Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Aluminium Utensils - Gujranwala PDF
Загружено:
Naeem NawazОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Aluminium Utensils - Gujranwala PDF
Загружено:
Naeem NawazАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
2019
Cluster Profile
Aluminium Utensils, Gujranwala
Turn Potential Into Profit
Small and Medium Enterprises Development Authority (SMEDA)
Ministry of Industries and Production (MoI&P)
Government of Pakistan
4th Floor, Building No. 3, Aiwana-e-Iqbal Complex Egerton Road Lahore
www.smeda.org.pk
P: 111 111 456
Cluster Profile – Aluminium Utensils Gujranwala 1
Table of Contents
1 Description of Cluster 2
1.1 Introduction 2
1.2 Defining the Products 2
1.3 Core Cluster Actors 2
1.4 Other Support Actors 3
1.5 Geographical Location 4
2 Analysis of Business Operation 5
2.1 Production Process Flow 5
2.2 Raw Materials 6
2.3 Technology Status and Quality Standards Requirement 6
2.4 Sales and Marketing Analysis 6
2.4.1 Local Market Trade 6
2.4.2 International Market 7
2.5 Global Trade 7
2.6 Financing 8
2.7 Human Resource Management 9
3 Institutional Setup 9
3.1 Entrepreneurs Associations 9
3.2 Support Institutions 9
3.3 Banks and Financial Institutions 10
4 Major Issues and Problems 10
5 Suggestions and Recommendations 12
6 Investmenmt Opportunities in Cluster 13
Small and Medium Enterprises Development Authority (SMEDA)
Cluster Profile – Aluminium Utensils Gujranwala 2
1 Description of Cluster
1.1 Introduction
Gujranwala is playing a major role to support the economy of Pakistan. It is an industrially
developed district in the country. Keeping in view the availability of raw-material and skilled labor,
Gujranwala district supports a variety of industries. It is considered manufacturing hub of
electrical home appliance, light engineering goods, kitchen utensils, plastic products and ceramic
sanitary wares.
Gujranwala region is well-known for manufacturing of aluminium utensils in Pakistan. People have
been associated with this sector prior to partition. Utensils Industry mainly exists at SME level and
comprises of labor intensive units having semi-mechanized manufacturing facilities. Overall
production of Gujranwala aluminium utensils cluster is estimated to be 60,000 tons per annum
with capacity utilization of 40%. The cluster provides direct employment to more than 18,000
individuals across the region.
As far as expenditure and revenue of aluminium utensils is concerned; the costing of a typical
utensil shows that around 56% is the cost of raw material, 17% is of labor, 17% is of gas and
electricity and around 10% is of administrative and operating expenses. Whereas, on average 8-
10 percent of the total cost contributes to the profit margin of the owner.
Current status of the cluster is considered as stagnant due to a number of reasons such as undue
delays in the export refunds, power cuts, limited opportunities of training and development
support, lack of business development service providers and unavailability of raw material from
local market.
1.2 Defining the Products
Aluminium cookware is popular for cooking purposes as it is used for kitchen utensils. Its good
thermal conductivity, light weight, resistance to numerous forms of corrosion makes it popular.
However, uncoated and anodized aluminium utensils can be reactive with acidic foods.
The product range covers all types of aluminium utensils used in households, hotels, hospitals,
canteens and other places for cuisine. The major products include cooking casserole sets, frying
pan, sauce pan, wok, backing disk, pressure cookers etc. These utensils are manufactured in
various sizes, shapes, designs and finish qualities including metal, mirror and non-stick coated.
Major aluminium utensils manufacturing brands in Gujranwala include Sonex, Casio, Kitchen King,
Chef, Majestic, Trophy and Kiran.
1.3 Core Cluster Actors
There are around 450 manufacturing units across the region, majority of the units are operating
at small scales. The breakup of the manufacturing units is as follows:
Small and Medium Enterprises Development Authority (SMEDA)
Cluster Profile – Aluminium Utensils Gujranwala 3
Table 1: Aluminium Utensils Cluster, Gujranwala
Capacity Per Unit / Product
Size No. of Units Market
day Quality
Large Unit 50 2-7 ton High, Medium Export/Local
Medium Unit 100 1 ton High, Medium Local/Export
Small Unit 300 500 kgs Medium, Low Local
Source: Gujranwala Chamber of Commerce & Industry (GCCI) and Directory of Industrial Establishments
Industries & Commerce Department Government of Punjab
1.4 Other Support Actors
The key cluster support actors who provide support services to core cluster in the area are
including but not limited to raw material suppliers, finishing and packaging service providers.
Table 2: Other Support Actors, Utensils Cluster Gujranwala
Description Details
Around 30 units are providing packaging and wrapping services to
Packaging
Gujranwala Aluminium Utensil Cluster.
50 units are operating in Gujranwala region to provide Bakelite supplies;
Bakelite Supplies Bakelite is an early form of brittle plastic used in short body handle (side
handles) and long body handle of the utensils.
Generally, handles used for aluminium utensils are not manufactured by
Handle Makers utensils manufacturers themselves. Approximately, 50 handle makers
are providing such products to the cluster.
