Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Cloud Computing Guide
Загружено:
swetaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cloud Computing Guide
Загружено:
swetaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cloud computing 1OX18MCA71
SL.NO CONTENTS PG.NO
1. INTRODUCTION 1
2. ABSTRACT 2
3. WHAT IS CLOUD COMPUTING? 3
4. HISTORY OF CLOUD COMPUTING? 4
5. ARCHITECTURE OF CLOUD COMPUTING 5-7
6. TYPES OF CLOUD COMPUTING? 8-12
7. COMPONENTS OF CLOUD COMPUTING 13
8. RECENT DEVELOPMENT OF CLOUD COMPUTING 14
9. ADVANTAGES OF CLOUD COMPUTING 15
10. CONCLUSION 16
11. REFERENCE 17
Introduction
DEPT OF MCA Page 1
Cloud computing 1OX18MCA71
Cloud computing is Internet-based computing, whereby shared resources, software, and information are
provided to computers and other devices on demand, like the electricity grid.
Cloud computing is a paradigm shift following the shift from mainframe to client–server in the early 1980s.
Details are abstracted from the users, who no longer have need for expertise in, or control over, the technology
infrastructure "in the cloud" that supports them.
DEPT OF MCA Page 2
Cloud computing 1OX18MCA71
ABSTRACT
Cloud computing is Internet based computing where virtual shared servers provide software, infrastructure,
platform, devices and other resources and hosting to customers on a pay-as-you-use basis. All information that a
digitized system has to offer is provided as a service in the cloud computing model. Users can access these
services available on the "Internet cloud" without having any previous know-how on managing the resources
involved. Thus, users can concentrate more on their core business processes rather than spending time and
gaining knowledge on resources needed to manage their business processes.
DEPT OF MCA Page 3
Cloud computing 1OX18MCA71
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is Internet based computing where virtual shared servers provide software, infrastructure,
platform, devices and other resources and hosting to customers on a pay-as-you-use basis. All information that a
digitized system has to offer is provided as a service in the cloud computing model.
Users can access these services available on the "Internet cloud" without having any previous know-how on
managing the resources involved. Thus, users can concentrate more on their core business processes rather than
spending time and gaining knowledge on resources needed to manage their business processes.
Cloud computing customers do not own the physical infrastructure; rather they rent the usage from a third -
party provider. This helps them to avoid huge. They consume resources as a service and pay only for resources
that they use. Most cloud computing infrastructures consist of services delivered through common centers and
built on servers.
Sharing resources amongst can improve, as servers are not unnecessarily left idle, which can reduce costs
significantly while increasing the speed of application development.
DEPT OF MCA Page 4
Cloud computing 1OX18MCA71
History Concept originated from telecommunication companies changing to VPN
1999: Salesforce.com ‐ Delivery of applications via web
2002: Amazon launches Amazon Web Services (AWS)
2006: Google Docs, Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)
2008: Eucalyptus
2009: Microsoft Azure
DEPT OF MCA Page 5
Cloud computing 1OX18MCA71
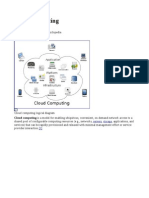
Architecture
Cloud architecture, the systems architecture of the software systems involved in the delivery of cloud
computing, typically involves multiple cloud components communicating with each other over application
programming interfaces, usually web services.
Cloud computing sample architecture
This resembles the UNIX philosophy of having multiple programs each doing one thing well and working
together over universal interfaces. Complexity is controlled and the resulting systems are more manageable than
their monolithic counterparts.
The two most significant components of cloud computing architecture are known as the front end and the back
end. The front end is the part seen by the client, i.e. the computer user. This includes the client’s network (or
computer) and the applications used to access the cloud via a user interface such as a web browser.
DEPT OF MCA Page 6
Cloud computing 1OX18MCA71
The back end of the cloud computing architecture is the ‘cloud’ itself, comprising various computers, servers
and data storage devices.
