Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
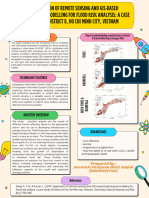
26 Stromewaterdrainageforunderpass
Загружено:
W Dwi PОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
26 Stromewaterdrainageforunderpass
Загружено:
W Dwi PАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.
net/publication/321422067
Storm Water Drainage for Underpass
Article · February 2017
CITATIONS READS
0 757
5 authors, including:
Dhaval M Patel
Shankersinh Vaghela Bapu Institute of Technology
39 PUBLICATIONS 31 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
Literature study on Tsunami Evacuation System in Mundra city View project
Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting of SVBIT College Vasan, Gandhinagar View project
All content following this page was uploaded by Dhaval M Patel on 01 December 2017.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
IJIRST –International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology| Volume 3 | Issue 09 | February 2017
ISSN (online): 2349-6010
Storm Water Drainage for Underpass
Kamal Patel Khushboo Patel
PG Student PG Student
Department of Civil Engineering Department of Civil Engineering
Shankersinh Vaghela Bapu Institute of Technology, India Shankersinh Vaghela Bapu Institute of Technology, India
Rajvansh Patel Kalgi Trivedi
PG Student PG Student
Department of Civil Engineering Department of Civil Engineering
Shankersinh Vaghela Bapu Institute of Technology, India Shankersinh Vaghela Bapu Institute of Technology, India
Dhaval M Patel
Assistant Professor
Department of Civil Engineering
Shankersinh Vaghela Bapu Institute of Technology, India
Abstract
The underpass of Ahmedabad city (Akhbarnagar underpass, Naranpura underpass, Incometex underpass, Mithakhadi underpass,
Thaltej underpass, Parimal garden underpass, Shahibaug underpass) are waterlogged every year during monsoon due to which
the whole traffic systems gets blocked for hours. Akhbarnagar underpass has a major issue such as traffic, water logging in
nearby areas, spreading diseases by water, blockage of storm drain & backflow of suction valve. Surrounding topography, Road
gradient, population data, rainfall data of previous year, sewer network analysis and improvement in pump capacity is required to
solve this problem. Also, vacuum sewerage system, kerb drain system, improvement in sewer network is the most important
possible solution for fight against storm water. Defects in current situation of underpass will overcome by using Quantum GIS &
Google earth pro software data, AutoCAD.
Keywords: Storm Water, Storm-Drain System, Underpass, Kerb Drain System, Filtered Channel
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________
I. INTRODUCTION
Storm Water
Storm water is water that originates during precipitation process & snow melt. In natural landscape such as forest, soil absorb
much of the storm water & plant help to hold it [1]. But unmanaged storm water can create two major issues such as flooding
(runoff water) & water pollution related to potential contaminants [2]. Also, storm water is an important resource for human’s
need. Techniques of storm water harvesting, water management, storm water drainage, purification can potentially make urban
environment self-sustaining. Storm water is a major cause of urban flooding which includes flash flooding, snow melt, heavy
rainfall & depends on catchment area. Storm water is a major cause of urban flooding which includes flash flooding snow melt,
heavy rainfall & depends on catchment area. Main problems arise due to storm water are blockage of drainage (storm drain) &
backflow of valve.
Tunnel
A tunnel is a passage way that carries people or vehicle to across a destination that have obstruction or to shorten the travelling
time [3].
Underpass
[4]
A place where a road or railroad crosses under another road or railroad is termed as underpass .
Storm Water Drainage
Storm drain system is designed to drain excess rain and ground water from impervious surfaces such as paved streets, car
parks, parking lots, footpaths, sidewalks, and roofs [5].
Basic information of Ahmedabad city
Generally Ahmedabad city is situated near the line of tropic of cancer and far from the coastal area due to which the cities have
their average temperature is 38˚C and during rainy season the humidity is affect the city due to which there is normal/heavy
rainfall takes place. Ahmadabad lies at 23.03°N 72.58°E in western India at 53 metres (174 ft) above sea level on the banks of
All rights reserved by www.ijirst.org 23
Storm Water Drainage for Underpass
(IJIRST/ Volume 3 / Issue 09/ 005)
the Sabarmati River, in north-central Gujarat [6].The Ahmedabad city have their average temperature is 38˚C and during rainy
season the humidity is affect the city due to which there is normal/heavy rainfall takes place. Ahmedabad has a hot, semi-arid
climate with marginally less rain than required for a tropical savanna climate. Sabarmati River spits city into two parts.