Chemicals make an important component of aluminium utensils
Chemical Suppliers manufacturing process. Industry’s demand of the same is being met by
15 suppliers in the region.
Color coating is used at the time of finishing of the product. This kind of
Color Coatings material is not available in Pakistan. Therefore, it is being imported from
China to meet the requirements of the local industry.
Metal is the prime raw material for the industry. Usually, large firms
import the same by themselves either in the form of finished product or
Metal Suppliers in the form of scrap material which is transformed into metal after
necessary treatment. Whereas small manufacturing units depend on
importers to meet their demands of raw material.
Small and Medium Enterprises Development Authority (SMEDA)
Cluster Profile – Aluminium Utensils Gujranwala 4
1.5 Geographical Location
The aluminium utensils cluster is scattered around Gujranwala city; however main concentrations
are at:
• Industrial Estate–II
• Nowshera Road
• Sheikhupura Road
• Mian Sansi Road
• Hafizabad Road
• Jinnah Road
• Muslim Road
• Bazar Ghulam Muhammad
• Kacha Khiyali Road
Small and Medium Enterprises Development Authority (SMEDA)
Cluster Profile – Aluminium Utensils Gujranwala 5
2 Analysis of Business Operation
2.1 Production Process Flow
The standard operations of the aluminium utensils’ business include process flow, business trade
cycle; and material and technological requirements to perform these business operations.
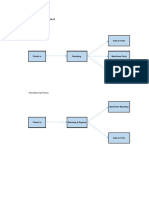
Figure 1: Production Process Flow Diagram
•Scrap is sorted to remove impurities.
Raw Material
Aluminium Scrap
•Scrap is melted in natural gas fired pit furnaces for making ingot or blocks. Later on, hot and cold rolling
to form metal sheets of required gauge, blank forming is done on presses while technology level is very
Melting & Re-
Rolling low.
•Then, sheets are cut into square shape pieces and these square pieces are cut in disk shape according to
Circle Cutting
the desired sizes by Circular Cutting Machine.
•The disks are pressed with dies put in Hydraulic Press for getting a shape according to the requirements
Drawing
of the container. The edges of the container are cutt with Spinning Machine.
•After cutting of the edges, the surface of container is cleaned with the sand paper and any remaining
spots are marked with a circle around them. The spots are removed by the use of buff machine and the
Buffing &
Grinding process is called buffing. Finally, lathe machine is used for cleaning and removing oil.
•Various chemicals including sulphuric acid, nitric acid are used for anodizing.
Anodizing
•Next, it is washed in boiled water (Calcium Hydro Oxide mixed in water) for removal of dust and paint is
Non Stick Coating
sprayed into the inner surface as well as outside the dry container with compressor.
•Then, punching of holes and pins for handle fitting by riveting machine is done.
Handle Fitting
•Finally, cleaning with cotton cloth is done and product is packed in box along with instruction booklet.
Packing
Small and Medium Enterprises Development Authority (SMEDA)
Cluster Profile – Aluminium Utensils Gujranwala 6
2.2 Raw Materials
The primary raw material for aluminium utensils manufacturing is aluminium category 3006.
Around 95% of the same is imported in the form of Aluminium ingot (99.7% purity) and waste /
scrap of aluminium foil, cables, PVC, Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced (ACSR), window
section, utensils, UBC etc.
Raw material demand of the industry is being met by the help of importers / traders from
Gujranwala, Lahore and Karachi. Large manufacturers also import the raw material directly.
Aluminium scrap and ingots are imported from countries across the globe including Afghanistan,
Russia, UK, Canada, Middle East, EU & Africa.
Moreover, packaging material and wood used in handles is also used as raw material for
aluminium utensils manufacturing.
2.3 Technology Status and Quality Standards Requirement
There is lack of use of modern manufacturing machines and techniques. Currently, semi-
automatic machinery is being used by the industry. The machines are locally made, labor oriented
and inexpensive as compared to modern machinery.
No specific quality standards and certifications are mandatory or being practiced by the industry.
2.4 Sales and Marketing Analysis
Gujranwala Aluminium Utensils Cluster is targeting export / international market; around 70
percent of the total production is exported; whereas only 30 percent is sold out in the domestic
market. Major importing countries and regions of Aluminium utensils cluster are Gulf States,
Europe, Africa, United Kingdom, United Arab Emirates, Spain, Saudi Arabia and Afghanistan.
2.4.1 Local Market Trade
Of the total production of aluminium utensils, thirty (30) percent is sold in domestic market, which
is quite challenging to handle due to lengthy and uncertain credit period. The major local markets
for this cluster are upper Punjab and Karachi region. In order to target local market,
manufacturers have developed a network of distributers across the country. Usually, 30 days’
credit cycle is maintained in context of local trades.
The sales and distribution network flow in local market trade is as follows;
Producer Distributer Wholesaler Retailer Consumer
Small and Medium Enterprises Development Authority (SMEDA)
Cluster Profile – Aluminium Utensils Gujranwala 7
Some of the manufacturers also have their own retail and distribution arrangements for
distribution of products. Additionally, export agents and local sales agents are also working to
facilitate sales of aluminium utensils.