This resembles the UNIX philosophy of having multiple programs each doing one thing well and working
together over universal interfaces. Complexity is controlled and the resulting systems are more manageable than
their monolithic counterparts. This resembles the UNIX philosophy of having multiple programs each doing
one thing well and working together over universal interfaces. Complexity is controlled and the resulting
systems are more manageable than their monolithic counterparts.
The two most significant components of cloud computing architecture are known as the front end and the back
end. The front end is the part seen by the client, i.e. the computer user. This includes the client’s network (or
computer) and the applications used to access the cloud via a user interface such as a web browser.
The back end of the cloud computing architecture is the ‘cloud’ itself, comprising various computers, servers
and data storage devices.
DEPT OF MCA Page 7
Cloud computing 1OX18MCA71
Types of Cloud Computing
Public cloud
Public clouds are made available to the general public by a service provider who hosts the cloud infrastructure.
Generally, public cloud providers like Amazon AWS, Microsoft and Google own and operate the infrastructure
and offer access over the Internet. With this model, customers have no visibility or control over where the
infrastructure is located. It is important to note that all customers on public clouds share the same infrastructure
pool with limited configuration, security protections and availability variances.
Public Cloud customers benefit from economies of scale, because infrastructure costs are spread across all users,
allowing each individual client to operate on a low-cost, “pay-as-you-go” model. Another advantage of public
cloud infrastructures is that they are typically larger in scale than an in-house enterprise cloud, which provides
clients with seamless, ondemand scalability. These clouds offer the greatest level of efficiency in shared
resources; however, they are also more vulnerable than private clouds.
A public cloud is the obvious choice when:
Your standardized workload for applications is used by lots of people, such as e-mail. You need to test and
develop application code. o You need incremental capacity (the ability to add compute resources for peak
times).
DEPT OF MCA Page 8
Cloud computing 1OX18MCA71
Private cloud
Private cloud is cloud infrastructure dedicated to a particular organization. Private clouds allow businesses to
host applications in the cloud, while addressing concerns regarding data security and control, which is often
lacking in a public cloud environment. It is not shared with other organizations, whether managed internally or
by a third-party, and it can be hosted internally or externally.
There are two variations of private clouds:
1. On-Premise Private Cloud: This type of cloud is hosted within an organization’s own facility. A businesses IT
department would incur the capital and operational costs for the physical resources with this model. On-Premise
Private Clouds are best used for applications that require complete control and configurability of the
infrastructure and security. 2. Externally Hosted Private Cloud: Externally hosted private clouds are also
exclusively used by one organization, but are hosted by a third party specializing in cloud infrastructure. The
service provider facilitates an exclusive cloud environment with full guarantee of privacy. This format is
recommended for organizations that prefer not to use a public cloud infrastructure due to the risks associated
with the sharing of physical resources.
Undertaking a private cloud project requires a significant level and degree of engagement to virtualized the
business environment, and it will require the
DEPT OF MCA Page 9
Cloud computing 1OX18MCA71
organization to reevaluate decisions about existing resources. Private clouds are more expensive but also more
secure when compared to public clouds. An Info-Tech survey shows that 76% of IT decision-makers will focus
exclusively on the private cloud, as these clouds offer the greatest level of security and control.
When is a Private Cloud for you?
o You need data sovereignty but want cloud efficiencies o You want consistency across services o You have
more server capacity than your organization can use o Your data center must become more efficient o You want
to provide private cloud services
Hybrid cloud
Hybrid Clouds are a composition of two or more clouds (private, community or public) that remain unique
entities but are bound together offering the advantages of multiple deployment models. In a hybrid cloud, you
can leverage third party cloud providers in either a full or partial manner; increasing the flexibility of
computing. Augmenting a traditional private cloud with the resources of a public cloud can be used to manage
any unexpected surges in workload
Hybrid cloud architecture requires both on-premise resources and off-site server based cloud infrastructure. By
spreading things out over a hybrid cloud, you keep each aspect of your business in the most efficient
environment possible. The downside is that you have to keep track of multiple cloud security platforms and
ensure that all aspects of your business can communicate with each other.
