Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Liquid Fuel & Energy Conversion
Загружено:
Eddie TaiАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Liquid Fuel & Energy Conversion
Загружено:
Eddie TaiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
File C6-87
October 2008
www.extension.iastate.edu/agdm
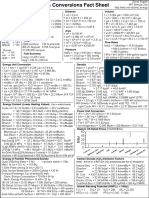
Liquid Fuel Measurements and Conversions
Liquid fuel measurements and conversions 1 barrel = 3,553,200 Btu – HHV *
Gasoline 1 barrel = 3,749 megajoules -- HHV *
1 gallon = 125,000 Btu – HHV * 1 barrel = 3,178,140 Btu – LHV *
1 gallon = 131.9 megajoules – HHV * 1 barrel = 3,353 megajoules – LHV *
1 gallon = 115,400 Btu – LHV * 1 liter = 22,351 Btu – HHV *
1 gallon = 121.7 megajoules – LHV * 1 liter = 23.6 megajoules – HHV *
1 gallon = .002791 metric tons 1 liter = 19.992 Btu – LHV *
1 barrel = 5,250,000 Btu – HHV * 1 liter = 21.1 megajoules – LHV *
1 barrel = 5,539 megajoules – HHV * Ethanol average density = .79 grams per milliliter
1 barrel = 4,846,800 Btu – LHV * Ethanol average density = .79 metric tons per cubic
1 barrel = 5,113 megajoules – LHV * meter
1 barrel = .1172 metric tons
Bio-diesel
1 liter = 33,025 Btu – HHV *
1 gallon = 126,206 Btu – HHV *
1 liter = 30,489 Btu – LHV *
1 gallon = 133.1 megajoules – HHV *
1 liter = 34.8 megajoules – HHV *
1 gallon = 117,093 Btu – LHV *
1 liter = 32.2 megajoules – LHV *
1 gallon = 123.5 megajoules – LHV *
1 metric ton = 8.5 barrels
1 barrel = 5,300,652 Btu – HHV *
1 metric ton = 1.351 kiloliters
1 barrel = 5,592 megajoules – HHV *
1 kiloliter = .740 metric tons
1 barrel = 4,917,906 Btu – LHV *
Diesel fuel 1 barrel = 5,188 megajoules – LHV *
1 gallon = 138,700 Btu – HHV * 1 liter = 33,344 Btu – HHV *
1 gallon = 146.3 megajoules – HHV * 1 liter = 35.2 megajoules – HHV *
1 gallon = 128,700 Btu – LHV * 1 liter = 30,936 Btu – LHV *
1 gallon = 135.8 megajoules – LHV * 1 liter = 32.6 megajoules – LHV *
1 gallon = .003192 metric tons 1 metric ton of biodiesel = 37.8 gigajoules
1 barrel = 5,825,400 Btu – HHV * Bio-diesel average density = .88 grams per milliliter
1 barrel = 6,146 megajoules – HHV * Bio-diesel average density = .88 metric tons per
1 barrel = 5,405,400 Btu – LHV * cubic meter
1 barrel = 5,703 megajoules LHV *
Residual Fuel
1 barrel = .1341 metric tons
1 gallon = 149,700 Btu – HHV *
1 metric ton = 7.5 barrels
1 gallon = 157.9 megajoules – HHV *
1 kiloliter = .839 metric tons
1 gallon = 138,400 Btu – LHV *
1 metric ton = 1.192 kiloliters
1 gallon = 146.0 megajoules – LHV *
1 liter = 36,645 Btu – HHV *
1 barrel = 6,287,400 Btu – HHV *
1 liter = 38.7 megajoules – HHV *
1 barrel = 6,633 megajoules – HHV *
1 liter = 34,003 Btu – LHV *
1 barrel = 5,812,800 Btu – LHV *
1 liter = 35.9 megajoules – LHV *
1 barrel = 6,133 megajoules – LHV *
Ethanol 1 liter = 39,551 Btu – HHV *
1 gallon = 84,600 Btu – HHV * 1 liter = 41.7 megajoules – HHV *
1 gallon = 89.3 megajoules – HHV * 1 liter = 36,565 Btu – LHV *
1 gallon = 75,670 Btu – LHV * 1 liter = 38.6 megajoules – LHV *
1 gallon = 79.8 megajoules – LHV *
Don Hofstrand
extension value-added agriculture specialist
co-director Ag Marketing Resource Center
641-423-0844
dhof@iastate.edu