2.4.2 International Market
When it comes to sales of the product in international market, 95 percent of these are made
through commercial agents or intermediaries such as national and international import / export
agents and traders. Only 5 percent of the total aluminium utensils exports are being handled by
the manufacturers of Gujranwala cluster directly. Pakistani trade exporters are leading the way
with sales in Middle East. Generally, 60 days’ cycle is maintained for international trade.
2.5 Global Trade
During the calendar year 2017, Pakistan exported aluminium utensils of worth US$ 22 million. The
export trends of aluminium products from Pakistan in recent 5 years in provided below.
Table 3: Pakistan’s Exports of Aluminium Utensils
Description 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
Pakistan’s Exports of
Aluminium Utensils (Value in US 28,372 29,312 25,969 23,593 22,421
$ Thousands)
Pakistan’s Exports Share in the
0.59% 0.62% 0.58% 0.53% 0.48%
World
Source: Trade Map (HS Code: 761510)
Figure 2: Pakistan Exports Bar Diagram
Pakistan's Exports of Aluminium Utensils
(USD Thousnad)
28,372 29,312
25,969
23,593 22,421
2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
Source: Trade Map (HS Code: 761510)
Small and Medium Enterprises Development Authority (SMEDA)
Cluster Profile – Aluminium Utensils Gujranwala 8
The details of total world exports and leading exporting countries of the aluminium utensils in the
world are provided below.
Table 4: World Exports and Leading Exporters of Aluminium Utensils (Value in US $ Thousands)
Exporters 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
World 4,775,005 4,697,548 4,503,950 4,456,868 4,684,836
China 2,386,739 2,382,234 2,323,052 2,254,062 2,409,765
Italy 430,472 346,586 320,853 324,141 356,622
France 321,216 287,513 263,579 287,538 304,254
Korea 211,333 210,220 197,798 189,588 166,513
Thailand 209,547 173,413 226,417 190,801 159,455
Other Countries 1,215,698 1,297,582 1,172,251 1,210,738 1,288,227
Source: Trade Map (HS Code: 761510)
Figure 3: Export Share of Leading Exporters
Other Countries
28%
China
Thailand 51%
3%
Korea France
4% 6% Italy
8%
China Italy France Korea Thailand Other Countries
Source: Trade Map (HS Code: 761510)
2.6 Financing
The funding from financial institutions is not popular among the industry stakeholders due to the
interest factor associated with financing. Generally, investors rely either on their personal
investment or friends and family sources of financing. However, almost all the registered financial
Small and Medium Enterprises Development Authority (SMEDA)
Cluster Profile – Aluminium Utensils Gujranwala 9
institutions of Pakistan have their branches within the geographical area of the cluster and are
providing the financing at competitive rates.
2.7 Human Resource Management
The aluminium utensils industry does not seek highly qualified workforce to perform technical
and management operations. Due to semi-automatic nature of technology, technical operations
are associated with skilled HR having training, diploma or certification in grinding; while
management positions are generally occupied by the owner managers. Human resource is
available in abundance and skills are traditionally inherited. Most of the labor is semi-skilled and
is trained on job. Furthermore, there are no specialized marketing or accounts departments in
small units. These units generate sales on the basis of personal contacts. Business accounts are
not maintained properly; therefore, certain problems related to tax return, monitoring and
evaluation are common in this cluster.
3 Institutional Setup
3.1 Entrepreneurs Associations
Gujranwala Chamber of Commerce & Industry (GCCI)
Address: Aiwan-e-Tijarat Road, Trust Plaza, Gujranwala
Tel: 055-9200391-4
Web: www.gcci.org.pk
3.2 Support Institutions
Regional Business Center (RBC) – Small & Medium Enterprises Development Authority
(SMEDA)
Address: GBC Building, Aiwan-e-Iqbal Road, Trust Plaza, Gujrnawala
Tel: 055-3734600
Web: www.smeda.org.pk
Trade Development Authority of Pakistan (TDAP)
Address: 20-E, Satellite Town, Pasroor Road, Gujranwala
Tel: 055-9200138 - 9
Web: www.tdap.gov.pk
Punjab Small Industrial Corporation (PSIC)
Address: Small Industrial Estate no. 2, G.T.Road, Gujranwala
Tel: 055-4283074
Small and Medium Enterprises Development Authority (SMEDA)
Cluster Profile – Aluminium Utensils Gujranwala 10
Web: www.psic.gop.pk
Govt. College of Technology (Glass & Ceramics), Shahdara
Address: Matchis Factory Gate No.1, National Fan Link Road G.T Road
Tel: 042-37901665
Gujranwala Business Centre (GBC)
Address: Aiwan-e-Tijarat Road, Trust Plaza, Gujranwala
Tel: 055-9200868
Web: www.gbc.org.pk
Gujranwala Tools, Die and Moulds Center. (GTDMC)
Address: Sialkot Bypass Chowk, Sialkot Road, Gujranwala
Tel: 055 - 3827321 - 23
Web: www.gtdmc.org.pk
Light Engineering Service Center (LESC-TEVTA)
Address: Small Industrial Estate no. 1, G.T. Road Gujranwala
Tel: 055 - 9200661, 9200800
3.3 Banks and Financial Institutions
Almost all the registered financial institutions of Pakistan have their branches in the cluster and
provide the financing at competitive rates.
