДокумент1 страницаPump (English) TemplateMichael HaiseОценок пока нет
- Orifice CalculationsДокумент4 страницыOrifice CalculationsTsouki TsoukiОценок пока нет
- Cakasa Cakasa: Sea Water Filter Inlet Ine Input Description Unit General DataДокумент6 страницCakasa Cakasa: Sea Water Filter Inlet Ine Input Description Unit General DatasterlingОценок пока нет
- Orifice SizingДокумент1 страницаOrifice SizingMarco D'OnofrioОценок пока нет
- Orifice Calc: GasДокумент4 страницыOrifice Calc: GasJames R. Lawrence Sr.100% (6)
- Orifice PlatesДокумент20 страницOrifice PlatesAntonio GallegosОценок пока нет
- Orifice Flow Calculator For Gases, Steam, and VaporsДокумент2 страницыOrifice Flow Calculator For Gases, Steam, and Vaporsbakhtyar21Оценок пока нет
- Understanding NPSHДокумент34 страницыUnderstanding NPSHeliyanto budiartoОценок пока нет
- Air Consumption Rev 1Документ1 страницаAir Consumption Rev 1Cahyadi YadiОценок пока нет
- Sizing Calculation Spreadsheet PSVДокумент1 страницаSizing Calculation Spreadsheet PSVkenoly123Оценок пока нет
- Restriction Orifice Sizing CalculationДокумент2 страницыRestriction Orifice Sizing CalculationSiLan Subramaniam100% (1)
- Steam tracing simulation determines Process Fluid TemperatureДокумент74 страницыSteam tracing simulation determines Process Fluid TemperaturecybermineОценок пока нет
- Knock Out Drum Sizing Parameters Value Unit Remark: Gas Outlet NozzleДокумент11 страницKnock Out Drum Sizing Parameters Value Unit Remark: Gas Outlet Nozzlejazeel alaviОценок пока нет
- Calculation of Orifice CoefficientДокумент18 страницCalculation of Orifice Coefficientvinayjoshi270586Оценок пока нет
- MPCL Flare KOD Pump 11442-DS-103 - IFC2 18-06-2013Документ2 страницыMPCL Flare KOD Pump 11442-DS-103 - IFC2 18-06-2013zohaib_farooqОценок пока нет
- Orifice Plate CalculationДокумент3 страницыOrifice Plate Calculationnixsol75Оценок пока нет
- Calculation Sheet For Pump Hydraulic (Fps Unit)Документ1 страницаCalculation Sheet For Pump Hydraulic (Fps Unit)chemical todiОценок пока нет
- Rupture Disk SizingДокумент2 страницыRupture Disk Sizingabhishek shindeОценок пока нет
- Gas Line Size-1Документ12 страницGas Line Size-1svnaik14Оценок пока нет
- CPF-010 Utility Line Sizing Attachment - 0Документ31 страницаCPF-010 Utility Line Sizing Attachment - 0goodspeed_phОценок пока нет
- Line Single PhaseДокумент2 страницыLine Single PhasehussamОценок пока нет
- Valve Sizing SelectionДокумент15 страницValve Sizing SelectionbariОценок пока нет
- PUMP CALCULATION SHEETДокумент4 страницыPUMP CALCULATION SHEETMuhammad BilalОценок пока нет
- Flow Meter Sizing MOSДокумент11 страницFlow Meter Sizing MOSra9622Оценок пока нет
- Pump NPSHA calculation sheetДокумент2 страницыPump NPSHA calculation sheetNena Jessi Love100% (1)
- Open TankДокумент27 страницOpen Tankhgagselim2012Оценок пока нет
- Orifice Plate Calculator Pressure Drop CalculationsДокумент4 страницыOrifice Plate Calculator Pressure Drop CalculationsAnderson Pioner100% (1)
- Pipe Thickness Calculation For Straight Pipe Under Internal PressureДокумент7 страницPipe Thickness Calculation For Straight Pipe Under Internal PressureMakhdoom Ibad HashmiОценок пока нет
- Orifice Calc Gas Rev 0Документ1 страницаOrifice Calc Gas Rev 0edufragaОценок пока нет
- Restriction Orifice SizingДокумент5 страницRestriction Orifice SizingjoeОценок пока нет