Page 2 File C6-87
LP Gas (liquefied petroleum gas – propane) Barrels of petroleum or related products
1 gallon = 91,300 Btu – HHV * (bbl) measurements and conversions
1 gallon = 96.3 megajoules – HHV *
Crude Oil (based on worldwide average
1 gallon = 83,500 Btu – LHV *
1 gallon = 88.1 megajoules – LHV * gravity)
1 barrel = 3,834,600 Btu – HHV * 1 barrel = 42 gallons
1 barrel = 4,046 megajoules – HHV * 1 drum = 55 gallons
1 barrel = 3,507,000 Btu – LHV * 1 metric drum = 52.8 gallon
1 barrel = 3,700 megajoules – LHV * 1 gallon = .0182 drum
1 liter = 24,121 Btu – HHV * 1 gallon = .0189 metric drum
1 liter = 25.4 megajoules – HHV * 1 gallon = 138,100 Btu – HHV *
1 liter = 22,061 Btu – LHV * 1 gallon = 145.7 megajoules – HHV *
1 liter = 23.3 megajoules – LHV * 1 gallon = 131,800 Btu – LHV *
1 barrel = .086 metric tons 1 gallon = 139.0 megajoules – LHV *
1 metric ton = 11.6 barrels 1 gallon = .003247 metric tons
1 kiloliter = .542 metric tons 1 gallon = .0038 kiloliters
1 metric ton = 1.844 kiloliters 1 gallon = .0238 barrels
1 barrel = 5,800,200 Btu – HHV *
Methanol 1 barrel = 6,119 megajoules – HHV *
1 gallon = 64,600 Btu – HHV * 1 barrel = 5,535,600 Btu – LHV *
1 gallon = 68.2 megajoules – HHV * 1 barrel = 5,840 megajoules – LHV *
1 gallon = 56,560 Btu –LHV * 1 barrel = .13637 metric tons
1 gallon = 59.7 megajoules – LHV * 1 barrel = .159 kiloliters
1 barrel = 2,713,200 Btu – HHV * 1 liter = 36,486 Btu – HHV *
1 barrel = 2,862 megajoules – HHV * 1 liter = 38.5 megajoules – HHV *
1 barrel = 2,375,520 Btu -- LHV * 1 liter = 34,822 Btu – LHV *
1 barrel = 2,506 megajoules – LHV * 1 liter = 36.7 megajoules – LHV *
1 liter = 17,067 Btu – HHV * 1 kiloliter = .8581 metric tons
1 liter = 18.0 megajoules – HHV * 1 kiloliter = 6.2898 barrels
1 liter = 14,943 Btu – LHV * 1 kiloliter = 264.17 gallons
1 liter = 15.8 megajoules – LHV * 1 kiloliter = 1 cubic meter
1 metric ton = 1.165 kiloliters
Butane
1 metric ton = 7.33 barrels
1 gallon = 103,000 Btu – HHV *
1 metric ton = 307.86 gallons
1 gallon = 108.7 megajoules – HHV *
1 gallon = 93,000 Btu – LHV * 1 barrel of crude oil = 44.60 gallons of petroleum
1 gallon = 98.1 megajoules – LHV * products
1 barrel = 4,326,000 Btu – HHV *
1 barrel = 4,564 megajoules – HHV * Gallons Percent
1 barrel = 3,906,000 Btu -- LHV * Finished motor gasoline 19.40 44
1 barrel = 4,121 megajoules – LHV * Distillate fuel oil 10.50 24
1 liter = 27,213 Btu – HHV * Kero-type jet fuel 4.12 9
1 liter = 28.7 megajoules – HHV * Petroleum coke 2.23 5
1 liter = 24,571 Btu – LHV * Still gas 1.81 4
1 liter = 25.9 megajoules – LHV * Residual fuel oil 1.68 4
Liquefied refiner gas 1.51 3
Asphalt and road oil 1.34 3
Other 2.01 4
File C6-87 Page 3
Oil Equivalents Refined petroleum products
A barrel (metric ton) of oil equivalent is a unit of 1 metric ton motor gasoline = 8.53 barrels
energy based on the approximate energy released by 1 metric ton LP-gas (liquefied petroleum gas) (pro-
burning one barrel (metric ton) of crude oil. pane) = 11.6 barrels
1 metric ton natural gas = 10 barrels
1 barrel oil equivalent (bboe) = .1364 metric tons oil 1 metric ton NGL (natural gas liquids) = 10.4 barrels
equivalent