4 Major Issues and Problems
Following are the major issues restricting the growth and development of aluminium utensils
manufacturing cluster in the region:
Export / Tax Refunds: Long delays in tax / export refunds are striking the financial position of the
cluster quite badly, hence pushing the financially stable industry into uncertainty.
Lack of Quality Assurance: There is no appropriate system for quality control of raw material and
production process. Neither material analysis nor mechanical testing of products is carried out.
Hence, variation in product quality persists. At all levels of work in process, the relevant foremen
are responsible for keeping a check on quality on the behalf of their departments. After
completion of the production process, different types of in-house tests are conducted for quality
assurance purposes as well as meeting the buyer’s requirements.
Technology: Aluminium Utensils cluster is highly dependent on the low quality raw material i.e.
aluminium scrap and waste. Wastage rate is high due to use of old technology. There is an urgent
Small and Medium Enterprises Development Authority (SMEDA)
Cluster Profile – Aluminium Utensils Gujranwala 11
necessity to improve the value chain of utensils manufacturing cluster particularly in the areas of
product quality, designing and technology to improve operational process.
Following are some key technology related issues:
• High rate of waste of energy and materials. Aluminium circle recovery is around 50% -
60% through traditional ways of melting and re-rolling.
• Higher rejection rates.
• No heat control in melting.
• Low production capacity.
• Lack of energy saver and efficient equipment.
• High rate of injuries to labor during work on manual machines.
• No covering on molten metal.
Training and Development: There is a lack of technical training and courses offered by public or
private institutions for developing the capabilities of the human capital. Industry has to altogether
train individuals on job which affects productivity.
Energy Concerns: Electricity and gas constraints are of major concern to the industry as cost of
doing business increases hence damaging the cluster productivity.
Melting and Rolling: Melting and rolling is an important step of the process to convert scrap into
a major raw material component i.e. aluminium sheet. Domestic equipment and technology used
for melting and rolling purposes is conventional and needs considerable up-gradation to meet the
industry requirements. Generally, investors show little interest in melting and rolling business
activity due to lack of modern technology. Therefore, industry has to rely on international
suppliers; China is the biggest supplier to Pakistan.
Environmental Concerns: Industrial smoke and acidic water are of major concern to the
aluminium utensils cluster. In the anodizing process, sulfuric acid fumes are released that are
hazardous to employees and local community, for which there is no waste management system
in place. In addition to that, lack of absorbing machines in melting furnaces for dissolution of black
smoke and acidic gases in the atmosphere are also of serious concern for the environment.
Technology and expertise are required in handling and minimizing the impact on environment.
Human Resource: Most of the labor is semi-skilled and trained on job. TEVTA and other institutes
in the region have not been conducting any specialized training for utensils industry. Due to lack
of finance and infrastructural facilities at their end, the small companies can only afford to employ
ordinary level workforce. Hence, at the initial stage, an entrepreneur has to work with relatively
unskilled workers. Highly educated and skilled personnel do not prefer joining small and medium
enterprises, as SME cannot afford their high remuneration demands.
Smuggling: Smuggling of aluminium utensils has a significant impact on the cluster. Finished
products are smuggled from Iran, Afghanistan and Turkey which negatively affects the cluster and
Pakistan’s export of aluminium utensils. The cost of doing business is higher in Pakistan as
compared to competitors due to expensive energy, under-utilized capacity of production, semi-
Small and Medium Enterprises Development Authority (SMEDA)
Cluster Profile – Aluminium Utensils Gujranwala 12
mechanized equipment and old technology. It makes the industry less competitive to other
nations; therefore, it is hard for local manufacturers to compete with the smugglers who smuggle
units at hand in the export market.
International Competition: China and India are the biggest competitors of Pakistan in
international export market. Both of the countries possess modern technology and fully
automated machinery and equipment which leads to higher production rate with low human
resource requirements and cost of doing business. Despite this fact, Pakistan still has a good
market share due to better quality and uniqueness of the product; however, the lower product
prices offered by the competitors pose serious threat to Pakistan’s market share.
High Tariff Rates: Other than modern and mechanized equipment and technology; high tariff
rates and VAT on import of aluminium scrape is a big challenge to the industry resulting in a
decline in the production rate as well as achievement of significant breakthrough in the import of
raw material and utensils’ export.
China Imports: Since the year 2015, the import of Chinese utensils by Pakistan has increased due
to increase in import duty on aluminium scrap which is basic raw material for manufacturing of
aluminium utensils. This increase in duty initiated a decline in the imports and production which
consequently opened the door for Chinese products in the local market.
5 Suggestions and Recommendations
Ø Government needs to take necessary actions to streamline the tax refunds.
