Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Differential Diagnosis of Stroke
Загружено:
Anonymous 7dsX2F8nИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Differential Diagnosis of Stroke
Загружено:
Anonymous 7dsX2F8nАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
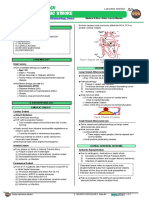
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF STROKE
A patient presents with right sided hemiplegia????
Features Cerebral embolus Cerebral Thrombosis Intracerebral hemorrhage Primary subarachnoid
hemorrhage
Time of onset Can occur any time Usually occurs during sleep Usually occurs during activity Usually occurs during activity
(eg: sexual intercourse)
Onset Sudden Gradual (but patient may have Sudden Sudden
3
history of previous TIA)
Headache/vomiting - - Yes Yes (thunderstorm headache)
Loss of consciousness - - Yes 50% of cases
Signs of meningeal - - Only if hemorrhage becomes Yes
irritation secondary SAH
Hypertension - Common Most important Common in old patients
predisposing factor
Risk Factors/ Types Cerebral infarct: i) Lacunar Infarct: i) Charchot bouchard i) Rupture of berry aneurysm
1
Ophthalmic , MCA, ACA, PCA, Hypertension, diabetes, aneurysm (microaneurysms ii) A-V malformation
Vertebrobasilar. hyperlipidemia in perforating vessels in iii) Trauma
Hypertensive patients)
Risk factors: ii) Cerebral Infarct: MCA, ii) Amyloid angiopathy Rupture of berry aneurysm
i) Atrial fibrillation ACA, PCA, Vertebrobasilar iii) Bleeding disorders i) Hypertension
ii) Recent M.I artery involvement (Leukemia, ii) Smoking
iii) Vulvular heart disease (M.S) R.f: Diabetes, hypercoaguble thrombocytopenia, iii) Connective tissue disorder
iv) Infective endocarditis states, hyperlipedemia hemophilia, DIC) (Marfan, Ehlor danlos)
v) Prosthetic valves iv) Anticoagulant therapy iv) APKD
v) Liver disease v) Neurofibromatosis-I
vi) Substance misuse vi) Coartaction of aorta
(cocaine, alcohol,
amphetamine)
Most common site MCA MCA Basal ganglia (putamen)
Other findings i) Atrial fibrillation Carotid bruit Hypertensive retinopathy i) Subhyaloid hemorrhage
ii) Myocardial infarction history may be there ii) Hypertensive retinopathy
iii) Vulvular heart disease (mitral May be history of Bleeding in older patients
stenosis) disorders, Anticoagulant iii) May have history of
iv) Infective endocarditis therapy, alcoholism, liver Coartaction of aorta, Marfan
v) Carotid bruit disease syndrome, Ehlor danlos
syndrome,
Neurofibromatosis-I, Adult
polycystic kidney disease
Compiled by: SHAHERYAR ALI JAFRI Ref: D/D by Shabbir nasir, CMDT, Kaplan
Features Cerebral embolus Cerebral Thrombosis Intracerebral hemorrhage Primary subarachnoid
hemorrhage
CSF analysis Normal Normal Normal until unless there is Hemorrhagic with
secondary SAH xanthocromia
Angiography Shows the site of obstruction i) Site of obstruction i) Aneurysm/ Charcot Berry aneurysm may be seen
ii) Carotid atheroma may be bouchard in young patients and
seen ii) AV malformation may be bleeding point can be
seen recognized.
Treatment i) Immediate Immediate i) Immediate i) Immediate
As needed As needed ABC/ IV line/ Foley ABC/ IV line/ Foley
ii) Primary i) Primary catheter catheter, lower blood
t-PA within 3 hours t-PA within 3 hours Lower blood pressure pressure, reduce ICP
iii) Secondary ii) Secondary (MAP=130), reduce ICP. ii) Primary and Adjuvant
a) Aspirin or Dipyridamole Aspirin (24 hours after t-PA) ii) Primary Nimodepine,
b) Anticoagulants esp if embolus If allergic: give Dipyridamole Surgical evacuation of ii) Secondary
was of cardiac source hematoma Surgical clipping and coiling
iii) Secondary to prevent re-bleeding then
Seizure prophylaxis, Give i/V fluids to make I/V
steroids for cerebral edema, volume expansion and
Treat the underlying prevent vasospasm., VP
disorder, I/V recombinant shunting for hydrocephalus,
factor VIII. Oral / iv NaCl to compensate
renal salt wasting
Note:
1. Occlusion of ophthalmic artery (Central retinal artery) by thrombus is not clinically significant b/c of collaterals but embolus to ophthalmic
artery can lead to unilateral TIA called Amaurosis fugax.