1 barrel oil equivalent = approximately 1.364 million Liquid fuels
kilocalories 1 cubic meter = 6.289 barrels
1 barrel oil equivalent = approximately 5.73 giga- 1 barrel = 159 liters
joules 1 barrel = 42 US gallons
1 barrel oil equivalent = approximately .20 metric 1 U.S. gallon = 231 cubic inches
tons of hard coal 1 U.S. gallon = .1337 cubic feet
1 barrel oil equivalent = approximately .41 metric 1 U.S. gallon = 3.785 liters
tons of lignite coal 1 U.S. gallon = .8321 imperial gallons
1 barrel oil equivalent = approximately 1.64 1 U.S. gallon = .0238 barrels
metawatt-hours 1 U.S. gallon = .003785 cubic meters
1 million barrels oil equivalent = .16 billion cubic 1 liter = 61.02 cubic inches
meters natural gas 1 liter = .03531 cubic feet
1 million barrels oil equivalent = 5.61 billion cubic 1 liter = .2642 U.S. gallons
feet natural gas 1 liter = .22 imperial gallons
1 million barrels oil equivalent = .12 million metric 1 liter = .00629 barrels
tons of liquefied natural gas 1 liter = .001 cubic meters
1 million barrels oil equivalent = 5.8 trillion Btus
1 million barrels oil equivalent = .14 million metric Flow Rate
tons oil equivalent 1 barrel per hour = 137.8 cubic feet per day
1 metric ton oil equivalent (toe) = 7.33 barrels oil 1 barrel per hour = 49,187 cubic feet per year
equivalent 1 barrel per hour = 1,008 U.S. gallons per day
1 metric ton oil equivalent = approximately 10 mil- 1 barrel per hour = 367,920 U.S. gallons per year
lion kilocalories 1 barrel per hour = 839.3 imperial gallons per day
1 metric ton oil equivalent = approximately 42 giga- 1 barrel per hour = 306,345 imperial gallons per year
joules 1 barrel per hour = 3,815 liters per day
1 metric ton oil equivalent = approximately 1.5 met- 1 barrel per hour = 1,392,475 liters per year
ric tons of hard coal 1 gallon per hour = .5712 barrels per day
1 metric ton oil equivalent = approximately 3 metric 1 gallon per hour = 207.92 barrels per year
tons of lignite coal 1 liter per hour = .1510 barrels per day
1 metric ton oil equivalent = approximately 12 1 liter per hour = 55.10 barrels per year
megawatt-hours
1 million metric tons oil equivalent = 1.111 billion
cubic meters natural gas
1 million metric tons oil equivalent = 39.2 billion
cubic feet natural gas
1 million metric tons oil equivalent = .805 million
tons liquefied natural gas
1 million metric tons oil equivalent = 7.33 million
barrels oil equivalent
Page 4 File C6-87
Fuel usage measurements and conver- References
sions Bioenergy Feedstock Information Network: http://
1 mile per gallon = .264 miles per liter bioenergy.ornl.gov/
1 mile per gallon = .425 kilometers per liter Biomass Energy Datebook, U.S. Department of En-
1 mile per gallon = 235 liters per 100 kilometers ergy: http://cta.ornl.gov/bedb/appendix_a.shtml
1 mile per gallon = 100 gallons per 100 miles BP Conversion Factors: http://www.bp.com/conver-
1 mile per liter = 3.79 miles per gallon sionfactors.jsp
1 mile per liter = 1.609 kilometers per liter ConvertIt: http://www.convertit.com/Go/ConvertIt/
1 mile per liter = 62.15 liters per 100 kilometers Measurement/Converter.ASP
1 kilometer per liter = 2.35 miles per gallon Energy Information Administration: http://www.eia.