Ø Industry needs to maintain quality assurance mechanism.
Ø As mentioned above, industry lacks facilities of technical training programs and
courses for HR development. Therefore, training and development facilities should be
established to offer such courses.
Ø Technical assistance for best practiced modern production management techniques.
Ø Awareness and consultancy for:
§ Raw material testing (use of portable XRF for sorting of scarp)
§ Mechanism for reduction in smuggling of product
§ Energy subsidy
§ Temperature measuring
§ Product quality enhancement
§ Energy audit and efficiency
§ Workforce safety measures
§ Waste management
Small and Medium Enterprises Development Authority (SMEDA)
Cluster Profile – Aluminium Utensils Gujranwala 13
Ø Technology and expertise are required in handling of smoke and waste to minimize
the impact on environment. Therefore, installation of equipment and process for
dissolving smoke & acidic gases needs to be ensured by the concerned authorities.
6 Investmenmt Opportunities in Cluster
There are Investment opportunities in the following business areas in aluminium utensils cluster
Gujranwala.
Ø Melting and Rolling Unit
There are ample business opportunities in the field of melting and rolling for local
entrepreneurs. The production in Gujranwala is 60,000 tons per year of Aluminium utensils
with 40 percent capacity utilization. Key raw / input material is Aluminium blocks or circles
which are made by scrap. However, existing establishments / arrangements of converting
aluminium scrap to blocks and circles are not meeting the demand of the local industry. This
gap is being met through import of blocks / circles, mainly from china.
Ø Energy Saving Company (ESCO)
The issue of energy consumption has been of growing concern across the cluster not only
due to its immediate impact on production costs but also because of its considerable impact
on environmental sustainability. Currently, energy audit and other energy related services
are not readily offered across the region. Therefore, Energy Saving Company (ESCO) has good
potential in this cluster.
Ø Business Development Service Providers (BDSPs)
There is decent potential for BDSPs to provide human resources of this sector with pre-
requisite skill set and expertise. Further, consultancy / advice and equipment fabrication /
delivery related to environmental impact and management of emissions / waste water etc.
also has a good demand in the local industry.
Ø Balancing Modernization & Replacement Technology
As Gujranwala Aluminium Cluster is facing many challenges with regard to productivity as
manual and semi-automatic machinery & equipment and production process is prevalent.
So, there are bright opportunities for investment in technology upgrade and process
improvement.
Small and Medium Enterprises Development Authority (SMEDA)
Вам также может понравиться
- Portrait of an Industrial City: 'Clanging Belfast' 1750-1914От EverandPortrait of an Industrial City: 'Clanging Belfast' 1750-1914Оценок пока нет
- Scrap Metal Merchants BizHouse - UkДокумент2 страницыScrap Metal Merchants BizHouse - UkAlex BekeОценок пока нет
- Fab Hind Tyre Recycling PlantДокумент4 страницыFab Hind Tyre Recycling PlantVarun NairОценок пока нет
- India - Seafood NRIДокумент81 страницаIndia - Seafood NRISiraj KuvakkattayilОценок пока нет
- 54 E1 (Uic 54)Документ2 страницы54 E1 (Uic 54)NMC Industries Pvt.LtdОценок пока нет
- Mitsubishi Materials Group Corporate Profile and Global OperationsДокумент16 страницMitsubishi Materials Group Corporate Profile and Global OperationsAnton AviyantoОценок пока нет
- Turkish Metal Industry Report HighlightsДокумент25 страницTurkish Metal Industry Report HighlightsRoman SuprunОценок пока нет
- Aluminum SectorДокумент16 страницAluminum Sectortomahawk1212Оценок пока нет
- New YorkДокумент9 страницNew YorkrashidasmiОценок пока нет
- Rail A 75: Headquarters: Registered Office: Administrative Offices and Warehouse: Middle East BranchДокумент2 страницыRail A 75: Headquarters: Registered Office: Administrative Offices and Warehouse: Middle East BranchfrancoОценок пока нет
- Botswana Manufacturers DirectoryДокумент43 страницыBotswana Manufacturers Directoryindienkhan0% (1)
- 2007 World Copper Fact BookДокумент66 страниц2007 World Copper Fact Bookaclarke100% (2)
- World Raw SuppliersДокумент26 страницWorld Raw SuppliersFahim AbdinОценок пока нет
- BETP - Exp Clientele Dir 2012 - 03may2012Документ187 страницBETP - Exp Clientele Dir 2012 - 03may2012Fernando EndayaОценок пока нет
- Dry Granulation: Made by GerteisДокумент14 страницDry Granulation: Made by GerteisBinh NguyenОценок пока нет
- Tyres Recycling Disposal BizHouse - UkДокумент2 страницыTyres Recycling Disposal BizHouse - UkAlex BekeОценок пока нет
- ExportДокумент18 страницExportUsha BastikarОценок пока нет
- Lead Waste Recyclers ListДокумент72 страницыLead Waste Recyclers ListukalОценок пока нет