DEPT OF MCA Page 10
Cloud computing 1OX18MCA71
Here are a couple of situations where a hybrid environment is best:
Your company wants to use a SaaS application but is concerned about security. o Your company offers services
that are tailored for different vertical markets. You can use a public cloud to interact with the clients but keep
their data secured within a private cloud. o You can provide public cloud to your customers while using a
private cloud for internal IT
Components:-
SaaS (software as a service): SaaS refers to software that’s made available as a web-based service. Because you
can access the software remotely, you don’t need additional hardware to use or run it. Furthermore, you don’t
have to worry about the software’s installation, setup, maintenance or upgrades. An example of SaaS is a site
that allows you to create, save and access documents online. Utility computing: The predecessor of cloud
computing, utility computing provides the ability to access storage and virtual servers on demand. Cloud-based
web services: Similar to Saas, web services in the cloud allow you to offer services online, such as credit card
processing services, employee payroll processing or viewing an interactive map. MSP (managed service
providers):
The grandfather of cloud computing, an MSP delivers applications to IT instead of end-users. An MSP example
includes an email virus-scanning service. IaaS (infrastructure as a service): IaaS refers to computer
infrastructure (e.g., virtualization) that’s delivered as a service. A data center that offers outsourced software and
servers may use saaS for its operations.
DEPT OF MCA Page 11
Cloud computing 1OX18MCA71
In 2007, Google, IBM, and a number of universities embarked on a large scale cloud computing research
project. In early 2008, Eucalyptus became the first open source AWS API compatible platform for deploying
private clouds.
By mid-2008, Gartner saw an opportunity for cloud computing "to shape the relationship among consumers of
IT services, those who use IT services and those who sell them”, and observed that "organizations are switching
from company-owned hardware and software assets to per-use service-based models" so that the "projected shift
to cloud computing ... will result in dramatic growth in IT products in some areas and significant reductions in
other areas.”
DEPT OF MCA Page 12
Cloud computing 1OX18MCA71
Advantages of Cloud Computing
The following are some of the possible advantages of cloud computing: Flexibility There is a high rate of
flexibility when using cloud computing because people can opt out of  using it whenever they want too. One
of the  major benefit of cloud computing is that there is no limitation of place and medium. We can access our
applications and data anywhere in the world, on any system. These are the main reasons, which attract people to
use  this method. Low Cost Companies can save big by employing cloud computing as it eliminates cost for
hardware and software. With cloud computing, company uses the resources of the hosting company to store
their data and applications. Companies also pay for use of the software and programs by paying a subscription
fee. The cost of using cloud resources is very economical for resources such as centralized, real estate,
bandwidth, and power. Users will also save money on software updates, management costs, and data storage
costs. It is a cheaper way to maintain the software and it will save time, as the developers keep track of updates
and maintain your programs while you use it. Speed & Scales Traditional methods to buy and configure
hardware and software are time consuming. There is no need to purchase and setup hardware manually when
using the cloud computing method. Cloud computing provides a rapid deployment model that enables
applications to grow quickly to match increasing usage requirements. Depending upon their needs the user can
quickly scale up or scale down. Easier Management of Data and Information Since all data are located on a
centralized location, data are more organized
Device Diversity We can access our applications and data anywhere in the world, on any system. Cloud
Computing Services can be accessed through various different electronic devices that are able to have access to
the internet. These devices would include and i pad, Smartphone, Laptop, or desktop computer. Increased
Storage Capacity Increased Storage Capacity is another benefit of the cloud computing, as it can store more data
as compared to a personal computer. So it saves us from the upgrading computer memory that helps reduce the
cost for companies and users. Easy to Learn and Understand Thus allowing you to save hundreds and thousands
of dollars in implementing any new system and making arrangements for training on the same. Since people are
quiet used to cloud applications like GMail, Google Docs, so anything related to the same is most likely to be
understood by the users. Automatic Updating It saves companies time and effort to update multiples server. On
the other hand, it also helps users to download updates for the software. Once the server gets updated the users
can get the updates without doing anything. Customize Setting Cloud computing also allows you to customize
your business applications. This is a great benefit because the world of online business is very competitive.