2. Embolus is sudden whereas thrombus is gradual b/c as long as thrombus is enlarging, collaterals are developing.
3. TIA: It is a transient neurological deficit due to vascular insufficiency which completely recovers within 24 hours. 90% cases are due to
embolism. Usual duration is few minutes. Amaurosis fugax is one of its type which causes Transient unilateral painless loss of vision.
TIA may be a warning sign that stroke is gonna happen. Esp a Thrombotic event in future (remember: although 90% TIA is an embolic event)
4. COMA: Infarction in either the carotid or vertebrobasilar territory may lead to loss of consciousness.
5. Most accurate test to detect Cerebral Ischemia is Diffusion weighted MRI.
IMMEDIATE INVESTIGATION: CT-scan without contrast
LABS/Tests for Ischemic stroke: CBC, ESR, BSR, TEST FOR SYPHILIS, LUPUS ANTICOAGULANT, LIPID PROFILE, ECG, BLOOD CULTURE (if I.E),
Echocardiography, Holter monitoring (If arrhythmias ) , Bubble study Echo to detect Patent foramen ovale LABS/Tests for hemorrhagic stroke:
CBC, ESR, BSR, PT, apTT, Bleeding time, LFTs, RFTs.
Compiled by: SHAHERYAR ALI JAFRI Ref: D/D by Shabbir nasir, CMDT, Kaplan
Вам также может понравиться
- I. Neuro-Ophthalmic Manifestations of StrokeДокумент7 страницI. Neuro-Ophthalmic Manifestations of Strokeanton MDОценок пока нет
- 200 Special Topics For 42 BCSДокумент187 страниц200 Special Topics For 42 BCSRezaul RazibОценок пока нет
- Cardio Day 3 TemplateДокумент24 страницыCardio Day 3 TemplateMikeОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular Pathology: Hypertensive RetinopathyДокумент7 страницCardiovascular Pathology: Hypertensive RetinopathyTom TsouОценок пока нет
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: Darpen Subhashbhai Mori Group 2, MD 3BДокумент13 страницHemorrhagic Stroke: Darpen Subhashbhai Mori Group 2, MD 3BDarpen MoriОценок пока нет
- Intracerebral Hemorrhage ICH Etiology, AtfДокумент10 страницIntracerebral Hemorrhage ICH Etiology, Atfsiti.220010019Оценок пока нет
- Lec 3 Raised Intracranial PressureДокумент9 страницLec 3 Raised Intracranial PressureEmily MurrayОценок пока нет
- Ischemic Stroke Maria Grace Ang-De Guzman, MDДокумент9 страницIschemic Stroke Maria Grace Ang-De Guzman, MDJohn Benedict Bondoc100% (3)
- Long Case StrokeДокумент5 страницLong Case StrokeAzizan HannyОценок пока нет
- Ajith Kumar P MPT Cardiopulmonary SciencesДокумент30 страницAjith Kumar P MPT Cardiopulmonary SciencesSuhana JahangeerОценок пока нет
- Overview of Stroke - Knowledge at AMBOSSДокумент19 страницOverview of Stroke - Knowledge at AMBOSSandimija16Оценок пока нет
- Prelim 118 NotesДокумент6 страницPrelim 118 NotesMicah Huns San JuanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 18 - Pericardial Disease - 1Документ10 страницChapter 18 - Pericardial Disease - 1ganeabaicudragosОценок пока нет
- Vascular Disease-Lecture Prof SyukriДокумент109 страницVascular Disease-Lecture Prof SyukriYayatRuslan100% (1)
- Cardiology Revision DR - Ahmed MowafyДокумент35 страницCardiology Revision DR - Ahmed MowafyMohamed AlsaabОценок пока нет
- Neuro-Onkologi: Bagian/SMF Saraf FK-UGM/RS Dr. Sardjito YogyakartaДокумент59 страницNeuro-Onkologi: Bagian/SMF Saraf FK-UGM/RS Dr. Sardjito YogyakartaNovasiska Indriyani HutajuluОценок пока нет
- Acute Ischemia of The Lower Limb (LL) : Sudden Occlusion of A Previously Patent Artery Supplying A LimbДокумент4 страницыAcute Ischemia of The Lower Limb (LL) : Sudden Occlusion of A Previously Patent Artery Supplying A LimbOmar MohammedОценок пока нет