- Automated Vehicle Scrapping and Recycling UnitДокумент12 страницAutomated Vehicle Scrapping and Recycling UnitrabinОценок пока нет
- Find Residential Recycling Options in CalgaryДокумент12 страницFind Residential Recycling Options in Calgarymahmood-Оценок пока нет
- 2016 10 17 ICSG Factbook 2016 PDFДокумент64 страницы2016 10 17 ICSG Factbook 2016 PDFxichengren100% (1)
- About Batteries and RecyclingДокумент5 страницAbout Batteries and RecyclingSidhantMannОценок пока нет
- Jordan 100Документ51 страницаJordan 100seherucarОценок пока нет
- Rubber & Plastics - CompaniesДокумент10 страницRubber & Plastics - CompaniesMario StrašniОценок пока нет
- Manufacturing SectorДокумент21 страницаManufacturing SectorVictoria SalazarОценок пока нет
- Eco-disposals simplifiedДокумент10 страницEco-disposals simplifiedZar EnterpriserОценок пока нет
- ContactsДокумент2 страницыContactsDipesh PuriОценок пока нет
- Build Asia Catalog 2019Документ347 страницBuild Asia Catalog 2019zeeshan tanveerОценок пока нет
- Atlas Product ManualДокумент165 страницAtlas Product ManualAndrew WallworkОценок пока нет
- Recyclers of Non Ferrous MetalsДокумент63 страницыRecyclers of Non Ferrous Metalsmujib uddin siddiquiОценок пока нет
- Mgmi PDFДокумент40 страницMgmi PDFDaneshwer VermaОценок пока нет
- Woodford Halse Business DirectoryДокумент3 страницыWoodford Halse Business DirectoryJohn WilliamsОценок пока нет
- Tin Plate Contacts.Документ43 страницыTin Plate Contacts.api-20010854Оценок пока нет
- Detailed Profile of CAPEXIL DelegationДокумент23 страницыDetailed Profile of CAPEXIL DelegationYogesh ChhaprooОценок пока нет
- JULY 2015 Surplus Record Machinery & Equipment DirectoryДокумент759 страницJULY 2015 Surplus Record Machinery & Equipment DirectorySurplus RecordОценок пока нет
- Buildasia Event Catalog 2010Документ61 страницаBuildasia Event Catalog 2010info2nafeesОценок пока нет
- Certain Activated Carbon From ChinaДокумент122 страницыCertain Activated Carbon From ChinaHạnhNguyễnОценок пока нет
- Indian Label Industry OverviewДокумент21 страницаIndian Label Industry Overviewlalit2585100% (1)
- Albanian Delegation 07122010Документ20 страницAlbanian Delegation 07122010Devaky_Dealish_182Оценок пока нет
- Kenya Export Market Development ProgrammeДокумент6 страницKenya Export Market Development ProgrammeCraft AfrikaОценок пока нет
- EuroChem - Europe - Final PDFДокумент36 страницEuroChem - Europe - Final PDFYuvrajОценок пока нет
- Bangladesh Software & IT Exporter Directory 2016Документ49 страницBangladesh Software & IT Exporter Directory 2016Ejaz AhmedОценок пока нет
- Equipment Catalogue - 2015-Web PDFДокумент42 страницыEquipment Catalogue - 2015-Web PDFKim MoggОценок пока нет
- Ankit Majmudar - Module 3 - How To Find Foreign Buyer - AMA PDFДокумент21 страницаAnkit Majmudar - Module 3 - How To Find Foreign Buyer - AMA PDFhimanshuОценок пока нет
- IBEF Auto Components 261112Документ37 страницIBEF Auto Components 261112asingh0001Оценок пока нет
- List of Certified Manufacturer'S Under "Tested Product Certificate (TPC) " CategoryДокумент4 страницыList of Certified Manufacturer'S Under "Tested Product Certificate (TPC) " CategoryArvind DharmarajОценок пока нет
- Broshure Heavy Industry enДокумент24 страницыBroshure Heavy Industry enMahendra Donizar100% (1)
- List of E-Waste RecyclerДокумент12 страницList of E-Waste RecyclerSheshnath VermaОценок пока нет
- Tianjin In-rich Casting Co.,ltd Manhole Covers and Steel Gratings Since 1980sДокумент24 страницыTianjin In-rich Casting Co.,ltd Manhole Covers and Steel Gratings Since 1980sHarry King Corral AvenidoОценок пока нет
- Srma Steel News: Steel Re-Rolling Mills Association of IndiaДокумент20 страницSrma Steel News: Steel Re-Rolling Mills Association of Indiaflytorahul100% (1)
- Offer STP Abhishek SirДокумент6 страницOffer STP Abhishek SirA8304008005Оценок пока нет
- Company Profile 2Документ7 страницCompany Profile 2R Saravana KumarОценок пока нет
- Minerals and Metal Review July 2012 - 3Документ20 страницMinerals and Metal Review July 2012 - 3Sundaravaradhan IyengarОценок пока нет
- Alu ChlorideДокумент12 страницAlu ChlorideindusexposiumОценок пока нет
- 3.0 Cutter Suction Dredger BookДокумент79 страниц3.0 Cutter Suction Dredger BookSumsil ArafinОценок пока нет
- Electrical Home Appliances - Gujranwala 2019Документ14 страницElectrical Home Appliances - Gujranwala 2019Ahsan SafdarОценок пока нет
- Wooden Furniture - GujratДокумент11 страницWooden Furniture - GujratMehdiОценок пока нет
- Bedwear - Multan 2019Документ12 страницBedwear - Multan 2019Usman ManiОценок пока нет
- Cotton Ginning Cluster ProfileДокумент14 страницCotton Ginning Cluster ProfileAli HamzaОценок пока нет
- Hosiery Products Cluster of FaisalabadДокумент11 страницHosiery Products Cluster of FaisalabadOUSMAN SEIDОценок пока нет
- Agricultural Implements - SargodhaДокумент10 страницAgricultural Implements - SargodhaAdnan AshrafОценок пока нет
- Ob Final List April 2012Документ5 страницOb Final List April 2012Naeem NawazОценок пока нет