DEPT OF MCA Page 13
Cloud computing 1OX18MCA71
Disadvantages of cloud computing:
Dependency
The following are some of the possible disadvantages of cloud computing: Dependency One major
disadvantages of cloud computing is user’s dependency on the provider. Internet users don’t have their data
stored with them. Risk Cloud computing services means taking services from remote servers. Â There is always
insecurity regarding stored documents because users do not have control over their software. Nothing can be
recovered if their servers go out of service. Requires a Constant internet connection The most obvious
disadvantage is that Cloud computing completely relies on network connections. It makes your business
dependent on the reliability of your Internet connection. When it’s offline, you’re offline. If you do not have an
Internet connection, you can’t access anything, even your own data. A dead internet connection means no work.
Similarly, a low-speed Internet connection, such as that found with dial-up services, makes cloud computing
painful at best and often impossible. Webbased apps often require a lot of bandwidth to download, In other
words, cloud computing isn’t for the slow connection. Security Security and privacy are the biggest concerns
about cloud computing. Companies might feel uncomfortable knowing that their data is stored in a virtual
server which makes responsibility on the security of the data difficult to determine and even users might feel
uncomfortable handing over their data to a third party. Privacy is another big issue with the cloud computing
server. To make cloud servers more secure to ensure that a clients data is not accessed by any unauthorized
users, cloud service providers have developed password protected accounts, security servers through which all
data being transferred must pass and data encryption technique. Migration problem is also a big concern about
cloud computing. If the user wants to switch to some other Provider then it is not easy to transfer huge data from
one provider to another.
DEPT OF MCA Page 14
Cloud computing 1OX18MCA71
Conclusion
So, while cloud computing is really great and you’re probably already using it, either for business of for
personal means, here’s what we’ve learned from taking a look at the pros and cons:
Cloud computing is a really cheap way for companies to have all the resources they need in once place.
It’s a much better way to spread your resources, and it becomes easier to access things from longer
distances.
But…
Is cloud computing really all that safe? For instance, while cloud computing has backups, if something
was to go wrong… do you have your own personal backup? Is cloud computing as private as you
think it is? Is your data secured or can anyone access it?
So there you have it! Everything you need to know about cloud computing; what it is, how to use it, and some
pros and cons!
DEPT OF MCA Page 15
Cloud computing 1OX18MCA71
References
www.google.com
www.wilkipedia.com
www.studymafia.org
DEPT OF MCA Page 16
Вам также может понравиться
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingОт EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingОценок пока нет
- Abstract-: Keywords: Applications, Architecture, Business Component of CloudДокумент15 страницAbstract-: Keywords: Applications, Architecture, Business Component of CloudKrishna BoreddyОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionОт EverandCloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionОценок пока нет
- Shri Ramswaroop Memorial University: Submitted To Mr. Anand RaiДокумент19 страницShri Ramswaroop Memorial University: Submitted To Mr. Anand RaiAaqib KhanОценок пока нет
- Cloud computing: Moving IT out of the officeОт EverandCloud computing: Moving IT out of the officeBCS, The Chartered Institute for ITОценок пока нет
- nisha report3.....Документ19 страницnisha report3.....abdulqaiyum710636Оценок пока нет