1 kilometer per liter = .6215 miles per liter doe.gov/
1 kilometer per liter = 100 liters per 100 kilometers Energy Information Administration - Energy Kids
1 kilometer per liter = 42.5 gallons per 100 miles Page: http://www.eia.doe.gov/kids/energyfacts/sci-
ence/energy_calculator.html
* Energy contents are expressed as either High Fuel Consumption Converter – Unit Converter:
(gross) Heating Value (HHV) or Lower (net) Heating http://www.unitconversion.org/unit_converter/fuel-
Value (LHV). LHV is closest to the actual energy consumption.html
yield in most cases. HHV (including condensation of Iowa Energy Center, Iowa State University: http://
combustion products) is greater by between 5% (in www.energy.iastate.edu/
the case of coal) and 10% (for natural gas), depend- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page
ing mainly on the hydrogen content of the fuel. For
most biomass feed-stocks this difference appears
to be 6-7%. The appropriateness of using LHV or
HHV when comparing fuels, calculating thermal
efficiencies, etc. really depends upon the applica-
tion. For stationary combustion where exhaust gases
are cooled before discharging (e.g. power stations),
HHV is more appropriate. Where no attempt is
made to extract useful work from hot exhaust gases
(e.g. motor vehicles), the LHV is more suitable. In
practice, many European publications report LHV,
whereas North American publications use HHV
(Source: Bioenergy Feedstock Network -- http://bio-
energy.ornl.gov/)
. . . and justice for all Issued in furtherance of Cooperative Extension work, Acts of May 8 and June
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) prohibits discrimination in all 30, 1914, in cooperation with the U.S. Department of Agriculture. Jack M.
its programs and activities on the basis of race, color, national origin, gender, Payne, director, Cooperative Extension Service, Iowa State University of Science
religion, age, disability, political beliefs, sexual orientation, and marital or family and Technology, Ames, Iowa.
status. (Not all prohibited bases apply to all programs.) Many materials can
be made available in alternative formats for ADA clients. To file a complaint
of discrimination, write USDA, Office of Civil Rights, Room 326-W, Whitten
Building, 14th and Independence Avenue, SW, Washington, DC 20250-9410 or
call 202-720-5964.
Вам также может понравиться
- Refinery Electrical Safety AuditДокумент3 страницыRefinery Electrical Safety AuditSankara SubramanianОценок пока нет
- Def - 90 - 110 - WSM 2,25 2,5 v8 200tdiДокумент880 страницDef - 90 - 110 - WSM 2,25 2,5 v8 200tdistefaan83100% (1)
- Process Data Sheet for CompressorsДокумент2 страницыProcess Data Sheet for CompressorsEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- PTTP ProcessSafetyFundamentalsДокумент12 страницPTTP ProcessSafetyFundamentalsAnonymous q2iHVfОценок пока нет
- Conversion Factors and ConstantsДокумент1 страницаConversion Factors and ConstantsM KEVIN ANANDA PUTRA PRADANAОценок пока нет
- Conversion FactorsДокумент1 страницаConversion FactorsSiew Chung KiОценок пока нет
- API 571 Reference Card: Common Corrosion Mechanisms and Failures in RefineriesДокумент7 страницAPI 571 Reference Card: Common Corrosion Mechanisms and Failures in Refinerieszackyat7976100% (1)
- Gas Facilities Audit ChecklistДокумент2 страницыGas Facilities Audit ChecklistEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Units Conversion PDFДокумент17 страницUnits Conversion PDFmusaveerОценок пока нет
- LNG ConverstionTableДокумент4 страницыLNG ConverstionTablexxxhanzОценок пока нет
- Energy Industry Conversions LRGДокумент2 страницыEnergy Industry Conversions LRGmaxrobnsonОценок пока нет
- ThermoDynamics Conversion Table PDFДокумент1 страницаThermoDynamics Conversion Table PDFCloie Chavez100% (1)
- Ul 142 Aboveground TanksДокумент2 страницыUl 142 Aboveground TanksCarlos Morales PérezОценок пока нет