- Ferris Clinical Advisor 2022 1St Edition Fred F Ferri Full ChapterДокумент67 страницFerris Clinical Advisor 2022 1St Edition Fred F Ferri Full Chaptermichael.walker630100% (15)
- CVD CSDTДокумент3 страницыCVD CSDTrazeebhasssanОценок пока нет
- Medicine Revision - Neurology TableДокумент10 страницMedicine Revision - Neurology TableUnomoshОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology CVA (Final2)Документ10 страницPathophysiology CVA (Final2)Jayselle Costes FelipeОценок пока нет
- Definition of Stroke: Risk FactorsДокумент12 страницDefinition of Stroke: Risk FactorsNik Fatnin YusoffОценок пока нет
- Vascular Surgery TNДокумент4 страницыVascular Surgery TNVictor Matias BarriosОценок пока нет
- Recent Developments in The Acute Treatment of Intracerebral HemorrhageДокумент163 страницыRecent Developments in The Acute Treatment of Intracerebral HemorrhageRohamonangan TheresiaОценок пока нет
- StrokeДокумент53 страницыStrokeGhinaSofianaLestari100% (1)
- Clinical AutopsyДокумент2 страницыClinical Autopsyapi-352560644Оценок пока нет
- IntraCranial HemorrhageДокумент1 страницаIntraCranial HemorrhageTasya MeidyОценок пока нет
- Arterial Diseases 2010Документ25 страницArterial Diseases 2010viKиҼswAяAи LiиGaMОценок пока нет
- Hemorrhagic Stroke Management DR GaneshДокумент67 страницHemorrhagic Stroke Management DR GaneshDr Ganeshgouda MajigoudraОценок пока нет
- Disorders of The Brainstem and Cranial Nerves SY 2022-2023Документ141 страницаDisorders of The Brainstem and Cranial Nerves SY 2022-2023Geraldine Teopy100% (1)
- Causes of Clubbing:: Cardiac Murmurs and Location Best HeardДокумент3 страницыCauses of Clubbing:: Cardiac Murmurs and Location Best HeardMichelle De FreitasОценок пока нет
- Materi 12 IMELS - Trombosis Emboli Paru, Iskemik Tungkai Akut - KritisДокумент64 страницыMateri 12 IMELS - Trombosis Emboli Paru, Iskemik Tungkai Akut - KritismaharyadyОценок пока нет
- Family Medicine EORДокумент159 страницFamily Medicine EORAndrew BowmanОценок пока нет
- SeizuresДокумент5 страницSeizuresLeah SalcedoОценок пока нет
- CVS Examination - 16-11-2021Документ60 страницCVS Examination - 16-11-2021KUMUTHA MALAR A/P PARMESWARANОценок пока нет
- AMC Part 1 CAT MCQ Examination Important TopicsДокумент23 страницыAMC Part 1 CAT MCQ Examination Important TopicsSOMANATHAN UMAHSUTHANОценок пока нет
- NM Revalida Compilation 3A 1Документ193 страницыNM Revalida Compilation 3A 1Xander Alegado MarikitОценок пока нет
- Week 10 - Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, ArrhythmiaДокумент14 страницWeek 10 - Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, Arrhythmiashivani patel100% (1)
- PCP Glossary of Diseases 1Документ1 страницаPCP Glossary of Diseases 1Aria Jean MostajoОценок пока нет
- Tumors 0F CNS-1Документ25 страницTumors 0F CNS-1Mo HamoudОценок пока нет
- Pediatric StrokeДокумент43 страницыPediatric StrokePrachiti KarodeОценок пока нет
- Vasculitis by VinhДокумент4 страницыVasculitis by VinhTovin NguyenОценок пока нет
- Mitral StenosisДокумент2 страницыMitral StenosisitsmailbbkОценок пока нет
- ShockДокумент1 страницаShockWong Liang TungОценок пока нет
- Acute Ischemic Stroke: Etiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnostics, TreatmentДокумент7 страницAcute Ischemic Stroke: Etiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnostics, TreatmentAfrah AbdulОценок пока нет
- IM - Cardiomyopathy and MyocarditisДокумент9 страницIM - Cardiomyopathy and MyocarditisElisha BernabeОценок пока нет
- Seminar On Management of StrokeДокумент54 страницыSeminar On Management of Stroke7762n9qsntОценок пока нет
- 4.18 Mankad Echo in Systemic DiseaseДокумент97 страниц4.18 Mankad Echo in Systemic DiseaseDiana_anca6Оценок пока нет