- Small Bore Orifice For Gas Flow PDFДокумент4 страницыSmall Bore Orifice For Gas Flow PDFManufacturer VerifyОценок пока нет
- Erosion Velocity CalculationsДокумент9 страницErosion Velocity CalculationsMANISH GUPTAОценок пока нет
- Weymouth Gas Flow CalculationsДокумент44 страницыWeymouth Gas Flow CalculationsPierre GermaineОценок пока нет
- Calculation of Orifice Plate DiameterДокумент2 страницыCalculation of Orifice Plate DiameterPhyu Mar Thein Kyaw100% (1)
- API 2000 guidance for inert gas blanketing of tanksДокумент2 страницыAPI 2000 guidance for inert gas blanketing of tankssandeshОценок пока нет
- Allowable DP CalculationДокумент22 страницыAllowable DP CalculationAJAY1381Оценок пока нет
- E3 Field Development Production Separator DesignДокумент5 страницE3 Field Development Production Separator DesignhaiderОценок пока нет
- Calculation of Orifice Plate Hole DiameterДокумент3 страницыCalculation of Orifice Plate Hole DiameterhiuОценок пока нет
- Liquid Orifice SizingДокумент8 страницLiquid Orifice SizingrmaganОценок пока нет
- Trunnion CalculationДокумент92 страницыTrunnion CalculationkarunaОценок пока нет
- Restriction Orifice Diamater CalculationДокумент1 страницаRestriction Orifice Diamater CalculationkodeesОценок пока нет
- Control Valve CalcДокумент7 страницControl Valve Calcartneves100% (1)
- Pressure Relief Valve Sizing and Selection CheckДокумент2 страницыPressure Relief Valve Sizing and Selection CheckGiftObionochieОценок пока нет
- Orifice Plate ReportДокумент1 страницаOrifice Plate ReportdsdeОценок пока нет
- Gas Line Sizing by API 14E Method Revision #: ??: Pressure Drop (Fittings Etc) Elbows, Tees Elbows, Tees Elbows, TeesДокумент4 страницыGas Line Sizing by API 14E Method Revision #: ??: Pressure Drop (Fittings Etc) Elbows, Tees Elbows, Tees Elbows, Teesusaid saifullahОценок пока нет
- Flow and Pressure Drop in Valves and FittingsДокумент5 страницFlow and Pressure Drop in Valves and FittingsĐoàn TrangОценок пока нет
- Centrifugal Pump SizingДокумент11 страницCentrifugal Pump SizingDavid Muñoz CastroОценок пока нет
- Pressure DropДокумент19 страницPressure DropGigis Kintan MyarthalunaОценок пока нет
- Pressure DropДокумент5 страницPressure Dropalexmuchmure2158Оценок пока нет
- Gas Line SizingДокумент11 страницGas Line SizingEbby OnyekweОценок пока нет
- TEMA Type E Heat Exchanger DesignДокумент8 страницTEMA Type E Heat Exchanger DesignLEONARDO MOLERO CLEMENTEОценок пока нет
- SCR Heat Exchanger Design 2018 For NO PHASE CHANGEДокумент37 страницSCR Heat Exchanger Design 2018 For NO PHASE CHANGEAnonymous 1uUqRkc9p8100% (1)
- Natural Bend Radius Cal Rev. C PDFДокумент3 страницыNatural Bend Radius Cal Rev. C PDFhamid sobirin100% (2)
- Pipeline Calculations (Bend Radius, Buoyancy Forces, Thrust Block CalculationsДокумент11 страницPipeline Calculations (Bend Radius, Buoyancy Forces, Thrust Block CalculationsSaqib LaeeqОценок пока нет
- Relative Discharging Power of Pipe LineДокумент1 страницаRelative Discharging Power of Pipe LinealvinchuanОценок пока нет
- SSP Simplified Submission Process OverviewДокумент1 страницаSSP Simplified Submission Process OverviewalvinchuanОценок пока нет
- DD - 22 Floatation of Circular PipeДокумент6 страницDD - 22 Floatation of Circular PipealvinchuanОценок пока нет
- Mass BalanceДокумент4 страницыMass BalancealvinchuanОценок пока нет