- My Seminar Report On Cloud ComputingДокумент18 страницMy Seminar Report On Cloud ComputingKevin NettarОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing - Lecture 1Документ21 страницаCloud Computing - Lecture 1Muhammad FahadОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing EssentialsДокумент15 страницCloud Computing EssentialsHASIB205Оценок пока нет
- Cloud ComputingДокумент15 страницCloud ComputingAtharvaОценок пока нет
- FOG COMPUTING: AN ABLE EXTENSION TO CLOUDДокумент16 страницFOG COMPUTING: AN ABLE EXTENSION TO CLOUDMinahil Ahmad100% (1)
- Cloud Computing: SIST MangattuparambaДокумент23 страницыCloud Computing: SIST MangattuparambaarundutchОценок пока нет
- Name Vidhi Thapa: Course - B.SC It SEM 6thДокумент14 страницName Vidhi Thapa: Course - B.SC It SEM 6thFroh FrgjОценок пока нет
- Cloud ComputingДокумент20 страницCloud ComputingAthavanRamachandran100% (1)
- Cloud ComputingДокумент5 страницCloud ComputingNeetu GowdarОценок пока нет
- Cloud ComputingДокумент25 страницCloud ComputingANU_ECIMT100% (5)
- Basic PPT On Cloud ComputingДокумент32 страницыBasic PPT On Cloud ComputingSavyasachi Vats54% (13)
- Cloud ComputingДокумент16 страницCloud ComputingKranthi kumarОценок пока нет
- Term Paper On Cloud ComputingДокумент14 страницTerm Paper On Cloud ComputingShifath Shams50% (2)
- Detailed Overview of Cloud ComputingДокумент18 страницDetailed Overview of Cloud ComputingAravind Kumar CSОценок пока нет
- Synopsis On CLOUD COMPUTING by Prashant GuptaДокумент6 страницSynopsis On CLOUD COMPUTING by Prashant GuptaPrashant GuptaОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing in Resource ManagementДокумент6 страницCloud Computing in Resource ManagementIJEMR JournalОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing BasicsДокумент16 страницCloud Computing BasicsRonak ChawlaОценок пока нет
- Seminar ReportДокумент17 страницSeminar Reportshinchan noharaОценок пока нет
- Seminar ReportДокумент17 страницSeminar Reportshinchan noharaОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is A Model For Enabling Ubiquitous, Convenient, On-Demand Network Access To AДокумент10 страницCloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is A Model For Enabling Ubiquitous, Convenient, On-Demand Network Access To ABharath MadalaОценок пока нет
- Cloud ComputingДокумент38 страницCloud ComputingjivasaОценок пока нет
- What Is Cloud Computing?: Luit Infotech Private LimitedДокумент6 страницWhat Is Cloud Computing?: Luit Infotech Private LimitedKaleab FekaduОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing: A Synopsis OnДокумент8 страницCloud Computing: A Synopsis OnShoaib AhmedОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing: Mini Project Work Entiled OnДокумент24 страницыCloud Computing: Mini Project Work Entiled OnZeanav KhanОценок пока нет
- Pocomo Projected Collaboration Using Mobile DeviceДокумент20 страницPocomo Projected Collaboration Using Mobile DevicebavithaОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing: This Article Appears To Contain A Large Number The - Please If You CanДокумент17 страницCloud Computing: This Article Appears To Contain A Large Number The - Please If You Cansrinu25Оценок пока нет
- Cloud ComputingДокумент20 страницCloud ComputingxyzОценок пока нет
- Cloud ComputingДокумент11 страницCloud ComputingLvenkatesh VenkateshОценок пока нет
- Seminar Report: Submitted By: Arpit Rawat Roll No: UE7308 Cse 7 SemДокумент20 страницSeminar Report: Submitted By: Arpit Rawat Roll No: UE7308 Cse 7 SemJatinder SinghОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing: Submitted By: Divya Khandelwal B.Tech (CSE) 7 Sem 0271352707Документ31 страницаCloud Computing: Submitted By: Divya Khandelwal B.Tech (CSE) 7 Sem 0271352707divya25sepОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing ExplainedДокумент17 страницCloud Computing Explainedsaurabh128Оценок пока нет
- CL Cloudintro PDFДокумент9 страницCL Cloudintro PDFaamir_malikОценок пока нет
- Compiled Note On Cloud Computing - 2Документ44 страницыCompiled Note On Cloud Computing - 2Suresh SinghОценок пока нет