- hemiplegia دكتور عزونيДокумент4 страницыhemiplegia دكتور عزونيRaed AlhnaityОценок пока нет
- MS TopicsДокумент1 страницаMS Topicsjamie carpioОценок пока нет
- MCQ 1. Heart Sound Heart Sound S1 S2Документ7 страницMCQ 1. Heart Sound Heart Sound S1 S2Atirah AaОценок пока нет
- Week 5-14 Notes 3 (Dragged) 6Документ1 страницаWeek 5-14 Notes 3 (Dragged) 6navkkirangillОценок пока нет
- Bab IiДокумент13 страницBab IiNanda SusiloОценок пока нет
- CARDIAC TUMORS TransДокумент12 страницCARDIAC TUMORS TransjeccomОценок пока нет
- Endocarditis: (Post Strep Infection)Документ8 страницEndocarditis: (Post Strep Infection)Eben Ezar Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Differential Diagnosis of StrokeДокумент2 страницыDifferential Diagnosis of Strokeamna_badar1Оценок пока нет
- Medicina 4 Neuro Neumo PDFДокумент19 страницMedicina 4 Neuro Neumo PDFKarol M MChОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology RevisedДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology RevisedkaechannyuОценок пока нет
- 3 - Important Topics For The AMC Part 1 MCQ CAT ExaminationДокумент23 страницы3 - Important Topics For The AMC Part 1 MCQ CAT ExaminationMohd FaizhakimОценок пока нет
- Skuy LaДокумент7 страницSkuy LaAnonymous 7dsX2F8nОценок пока нет
- Film RecomendДокумент1 страницаFilm RecomendAnonymous 7dsX2F8nОценок пока нет
- AsuasuasususuДокумент67 страницAsuasuasususuAnonymous 7dsX2F8nОценок пока нет
- Therapeutic Use of Stem Cells in Treatment of Burn Injuries: Summary ArticleДокумент8 страницTherapeutic Use of Stem Cells in Treatment of Burn Injuries: Summary ArticleAnonymous 7dsX2F8nОценок пока нет
- Exercise Training For Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisДокумент9 страницExercise Training For Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisAnonymous 7dsX2F8nОценок пока нет
- Myocardial Infarction, Atrial Fibrillation and Mortality: Timing Is EverythingДокумент2 страницыMyocardial Infarction, Atrial Fibrillation and Mortality: Timing Is EverythingAnonymous 7dsX2F8nОценок пока нет
- Etiologi & Penatalaksanaan Dub: Erald Giovanny Hasiholan Simatupang FAA 115 027Документ6 страницEtiologi & Penatalaksanaan Dub: Erald Giovanny Hasiholan Simatupang FAA 115 027Anonymous 7dsX2F8nОценок пока нет
- ISMKI InductionДокумент19 страницISMKI InductionAnonymous 7dsX2F8nОценок пока нет
- Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics: M. Filomena Teodoro, Carla SimãoДокумент7 страницJournal of Computational and Applied Mathematics: M. Filomena Teodoro, Carla SimãoAnonymous 7dsX2F8nОценок пока нет
- NIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptДокумент18 страницNIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptAnonymous 7dsX2F8nОценок пока нет
- Read MeyppppppppppppppoooooДокумент2 страницыRead MeyppppppppppppppoooooAnonymous 7dsX2F8nОценок пока нет
- Kjim 2016 098Документ9 страницKjim 2016 098Anonymous 7dsX2F8nОценок пока нет
- Acute Diarrhea in AdultsДокумент2 страницыAcute Diarrhea in AdultsAnonymous 7dsX2F8nОценок пока нет
- Heart Failure: Preventing Disease and Death WorldwideДокумент39 страницHeart Failure: Preventing Disease and Death WorldwideAnonymous 7dsX2F8nОценок пока нет
- Inborn Errors or MetabolismДокумент25 страницInborn Errors or MetabolismAnonymous 7dsX2F8nОценок пока нет
- ETCO2 ReadingДокумент19 страницETCO2 ReadingTuan TrinhОценок пока нет
- (Becker, 2009) Satulogenesis 30 Years LaterДокумент8 страниц(Becker, 2009) Satulogenesis 30 Years LaterZooTEKОценок пока нет