- Diversity FactorДокумент3 страницыDiversity FactorgafscottОценок пока нет
- Extracts PG - 12 &13 of SS636Документ2 страницыExtracts PG - 12 &13 of SS636alvinchuanОценок пока нет
- DG Flowrate Comparison PDFДокумент1 страницаDG Flowrate Comparison PDFalvinchuanОценок пока нет
- Extracts PG - 12 &13 of SS636Документ2 страницыExtracts PG - 12 &13 of SS636alvinchuanОценок пока нет
- Solve Differential EquationДокумент4 страницыSolve Differential EquationalvinchuanОценок пока нет
- SSP Simplified Submission Process OverviewДокумент1 страницаSSP Simplified Submission Process OverviewalvinchuanОценок пока нет
- Heat Loss From An Insulated Pipe CalculationsДокумент2 страницыHeat Loss From An Insulated Pipe CalculationsalvinchuanОценок пока нет
- Extracts of SS636Документ2 страницыExtracts of SS636alvinchuanОценок пока нет
- Singapore Rainfall Equations PDFДокумент2 страницыSingapore Rainfall Equations PDFalvinchuanОценок пока нет
- Extracts PG - 12 &13 of SS636Документ2 страницыExtracts PG - 12 &13 of SS636alvinchuanОценок пока нет
- Auto ClaveДокумент1 страницаAuto ClavealvinchuanОценок пока нет
- ABCWatersDesignGuidelines 2011Документ104 страницыABCWatersDesignGuidelines 2011Jackson TanОценок пока нет
- Extracts PG - 12 &13 of SS636Документ2 страницыExtracts PG - 12 &13 of SS636alvinchuanОценок пока нет
- Bio Detention BasinДокумент45 страницBio Detention BasinalvinchuanОценок пока нет
- SS 532-2016+corr 1 - PreviewДокумент11 страницSS 532-2016+corr 1 - PreviewalvinchuanОценок пока нет
- Pipe thickness calculations as per ASME B31.3Документ1 страницаPipe thickness calculations as per ASME B31.3alvinchuanОценок пока нет
- PE Pipeline Analysis & CalculationДокумент2 страницыPE Pipeline Analysis & CalculationalvinchuanОценок пока нет
- PE Pipeline Analysis & CalculationДокумент2 страницыPE Pipeline Analysis & CalculationalvinchuanОценок пока нет
- PE Pipeline Analysis & CalculationДокумент2 страницыPE Pipeline Analysis & CalculationalvinchuanОценок пока нет
- API Sizing KIM - XLSMДокумент1 страницаAPI Sizing KIM - XLSMalvinchuanОценок пока нет
- PE Pipeline Analysis & CalculationДокумент2 страницыPE Pipeline Analysis & CalculationalvinchuanОценок пока нет
- ConsumptionДокумент2 страницыConsumptionalvinchuanОценок пока нет
- Slno Description Symbol Unit Value: Calculation of Shell ThicknessДокумент2 страницыSlno Description Symbol Unit Value: Calculation of Shell ThicknessalvinchuanОценок пока нет
- Pipeline Analysis & Calculation Environment: Pipe SelectionДокумент6 страницPipeline Analysis & Calculation Environment: Pipe SelectionalvinchuanОценок пока нет
- Expansion Tank SizingДокумент2 страницыExpansion Tank SizingSK NGОценок пока нет
- CAT-01-Rural/Kan/PDP Direct Candidate CAT-01-Rural/Kan/PDP Direct Candidate CAT-01-Rural/Kan/PDP Direct CandidateДокумент1 страницаCAT-01-Rural/Kan/PDP Direct Candidate CAT-01-Rural/Kan/PDP Direct Candidate CAT-01-Rural/Kan/PDP Direct Candidatejai pattedОценок пока нет
- Soil Investigations & Testing For The Proposed Road 1 North, Kidurong Industrial Estate (Kinda) For Bintulu Development Authority PDFДокумент8 страницSoil Investigations & Testing For The Proposed Road 1 North, Kidurong Industrial Estate (Kinda) For Bintulu Development Authority PDFracing.phreakОценок пока нет
- LA413001 PDC Intermittant Operation PDFДокумент2 страницыLA413001 PDC Intermittant Operation PDFGino PierОценок пока нет