- Conversion FactorДокумент3 страницыConversion FactorAniket AngreОценок пока нет
- Concrete Slab Load Calculation PDFДокумент54 страницыConcrete Slab Load Calculation PDFEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Conversion FactorДокумент4 страницыConversion Factorpks_2410Оценок пока нет
- Oil & Gas Unit ConversionsДокумент4 страницыOil & Gas Unit ConversionsHitesh Agja100% (1)
- BP's Energy Conversion Factors TableДокумент2 страницыBP's Energy Conversion Factors TableHvalbye Capital Markets100% (1)
- Conversion Table and WeavingДокумент4 страницыConversion Table and WeavingAbu AlaynaОценок пока нет
- Natural Gas ConversionДокумент5 страницNatural Gas ConversionWiwid MurdanyОценок пока нет
- Mmbtu FundasДокумент18 страницMmbtu FundasSambuddha BhattacharyaОценок пока нет
- LNG ConverstionTableДокумент7 страницLNG ConverstionTableLeite AddyОценок пока нет
- Introduction Thermal Oil Heaters Type VTOДокумент7 страницIntroduction Thermal Oil Heaters Type VTOMomar Talla DiawОценок пока нет
- Pulp and Paper Production From EFBДокумент9 страницPulp and Paper Production From EFBEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- RISK ASSESSMENT MATRIXДокумент1 страницаRISK ASSESSMENT MATRIXEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- LNG vapor conversion tablesДокумент4 страницыLNG vapor conversion tableschandirandelhiОценок пока нет
- Basic Conversion SheetДокумент2 страницыBasic Conversion SheetkessbrokerОценок пока нет
- Citroen c2 2003 Manual PDFДокумент198 страницCitroen c2 2003 Manual PDFCHARLESОценок пока нет
- Conversion FactorsДокумент2 страницыConversion FactorsArdy PrasetyoОценок пока нет
- Flare Gas Recovery & Zero Flare SolutionsДокумент16 страницFlare Gas Recovery & Zero Flare SolutionsEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Liquid Fuel Measurements and ConversionsДокумент4 страницыLiquid Fuel Measurements and ConversionsrhazoorОценок пока нет
- Unit Conversion - Oil Industry ConversionsДокумент9 страницUnit Conversion - Oil Industry Conversionsal4782Оценок пока нет
- Energy Conversion Basics ConceptsДокумент7 страницEnergy Conversion Basics ConceptsKristine AlmarezОценок пока нет
- Back To Index: Prefix UnitДокумент4 страницыBack To Index: Prefix UnitchandirandelhiОценок пока нет
- Bioenergy ConvДокумент4 страницыBioenergy ConvErie HaryantoОценок пока нет
- Units Conversion TableДокумент1 страницаUnits Conversion Tabledavibraga8041Оценок пока нет
- Comparision of Shutlleless and Shuttle Looms 1Документ1 страницаComparision of Shutlleless and Shuttle Looms 1amar9247Оценок пока нет
- Oil Industry ConversionДокумент7 страницOil Industry ConversionPhil RadyОценок пока нет
- Bioenergy Conversion FactorsДокумент4 страницыBioenergy Conversion FactorsAhmet SeçenОценок пока нет
- Energy Conversion Fact SheetДокумент3 страницыEnergy Conversion Fact SheetAzeem ButtОценок пока нет
- Unitsandconversions 1Документ2 страницыUnitsandconversions 1Andris BakhtiarОценок пока нет
- Course: Measuring Energy in Economics and PolicyДокумент11 страницCourse: Measuring Energy in Economics and PolicyVIVEK SAINIОценок пока нет
- Bp-Statistical-Review-Of World Energy-2017-Approximate-Conversion-Factors PDFДокумент4 страницыBp-Statistical-Review-Of World Energy-2017-Approximate-Conversion-Factors PDFingbarragan87Оценок пока нет
- Unit Conversion TableДокумент1 страницаUnit Conversion Tablenirdesh_chauhanОценок пока нет
- Close Window Print This Page: Units of MeasureДокумент2 страницыClose Window Print This Page: Units of MeasureGeorge John AmegashieОценок пока нет
- Conversion Table LNGДокумент3 страницыConversion Table LNGKazi Anwarul Azim SohelОценок пока нет
- Conversion FactorsДокумент2 страницыConversion FactorsdhavalshahicОценок пока нет
- Approximate conversion factors between energy unitsДокумент1 страницаApproximate conversion factors between energy unitskishorekudapaОценок пока нет
- Conversion UnitsДокумент4 страницыConversion UnitsAngelo IntiaОценок пока нет