Ahmedabad city have many well-known underpasses such as Akhbarnagar underpass, Naranpura underpass, Incometex
underpass, Mithakhadi underpass, Thaltej underpass, Parimal garden underpass, Shahibaug underpass are major underpasses of
the city.
Site Information
Akhbarnagar underpass lies at Latitude 23.0665694° N Longitude 72.5596109° E. The underpasses of Ahmedabad city are
waterlogged every year during monsoon due to which the whole traffic system gets blocked for hours. Recently, Akhbarnagar
underpass was blocked due to 4 inches rainfall on 4 th Aug, 2016 [7] and Parimal garden underpass was blocked due to rainfall 124
mm (around 5 inches) on 5th Aug,2016 [8].
Height of underpass from road is in between 5.5 to 7m.
In underpass main drainage line diameter is 1800mm (1.8m).
There are 5 no of pumps are used for pumping out of water stored in underpass.
Pumping water is uplift on the bridge of the underpass.
II. STUDY AREA
Fig. 1: Akhbarnagar Underpass Fig. 2: Satellite image of Akhbarnagar Underpass
Table – 1
Pumps
No. of pumps Horse Power
1 Nos. 50
2 Nos. 40
2 Nos. 25
III. PROBLEM STATEMENT
The Akhbarnagar underpass is waterlogged every year during monsoon due to which the whole traffic system gets blocked for
hours. Recently, Akhbarnagar underpass was blocked due to 4 inches rainfall on 4 th Aug,2016 [7].
Fig. 3: Akhbarnagar Underpass
All rights reserved by www.ijirst.org 24
Storm Water Drainage for Underpass
(IJIRST/ Volume 3 / Issue 09/ 005)
A main problem is underpass having a small size of storm drain filtration channel so it cannot filter bulk of runoff storm-
water. Lack of inspection of filtration channel its causes Blockage of storm drainage and backflow of suction valve. Its causes
major issues such as traffic and water logging in nearby areas. There is some topography difference (gravity) in land difference
between surrounding areas and underpass due to which it can makes the water logging condition directly/indirectly manner.
There is also some topography difference (gravity) in the drainage provisions in underpass and near areas. Due to heavily
waterlogged in underpass and near surrounding areas, act as a breeding places of mosquitoes. So the numbers of people in
Akhbarnagar area are suffered with diseases like malaria and dengue.
IV. OBJECTIVES
To identify problems and locations of repetitive water logging at Akhbarnagar underpass.
To understand study of flood prone areas and to assess impact of water logging.
To solve traffic problem of underpass waterlogged during storm water.
To improve the backflow of storm water drainage.
To recommend Engineering Solutions for preventing water logging in underpass.
To identify topography and slop of our study area.
To make a georeference image of our study area.
Use of Quantum GIS and Global Mapper to analysis existing drainage system & topography of study area.
V. SCOPE OF STUDY
To solve problem of blockage of water in storm drain.
To solve traffic problem caused by stock water in underpass.
To decrease spreading of disease at nearby areas.
To collect the storm water from the storm drain and use for irrigation purpose.
To implement of Kerb drain system.
To improve sewer network system of nearby areas and underpasses.
