Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
2.01 Notes
Загружено:
rockfaith20Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
2.01 Notes
Загружено:
rockfaith20Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lesson 2.
01
Main Idea (page #) DEFINITION OR SUMMARY EXAMPLE or DRAWING
The two ways of classifying triangles are by their Right Isosceles Triangle: 90 degree angles
sides and by their angles. with at least two congruent sides
Classifying Triangles (P1)
Hash marks on the sides of triangles show what sides are
equal.
The sum of the measures of
Triangle Sums Theorem (P2)
the angles in a triangle adds up to 180 degrees.
Acute Triangle: has THREE acute (less than 90°) angles
Right Triangle: has EXACTLY ONE right (equals 90°) angle
Naming Triangles (P3)
Obtuse Triangle: has EXACTLY ONE obtuse (MORE than 90°)
Naming by angles
angle
Equiangular: has three equal angles
Equilateral Triangle: has THREE congruent sides
Naming by sides (P3) Isosceles Triangle: has AT LEAST two congruent sides
Scalene Triangle: has NO congruent sides
If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the two angles
Isosceles Triangle Theorem (P4) opposite those sides (called base angles) are
congruent.
AB ≅ BC, so <C ≅ <A. <B is called the vertex
angle. <A and <C are called the base angles.
Lesson 2.01
If you extend one end of a side past the vertices, you can
create exterior angles on the triangle.
Outside the Triangle (P7)
The angles that are not sitting right next to the
exterior angle are remote angles.
Angle D is an exterior angle
Angles B and C are remote angles
The measure of each exterior angle of a triangle
equals the sum of the measure of its
Triangle Exterior Angle
two remote interior angles.
Theorem (P8) Angle A + Angle B = Angle ACD
Adjacent angles along a line add up to 180°. 67° + 74° = 140°
Angle C + Angle ACD = 180°
40° + 140° = 180°
Triangle Inequality Theorem The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle
(P9) is greater than the third side.
AB +BC > AC
BC + AC > AB
AC + AB >BC
Вам также может понравиться
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Best Buy Order Receipt DetailsДокумент2 страницыBest Buy Order Receipt Detailsrockfaith20Оценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Math Resource Part II - Geometry 452344 PDFДокумент34 страницыMath Resource Part II - Geometry 452344 PDFHanna Sarriniemi100% (1)
- MR3 SolutionsДокумент27 страницMR3 SolutionsViet Quoc HoangОценок пока нет
- Hobson's Trigonometry 4th - Ed B WДокумент414 страницHobson's Trigonometry 4th - Ed B WJust Barry100% (5)
- Kansas Election Standards - Recounts and ContestsДокумент6 страницKansas Election Standards - Recounts and Contestsrockfaith20Оценок пока нет
- Analysis of GC ArticleДокумент1 страницаAnalysis of GC Articlerockfaith20Оценок пока нет
- Biology Final Exam Study GuideДокумент2 страницыBiology Final Exam Study Guiderockfaith20Оценок пока нет
- Circles Geometry GuideДокумент102 страницыCircles Geometry GuideAsish ThampiОценок пока нет
- Trigonometry Exact Values WorksheetДокумент4 страницыTrigonometry Exact Values WorksheetMaged YassaОценок пока нет
- AnswersДокумент44 страницыAnswersStephanieОценок пока нет
- Angles Properties in CirclesДокумент13 страницAngles Properties in CirclesnidojanОценок пока нет
- Intersection and Resection - Docx GRP 555555Документ5 страницIntersection and Resection - Docx GRP 555555Priyanshu PathakОценок пока нет
- WINSEM2019-20 STS3006 SS VL2019205007330 Reference Material II 05-Jan-2020 Geometry and Mensuration STS3006 3007Документ18 страницWINSEM2019-20 STS3006 SS VL2019205007330 Reference Material II 05-Jan-2020 Geometry and Mensuration STS3006 3007Srinivasan Saai Mahesh 16BCE0559Оценок пока нет
- Maths IBДокумент376 страницMaths IBAddalla veerrajuОценок пока нет
- Similar Triangles + IdentityДокумент3 страницыSimilar Triangles + IdentityAceZetaОценок пока нет
- Maths Part2 PDFДокумент25 страницMaths Part2 PDFSeenu KОценок пока нет
- GRADE XI MATH PRACTICE ON MULTIPLE AND SUBMULTIPLE ANGLESДокумент5 страницGRADE XI MATH PRACTICE ON MULTIPLE AND SUBMULTIPLE ANGLES8D Audio TuneОценок пока нет
- Drill Ex 7 Answers Nq4nucgДокумент48 страницDrill Ex 7 Answers Nq4nucgdevang tank100% (2)
- Chapter 1Документ25 страницChapter 1Noor Faizah ZohardinОценок пока нет
- Assessment Task Problem Set: X X X X X XДокумент4 страницыAssessment Task Problem Set: X X X X X XEly BОценок пока нет
- Ed Math 3 TrigonometryДокумент2 страницыEd Math 3 TrigonometryShiera Saletrero SimbajonОценок пока нет
- Mathematical Aptitude Model Test Paper For MBAДокумент5 страницMathematical Aptitude Model Test Paper For MBAashuokОценок пока нет
- Cbse Mathematics Sa1 Solved 05Документ4 страницыCbse Mathematics Sa1 Solved 05harshaОценок пока нет
- Parts of A TriangleДокумент3 страницыParts of A TriangleMari Cel100% (1)
- Sine and Cosine Rule pdf1Документ17 страницSine and Cosine Rule pdf1Tafadzwa D Chidavaenzi0% (1)
- MCR 3U1 Trigonometry AssignmentДокумент9 страницMCR 3U1 Trigonometry AssignmentBrady CousinsОценок пока нет
- Trigonometry - Primary Trigonometric Ratios - All Level2 All PDFДокумент12 страницTrigonometry - Primary Trigonometric Ratios - All Level2 All PDFElaine Batista0% (1)
- Pythagoras' Theorem and Its ApplicationsДокумент12 страницPythagoras' Theorem and Its ApplicationscleobuloОценок пока нет
- Balkan MO-1987Документ1 страницаBalkan MO-1987OklaОценок пока нет
- 146 Chapter 13. The Trigonometric Functions (LECTURE NOTES 9)Документ15 страниц146 Chapter 13. The Trigonometric Functions (LECTURE NOTES 9)Brendon MuriraОценок пока нет
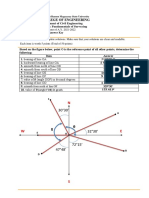
- CE 214 Quiz 2 Answer KeyДокумент2 страницыCE 214 Quiz 2 Answer KeyJerome M JaldoОценок пока нет
- St. Mary's School, Dwarka Holiday Homework Class XII Subject: Mathematics Week 2 Worksheet 2Документ5 страницSt. Mary's School, Dwarka Holiday Homework Class XII Subject: Mathematics Week 2 Worksheet 2ParayulaОценок пока нет
- UM Plane Spherical TrigoДокумент5 страницUM Plane Spherical TrigogoddowonОценок пока нет
- Review: Lesson 1: The Six Trigonometric Ratios Lesson 2: Trigonometric Ratio of Special AnglesДокумент16 страницReview: Lesson 1: The Six Trigonometric Ratios Lesson 2: Trigonometric Ratio of Special AnglesJennifer JLo VivasОценок пока нет