- Seminar On Cloud ComputingДокумент16 страницSeminar On Cloud Computingtsegab bekele80% (5)
- Cloud computing: On-demand access to shared computing resourcesДокумент10 страницCloud computing: On-demand access to shared computing resourcessri_bujjiОценок пока нет
- Survey of Cloud ComputingДокумент13 страницSurvey of Cloud ComputingijwscОценок пока нет
- DOM205 - Individual Project - Cloud Computing ABHARIKA MOHANTYДокумент18 страницDOM205 - Individual Project - Cloud Computing ABHARIKA MOHANTYAbharika MohantyОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing DraftДокумент14 страницCloud Computing Draftakhil829208Оценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing: - BY Banu Pooja Kannikanti 17H71A05C4Документ19 страницCloud Computing: - BY Banu Pooja Kannikanti 17H71A05C4Bhavana GummaОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing: History, Architecture, Security Issues: March 2015Документ8 страницCloud Computing: History, Architecture, Security Issues: March 2015Prabhakar VermaОценок пока нет
- Cloud ComputingДокумент19 страницCloud ComputingDikshith RoshanОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing and Satellite ImageryДокумент9 страницCloud Computing and Satellite ImageryAnupam TiwariОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computoing Module IДокумент24 страницыCloud Computoing Module IJEEVA P GОценок пока нет
- 21BLC1269 Cao ProjectДокумент8 страниц21BLC1269 Cao Projectishika.sarkar.501Оценок пока нет
- Lec01 - Introduction To Cloud ComputingДокумент72 страницыLec01 - Introduction To Cloud ComputingAhmed AbdallaОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 1: Introduction To Cloud ComputingДокумент36 страницChapter - 1: Introduction To Cloud ComputingPreet ChahalОценок пока нет
- CloudДокумент11 страницCloudcherry grootОценок пока нет
- Visvesvaraya Technological University Belgaum: A Seminar Report On Cloud ComputingДокумент13 страницVisvesvaraya Technological University Belgaum: A Seminar Report On Cloud ComputingNeha TiwariОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing: January 2020Документ89 страницCloud Computing: January 2020shОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing Is ComputationДокумент15 страницCloud Computing Is ComputationchalembaОценок пока нет
- Security Issues in Cloud ComputingДокумент19 страницSecurity Issues in Cloud ComputingSalau DamilolaОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Cloud Computing: Key Concepts and HistoryДокумент15 страницIntroduction to Cloud Computing: Key Concepts and HistoryAakash SoniОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing SeminarДокумент21 страницаCloud Computing SeminarEllen Jane Cantuba GuardianОценок пока нет
- Cloud ComputingДокумент14 страницCloud ComputingNabeela Khaled100% (1)
- CertyIQ AZ-900 UpdatedExam Dumps - 2022 Part 2Документ27 страницCertyIQ AZ-900 UpdatedExam Dumps - 2022 Part 2sandro marcelinoОценок пока нет
- Sensors: A Digital-Analog Hybrid System-on-Chip For Capacitive Sensor Measurement and ControlДокумент14 страницSensors: A Digital-Analog Hybrid System-on-Chip For Capacitive Sensor Measurement and ControlChao-Shiun WangОценок пока нет
- Port Pin Outs: Pin # Function I/OДокумент6 страницPort Pin Outs: Pin # Function I/OHector VillarrealОценок пока нет
- Backup As A Service in 3 StepsДокумент6 страницBackup As A Service in 3 StepsLuis OlavarrietaОценок пока нет
- ABP - IO Implementing - Domain - Driven - DesignДокумент109 страницABP - IO Implementing - Domain - Driven - DesignddoruОценок пока нет
- Django SetupДокумент11 страницDjango SetupSandeep Chowdary MuthineniОценок пока нет
- SWE2004 - Software Design and ArchitectureДокумент20 страницSWE2004 - Software Design and ArchitecturePradhyumna GundaОценок пока нет
- DICT Programs and ProjectsДокумент1 страницаDICT Programs and ProjectsJeru Mac100% (2)
- Roles in Data - Learn - Microsoft DocsДокумент4 страницыRoles in Data - Learn - Microsoft DocsJimit ShahОценок пока нет