- Conversion Fac Tors LengthДокумент1 страницаConversion Fac Tors Lengthmajade manimtimОценок пока нет
- Conversion Tables & Formulas Guide for Agriculture, Energy & CommoditiesДокумент2 страницыConversion Tables & Formulas Guide for Agriculture, Energy & CommoditiesnazarasimОценок пока нет
- QP Conversion FactorsДокумент4 страницыQP Conversion Factorsthe CommissionОценок пока нет
- Factores de ConversionДокумент5 страницFactores de ConversionCristian SanguchoОценок пока нет
- Tablas de ConversionДокумент5 страницTablas de ConversionFisicoquimica ULSОценок пока нет
- 1.1 System of Units - ME 303-CE31S8 - Engineering Utilities 2 (Basic Mechanical Engineering)Документ2 страницы1.1 System of Units - ME 303-CE31S8 - Engineering Utilities 2 (Basic Mechanical Engineering)RYAN JOSEPH QUIMOОценок пока нет
- HN Conversion FactorДокумент4 страницыHN Conversion FactorMathew MammenОценок пока нет
- Oil Industry Conversions GuideДокумент9 страницOil Industry Conversions GuideWagus GinanjarОценок пока нет
- Convert Barrels To TonnesДокумент1 страницаConvert Barrels To TonnesGeorge John AmegashieОценок пока нет
- Tonne of Oil EquivalentДокумент2 страницыTonne of Oil EquivalentIvana Radić100% (1)
- BP Conversion 1Документ2 страницыBP Conversion 1Zul AdamОценок пока нет
- BP - Conversion FactorsДокумент2 страницыBP - Conversion FactorsMohit KabraОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics Demystified - A Self-Teaching Guide 261 PDFДокумент1 страницаThermodynamics Demystified - A Self-Teaching Guide 261 PDFhamid vahedil larijaniОценок пока нет
- PengukuranДокумент3 страницыPengukuranUdin TajudinОценок пока нет
- ConversionTable YTДокумент2 страницыConversionTable YTnoreen tonogОценок пока нет
- Approximate Conversion Factors Marketers Need To KnowДокумент2 страницыApproximate Conversion Factors Marketers Need To KnowwinarnobОценок пока нет
- 02 Common Converstion FactorsДокумент1 страница02 Common Converstion FactorsDarleen PeraltaОценок пока нет
- Tugas MetroДокумент14 страницTugas MetroAdeliya Afriyani KusumaningtyasОценок пока нет
- Crude Oil (Conversions)Документ3 страницыCrude Oil (Conversions)Carolo DemoОценок пока нет
- MLAB UnitsДокумент1 страницаMLAB UnitsSushaine TanОценок пока нет
- Authrisation Letter - RFID - TemplateДокумент1 страницаAuthrisation Letter - RFID - TemplateEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Status Indicators: YOGA 900-13ISK For BIZ Hardware Maintenance ManualДокумент1 страницаStatus Indicators: YOGA 900-13ISK For BIZ Hardware Maintenance ManualEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- LNG Unloading Jetty General LayoutДокумент1 страницаLNG Unloading Jetty General LayoutEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Energy Data and Report Malaysia (2016) PDFДокумент20 страницEnergy Data and Report Malaysia (2016) PDFEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Setia Alam P11 Plot PlanДокумент1 страницаSetia Alam P11 Plot PlanEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Energy Commission Report 2016Документ2 страницыEnergy Commission Report 2016Eddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Gas Composition - East Malaysia AG FieldДокумент1 страницаGas Composition - East Malaysia AG FieldEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Acoustic Research TSW Speaker BrochureДокумент6 страницAcoustic Research TSW Speaker BrochureEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Vessel CNGДокумент1 страницаVessel CNGEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Pages From Masterplan-2018Документ1 страницаPages From Masterplan-2018Eddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Preliminary Due Diligence: Item Key Evaluation A Technology & ProductsДокумент4 страницыPreliminary Due Diligence: Item Key Evaluation A Technology & ProductsEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Infield Flowlines Riser Coating DetailsДокумент4 страницыInfield Flowlines