To reduce natural disaster impacts
VI. METHODOLOGY
1) Step 1 : Abstract
2) Step 2 : Introduction
3) Step 3 : Problem statement
4) Step 4 : Objectives
5) Step 5 : Scope of study
6) Step 6 : Present scenario
7) Step 7 : Data collection
8) Step 8 : Conclusion
VII. PROBLEM SOLUTION
Fig. 4: ACO Kerb Drain System
Kerb drain system is a one of the most important possible solution for preventing blockage of underpass due to storm water. It’s
generally provided on edges of footpath [9]. (Refer fig.4) kerb drain system is to be designed to keep in mind the maximum
All rights reserved by www.ijirst.org 25
Storm Water Drainage for Underpass
(IJIRST/ Volume 3 / Issue 09/ 005)
quantity of runoff water possibility. Main advantage is kerb block height is higher than width because it collects a lot quantity of
water rather than horizontal filter channel. As per fluid property, Upper layer of runoff water has maximum speed with compare
to lower layer. If vertical drain (kerb drain) is provided throughout the length of underpass then we make sure it fights against the
storm water in underpass. Carriage ways has a minor slop towards pavement or footpath so quantity of runoff water is more
towards pavement side. As shown fig.4 kerb has to be designed as it collect water easily and supply forward by gravity itself. As
per users or customers requirement we can design its pattern, size, hole diameter, height, width, etc. 30% problem will solve by
increasing number of storm drain filtration channel towards underpass and centre of carriageway of underpass.
Present Condition with Images
Fig. 5: Horizontal filter channel at starting of Underpass Fig. 6: British time storm water pipeline
Fig. 7: Pumping well
VIII. DATA COLLECTION
Table – 2
Data Collection
Rainfall data of Ahmadabad city , 2014
Month Date Rainfall
July 16/7/14 3.00 mm
July 17/7/14 33.00 mm
July 18/7/14 16.00 mm
July 19/7/14 36.00 mm
July 20/7/14 04.00 mm
July 24/7/14 42.00 mm
July 25/7/14 23.00 mm
July 26/7/14 02.00 mm
July 27/7/14 04.00 mm
July 30/7/14 176.00 mm
July 31/7/14 05.00 mm
All rights reserved by www.ijirst.org 26
Storm Water Drainage for Underpass
(IJIRST/ Volume 3 / Issue 09/ 005)
August 1/8/14 NIL
August 2/8/14 0.50 mm
August 3/8/14 06.00mm
August 6/8/14 05.50 mm
August 7/8/14 06.00 mm
August 9/8/14 NIL
August 13/8/14 01.00 mm
August 14/8/14 NIL
August 17/8/14 0.50 mm
August 24/8/14 1.50 mm
August 25/8/14 29.00 mm
August 26/8/14 NIL
August 30/8/14 09.00 mm
August 31/8/14 55.00 mm
September 1/9/14 32.00 mm
September 2/9/14 34.50 mm
September 3/9/14 NIL
September 4/9/14 04.00 mm
September 5/9/14 04.00 mm
September 6/9/14 NIL
September 7/9/14 NIL
September 8/9/14 1.50 mm
September 9/9/14 96.00 mm
September 10/9/14 6.50 mm
September 11/9/14 12.00 mm
September 12/9/14 5.00 mm
September 13/8/14 0.50 mm
September 14/8/14 1.50 mm
September 15/8/14 0.50 mm
Total = 646.00 mm
Table – 3
Data Collection
Rainfall data of Ahmadabad city , 2015
Month Date Rainfall
June 3/6/15 0.5 mm
June 25/6/15 87.50 mm
July 8/7/15 1.50 mm
July 22/7/15 5.00 mm
July 23/7/15 1.00 mm
July 25/7/15 13.00 mm
July 26/7/15 103.00 mm
July 27/7/15 85.00 mm
July 28/7/15 140.00 mm
July 29/7/15 114.00 mm
July 30/7/15 8.00 mm
July 31/7/15 NIL
July 8/7/15 1.50 mm
July 22/7/15 5.00 mm
July 23/7/15 1.00 mm
July 25/7/15 13.00 mm
July 26/7/15 103.00 mm
July 27/7/15 85.00 mm
July 28/7/15 140.00 mm
July 29/7/15 114.00 mm
July 30/7/15 8.00 mm
July 31/7/15 NIL
September 18/8/15 42.00 mm
September 20/8/15 01.00 mm
September 21/8/15 06.50 mm
September 22/8/15 45.00 mm
September 23/8/15 03.75 mm
TOTAL = 875.00 mm
All rights reserved by www.ijirst.org 27
Storm Water Drainage for Underpass
(IJIRST/ Volume 3 / Issue 09/ 005)
Table – 4
Data Collection
Rainfall data of Ahmadabad city , 2016
Month Date Rainfall
June 4/7/16 17.50 mm
June 5/7/16 91.00 mm
June 12/7/16 20.00 mm
June 13/7/16 30.00 mm
June 14/7/16 36.00 mm
June 15/7/16 13.00 mm
June 17/7/16 09.00 mm
June 18/7/16 06.00 mm
June 19/7/16 NIL
June 20/7/16 05.00 mm
June 25/7/16 06.00 mm
June 28/7/16 04.50 mm
June 29/7/16 24.50 mm
June 30/7/16 13.00 mm
Total = 266.00 mm
Fig. 8: Population of nearby areas of Akhabarnagar underpass
IX. CONCLUSION
Akhbarnagar underpass has a vast problem of water logging due to storm water. To overcome this problem Ahmedabad
Municipal Corporation has to pay special attention on inspection of storm drain filtration channel. 30 % problem will solve if
AMC team increase the number of storm drain filtered channel. Also Ahmedabad Municipal Corporation has to pay special on
cleaning of storm drain pipes for batter flow of water. It can reduce the problem up to 20%.