- Rtow User GuideДокумент124 страницыRtow User GuideKanav KashyapОценок пока нет
- List of books and standards on vibratory machine foundationsДокумент5 страницList of books and standards on vibratory machine foundationsMiminoRusОценок пока нет
- Image Processing: CSE4019 Project Review-1Документ4 страницыImage Processing: CSE4019 Project Review-1Prithviraj N indiОценок пока нет
- CMMДокумент28 страницCMMArun Raj A CОценок пока нет
- Mil STD 100gДокумент84 страницыMil STD 100glogonwheelerОценок пока нет
- CaFSET (Antigua) Office Workbook - Sixth Edition - Programming Concepts Sample PagesДокумент4 страницыCaFSET (Antigua) Office Workbook - Sixth Edition - Programming Concepts Sample PagescafsetОценок пока нет
- The Orderflows Bulge Michael ValtosДокумент51 страницаThe Orderflows Bulge Michael Valtosmr100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in T.L.E. - Exploratory DraftingДокумент3 страницыLesson Plan in T.L.E. - Exploratory DraftingCRIISSY100% (2)
- Cheryl reyes-ACTIVITYДокумент4 страницыCheryl reyes-ACTIVITYCheryl ReyesОценок пока нет
- 4SI0 01 Rms 20170823Документ13 страниц4SI0 01 Rms 20170823subodya alahakoonОценок пока нет
- Cp12 Pps 3274c Me Ds 001 Data Sheet Hvac Sunyaragi Rev.0Документ1 страницаCp12 Pps 3274c Me Ds 001 Data Sheet Hvac Sunyaragi Rev.0Triana Rosma Fikriyati DinaОценок пока нет
- Charles F. Kettering Biography: Quick FactsДокумент4 страницыCharles F. Kettering Biography: Quick Factsrakin hossainОценок пока нет
- Reboiler Selection CriteriaДокумент5 страницReboiler Selection CriteriamineralgroupstmfiОценок пока нет
- Theory of ErrorsДокумент43 страницыTheory of Errorsjaybh575Оценок пока нет
- Thesis University of AucklandДокумент4 страницыThesis University of Aucklandaflpbpcnhjpwkd100% (2)
- WelcomeДокумент10 страницWelcomeappp2711Оценок пока нет
- Midlands State University Library Department Course: Information Literacy Skills (Hcs135)Документ7 страницMidlands State University Library Department Course: Information Literacy Skills (Hcs135)Loveniah Yemurai MbakataОценок пока нет
- Technology Development for InSb Infrared ImagersДокумент6 страницTechnology Development for InSb Infrared ImagersSukhmander SinghОценок пока нет
- Lecture on the ancient Cappadocian language and its hellenizationДокумент4 страницыLecture on the ancient Cappadocian language and its hellenizationSimeon TsolakidisОценок пока нет
- Quantitative GeneticsДокумент31 страницаQuantitative GeneticsMamtaОценок пока нет
- International Conference of Advance Research and Innovation (ICARI-2015) PDFДокумент1 страницаInternational Conference of Advance Research and Innovation (ICARI-2015) PDFAbhilash KumarОценок пока нет
- KrokДокумент20 страницKrokYurii KovalivОценок пока нет
- Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion (Mic)Документ2 страницыMicrobiologically Influenced Corrosion (Mic)MohamedОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2: Problem Solving Through Flowcharts 1Документ14 страницLesson 2: Problem Solving Through Flowcharts 1catherine carreonОценок пока нет
- Reliability Centered SparesДокумент2 страницыReliability Centered SparesMoustafa HelmyОценок пока нет
- Himachal Pradesh PDFДокумент17 страницHimachal Pradesh PDFAbhinav VermaОценок пока нет
- Allen Fisher PoemsДокумент28 страницAllen Fisher PoemsArkava DasОценок пока нет