- PK Saadiq Home Finance Pricing NoticeДокумент1 страницаPK Saadiq Home Finance Pricing NoticeNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- Website NTCДокумент3 страницыWebsite NTCNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- Where A Sunna ComesДокумент1 страницаWhere A Sunna ComesNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- HistoryДокумент1 страницаHistoryNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- Ideology of Pakistan AssingmentДокумент8 страницIdeology of Pakistan AssingmentPrinCe Amman93% (58)
- Agricultural Implements - SargodhaДокумент10 страницAgricultural Implements - SargodhaAdnan AshrafОценок пока нет
- Our Publications:: Chapter 7: Preparing For The Next Wave of Developments Under CPECДокумент9 страницOur Publications:: Chapter 7: Preparing For The Next Wave of Developments Under CPECNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- HistoryДокумент1 страницаHistoryNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- Towards Pro Poor Budgeting Analysis of Peshawar and Haripur Districts Budget Allocations and Spending (W 168)Документ28 страницTowards Pro Poor Budgeting Analysis of Peshawar and Haripur Districts Budget Allocations and Spending (W 168)Naeem NawazОценок пока нет
- To The Liberal FascitsДокумент2 страницыTo The Liberal FascitsNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- Pharma Cluster ProfileДокумент10 страницPharma Cluster ProfileNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- Frequency of Thrombocytopenia in Neonatal Sepsis: Dr. Nadia GulДокумент9 страницFrequency of Thrombocytopenia in Neonatal Sepsis: Dr. Nadia GulNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- PovertyДокумент1 страницаPovertyNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- House JobДокумент2 страницыHouse JobNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- Rewritten SampleДокумент1 страницаRewritten SampleNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- EveryoneДокумент1 страницаEveryoneNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- HSPДокумент1 страницаHSPNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- Commerce: Johar College of Science andДокумент3 страницыCommerce: Johar College of Science andNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- Johar College Mathematics Part II Objective QuestionsДокумент3 страницыJohar College Mathematics Part II Objective QuestionsNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- Mughal Empire : Business Ethics (Bba - 409)Документ32 страницыMughal Empire : Business Ethics (Bba - 409)Ishleen Alexander100% (3)
- CLGДокумент1 страницаCLGNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- EveryoneДокумент1 страницаEveryoneNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- CastroДокумент1 страницаCastroNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- Faisalabad: Government College UniversityДокумент1 страницаFaisalabad: Government College UniversityNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- Faisalabad: Government College UniversityДокумент2 страницыFaisalabad: Government College UniversityNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- Bs MathematicsДокумент2 страницыBs MathematicsNaeem NawazОценок пока нет
- Linear Algebra Exam for BS-CS Semester 2Документ2 страницыLinear Algebra Exam for BS-CS Semester 2Naeem NawazОценок пока нет
- 1a. Lion Titco Company ProfileДокумент12 страниц1a. Lion Titco Company ProfileIFTIKUETОценок пока нет
- Benfits of Wood Scrap 1Документ1 страницаBenfits of Wood Scrap 1Greenstakes Recycling SolutionsОценок пока нет
- Brochure SouthpartnersДокумент19 страницBrochure SouthpartnersStanislau Felix Garcia RomeroОценок пока нет
- Bangladeshi Sculptors: Novera Ahmed and PioneersДокумент36 страницBangladeshi Sculptors: Novera Ahmed and PioneersGeorge LukeОценок пока нет
- NameДокумент18 страницNameDharamОценок пока нет
- Complete Steel Plant SpecificationДокумент250 страницComplete Steel Plant SpecificationJesus SevillaОценок пока нет
- Afar Job Order CostingДокумент20 страницAfar Job Order CostingBridget Zoe Lopez Batoon100% (1)
- ERIEZ Tambor Magnético (RB-380N)Документ4 страницыERIEZ Tambor Magnético (RB-380N)angelsiddhartaОценок пока нет
- SCO-Soft Corporate OfferДокумент2 страницыSCO-Soft Corporate OfferTrindra PaulОценок пока нет
- Location Factors: Aluminum, Copper, Natural Gas Refining, Petroleum Refining, Synthetic FibersДокумент12 страницLocation Factors: Aluminum, Copper, Natural Gas Refining, Petroleum Refining, Synthetic FibersKranti KumarОценок пока нет
- GlaucusResearch Report On China Metal Recycling Holdings Ltd-HK0773-Strong Sell January 28 2013Документ38 страницGlaucusResearch Report On China Metal Recycling Holdings Ltd-HK0773-Strong Sell January 28 2013Billy LeeОценок пока нет
- Sample Feasibility StudyДокумент9 страницSample Feasibility StudyRey Mart100% (3)
- A Project On Analysing Lam Coke in MMTCДокумент56 страницA Project On Analysing Lam Coke in MMTCHriday PrasadОценок пока нет