REFERENCES
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stormwater.
[2] http://research.omicsgroup.org/index.php/Stormwater
[3] https://eprints.usq.edu.au/617/1/RamKumarM.KANNAPIRAN-2005.pdf
[4] http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/underpass
[5] http://gta-myths.wikia.com/wiki/Storm_Drains
[6] http://funsgood.in/post/7987840_4/Ahmedabad-Wikipedia-the-free.html
[7] http://epaper.timesofindia.com/Repository/getimage.dll?path=AMIR/2016/08/04/8/Img/Pc0080400.jpg
[8] https://pbs.twimg.com/media/CpElcGmUMAA6VED.jpg
[9] https://i.ytimg.com/vi/hH7eplaznA4/maxresdefault.jpg
[10] http://www.aco.co.uk/uploads/4DEF6B16_CE1E.jpg?width=577&height=454
[11] Herrenknecht AG, “Tunnel Construction”, (2005).
[12] Loftis, J.D. “Development of a Large-Scale Storm Surge and High-Resolution Sub-Grid Inundation Model for Coastal Flooding Applications of a Case
Study During Hurricane Sandy” Ph.D. Dissertation, Virginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William and Mary, (2014).
[13] New York City Buildings, “NYC DOITT GIS Data: NYC Building Heights and Footprints”, (2013).
[14] O. Kusakabe, K. Fujita & Y, Miyazaki, “Geotechnical Aspects of Underground Construction in Soft Ground”, A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam, (1999).
All rights reserved by www.ijirst.org 28
Storm Water Drainage for Underpass
(IJIRST/ Volume 3 / Issue 09/ 005)
[15] Reina, Peter. Double Duty: “Smart thinking fits Malaysian highway into stormwater tunnel, Engineering” News Record by McGraw-Hill Companies.
(2005).
[16] Scott M. Kozel, “Hampton Road Area Interstates and Freeways”, Roads to the Future, retrieved from, (2003).
[17] ACO Water Management department, ACO Technologies plc, May 2016.
[18] TM Megaw & JV Bartlett, “Tunnels (Planning, Design, Construction), Volume-1.” Ellis Hardwood Ltd, Chichester, (1981).
[19] Von Storch K “Reliable groundwater management: the continuous improvement method”, 2004.
[20] Westerink, J.J., R.A. Luettich, and J. Muccino. “Modeling tides in the western North Atlantic using unstructured graded grids”. Tellus 46A: 178-199,
(1994).
[21] Zularisam, KUKTEM Report, (2004).