Riser Coating DetailsEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Pages From Plasma Water TreatmentДокумент2 страницыPages From Plasma Water TreatmentEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- NIT - Tender For Land in PortДокумент1 страницаNIT - Tender For Land in PortEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Development of Resonant Magnetic Field MicrosensorsДокумент22 страницыDevelopment of Resonant Magnetic Field MicrosensorsEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Corrosion - by DR - Kallol Mondal, Department of Metallurgy and Material Science, IIT KanpurДокумент3 страницыCorrosion - by DR - Kallol Mondal, Department of Metallurgy and Material Science, IIT KanpurEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Pages From Investment in Catalyst and MaerogelДокумент1 страницаPages From Investment in Catalyst and MaerogelEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- UTM Wifi Guide Complete4Документ10 страницUTM Wifi Guide Complete4Eddie TaiОценок пока нет
- MGP-i For Jetties (Final)Документ2 страницыMGP-i For Jetties (Final)Eddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Gas Facilities Audit ChecklistДокумент4 страницыGas Facilities Audit ChecklistEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- TH - English PDFДокумент87 страницTH - English PDFEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- EW1-Temporary Site LayoutДокумент1 страницаEW1-Temporary Site LayoutEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- LS1 PDFДокумент1 страницаLS1 PDFEddie TaiОценок пока нет
- Compatibility Chart For ChemicalsДокумент3 страницыCompatibility Chart For Chemicalscnaren67Оценок пока нет
- CP - Original Lubricants PDFДокумент4 страницыCP - Original Lubricants PDFJan HendriksОценок пока нет
- PRODUKTINFO Old Wood Anwendung enДокумент29 страницPRODUKTINFO Old Wood Anwendung enblancofrank545Оценок пока нет
- Powerplant Engineering NotesДокумент189 страницPowerplant Engineering NotesMilan LamichhaneОценок пока нет
- Sop BiogasДокумент2 страницыSop BiogasHaridarshan PatelОценок пока нет
- Ujjwala Saga PDFДокумент84 страницыUjjwala Saga PDFRishi ModiОценок пока нет
- Internship Report On Process of PPLДокумент23 страницыInternship Report On Process of PPLShannОценок пока нет
- TBN 1Документ11 страницTBN 1Ben Karthiben NathanОценок пока нет
- Incinerator Opermanual2 en PDFДокумент22 страницыIncinerator Opermanual2 en PDFcap.mucino100% (1)
- Romeo PdvsaДокумент16 страницRomeo PdvsaAnonymous LSPoghJ5nОценок пока нет
- High-Pressure 100 Barg Oil-Flooded Screw Compressor: Yasushi AmanoДокумент5 страницHigh-Pressure 100 Barg Oil-Flooded Screw Compressor: Yasushi AmanoJano AhalloubОценок пока нет
- Service Interval ExcaДокумент6 страницService Interval ExcaAmir Bambang YudhoyonoОценок пока нет
- Thermal Engineering IДокумент8 страницThermal Engineering IPujith PjОценок пока нет
- CDP Conversion of Fuel Data To MWH 2016Документ11 страницCDP Conversion of Fuel Data To MWH 2016Luz DuarteОценок пока нет
- Marine Diesel Engines 20V 1163 M74 for fast vesselsДокумент2 страницыMarine Diesel Engines 20V 1163 M74 for fast vesselsJM MagayanesОценок пока нет
- Bharat Petroleum Corporation LimitedДокумент17 страницBharat Petroleum Corporation LimitedBhakti KaliaОценок пока нет
- Petroleum Facilites of Germany 1945 106Документ10 страницPetroleum Facilites of Germany 1945 106ENAK9000100% (2)
- 4 1-Lat Exceptions To API 614Документ5 страниц4 1-Lat Exceptions To API 614remsorОценок пока нет
- b99 015Документ4 страницыb99 015Tudor RatiuОценок пока нет
- Nuclear Fuel ReprocessingДокумент33 страницыNuclear Fuel ReprocessingMuhamed FahadОценок пока нет
- List of UN Numbers 0000 to 0299 for Explosives and Blasting AgentsДокумент62 страницыList of UN Numbers 0000 to 0299 for Explosives and Blasting AgentsTimuçin ÇolakelОценок пока нет
- GT125 250 Service ManualДокумент0 страницGT125 250 Service ManualJeferson SilvaОценок пока нет