- Sophos XG Firewall Virtual Appliance Microsoft Hyper-V: Getting Started GuideДокумент9 страницSophos XG Firewall Virtual Appliance Microsoft Hyper-V: Getting Started GuideHadi AlatrashОценок пока нет
- Embedded Systems Design: A Unified Hardware/Software IntroductionДокумент29 страницEmbedded Systems Design: A Unified Hardware/Software Introductiondayat_ridersОценок пока нет
- Principles of Information Security 4th Edition Whitman Chapter 1 SolutionsДокумент51 страницаPrinciples of Information Security 4th Edition Whitman Chapter 1 SolutionsJen Lee73% (11)
- Iso Iec 27032 2012 CompressДокумент4 страницыIso Iec 27032 2012 CompressBruno LopesОценок пока нет
- ESA 9-6 CLI Reference GuideДокумент324 страницыESA 9-6 CLI Reference GuidegreatkudoОценок пока нет
- Assembly Language For x86 ProcessorsДокумент59 страницAssembly Language For x86 ProcessorsTuấn AnhОценок пока нет
- Current LogДокумент62 страницыCurrent LogPatricia MalpartidaОценок пока нет
- Fortiddos 2013 Upb-1Документ33 страницыFortiddos 2013 Upb-1jramongvОценок пока нет
- Building A Secure Local Area NetworkДокумент71 страницаBuilding A Secure Local Area Networkhosny1234Оценок пока нет
- SRS For ATM SystemДокумент21 страницаSRS For ATM SystemUrja DhabardeОценок пока нет
- Base IOTДокумент99 страницBase IOTnguyenbaviet89Оценок пока нет
- Icf 7 MelcsДокумент4 страницыIcf 7 Melcsal lenОценок пока нет
- Centralized IAM supports complianceДокумент4 страницыCentralized IAM supports complianceashishvdОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Malicious Code Types and TrendsДокумент27 страницIntroduction to Malicious Code Types and TrendsFLEXCODEC TECHОценок пока нет
- Red Team Guide (Review Edition)Документ189 страницRed Team Guide (Review Edition)Martin gufОценок пока нет
- Domain Controller and Active Directory Project Networking 1Документ23 страницыDomain Controller and Active Directory Project Networking 1Amine BatrounyОценок пока нет
- Lecture 17 MultipliersДокумент30 страницLecture 17 MultipliersgsonОценок пока нет
- Board CS2 2020Документ3 страницыBoard CS2 2020Amitava GhoshОценок пока нет
- Computer Components ExplainedДокумент10 страницComputer Components ExplainedAlyssaОценок пока нет
- The 6 Stages of Data Processing: Collection, Preparation, Input, Processing, Output, and StorageДокумент12 страницThe 6 Stages of Data Processing: Collection, Preparation, Input, Processing, Output, and StorageRishabh VermaОценок пока нет
- Mukesh SharmaДокумент2 страницыMukesh SharmaRaj RajОценок пока нет
- Designing Data-Intensive Applications: The Big Ideas Behind Reliable, Scalable, and Maintainable SystemsОт EverandDesigning Data-Intensive Applications: The Big Ideas Behind Reliable, Scalable, and Maintainable SystemsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (6)
- Notion for Beginners: Notion for Work, Play, and ProductivityОт EverandNotion for Beginners: Notion for Work, Play, and ProductivityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (7)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveОт EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveОценок пока нет
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessОт EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessОценок пока нет
- Excel for Finance and Accounting: Learn how to optimize Excel formulas and functions for financial analysis (English Edition)От EverandExcel for Finance and Accounting: Learn how to optimize Excel formulas and functions for financial analysis (English Edition)Оценок пока нет
- Change Management for Beginners: Understanding Change Processes and Actively Shaping ThemОт EverandChange Management for Beginners: Understanding Change Processes and Actively Shaping ThemРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Excel 2023: A Comprehensive Quick Reference Guide to Master All You Need to Know about Excel Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts with Real-World ExamplesОт EverandExcel 2023: A Comprehensive Quick Reference Guide to Master All You Need to Know about Excel Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts with Real-World ExamplesОценок пока нет