All rights reserved by www.ijirst.org 29
View publication stats
Вам также может понравиться
- 9 ways urban trees help citiesДокумент2 страницы9 ways urban trees help citiesW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- RCC Box Jacking: Underground Construction Without Disrupting TrafficДокумент14 страницRCC Box Jacking: Underground Construction Without Disrupting TrafficSanjay EvaneОценок пока нет
- HGДокумент10 страницHGW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- 9 ways urban trees help citiesДокумент2 страницы9 ways urban trees help citiesW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- Winning Ramadan With DigitalДокумент20 страницWinning Ramadan With DigitalDarmawan YopiОценок пока нет
- Rain in Architecture and Urban Design PDFДокумент8 страницRain in Architecture and Urban Design PDFW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- Daylighting Performance in An Atrium With ETFE Cushion Roof and in An ETFE-Encapsulated Panel StructureДокумент6 страницDaylighting Performance in An Atrium With ETFE Cushion Roof and in An ETFE-Encapsulated Panel StructureW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- Walkways, Sidewalks, and Public Spaces: 13.1 PurposeДокумент12 страницWalkways, Sidewalks, and Public Spaces: 13.1 Purposechristopher domingoОценок пока нет
- Rain in Architecture and Urban Design PDFДокумент8 страницRain in Architecture and Urban Design PDFW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- Policy 62 Guidance Document Nov2018Документ12 страницPolicy 62 Guidance Document Nov2018W Dwi PОценок пока нет
- ETFE - The New Fabric RoofДокумент5 страницETFE - The New Fabric RoofCamila GonzalezОценок пока нет
- 10 Principles of Waterfront DevelopmentДокумент12 страниц10 Principles of Waterfront DevelopmentarchsubhankarОценок пока нет
- Daylighting Performance in An Atrium With ETFE Cushion Roof and in An ETFE-Encapsulated Panel StructureДокумент6 страницDaylighting Performance in An Atrium With ETFE Cushion Roof and in An ETFE-Encapsulated Panel StructureW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- Rain in Architecture and Urban DesignДокумент22 страницыRain in Architecture and Urban DesignW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- A Study On Waterfront Development - Case Study of Moganshan District, Shanghai, ChinaДокумент10 страницA Study On Waterfront Development - Case Study of Moganshan District, Shanghai, ChinaW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- 26 StromewaterdrainageforunderpassДокумент8 страниц26 StromewaterdrainageforunderpassW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- The Zero Moment of Truth Macro Study - Research Studies PDFДокумент19 страницThe Zero Moment of Truth Macro Study - Research Studies PDFW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- Furniture DesignДокумент26 страницFurniture DesignRobert CastroОценок пока нет
- Park Classifications: Urban ParksДокумент8 страницPark Classifications: Urban ParksW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- Kaetegori InstagramДокумент1 страницаKaetegori InstagramW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- Section 23 - Tourist Commercial PDFДокумент4 страницыSection 23 - Tourist Commercial PDFW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- CatalogДокумент84 страницыCatalogW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- Tanuwidjaja Creative and Participative-For PetraДокумент9 страницTanuwidjaja Creative and Participative-For PetragunteitbОценок пока нет
- Tanuwidjaja Creative and Participative-For PetraДокумент9 страницTanuwidjaja Creative and Participative-For PetragunteitbОценок пока нет
- Freepik Premium License TermsДокумент1 страницаFreepik Premium License TermsNguyen Viet Trung (FPL HCMK13.3)100% (1)
- Fonts Used in Design: Galano Grotesque & ViburДокумент1 страницаFonts Used in Design: Galano Grotesque & ViburW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- Cultural and Tourism Planning As Tool For City RevitalizationДокумент16 страницCultural and Tourism Planning As Tool For City RevitalizationW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- Asefyls3 FaqДокумент4 страницыAsefyls3 FaqW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- 3 Asef Young Leaders SummitДокумент4 страницы3 Asef Young Leaders SummitW Dwi PОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Center 14 - On Landscape Urbanism - BookДокумент181 страницаCenter 14 - On Landscape Urbanism - Bookdean j almy IIIОценок пока нет