- Adoption Authorities and Agencies Under Juvenile Justice Act, 2015Документ10 страницAdoption Authorities and Agencies Under Juvenile Justice Act, 2015DebanjanaChakrabortyОценок пока нет
- PacmakerДокумент37 страницPacmakerSalman HabeebОценок пока нет
- UNICEF Birth Registration in Health SystemsДокумент56 страницUNICEF Birth Registration in Health SystemsSamson AreketeОценок пока нет
- Landmark Case: Indian Medical Association Vs V.P. ShanthaДокумент4 страницыLandmark Case: Indian Medical Association Vs V.P. ShanthaRiken TandelОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 The Molecules of CellsДокумент5 страницChapter 3 The Molecules of Cellsmzunl25476Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 3Документ6 страницLesson 3api-316910625Оценок пока нет
- World Persp 2008 - FinalДокумент248 страницWorld Persp 2008 - FinalBuğra EgeliОценок пока нет
- Application FormДокумент3 страницыApplication FormSandeepSalagalaОценок пока нет
- Zero B Product PresentationДокумент27 страницZero B Product PresentationKalyan DeshpandeОценок пока нет
- Blood Groups PPT by TKR&SRДокумент24 страницыBlood Groups PPT by TKR&SRseshagiriОценок пока нет
- Astm A 10.11Документ13 страницAstm A 10.11edu_caneteОценок пока нет
- Regulation On Blended Oils - DR Prabodh HaldeДокумент30 страницRegulation On Blended Oils - DR Prabodh HaldeAahana LabsОценок пока нет
- Soal Semester Genap Kelas X 2019Документ7 страницSoal Semester Genap Kelas X 2019Aris SulistyoОценок пока нет
- Review of Urban Drainage, 4th Edition, by David Butler, Christopher James Digman, Christos Makropoulos, and John W. DaviesДокумент1 страницаReview of Urban Drainage, 4th Edition, by David Butler, Christopher James Digman, Christos Makropoulos, and John W. DaviesJhon Edison Bravo Buitrago100% (1)
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy: Instructor's ManualДокумент68 страницCognitive-Behavioral Therapy: Instructor's ManualzingpalmsОценок пока нет
- Steinmann PinДокумент3 страницыSteinmann Pinrachelmores12Оценок пока нет
- Home Study Course-HomeopathДокумент155 страницHome Study Course-HomeopathAzad Ansari67% (6)
- Let'S Dive Deeply!: Discussion Points: Read The Case Scenario and Relate It To The TheoryДокумент1 страницаLet'S Dive Deeply!: Discussion Points: Read The Case Scenario and Relate It To The TheoryAnn Mariz DominguezОценок пока нет
- Chaos, Solitons and Fractals: Vinay Kumar Reddy Chimmula, Lei ZhangДокумент6 страницChaos, Solitons and Fractals: Vinay Kumar Reddy Chimmula, Lei ZhangS AbdОценок пока нет
- 2 Tissue Culture at Home ReportДокумент7 страниц2 Tissue Culture at Home ReportXwag 12Оценок пока нет
- 10 Hours OshaДокумент247 страниц10 Hours OshaJose BastidasОценок пока нет
- Post-Operative Criterion Based Rehabilitation of Acl Repairs: A Clinical CommentaryДокумент14 страницPost-Operative Criterion Based Rehabilitation of Acl Repairs: A Clinical CommentaryferryОценок пока нет
- Otda Foil Request 2Документ4 страницыOtda Foil Request 2sammyschwartz08Оценок пока нет
- Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support in Adults (ACLS) : SubtitleДокумент30 страницAdvanced Cardiovascular Life Support in Adults (ACLS) : SubtitleMohamad El SharОценок пока нет
- TRAINING WORKSHOP FOR TRADITIONAL HERBAL MEDICAL PRACTIONERS Ode OmuДокумент2 страницыTRAINING WORKSHOP FOR TRADITIONAL HERBAL MEDICAL PRACTIONERS Ode OmuOlatunji Adebisi TundeОценок пока нет
- Unit 14. Nursing DocumentationДокумент6 страницUnit 14. Nursing Documentationputridelia yalanavilaОценок пока нет
- Method Statement For Lifting WorksДокумент12 страницMethod Statement For Lifting WorksRachel Flores85% (26)
- 839 FullДокумент5 страниц839 Fullwinda athyaОценок пока нет