- Design and Build Modern Datacentres, A to Z practical guideОт EverandDesign and Build Modern Datacentres, A to Z practical guideРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Computer Science Beginners Crash Course: Coding Data, Python, Algorithms & HackingОт EverandComputer Science Beginners Crash Course: Coding Data, Python, Algorithms & HackingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (12)
- Excel for Beginners 2023: A Step-by-Step and Quick Reference Guide to Master the Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts in Excel with Practical Examples | A Complete Excel Shortcuts Cheat SheetОт EverandExcel for Beginners 2023: A Step-by-Step and Quick Reference Guide to Master the Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts in Excel with Practical Examples | A Complete Excel Shortcuts Cheat SheetОценок пока нет
- Learn Power BI: A beginner's guide to developing interactive business intelligence solutions using Microsoft Power BIОт EverandLearn Power BI: A beginner's guide to developing interactive business intelligence solutions using Microsoft Power BIРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Product Operations: How successful companies build better products at scaleОт EverandProduct Operations: How successful companies build better products at scaleОценок пока нет
- A Modern Enterprise Architecture Approach: Enterprise ArchitectureОт EverandA Modern Enterprise Architecture Approach: Enterprise ArchitectureРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (3)
- The AI-Powered Product Manager: Combining Strategy and TechnologyОт EverandThe AI-Powered Product Manager: Combining Strategy and TechnologyРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Creating Online Courses with ChatGPT | A Step-by-Step Guide with Prompt TemplatesОт EverandCreating Online Courses with ChatGPT | A Step-by-Step Guide with Prompt TemplatesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (4)
- Power BI for Jobseekers: Learn how to create interactive dashboards and reports, and gain insights from the data (English Edition)От EverandPower BI for Jobseekers: Learn how to create interactive dashboards and reports, and gain insights from the data (English Edition)Оценок пока нет
- Microsoft Access Guide to Success: From Fundamentals to Mastery in Crafting Databases, Optimizing Tasks, & Making Unparalleled Impressions [III EDITION]От EverandMicrosoft Access Guide to Success: From Fundamentals to Mastery in Crafting Databases, Optimizing Tasks, & Making Unparalleled Impressions [III EDITION]Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (8)
- Agile Metrics in Action: How to measure and improve team performanceОт EverandAgile Metrics in Action: How to measure and improve team performanceОценок пока нет
- Google Cloud Cookbook: Practical Solutions for Building and Deploying Cloud Services, 1st EditionОт EverandGoogle Cloud Cookbook: Practical Solutions for Building and Deploying Cloud Services, 1st EditionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Fundamentals of Data Engineering: Plan and Build Robust Data SystemsОт EverandFundamentals of Data Engineering: Plan and Build Robust Data SystemsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Balanced Scorecards and Operational Dashboards with Microsoft ExcelОт EverandBalanced Scorecards and Operational Dashboards with Microsoft ExcelРейтинг: 2 из 5 звезд2/5 (1)
- Monolith to Microservices: Evolutionary Patterns to Transform Your MonolithОт EverandMonolith to Microservices: Evolutionary Patterns to Transform Your MonolithРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)











































































































![Microsoft Access Guide to Success: From Fundamentals to Mastery in Crafting Databases, Optimizing Tasks, & Making Unparalleled Impressions [III EDITION]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/610686937/149x198/9ccfa6158e/1713743787?v=1)