- 2 ReservoirsДокумент39 страниц2 ReservoirsRashed Ahmed0% (1)
- Azreenie Nazlyeen Binti Amjah - As2293c - 2020461732Документ1 страницаAzreenie Nazlyeen Binti Amjah - As2293c - 2020461732azreenieОценок пока нет
- Mainstreaming CCA and DRR in LDP2Документ45 страницMainstreaming CCA and DRR in LDP2MGVMon67% (3)
- Samarpan Steel Final EIA PDFДокумент326 страницSamarpan Steel Final EIA PDFGanesh N KОценок пока нет
- Disaster management: floods, earthquakes, cyclones and landslidesДокумент10 страницDisaster management: floods, earthquakes, cyclones and landslidesAshima GoelОценок пока нет
- I. Choose A, B, C, D For Each Gap in The Following SentencesДокумент6 страницI. Choose A, B, C, D For Each Gap in The Following SentencesThủy TrầnОценок пока нет
- Planning Irrigation Scheme RehabilitationДокумент123 страницыPlanning Irrigation Scheme RehabilitationsileshibekeleОценок пока нет
- CDO LandUse - CDRA Summary - Updatedmarch2020Документ20 страницCDO LandUse - CDRA Summary - Updatedmarch2020Wendel AbejoОценок пока нет
- Resilient Livelihoods - Disaster Risk Reduction For Food and Nutrition Security Framework Programme (FAO - 2013)Документ93 страницыResilient Livelihoods - Disaster Risk Reduction For Food and Nutrition Security Framework Programme (FAO - 2013)HayZara MadagascarОценок пока нет
- Kidde Co2 Product Manual 050128 PDFДокумент299 страницKidde Co2 Product Manual 050128 PDFFIRMANSYAHОценок пока нет
- DM Section 4 Drainage Design 3-18-14Документ161 страницаDM Section 4 Drainage Design 3-18-14Shoayful islamОценок пока нет
- StormHarvester Brochure V8Документ7 страницStormHarvester Brochure V8Ricardo TrejoОценок пока нет
- Engineering Geological and Geohazard Assessment Eg PDF FreeДокумент9 страницEngineering Geological and Geohazard Assessment Eg PDF FreeMEL VIRGIL BASTASAОценок пока нет
- DM Plan Mirsarai Upazila Chittagong District - English Version-2014Документ81 страницаDM Plan Mirsarai Upazila Chittagong District - English Version-2014CDMP BangladeshОценок пока нет
- Hydro HazardsДокумент156 страницHydro HazardsJane ErlanoОценок пока нет
- Delineation of Surface Water Using MODIS Satellite Image For Flood Forecast in The Mekong River BasinДокумент8 страницDelineation of Surface Water Using MODIS Satellite Image For Flood Forecast in The Mekong River Basinরোহন করОценок пока нет
- Future of Urban Water Manila Final CompДокумент64 страницыFuture of Urban Water Manila Final CompFrida Faye LacsamanaОценок пока нет
- Farm Size Factor Productivity and Returns To ScaleДокумент8 страницFarm Size Factor Productivity and Returns To ScaleAkshay YadavОценок пока нет
- Liberal Arts and Science Academy-Kwan-Williams-Aff-Grapevine-DoublesДокумент53 страницыLiberal Arts and Science Academy-Kwan-Williams-Aff-Grapevine-DoublesTruman ConnorОценок пока нет
- Naga City Case Studies: Risk-Sensitive Land Use Planning & Incentives For Disaster Risk ReductionДокумент60 страницNaga City Case Studies: Risk-Sensitive Land Use Planning & Incentives For Disaster Risk ReductionMichael Padilla0% (1)
- Project ReportДокумент116 страницProject ReportAnupam KumarОценок пока нет
- Poverty, Vulnerability and Underdevelopment in HaitiДокумент2 страницыPoverty, Vulnerability and Underdevelopment in HaitiThessalonica CañonОценок пока нет
- My Research AdamaДокумент41 страницаMy Research AdamaOz GОценок пока нет
- Reserve Report - Main - KomatiДокумент121 страницаReserve Report - Main - KomatiMaxmore KarumamupiyoОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Geography Rivers WorkbookДокумент43 страницыIGCSE Geography Rivers Workbookkamrunnisa100% (8)
- TECHBIDPARTAДокумент67 страницTECHBIDPARTAGobinda DasОценок пока нет
- Response To Charnwood Borough Council Core Strategy - West of Loughborough Sustainable Urban ExtensionДокумент8 страницResponse To Charnwood Borough Council Core Strategy - West of Loughborough Sustainable Urban ExtensionJonathan DrakeОценок пока нет
- Risk Based Design PDFДокумент10 страницRisk Based Design PDFashish_pradhan75Оценок пока нет
- HydrologyДокумент33 страницыHydrologyGregor KokotОценок пока нет