- Scrapzone Price ListДокумент2 страницыScrapzone Price Listshantanukulkarni007Оценок пока нет
- Project Report Rajuri Steel JalnaДокумент63 страницыProject Report Rajuri Steel Jalnasantosh83% (6)
- Metals and Mining in UkraineДокумент24 страницыMetals and Mining in UkraineAbhijeet BarveОценок пока нет
- Recycling aluminum from end-of-life vehicles in SerbiaДокумент6 страницRecycling aluminum from end-of-life vehicles in SerbiaManojlovic VasoОценок пока нет
- Life Cycle Costing - Great Square AutomobileДокумент6 страницLife Cycle Costing - Great Square AutomobileAdi KurniawanОценок пока нет
- SIVA- SELVA- SELVI- SANGEETHAДокумент24 страницыSIVA- SELVA- SELVI- SANGEETHAbj velОценок пока нет
- Building Coordinator HandbookДокумент37 страницBuilding Coordinator HandbookHélcio Vieira de Souza Jr.Оценок пока нет
- Crafts 15-22 PuppetsДокумент8 страницCrafts 15-22 PuppetsEndiОценок пока нет
- Charging Hot Metal To The EAF Using Consteel: SteelmakingДокумент6 страницCharging Hot Metal To The EAF Using Consteel: SteelmakingWISHAL FATIMAОценок пока нет
- Group 2 - Case 4 - China ClampsДокумент13 страницGroup 2 - Case 4 - China ClampsGeoffrey RoaringОценок пока нет
- Copper and Tin in Steel Scrap RecyclingДокумент15 страницCopper and Tin in Steel Scrap RecyclingakshukОценок пока нет
- Considerations for Using Alternative Iron Materials in EAFsДокумент12 страницConsiderations for Using Alternative Iron Materials in EAFsAlina StoroshchukОценок пока нет
- 03 34 11 - MSL Intel - Mughal Initiation - Capitalizing On The Global Base Metal FiestaДокумент15 страниц03 34 11 - MSL Intel - Mughal Initiation - Capitalizing On The Global Base Metal FiestaMehroz KhanОценок пока нет
- I02 Iron&steel Gs AD GCTДокумент6 страницI02 Iron&steel Gs AD GCTChiemela AmaechiОценок пока нет
- SURPLUSДокумент2 страницыSURPLUSRiyu RathodОценок пока нет
- Diagnostic Study Report of Bell and Metal ClusterДокумент70 страницDiagnostic Study Report of Bell and Metal Clustererkant007100% (1)
- Nucor at a Crossroad - Strategic AnalysisДокумент21 страницаNucor at a Crossroad - Strategic AnalysisRohit BhayanaОценок пока нет
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeОт EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (8)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionОт EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (542)
- High Performance Loudspeakers: Optimising High Fidelity Loudspeaker SystemsОт EverandHigh Performance Loudspeakers: Optimising High Fidelity Loudspeaker SystemsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- The Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesОт EverandThe Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- C++ Programming Language: Simple, Short, and Straightforward Way of Learning C++ ProgrammingОт EverandC++ Programming Language: Simple, Short, and Straightforward Way of Learning C++ ProgrammingРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Off-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemОт EverandOff-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemОценок пока нет
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionОт EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (331)
- Understanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveОт EverandUnderstanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (16)
- 8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionОт Everand8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (6)
- The Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesОт EverandThe Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Lithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsОт EverandLithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Ramblings of a Mad Scientist: 100 Ideas for a Stranger TomorrowОт EverandRamblings of a Mad Scientist: 100 Ideas for a Stranger TomorrowОценок пока нет
- The Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026От EverandThe Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Build Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionОт EverandBuild Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- The Graphene Revolution: The Weird Science of the Ultra-thinОт EverandThe Graphene Revolution: The Weird Science of the Ultra-thinРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- Beginner's Guide to Reading Schematics, Fourth EditionОт EverandBeginner's Guide to Reading Schematics, Fourth EditionРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (10)
- Operational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignОт EverandOperational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Digital Gold: The Beginner's Guide to Digital Product Success, Learn Useful Tips and Methods on How to Create Digital Products and Earn Massive ProfitsОт EverandDigital Gold: The Beginner's Guide to Digital Product Success, Learn Useful Tips and Methods on How to Create Digital Products and Earn Massive ProfitsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)